|
|
|
| Application of gamma-ray spectrum method in the exploration of fluorite deposits in southern Anhui Province, China |
| LIAN Xiang-Yu1,2, LUO Jian-Bing1,2 |
1. Anhui Nuclear Exploration Technology Central Institute, Wuhu 241000, China
2. Radioactive Resources and Environmental Engineering Research Center of Anhui Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Wuhu 241000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study conducted a profile spectrum survey in the southern Anhui Province using a portable gamma-ray spectrometer. Based on the differences in types and quantities of natural radioactive elements present in geological bodies, this study compared the stack plots of the characteristic parameters of U, Th, and K with geologic-topographic maps to further delineate the occurrence locations of ore bodies. Additionally, this study investigated the applicability of gamma-ray spectra to the exploration of fluorite deposits and provided empirical suggestions for parameter surveys and anomaly determination. The experimental results indicate that gamma-ray energy spectroscopy applies the exploration of fluorite minerals. Notably, Th can be used as a primary indicator, exhibiting low-amplitude anomalies, which correspond well with ore bodies. Besides, this element is applicable to other surrounding rock conditions. The analysis and verification from the perspective of environmental protection revealed that the gamma-ray radiation dose rates induced by fluorite vein ore bodies are far lower than their background values and can be used as a preliminary basis for ore prospecting.
|
|
Received: 12 April 2024
Published: 22 July 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
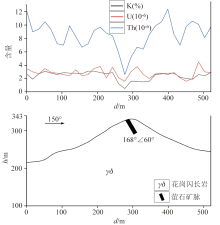
|
γ Spectral measurement profile of line 1
|
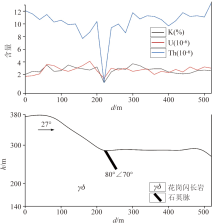
|
γ Spectral measurement profile of line 2
|

| 岩石 | w(K)/% | w(U)/10-6 | w(Th)/10-6 | 备注 | | 范围 | 平均值 | 范围 | 平均值 | 范围 | 平均值 | | 萤石矿石 | 0.7 ~ 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.8 ~ 2.1 | 1.7 | 0.7 ~ 4.3 | 3.3 | | | 花岗闪长岩 | 1.6 ~ 3.0 | 2.2 | 2.6 ~ 5.4 | 3.8 | 8.3 ~ 12.2 | 9.2 | | | 地表覆盖层(土壤) | 1.7 ~ 3.4 | 2.4 | 2.2 ~ 4.7 | 3.2 | 7.9 ~ 12.8 | 9.7 | | | 砂板岩[10] | 1.6 ~ 2.4 | 1.9 | 1.5 ~ 2.5 | 2.1 | 4.9 ~ 8.5 | 7.0 | | | 黄土或亚黏土[10] | 2.2 ~ 2.7 | 2.3 | 1.6 ~ 3.3 | 2.4 | 7.2 ~ 10.8 | 8.8 | | | 灰岩[11] | 2.8 ~ 4.9 | 3.6 | 2.8 ~ 5.5 | 3.9 | 14.8 ~ 54.7 | 28.5 | | | 酸性喷出岩[12] | 1.0 ~ 6.2 | 3.1 | 0.8 ~ 16.4 | 4.1 | 1.1 ~ 41.0 | 11.9 | | | 酸性侵入岩[12] | 0.1 ~ 7.6 | 3.1 | 0.1 ~ 30.0 | 4.1 | 0.1 ~ 253.1 | 25.7 | | | 中性侵入岩[12] | 0.1 ~ 6.2 | 2.1 | 0.1 ~ 23.4 | 3.2 | 6.4 ~ 106.0 | 12.2 | | | 化学沉积岩[12] | 0.02 ~ 8.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 ~ 26.7 | 3.6 | 0.03 ~ 132.0 | 14.9 | 包含碳酸盐岩 | | 碎屑沉积岩[12] | 0.01 ~ 9.7 | 1.5 | 0.1 ~ 80.0 | 4.8 | 0.22 ~ 362.0 | 12.4 | | | 变质火成岩[12] | 0.1 ~ 6.1 | 2.5 | 0.1 ~ 148.5 | 4.0 | 0.11 ~ 104.2 | 14.8 | | | 变质沉积岩[12] | 0.01 ~ 5.3 | 2.1 | 0.1 ~ 53.4 | 3.0 | 0.11 ~ 91.4 | 12.0 | |
|
Statistical of U, Th and K measurement values for different geological bodies
|

| 测量位置 | 40K比活度/
(Bq·kg-1) | 238U比活度/
(Bq·kg-1) | 232Th比活度/
(Bq·kg-1) | 备注 | 1号线萤石
脉矿附近 | 158.5 | 19.7 | 10.5 | 异常点附近取样测量 | | 167.4 | 20.8 | 11.3 | | 152.2 | 18.5 | 11.0 | | 183.4 | 22.4 | 12.5 | | 194.2 | 24.6 | 12.1 | 2号线石英
脉附近 | 221.9 | 17.2 | 2.8 | | 249.5 | 19.7 | 2.9 | | 237.8 | 18.9 | 3.0 | | 204.7 | 15.3 | 2.8 | | 261.2 | 20.1 | 3.6 | | 无异常点位 | 887.6 | 40.7 | 33.6 | |
|
Statistics of gamma energy spectral measurements of fluorite vein mines
|
| [1] |
赵鹏, 郑厚义, 张新, 等. 中国萤石产业资源现状及发展建议[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2020, 42(2):178-183.
|
| [1] |
Zhao P, Zheng H Y, Zhang X, et al. Resource actualities and demand countermeasures of fluorite in China[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2020, 42(2):178-183.
|
| [2] |
郑大中, 郑若锋. 萤石成矿机制的探讨[J]. 四川地质学报, 2005, 26(3):149-155.
|
| [2] |
Zheng D Z, Zheng R F. An approach to the ore-forming mechanism for fluorite deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2005, 26(3):149-155.
|
| [3] |
郑碧华, 陈劲民, 熊正烨. γ能谱测量及其应用[J]. 中山大学学报:自然科学版, 2005, 44(S1):158-160.
|
| [3] |
Zheng B H, Chen J M, Xiong Z Y. γ-ray spectrum measurement and its application[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2005, 44(S1):158-160.
|
| [4] |
刘菁华, 王祝文, 田钢, 等. 地面伽马能谱测量在浅覆盖区地质填图中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2003, 39(2):61-64.
|
| [4] |
Liu J H, Wang Z W, Tian G, et al. Application of ground gamma-spectrometry in geological mapping in shallow overburden areas[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2003, 39(2):61-64.
|
| [5] |
万建华, 熊盛青, 范正国. 航空伽马能谱测量方法技术现状与展望[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(3):386-391.
|
| [5] |
Wan J H, Xiong S Q, Fan Z G. The status and prospects of airborne gamma-ray spectrometry technology and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(3):386-391.
|
| [6] |
徐皓, 吕希华. 伽马能谱测量在乌拉嘎金矿外围柳树河地区找矿中的应用[J]. 吉林地质, 2009, 28(4):72-75.
|
| [6] |
Xu H, Lyu X H. Application of gamma-ray spectrum measure to the external prospecting of Wulaga gold deposit,Liushuhe area,Heilongjiang Province[J]. Jilin Geology, 2009, 28(4):72-75.
|
| [7] |
曹俊臣. 中国萤石矿床分类及其成矿规律[J]. 地质与勘探, 1987, 23(3):12-17.
|
| [7] |
Cao J C. The classification and minerogenic regularity of fluorite deposits in China[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1987, 23(3):12-17.
|
| [8] |
周涛发, 王彪, 范裕, 等. 庐枞盆地与A型花岗岩有关的磁铁矿—阳起石—磷灰石矿床——以马口铁矿床为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(10):3087-3098.
|
| [8] |
Zhou T F, Wang B, Fan Y, et al. Apatite-actinolite-magnetite deposit related to A-tpye granite in Luzong basin:Evidence from Makou iron deposit[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(10):3087-3098.
|
| [9] |
戴圣潜, 周存亭, 储东如, 等. 下扬子东南缘北段加里东期构造形迹新资料[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(6):670-672.
|
| [9] |
Dai S Q, Zhou C T, Chu D R, et al. New information of Caledonian tectonic features in the northern part of the southeastern margin of the lower Yangtze valley[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(6):670-672.
|
| [10] |
高峰. 地面伽马能谱测量在内蒙古赤峰浅覆盖区萤石矿勘查中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.
|
| [10] |
Gao F. Application of ground gamma-ray spectrometry in fluorite exploration in Chifeng shallow coverage area,Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2013.
|
| [11] |
程业勋, 王南萍, 侯胜利. 核辐射场与放射性勘查[M]. 北京: 地质出版社,2005:43-45.
|
| [11] |
Cheng Y X, Wang N P, Hou S L. Nuclear geophysical survey[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House,2005:43-45.
|
| [12] |
刘菁华, 王祝文, 郝立波, 等. 大兴安岭地区浅覆盖层对地面伽马能谱测量的影响[J]. 物探与化探, 2004, 28(2):111-113.
|
| [12] |
Liu J H, Wang Z W, Hao L B, et al. The influence of shallow overburden on ground-gamma spectrometry in Daxing'anling area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 28(2):111-113.
|
| [13] |
邹灏, 张寿庭, 方乙, 等. 天然萤石的放射性元素含量及其影响[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(3):478-484.
|
| [13] |
Zou H, Zhang S T, Fang Y, et al. The radioactive elements content of natual fluorite and its influence[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(3):478-484.
|
| [14] |
田义宗, 赵锋, 李钢. Beck公式在滨海新区辐射环境本底调查中的验证[J]. 中国辐射卫生, 2011, 20(3):336-337.
|
| [14] |
Tian Y Z, Zhao F, Li G. Verification of Beck formula in background investigation of radiation environment in Binhai New Area[J]. Chinese Journal of Radiological Health, 2011, 20(3):336-337.
|
| [15] |
International Commission ON Radiation Units and Measurements(ICRU). Gamma-ray spectrometry in the environment[R]. ICRU-53 Report,1994.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Qing-Song, XIA Ming-Zhe, WANG Chun-Lian, LI Ke-Kun, LIU Zeng-Zheng, JIANG Ji-Yong, JIANG Jian-Lang. Geological characteristics and origin of the Mogou fluorite deposit in Fangcheng County, Henan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1): 15-23. |
| [2] |
Hui-Xiong LU, En ZHANG, Bo FENG, Xu CHENG, Ben-Zan WEI, Shao-Shuai WANG, Fan FANG. An analysis of anomaly characteristics of aerial gamma spectrum and uranium metallogenic potential in Bashenghe area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(1): 59-65. |
|
|
|
|
