|
|
|
| Patterns and genesis of fluorine enrichment in shallow groundwater in the eastern start-up area of new and old kinetic energy conversion in Jinan, China |
DUAN Nai-Jin( ) ) |
| Shandong Geological Prospecting Institute of China Chemical Geology and Mine Bureau, Jinan 250013, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on the water quality analysis of 53 sets of shallow groundwater samples from the eastern start-up area, this study examined the distribution characteristics and genetic mechanisms of fluoride concentration (F-) using methods such as chemical composition diagrams, proportion coefficient analysis, correlation analysis, and hydrogeochemical modeling. The results indicate that the F- concentration in shallow groundwater ranges from 0 to 2.85 mg/L, with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 72.78%, and is unevenly distributed horizontally. Horizontally, shallow groundwater with a high F- concentration (also referred to as high-fluoride groundwater) is concentrated in the northwest and northern parts of the study area. Such groundwater exhibits complex hydrochemical types, and environments with weak alkalinity, low calcium, and high sodium favor fluoride ion enrichment. The F- enrichment in shallow groundwater is primarily influenced by climate, terrain, topography, and hydrogeological conditions. Primary mechanisms behind the formation of high-fluoride groundwater include the dissolution of fluorine-bearing minerals in shallow groundwater, as well as the evaporation and concentration of shallow groundwater itself. Additionally, the ion exchange and adsorption processes further contribute to F- enrichment. The F- concentration in shallow groundwater in the northern part of the study area exceeds the threshold of the human health risk index and thus should be dealt with. The results of this study provide a scientific basis for the management and utilization of high-fluoride groundwater resources.
|
|
Received: 23 January 2024
Published: 26 February 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
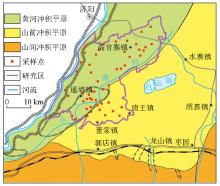
|
Distribution of shallow groundwater samples in the study area
|

化学
成分 | 最小值/
(mg·L-1) | 最大值/
(mg·L-1) | 均值/
(mg·L-1) | 标准差 | 变异系
数/% | | K+ | 0.00 | 9.69 | 1.00 | 1.49 | 149.69 | | Na | 19.10 | 525.00 | 157.90 | 124.55 | 78.88 | | Ca2+ | 40.20 | 407.00 | 150.24 | 76.35 | 50.823 | | Mg2+ | 25.30 | 265.00 | 74.13 | 39.48 | 53.26 | | S | 39.80 | 1430.00 | 226.89 | 236.46 | 104.22 | | Cl- | 33.40 | 806.00 | 177.32 | 130.80 | 73.77 | | HC | 302.00 | 966.00 | 586.68 | 158.07 | 26.95 | | F- | 0 | 3.00 | 0.96 | 0.70 | 72.78 | | pH | 7.26 | 8.00 | 7.67 | 0.19 | 2.46 | | TDS | 501.00 | 3 038.00 | 1 173.66 | 526.14 | 44.83 |
|
Statistical results of main chemical components characteristic in shallow groundwater
|
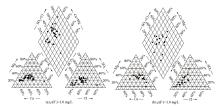
|
Piper trilinear diagram of groundwater in the study area
|
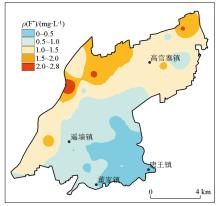
|
Distribution of F- mass concentration in shallow groundwater
|
O 3 - mass concentration
">
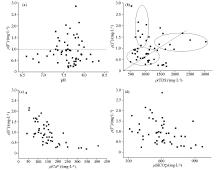
|
Relationship between F- and pH、TDS、Ca2+ 、HC mass concentration
|

地下水
化学类型 | HCO3-
Ca·Mg | HCO3·
Cl-Ca·
Na·Mg | HCO3·
SO4-Ca·
Na·Mg | HCO3·
Cl-Mg·
Ca | HCO3·
SO4-Na·
Mg | | ρ(F-)/(mg·L-1) | 0.49 | 0.578 | 0.714 | 0.896 | 1.903 |
|
The relationship between water chemistry type and F-
|

| 化学成分 | F | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | S | Cl- | | PH | TDS | | F | 1.000 | 0.007 | 0.251 | -0.687** | 0.103 | 0.050 | -0.279* | 0.347* | -0.011 | -0.077 | | K+ | 0.007 | 1.000 | 0.249 | -0.052 | 0.207 | 0.250 | 0.014 | 0.379** | 0.101 | 0.332* | | Na+ | 0.251 | 0.249 | 1.000 | -0.204 | 0.641** | 0.729** | 0.235 | 0.684** | -0.264 | 0.663** | | Ca2+ | -0.687** | -0.052 | -0.204 | 1.000 | 0.039 | 0.010 | 0.581** | -0.419** | -0.077 | 0.328* | | Mg2+ | 0.103 | 0.207 | 0.641** | 0.039 | 1.000 | 0.922** | 0.476** | 0.529** | -0.054 | 0.837** | | S | 0.050 | 0.250 | 0.729** | 0.010 | 0.922** | 1.000 | 0.357* | 0.508** | -0.145 | 0.866** | | Cl- | -0.279* | 0.014 | 0.235 | 0.581** | 0.476** | 0.357* | 1.000 | 0.009 | -0.005 | 0.612** | | HC | 0.347* | 0.379** | 0.684** | -0.419** | 0.529** | 0.508** | 0.009 | 1.000 | -0.166 | 0.452** | | pH | -0.011 | 0.101 | -0.264 | -0.077 | -0.054 | -0.145 | -0.005 | -0.166 | 1.000 | -0.164 | | TDS | -0.077 | 0.332* | 0.663** | 0.328* | 0.837** | 0.866** | 0.612** | 0.452** | -0.164 | 1.000 |
|
Correlation statistics of F- and main chemical components in shallow groundwater
|
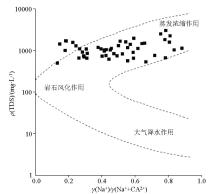
|
Gibbs distribution of shallow groundwater chemistry
|
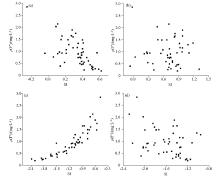
|
Relationship between fluorine content and saturation index of calcite (a), dolomite (b), fluorite (c),and gypsum (d) in shallow groundwater
|
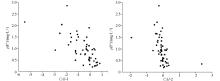
|
Relationship between fluorine content and chloro-alkaline index in shallow groundwater
|

受体
人群 | 非致癌健康风险指标 | 超标
样品数 | 超标率/% | | 极小值 | 极大值 | 均值 | 变异系数 | | 儿童 | 0.19 | 2.76 | 0.91 | 0.6 | 16 | 30.19 | | 成人 | 0.18 | 2.54 | 0.83 | 0.61 | 14 | 26.42 | 参数
取值 | IR/(L·
d-1) | EF/(d·
a-1) | ED/a | BW/kg | AT/d | RfD/(mg·
kg-1·d-1) | | 儿童 | 1.5 | 365 | 6 | 25.9 | 2 190 | 0.06 | | 成人 | 3.62 | 365 | 30 | 69.6 | 10 680 | 0.06 |
|
Results of health risk assessment for shallow groundwater
|
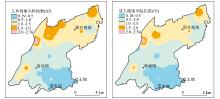
|
Risk assessment of F- in shallow groundwater for children and adults
|
| [1] |
宋天佑, 徐家宁, 程功臻, 等. 无机化学(下册)[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社,2010.
|
| [1] |
Song T Y, Xu J N, Cheng G Z, et al. Inorganic chemistry(volume II)[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2010.
|
| [2] |
张冰. 鲁西北平原高氟地下水分布规律及成因分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
|
| [2] |
Zhang B. Distribution law and cause analysis of high fluorine groundwater in northwest Shandong Plain[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2014.
|
| [3] |
何锦, 张福存, 韩双宝, 等. 中国北方高氟地下水分布特征和成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3):621-626.
|
| [3] |
He J, Zhang F C, Han S B, et al. The distribution and genetic types of high-fluoride groundwater in Northern China[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3):621-626.
|
| [4] |
荆秀艳, 李小珍, 王文姬, 等. 银川平原地下水中氟分布特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2022, 45(2):174-181.
|
| [4] |
Jing X Y, Li X Z, Wang W J, et al. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of fluorine in groundwater in Yinchuan Plain[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 45(2):174-181.
|
| [5] |
赵丽娜, 庞奖励, 杜欢欢, 等. 菏泽市苏家村饮用水质与地氟病关系的研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2011, 23(6):135-138.
|
| [5] |
Zhao L N, Pang J L, Du H H, et al. Study on relationship between drinking water quality and endemic fluorosis in sujia village of Heze City[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2011, 23(6):135-138.
|
| [6] |
余孟玲, 胡晓荣, 周莉. 四川某氟斑牙病区水源土壤和作物中的氟含量[J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(10):1991-1992.
|
| [6] |
Yu M L, Hu X R, Zhou L. Fluoride content in water source soil and crops in a dental fluorosis area in Sichuan[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(10):1991-1992.
|
| [7] |
朱法华, 张景荣. 饮水的化学组分与地氟病的关系[J]. 环境化学, 1996, 15(5):457-462.
|
| [7] |
Zhu F H, Zhang J R. Relationship between chemical composition of drinking water and endemic fluorosis[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1996, 15(5):457-462.
|
| [8] |
鲁涵, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 等. 巴楚县浅层地下水中氟的分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(11):3455-3463.
|
| [8] |
Lu H, Zeng Y Y, Zhou J L, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of fluorine in shallow groundwater of Bachu County[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(11):3455-3463.
|
| [9] |
胡虹羽, 卢国平, 李岩, 等. 琼北地区地热水中氟的富集规律[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(5):1633-1641.
|
| [9] |
Hu H Y, Lu G P, Li Y, et al. Study on enrichment of fluorine in geothermal water in Qiongbei area[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(5):1633-1641.
|
| [10] |
毛若愚, 郭华明, 贾永锋, 等. 内蒙古河套盆地含氟地下水分布特点及成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(2):260-268.
|
| [10] |
Mao R Y, Guo H M, Jia Y F, et al. Distribution characteristics and genesis of fluoride groundwater in the Hetao basin,Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2):260-268.
|
| [11] |
马诗敏, 徐新阳, 陈熙, 等. 松辽西部地区高氟地下水形成机理[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 35(10):1487-1491.
|
| [11] |
Ma S M, Xu X Y, Chen X, et al. Formation mechanism of high-fluorine groundwater in west area of Songliao[J]. Journal of Northeastern University:Natural Science, 2014, 35(10):1487-1491.
|
| [12] |
杨磊, 龚绪龙, 陆徐荣, 等. 连云港北部地区高氟地下水分布特征及成因[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(4):1161-1169.
|
| [12] |
Yang L, Gong X L, Lu X R, et al. Distribution and genesis of high-fluoride groundwater in northern Lianyungang area[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(4):1161-1169.
|
| [13] |
鲁孟胜, 韩宝平, 武凡, 等. 鲁西南地区高氟地下水特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1):294-302.
|
| [13] |
Lu M S, Han B P, Wu F, et al. Characteristics and genesis of high-fluorine groundwater in southwestern Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(1):294-302.
|
| [14] |
国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. GB 5749—2022生活饮用水卫生标准[S]. 北京: 标准出版社, 2022.
|
| [14] |
State Administration for Market Regulation, National Standardization Administration. GB 5749—2022 Sanitary Standards for Drinking Water[S]. Beijing: Standards Press, 2022.
|
| [15] |
孙一博, 王文科, 张春潮, 等. 关中盆地浅层高氟水形成演化机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2013, 40(6):117-122.
|
| [15] |
Sun Y B, Wang W K, Zhang C C, et al. Evolution mechanism of shallow high fluoride groundwater in the Guanzhong Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(6):117-122.
|
| [16] |
时雯雯, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 和田地区地下水中氟的分布特征及形成过程[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(1):155-164.
|
| [16] |
Shi W W, Zhou J L, Zeng Y Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and formation of fluorinein groundwater in Hetan Prefecture[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(1):155-164.
|
| [17] |
高宗军, 张福存, 安永会, 等. 山东高密高氟地下水成因模式与原位驱氟设想[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4):50-58.
|
| [17] |
Gao Z J, Zhang F C, An Y H, et al. Genetic model of high density and high fluorine groundwater in Shandong Province and conception of in situ fluorine removal[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4):50-58.
|
| [18] |
汤洁, 卞建民, 李昭阳, 等. 松嫩平原氟中毒区地下水氟分布规律和成因研究[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3):614-620.
|
| [18] |
Tang J, Bian J M, Li Z Y, et al. The distribution regularity and causes of fluoride in groundwater of the fluorosis area,Songnen Plain[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3):614-620.
|
| [19] |
钱会, 马致远, 李培月. 水文地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012.
|
| [19] |
Qian H, Ma Z Y, Li P Y. Hydrogeochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012.
|
| [20] |
Gibbs R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962):1088-1090.
|
| [21] |
沈照理. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社,1993.
|
| [21] |
Shen Z L. Hydrogeochemical basis[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House,1993.
|
| [22] |
刘春华, 王威, 杨丽芝, 等. 山东省地下水氟富集规律及其驱动机制[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(6):1962-1972.
|
| [22] |
Liu C H, Wang W, Yang L Z, et al. Driving mechanisms of fluorine ennrichment characteristics in groundwater,Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(6):1962-1972.
|
| [23] |
Guo H M, Zhang Y, Xing L N, et al. Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the town of Shahai in the Hetao Basin,Inner Mongolia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(11):2187-2196.
|
| [24] |
Rashid A, Guan D X, Farooqi A, et al. Fluoride prevalence in groundwater around a fluorite mining area in the flood plain of the River Swat,Pakistan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018,635:203-215.
|
| [25] |
Wu C, Wu X, Qian C, et al. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region,Northwest China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018,98:404-417.
|
| [26] |
Brindha K, Jagadeshan G, Kalpana L, et al. Fluoride in weathered rock aquifers of southern India:Managed aquifer recharge for mitigation[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(9):8302-8316.
|
| [27] |
Su C L, Wang Y X, Xie X J, et al. Aqueous geochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater in Datong Basin,Northern China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013,135:79-92.
|
| [28] |
施龙青, 何莉, 詹召伟, 等. 山东霄云煤矿砂岩高氟地下水成因及健康风险评价[J]. 中国科技论文, 2023, 18(9):993-999.
|
| [28] |
Shi L Q, He L, Zhan Z W, et al. Formation mechanism and health risk assessment of high fluoride groundwater in sandstone of Xiaoyun coal mine,Shandong Province[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2023, 18(9):993-999.
|
| [29] |
孟令华, 孔德金, 王磊, 等. 泰安市城区地下水重金属含量及健康风险评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(12):113-118.
|
| [29] |
Meng L H, Kong D J, Wang L, et al. The heavy metal content and health risk assessment of groundwater in urban area of Taian[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(12):113-118.
|
| [1] |
HU Sheng-Tao, ZHANG Xiang-Heng, HAN Ming-Zhi, TANG Shi-Kai, YU Lin-Hong, LI Jin-Peng, ZHANG Jie, ZHAO Guo-Peng, BAI Ying. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in a chemical industry agglomeration area of Yantai City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 1157-1164. |
| [2] |
SHI Xiao-Jin, LI Yuan-Yuan, HUANG Xian-Long. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of deep geothermal fluids in the Binhai New Area, Tianjin City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2): 316-322. |
|
|
|
|

