|
|
|
| Heavy metal transfer in the soil-rice system of Chongzuo and corresponding fitting models |
CHEN Shang-Ren1( ), ZHONG Xiao-Yu1, LI Jie1, YANG Min-Yun2, HUANG Juan1, CHEN Biao1, HE Yao-Ye1 ), ZHONG Xiao-Yu1, LI Jie1, YANG Min-Yun2, HUANG Juan1, CHEN Biao1, HE Yao-Ye1 |
1. Guangxi Institute of Geological Survey, Nanning 530031, China
2. Yizhou District Bureau of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Hechi 546300, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Chongzuo area, located in southwestern Guangxi, encompasses Jiangzhou District, Daxin County, and Longzhou County, with the majority featuring karst topography. This study focused on 242 samples of rice grains and their corresponding rhizosphere soils from contiguous farmland in the region. These samples were analyzed to measure the contents of 26 elements in the soils, including arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), and chromium (Cr), as well as the contents of As, Cd, mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb) in rice grains, using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), and atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS). By analyzing the characteristics of heavy metals in soils and rice grains, the influencing factors and fitting models of heavy metals from soils to rice grains were investigated. The results indicate that the content of oxides in soil was generally lower than the national average, while the content of heavy metals was relatively high, especially Cd and Hg. As and Cd in soils exhibited relatively high pollution risks. The contents of As, Cd, Hg, and Pb in rice grains from non-karst areas were generally higher than those from karst areas. The contents of As, Cd, Hg, and Pb in rice grains generally complied with food safety standards. As and Pb in rice grains showed significant correlations (dominated by negative correlations) with metal elements, non-metal elements, and oxides in rhizosphere soils, while Cd and Hg exhibited significant correlations with oxides in rhizosphere soils. Various fitting models of As in rice grains generally presented a coefficient of determination (R2) above 0.5, indicating better model performance than those for Cd, Hg, and Pb. After distinguishing between karst and non-karst areas, the R2 values of the fitting models were further improved. Among the factors influencing the contents of As, Cd, Hg, and Pb in rice grains, parent material played a more significant role than rice variety. This study preliminarily clarifies the key driving factors of heavy metal transfer in the soil-rice system in the karst area of Chongzuo, providing a theoretical and practical basis for the safe production of agricultural products, classification-based management of contaminated farmland, and policy formulation in similar karst areas of Southwest China.
|
|
Received: 09 April 2025
Published: 30 December 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
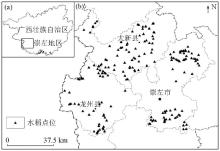
|
The location of the study area (a) and the distribution of sampling points (b)
|

| 参数 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | Mn | N | P | S | Mo | | 最大值 | 76.00 | 4.522 | 506.0 | 85.10 | 0.774 | 109.00 | 155.0 | 384.0 | 2742.0 | 5531 | 2768 | 1166.0 | 4.60 | | 最小值 | 1.93 | 0.086 | 25.4 | 8.51 | 0.065 | 5.92 | 10.1 | 22.7 | 63.4 | 1016 | 332 | 178.0 | 0.21 | | 平均值 | 17.70 | 0.780 | 108.0 | 31.00 | 0.270 | 39.95 | 43.4 | 130.0 | 331.5 | 2700 | 901 | 478.5 | 0.99 | | 全国平均值 | 10.3 | 0.205 | 66 | 25 | 0.076 | 27 | 30 | 71 | 580 | 1172 | 707 | 353 | 0.86 | | 元素 | B | Ge | Se | I | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | K2O | MgO | Na2O | SiO2 | Corg | pH | | 最大值 | 154.0 | 2.48 | 1.32 | 4.72 | 21.88 | 24.29 | 18.4 | 2.87 | 1.65 | 0.28 | 82.9 | 5.3 | 8.27 | | 最小值 | 16.6 | 0.73 | 0.24 | 0.46 | 4.60 | 0.15 | 1.86 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 17.07 | 0.52 | 4.85 | | 平均值 | 60.0 | 1.47 | 0.61 | 1.63 | 13.725 | 0.82 | 5.74 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 0.07 | 64.26 | 2.49 | 7.17 | | 全国平均值 | 51 | 1.4 | 0.26 | 2.4 | 13.14 | 2.85 | 4.49 | 2.36 | 1.48 | 1.28 | 64.96 | | |
|
Statistics of element contents in soil samples (N=242)
|

| 参数 | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | | 最小值 | 0.034 | 0.005 | 0.0009 | 0.036 | | 最大值 | 0.260 | 0.360 | 0.0300 | 0.090 | | 均值 | 0.120 | 0.018 | 0.0345 | 0.057 |
|
Statistics of element contents in Rice samples (N=242) 10-6
|
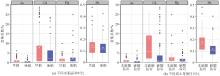
|
Histogram of heavy metal accumulation capacity in rice grains
|
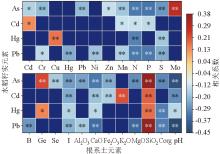
|
Correlation coefficients between rice grain and root soil element contents (N=242)
Note:“*”and “**” indicate that the regression model is significant at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively.
|

| 因子 | 早稻籽实 | 晚稻籽实 | | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | | 决定系数 | 0.52* | 0.19** | 0.21* | 0.23** | 0.57** | 0.31* | 0.6** | 0.47* | | 常数 | -1.49 | 4.92 | 0.11 | -0.34 | -1.43 | 2.14 | 2.30 | -0.49 | | As | 0.24** | - | - | - | 0.40** | - | - | 0.16** | | Cd | - | 0.38** | - | - | -0.17** | 0.42* | - | 0.07** | | Cr | 0.17** | | -0.62** | - | - | - | - | -0.12** | | Cu | - | -0.52** | - | - | - | - | - | | | Hg | - | - | -0.26* | | - | 0.45* | 0.47** | -0.09* | | Ni | - | - | 0.35** | - | 0.13** | - | 0.31** | - | | Zn | -0.12** | - | 0.19* | 0.13** | - | -0.54* | - | - | | Mn | - | -0.32** | - | - | - | - | -0.26** | - | | P | 0.2** | - | - | - | - | - | 0.4** | -0.16** | | S | 0.17* | -0.88* | | -0.23** | - | - | -0.81** | -0.21** | | Mo | - | 0.65** | 0.25** | - | - | - | - | | | B | -0.09* | | 0.36* | - | - | 0.61** | - | | | Ge | - | - | - | -0.38** | 0.35** | -1.85** | - | -0.3** | | Se | -0.21** | - | - | 0.17** | - | - | - | - | | I | - | - | -0.2* | - | - | - | - | - | | Al2O3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.33** | | CaO | -0.05** | - | - | -0.07** | - | -0.49** | - | - | | Fe2O3 | -0.38** | - | - | - | -0.58** | - | - | - | | K2O | 0.1** | 0.37** | -0.34** | 0.14** | - | - | - | - | | MgO | - | - | - | - | -0.2** | - | - | -0.1** | | Na2O | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -0.09* | | SiO2 | - | - | - | -0.27** | - | - | - | - | | Corg | -0.13* | 1** | - | - | - | - | -0.6** | 0.16* | | pH | -0.42** | - | - | - | - | - | - | -0.26* |
|
Parameters of fitting models for heavy metal elements in early and late rice grains
|

| 因子 | 岩溶区水稻籽实 | 非岩溶区水稻籽实 | | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | | 决定系数 | 0.41** | 0.46** | 0.51* | 0.34** | 0.57** | 0.41* | 0.74** | 0.52* | | 常数 | 4.13 | 7.54 | -0.16 | -0.44 | -4.41** | 2.97 | 1.65 | -2.39 | | As | 0.2** | - | - | - | 0.22** | - | 0.25** | - | | Cd | - | 0.67** | - | 0.06** | - | 0.9** | - | - | | Cr | - | - | - | - | - | - | -0.38** | - | | Cu | -0.41** | - | 0.28** | - | 0.31** | - | 0.68** | -0.21** | | Hg | - | - | 0.26** | -0.14** | -0.17** | 0.88** | - | -0.24** | | Ni | 0.39** | - | - | - | - | -0.97** | - | 0.49** | | Pb | - | - | - | - | -0.35** | - | - | 0.25** | | Zn | -0.23** | - | - | - | - | -1.06* | - | -0.33** | | Mn | - | - | -0.2** | - | - | - | - | -0.09** | | N | -1.08** | - | - | - | 0.24** | - | - | 0.22* | | P | -0.21** | - | 0.39** | -0.16** | 0.26** | - | 0.72** | 0.21** | | S | - | -1.16** | -0.39** | - | - | - | -1.4** | -0.17* | | B | - | - | - | - | - | 1.61** | - | -0.18** | | Ge | 0.38** | - | - | - | - | -1.8** | - | -0.19** | | Se | - | 0.79** | - | 0.16** | - | - | - | - | | Al2O3 | -0.71** | 0.93** | 0.32* | - | - | - | 0.59** | - | | CaO | - | -0.43** | 0.12** | - | - | - | - | -0.15** | | Fe2O3 | - | -1.07** | - | 0.11** | - | 1.04** | -0.93** | | | K2O | - | - | - | -0.08** | 0.18** | - | - | - | | MgO | - | - | - | - | -0.23** | - | - | - | | Na2O | 0.24** | -0.55** | - | - | - | - | - | - | | SiO2 | - | -1.07** | 0.49** | -0.08** | 0.9** | 1.52* | - | - | | Corg | 1.12** | - | -0.84** | 0.05** | - | - | - | - | | pH | - | -2.04** | - | - | - | -3.86** | - | 0.68** |
|
Parameters of fitting models for heavy metal elements in rice grains from karst and non-karst areas
|
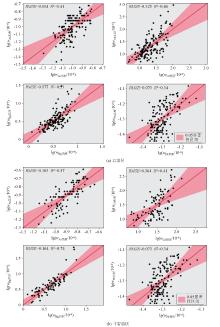
|
Comparison of prediction logarithm value and measured logarithm values of heavy metals in rice based on the best transfer model in different lithogenic zones
|
| [1] |
钱贞兵, 孙立剑, 徐升, 等. 淮河流域安徽段土壤重金属元素分布特征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2):193-200.
|
| [1] |
Qian Z B, Sun L J, Xu S, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soils of the Anhui section of the Huaihe River Basin[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2):193-200.
|
| [2] |
Luo X S, Yu S, Li X D. Distribution,availability,and sources of trace metals in different particle size fractions of urban soils in Hong Kong:Implications for assessing the risk to human health[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(5):1317-1326.
|
| [3] |
Xiao Q, Zong Y T, Lu S G. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan),Liaoning,Northeast China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 120:377-385.
|
| [4] |
Katoh Y, Sato T, Yamamoto Y. Determination of multielement concentrations in normal human organs from the Japanese[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2002, 90(1):57-70.
|
| [5] |
Feng D, Wang R X, Sun X A, et al. Heavy metal stress in plants:Ways to alleviate with exogenous substances[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 897:165397.
|
| [6] |
王玉军, 吴同亮, 周东美, 等. 农田土壤重金属污染评价研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(12):2365-2378.
|
| [6] |
Wang Y J, Wu T L, Zhou D M, et al. Research progress on evaluation of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(12):2365-2378.
|
| [7] |
张逸, 顾爱华. 镉、铅、汞对血管的损伤及其机制研究进展[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2020, 37(7):727-733.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Y, Gu A H. Advances on damage and mechanisms of Cd,Pb,and Hg to blood vessels[J]. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Medicine, 2020, 37(7):727-733.
|
| [8] |
Isiozor N M, Kunutsor S K, Vogelsang D, et al. Serum copper and the risk of cardiovascular disease death in Finnish men[J]. Nutrition,Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, 2023, 33(1):151-157.
|
| [9] |
刘情, 陈红燕, 唐豆豆, 等. 苏南典型区土壤—水稻系统中重金属迁移特征及定量模型研究[J]. 环境科技, 2016, 29(4):20-25.
|
| [9] |
Liu Q, Chen H Y, Tang D D, et al. Migration characteristics and quantitative model of heavy metals in the typical polluted areas of southern Jiangsu Province[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 29(4):20-25.
|
| [10] |
张厦, 宋静, 高慧, 等. 回归模型法推导油菜田土壤Cd限值的不确定性[J]. 环境科学研究, 2016, 29(8):1170-1179.
|
| [10] |
Zhang X, Song J, Gao H, et al. Uncertainty of deducing Cd limit value in rape field soil by regression model method[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 29(8):1170-1179.
|
| [11] |
Wei R H, Chen C, Kou M, et al. Heavy metal concentrations in rice that meet safety standards can still pose a risk to human health[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2023, 4:84.
|
| [12] |
王佳鑫, 侯青叶, 叶丹君, 等. 珠江三角洲不同成土母质发育水稻土镉活动性差异及其影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(1):197-207.
|
| [12] |
Wang J X, Hou Q Y, Ye D J, et al. Differences of cadmium mobility in paddy soils from different parent materials in the Pearl River Delta and its influencing factors[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(1):197-207.
|
| [13] |
蔡秋玲, 林大松, 王果, 等. 不同类型水稻镉富集与转运能力的差异分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(6):1028-1033.
|
| [13] |
Cai Q L, Lin D S, Wang G, et al. Differences in cadmium accumulation and transfer capacity among different types of rice cultivars[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(6):1028-1033.
|
| [14] |
邓齐玉, 赵银军, 林清, 等. 广西重金属镉的区域性分布特征与土壤污染状况评价[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(1):164-171,92.
|
| [14] |
Deng Q Y, Zhao Y J, Lin Q, et al. Regional distribuiton characterstics of cadmium and evaluation of soil pollution situation in Guangxi[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(1):164-171,92.
|
| [15] |
任杰, 曾杨, 张博伦, 等. 高地球化学背景地区重金属污染分布特征及源解析研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2024, 37(12):2745-2756.
|
| [15] |
Ren J, Zeng Y, Zhang B L, et al. Distribution characteristics and enrichment mechanisms of heavy metal pollution in high geochemical background areas[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2024, 37(12):2745-2756.
|
| [16] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [16] |
Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000.
|
| [17] |
侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020.
|
| [17] |
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Soil geochemical dataset of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020.
|
| [18] |
张倩, 刘湘伟, 税勇, 等. 黄河上游重金属元素分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 57(2):333-340.
|
| [18] |
Zhang Q, Liu X W, Shui Y, et al. Distribution of heavy metals in the upstream of Yellow River and ecological risk assessment[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2021, 57(2):333-340.
|
| [19] |
冯志刚, 刘秀明, 王世杰, 孙承兴. 中国湖南省西部吉首地区石灰岩风化剖面的矿物学和地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2002, 30(4):7-14.
|
| [19] |
Feng Z G, Liu X M, Wang S J, et al. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of the limestone weathering profile in Jishou,Western Hunan Province,China[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2002, 30(4):7-14.
|
| [20] |
Ghrefat H A, Yusuf N, Jamarh A, et al. Fractionation and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil samples collected along Zerqa River,Jordan[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 66(1):199-208.
|
| [21] |
Wang Q, Zeng X N, Song Q L, et al. Identification of key genes and modules in response to Cadmium stress in different rice varieties and stem nodes by weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10:9525.
|
| [22] |
Xia W W, Ghouri F, Zhong M H, et al. Rice and heavy metals:A review of cadmium impact and potential remediation techniques[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 957:177403.
|
| [23] |
马宏宏, 彭敏, 刘飞, 等. 广西典型碳酸盐岩区农田土壤—作物系统重金属生物有效性及迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1):449-459.
|
| [23] |
Ma H H, Peng M, Liu F, et al. Bioavailability,migration and enrichment characteristics of heavy metals in farmland soil-crop system in typical carbonate rock areas of Guangxi[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1):449-459.
|
| [24] |
曹宁, 孙彬彬, 曾道明, 等. 珠江三角洲西部典型乡镇稻米与根系土重金属元素含量关系研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5):739-752.
|
| [24] |
Cao N, Sun B B, Zeng D M, et al. Study on the relationship between the contents of heavy metals in rice and root soils in typical townships in the western Pearl River Delta[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5):739-752.
|
| [25] |
Zhao K L, Liu X M, Xu J M, et al. Heavy metal contaminations in a soil-rice system:Identification of spatial dependence in relation to soil properties of paddy fields[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1-3):778-787.
|
| [26] |
Ge Y N, Jia P H, Tian S K, et al. Cadmium distribution in rice:Understanding the role of plant nodes and growth stages[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2024, 362:124919.
|
| [27] |
余飞, 张风雷, 蒋玉莲, 等. 地质高背景区土壤—水稻系统重金属含量特征与综合质量评价[J]. 环境科学, 2025, 46(1):453-460.
|
| [27] |
Yu F, Zhang F L, Jiang Y L, et al. Characteristics and comprehensive quality assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop system of high geological background area[J]. Environmental Science, 2025, 46(1):453-460.
|
| [28] |
李冰, 王昌全, 代天飞, 等. 水稻子实对不同形态重金属的累积差异及其影响因素分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007, 13(4):602-610.
|
| [28] |
Li B, Wang C Q, Dai T F, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in rice seeds as influenced by metal speciation and soil properties[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2007, 13(4):602-610.
|
| [29] |
Lavado R S, Rodríguez M, Alvarez R, et al. Transfer of potentially toxic elements from biosolid-treated soils to maize and wheat crops[J]. Agriculture,Ecosystems & Environment, 2007, 118(1-4):312-318.
|
| [30] |
Karami M, Afyuni M, Khoshgoftarmanesh A H, et al. Grain zinc,iron,and copper concentrations of wheat grown in central Iran and their relationships with soil and climate variables[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(22):10876-10882.
|
| [31] |
Römkens P F A M, Guo H Y, Chu C L, et al. Prediction of Cadmium uptake by brown rice and derivation of soil-plant transfer models to improve soil protection guidelines[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(8-9):2435-2444.
|
| [32] |
黄勇, 欧阳渊, 刘洪, 等. 地质建造对土壤性质的制约及其生态环境效应——以西昌地区红壤为例[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4):196-212.
|
| [32] |
Huang Y, Ouyang Y, Liu H, et al. Restriction of geological formation on soil properties and its ecological environmental effects:Example from red soil in the Xichang area[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4):196-212.
|
| [33] |
李杰, 朱立新, 康志强. 南宁市郊周边农田土壤—农作物系统重金属元素迁移特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):43-52.
|
| [33] |
Li J, Zhu L X, Kang Z Q. Characteristics of transfer and their influencing factors of heavy metals in soil-crop system of peri-urban agricultural soils of Nanning,South China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):43-52.
|
| [34] |
周墨, 梅丽辉, 刘冰权, 等. 赣西地区土壤—水稻系统中重金属Cd元素地球化学特征与健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 2025, 52(1):278-288.
|
| [34] |
Zhou M, Mei L H, Liu B Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metal Cd in soil-rice system in Western Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2025, 52(1):278-288.
|
| [35] |
马宏宏, 彭敏, 郭飞, 等. 广西典型岩溶区农田土壤—作物系统Cd迁移富集影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3):1514-1522.
|
| [35] |
Ma H H, Peng M, Guo F, et al. Influencing factors of Cd migration and enrichment in farmland soil-crop system in typical karst areas of Guangxi[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3):1514-1522.
|
| [36] |
赵科理, 傅伟军, 戴巍, 等. 浙江省典型水稻产区土壤—水稻系统重金属迁移特征及定量模型[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(2):226-234.
|
| [36] |
Zhao K L, Fu W J, Dai W, et al. Characteristics and quantitative model of heavy metal transfer in soil-rice systems in typical rice production areas of Zhejiang Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(2):226-234.
|
| [1] |
SONG Yun-Hong, YANG Feng-Chao, LIU Kai, DAI Hui-Min, XU Jiang, YANG Ze. A multivariate statistical analysis of the distribution and influencing factors of heavy metal elements in the cultivated land of the Sanjiang Plain[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1064-1075. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Qin-Rui, LI Huan, DENG Yu-Fei, HUANG Yong, ZHANG Bo, XU Yi-bo. Distribution of heavy metal elements in soil of the Southeastern suburbs of Beijing and their enrichment characteristics in surface soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2): 490-501. |
|
|
|
|

