|
|
|
| Assessment of primary soil fertility indicators of different forest stand types in the Nanshan forest farm in Jiyuan City |
WANG Yong-Feng1,2( ), WANG Jian1,2,3,4( ), WANG Jian1,2,3,4( ), PANG Guo-Tao1,2,3,4, ZHU Wei-Ping5, WANG Ke-Chao1,4, WANG Xiao-En1,2,4, WANG Zu-Zhen1,2,4, LIU Jie1,2,4 ), PANG Guo-Tao1,2,3,4, ZHU Wei-Ping5, WANG Ke-Chao1,4, WANG Xiao-En1,2,4, WANG Zu-Zhen1,2,4, LIU Jie1,2,4 |
1. Yantai Geological Survey Center of Coastal Zone, China Geological Survey, Yantai 264000, China
2. Ministry of Natural Resources Observation and Research Station of Land-Sea Interaction Field in the Yellow River Estuary, Yantai 264000, China
3. Key Laboratory of Natural Resource Coupling Process and Effects, Beijing 100055, China
4. Field Scientific Observation and Research Station for Soil and Water Resources Security and Ecological Benefits in the Yellow River Basin (Henan Section), Zhengzhou 450000, China
5. China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural Resources, Beijing 100083,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Soil fertility is a significant indicator that measures the ability of soil to provide various nutrients required by vegetation and reflects the crop producing power of soil. To ascertain the soil fertility of different forest stand types in the Nanshan forest farm of Jiyuan City, this study investigated the soil of four forest stand types: Platycladus orientalis, Robinia pseudoacacia, Quercus variabilis, and walnut trees. It analyzed the soil nutrients of the forest stand types by determining the pH, organic matter, total nutrients (TN,TP,TK), and available nutrients (AN,AP,AK) of soil at different depths (0~40 cm). Moreover, it assessed the comprehensive soil fertility using the improved Nemerow comprehensive index method. The results show that: (1) Except pH, the physicochemical factors of the soil of the forest stand types in the study area exhibited moderate variations, and the soil TP, TK, AP, AK, and pH manifested significant differences; (2) With an increase in soil depth, the soil in the study area showed increased pH and bulk density, decreased organic matter, TN, and available nutrients, and almost unchanged TP and TK; (3) The assessment of soil nutrient abundance indicated that the TN, TP, and available nutrients were relatively poor in the soil of the study area; (4) Based on a comprehensive assessment, the soil fertility of four forest stand types at different depths decreased in the order of Robinia pseudoacacia, Quercus variabilis, Platycladus orientalis, and walnut trees. Their soil fertility was generally at an average level, with low values observed at depths ranging from 20 to 40 cm. The comprehensive analysis indicates that TN, TP, and available nutrients are deficient in the study area. Therefore, applying appropriate organic fertilizers, nitrogen, and phosphorus is recommended for the study area.
|
|
Received: 25 December 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
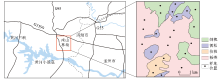
|
Location and sample distribution map of the research area
|

| 分级 | 有机质 | 全氮 | 全磷 | 全钾 | 碱解氮 | 有效磷 | 速效钾 | | 丰富 | >40 | >2 | >1 | >25 | >150 | >40 | >200 | | 较丰富 | 30~40 | 1.5~2.0 | 0.8~1.0 | 20~25 | 120~150 | 20~40 | 150~200 | | 中等 | 20~30 | 1.0~1.5 | 0.6~0.8 | 15~20 | 90~120 | 10~20 | 100~150 | | 较缺 | 10~20 | 0.75~1.0 | 0.4~0.6 | 10~15 | 60~90 | 5~10 | 50~100 | | 缺 | 6~10 | 0.5~0.75 | 0.2~0.4 | 5~10 | 30~60 | 3~5 | 30~50 | | 极缺 | <6 | <0.5 | <0.2 | <5 | <30 | <3 | <30 |
|
Classification standard of soil nutrient content
|

| 土壤属性 | 内梅罗分级指标 | | Xa | Xc | Xp | | 有机质/10-3 | 10 | 20 | 30 | | pH(≤7) | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6.5 | | pH(>7) | 9 | 8 | 7 | | 全氮/10-3 | 0.75 | 1.5 | 2 | | 全磷/10-3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1 | | 全钾/10-3 | 5 | 20 | 25 | | 碱解氮/10-6 | 60 | 120 | 180 | | 有效磷/10-6 | 5 | 10 | 20 | | 速效钾/10-6 | 50 | 100 | 200 | | 容重/(g·cm-3) | 1.45 | 1.35 | 1.25 |
|
Classification standards of soil attributes
|

| 养分指标 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% | 偏度 | 峰度 | | 有机质 | 12.90 | 58.00 | 22.30 | 24.33 | 8.62 | 35.43 | 1.60 | 3.01 | | 全氮 | 0.04 | 2.78 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 60.87 | 1.08 | 1.40 | | 全磷 | 0.18 | 0.94 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 38.29 | 0.41 | -0.46 | | 全钾 | 14.70 | 27.85 | 20.90 | 20.55 | 3.10 | 15.09 | 0.09 | -0.71 | | 碱解氮 | 18.10 | 177.40 | 58.04 | 67.66 | 37.53 | 55.47 | 1.19 | 0.91 | | 有效磷 | 0.50 | 10.10 | 4.2 | 4.19 | 2.05 | 48.93 | 0.63 | 0.39 | | 速效钾 | 18.00 | 264.00 | 54.0 | 68.15 | 41.37 | 60.70 | 1.78 | 4.89 | | 容重 | 0.95 | 1.86 | 1.42 | 1.40 | 0.16 | 11.43 | -0.37 | 0.42 | | pH | 6.32 | 8.39 | 7.73 | 7.59 | 0.49 | 6.46 | -1.08 | 0.61 |
|
Statistics of soil nutrients, bulk density and pH in the study area
|

| 理化性质 | 林分类型 | | 侧柏林 | 刺槐林 | 栓皮栎林 | 核桃林 | | 有机质 | 25.98±8.56a | 22.69±8.44a | 23.77±9.38a | 19.39±4.69a | | 全氮 | 0.98±0.62a | 0.92±0.57a | 0.82±0.52a | 0.90±0.24a | | 全磷 | 0.37±0.12a | 0.57±0.10b | 0.77±0.14c | 0.56±0.10b | | 全钾 | 18.97±2.44a | 24.06±1.44b | 22.81±1.80b | 17.19±1.19c | | 碱解氮 | 72.53±39.8a | 70.47±38.95a | 61.67±37.09a | 54.63±19.58a | | 有效磷 | 3.60±1.85ac | 5.91±1.73b | 4.77±2.22bc | 3.06±0.71a | | 速效钾 | 84.57±48.80a | 68.58±29.78ab | 41.96±16.15b | 55.75±13.09ab | | 容重 | 1.37±0.13a | 1.38±0.20a | 1.44±0.20a | 1.49±0.13a | | pH | 7.78±0.14a | 7.71±0.15a | 6.96±0.45b | 8.27±0.09c |
|
Soil physical and chemical characteristics of different stand types
|
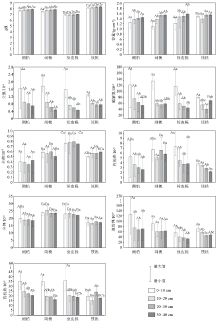
|
Results of variance analysis of soil physical and chemical indicators
|

| 分级 | 有机质 | 全氮 | 全磷 | 全钾 | 碱解氮 | 有效磷 | 速效钾 | | 丰富 | 7.95 | 4.55 | 2.27 | 6.82 | 6.82 | 0 | 1.14 | | 较丰富 | 10.23 | 6.82 | 10.23 | 50.00 | 4.55 | 0 | 3.41 | | 中等 | 52.27 | 29.55 | 21.59 | 38.64 | 7.95 | 1.14 | 18.18 | | 较缺 | 29.55 | 15.91 | 32.95 | 3.41 | 26.14 | 26.14 | 31.82 | | 缺 | 0 | 17.05 | 26.14 | 1.14 | 43.18 | 43.18 | 30.68 | | 极缺 | 0 | 26.14 | 6.82 | 0 | 11.36 | 29.55 | 14.77 |
|
Statistics of the proportion of soil nutrient classification in the study area %
|

| 林分 | 深度/cm | 土壤养分指标的标准化均值Pi | 肥力指数 | | pH | 容重 | 有机质 | 全氮 | 全磷 | 全钾 | 碱解氮 | 有效磷 | 速效钾 | P | 评价 | | 侧柏 | 0~10 | 2.36 | 1.68 | 2.81 | 2.11 | 1.12 | 2.08 | 1.87 | 1.03 | 2.10 | 1.36 | 中等 | | 10~20 | 2.24 | 1.66 | 2.54 | 1.17 | 1.05 | 1.91 | 1.16 | 0.72 | 1.42 | 1.07 | 中等 | | 20~30 | 2.17 | 1.19 | 2.43 | 1.06 | 0.87 | 1.94 | 0.93 | 0.60 | 1.33 | 0.95 | 差 | | 30~40 | 2.12 | 1.36 | 2.26 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 1.90 | 0.77 | 0.53 | 1.36 | 0.91 | 差 | | 刺槐 | 0~10 | 2.49 | 1.29 | 3.00 | 2.28 | 1.94 | 2.73 | 2.19 | 1.24 | 1.77 | 1.53 | 良 | | 10~20 | 2.28 | 1.68 | 2.58 | 1.16 | 1.73 | 2.92 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 1.19 | 1.20 | 中等 | | 20~30 | 2.23 | 0.95 | 2.68 | 0.81 | 1.87 | 2.71 | 0.80 | 1.33 | 0.88 | 1.12 | 中等 | | 30~40 | 2.17 | 0.96 | 2.64 | 0.65 | 1.70 | 2.70 | 0.86 | 1.15 | 1.25 | 1.06 | 中等 | | 栓皮栎 | 0~10 | 2.76 | 1.66 | 2.91 | 1.95 | 2.40 | 2.54 | 1.90 | 1.44 | 1.13 | 1.49 | 中等 | | 10~20 | 2.85 | 1.29 | 2.43 | 0.97 | 2.45 | 2.70 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 1.18 | 中等 | | 20~30 | 2.83 | 0.98 | 2.41 | 0.78 | 2.49 | 2.53 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 1.09 | 中等 | | 30~40 | 2.81 | 0.92 | 2.54 | 0.62 | 2.37 | 2.38 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 1.03 | 中等 | | 核桃 | 0~10 | 1.81 | 0.98 | 2.47 | 1.68 | 1.50 | 1.79 | 1.24 | 0.76 | 1.43 | 1.07 | 中等 | | 10~20 | 1.79 | 1.96 | 2.55 | 1.11 | 1.83 | 1.77 | 0.79 | 0.69 | 1.17 | 1.05 | 中等 | | 20~30 | 1.67 | 0.94 | 2.81 | 0.99 | 1.84 | 1.86 | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 差 | | 30~40 | 1.66 | 0.94 | 2.42 | 1.00 | 1.97 | 1.83 | 1.06 | 0.43 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 差 |
|
Comprehensive evaluation of soil fertility
|

| 土壤养分 | 林分类型 | | 侧柏林 | 刺槐林 | 栓皮栎林 | 核桃林 | | 有机质 | 中等 | 中等 | 中等 | 较缺 | | 全氮 | 较缺 | 较缺 | 较缺 | 较缺 | | 全磷 | 缺 | 较缺 | 中等 | 较缺 | | 全钾 | 中等 | 较丰 | 较丰 | 中等 | | 碱解氮 | 较缺 | 较缺 | 较缺 | 缺 | | 有效磷 | 缺 | 较缺 | 缺 | 缺 | | 速效钾 | 较缺 | 较缺 | 缺 | 较缺 |
|
Soil nutrient abundance and ridge status of different stands
|
| [1] |
Bloor J M G, Bardgett R D. Stability of above-ground and below-ground processes to extreme drought in model grassland ecosystems:Interactions with plant species diversity and soil nitrogen availability[J]. Perspectives in Plant Ecology,Evolution and Systematics, 2012, 14(3):193-204.

|
| [2] |
Li S, Lei Y D, Zhang Y Y, et al. Rational trade-offs between yield increase and fertilizer inputs are essential for sustainable intensification:A case study in wheat-maize cropping systems in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019,679:328-336.
|
| [3] |
胡庆海, 李俊华, 王学求, 等. 河北省永清县农耕区土壤肥力主要指标现状评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(6):1611-1619.
|
| [3] |
Hu Q H, Li J H, Wang X Q, et al. Evaluation of the primary soil fertility indices for the agricultural area of Yongqing County,Hebei Province[J]. Geophysicaland Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6):1611-1619.
|
| [4] |
纪萱, 陈立新, 薛洪祥. 不同林龄红松人工林土壤养分及微量元素的变化规律[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2007, 35(7):27-29.
|
| [4] |
Ji X, Chen L X, Xue H X. Changing rules of soil nutrients and microelements in Korean pine plantations of different ages[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2007, 35(7):27-29.
|
| [5] |
朱祖祥. 土壤学[M]. 北京: 农业出版社,1983.
|
| [5] |
Zhu Z X. Agrology[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press,1983.
|
| [6] |
樊星火, 葛红艳, 张参参, 等. 江西省生态公益林典型林分土壤肥力状况研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(11):84-92.
|
| [6] |
Fan X H, Ge H Y, Zhang C C, et al. Variations in soil fertility of typical non-commercial forest types in Jiangxi Province of Eastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(11):84-92.
|
| [7] |
沈仁芳, 孙波, 施卫明, 等. 地上—地下生物协同调控与养分高效利用[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(6):566-574.
|
| [7] |
Shen R F, Sun B, Shi W M, et al. Interactions between above-and below-ground organisms for nutrient-efficient utilization[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017, 32(6):566-574.
|
| [8] |
秦文静, 李小英, 许彦红, 等. 滇中地区典型公益林林分土壤养分及肥力研究[J]. 西部林业科学, 2022, 51(2):145-154.
|
| [8] |
Qin W J, Li X Y, Xu Y H, et al. Soil nutrients and fertility of typical public welfare forest in central Yunnan[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2022, 51(2):145-154.
|
| [9] |
周永维, 葛瑶, 艾宁, 等. 南泥湾湿地不同植被类型土壤养分变化规律与肥力评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(5):76-80,87.
|
| [9] |
Zhou Y W, Ge Y, Ai N, et al. Soil nutrient variation pattern and fertility evaluation in different vegetation types in Nanniwan wetland[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(5):76-80,87.
|
| [10] |
杜尚嘉, 吴海霞, 陈国德, 等. 五指山次生林群落土壤养分特征及肥力质量评价[J]. 热带农业科学, 2021, 41(12):18-24.
|
| [10] |
Du S J, Wu H X, Chen G D, et al. Soil nutrient characteristics and fertility quality evaluation of secondary forest communities in Wuzhishan[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2021, 41(12):18-24.
|
| [11] |
高君亮, 罗凤敏, 高永, 等. 阴山北麓不同土地利用类型土壤养分特征分析与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4):230-238.
|
| [11] |
Gao J L, Luo F M, Gao Y, et al. Analysis of soil nutrient characteristics under different land use patterns in the northern piedmont of Yinshan Mountain[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(4):230-238.
|
| [12] |
何林倩, 刘倩, 王德彩, 等. 基于数字土壤制图技术的土壤有机碳储量估算[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(2):591-600.
|
| [12] |
He L Q, Liu Q, Wang D C, et al. Estimation of soil organic carbon storage based on digital soil mapping technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(2):591-600.
|
| [13] |
施梦月. 基于时间序列HJ-1A/1B数据的林型识别[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2022.
|
| [13] |
Shi M Y. Forest type identification based on time series HJ-1A/1B data[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2022.
|
| [14] |
全国土壤普查办公室. 中国土壤[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社,1998.
|
| [14] |
National Soil Census Office. Chinese soil[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press,1988.
|
| [15] |
阎文杰, 吴启堂. 一个定量综合评价土壤肥力的方法初探[J]. 土壤通报, 1994, 25(6):245-247.
|
| [15] |
Yan W J, Wu Q T. Preliminary study on a quantitative and comprehensive evaluation method for soil fertility[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1994, 25(6):245-247.
|
| [16] |
高郯, 李江荣, 卢杰, 等. 色季拉山急尖长苞冷杉林不同坡向土壤养分及肥力研究[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4):1331-1341.
|
| [16] |
Gao T, Li J R, Lu J, et al. Soil nutrient and fertility of different slope directions in the Abies georgei var.smithii forest in Sejila Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4):1331-1341.
|
| [17] |
周伟, 王文杰, 张波, 等. 长春城市森林绿地土壤肥力评价[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(4):1211-1220.
|
| [17] |
Zhou W, Wang W J, Zhang B, et al. Soil fertility evaluation for urban forests and green spaces in Changchun City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(4):1211-1220.
|
| [18] |
邵明安, 王全九, 黄明斌. 土壤物理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006.
|
| [18] |
Shao M A, Wang Q J, Huang M B. Soil physics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006.
|
| [19] |
单奇华, 俞元春, 张建锋, 等. 城市森林土壤肥力质量综合评价[J]. 水土保持通报, 2009, 29(4):186-190,223.
|
| [19] |
Shan Q H, Yu Y C, Zhang J F, et al. Comprehensive estimation of soil fertility in urban forest[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 29(4):186-190,223.
|
| [20] |
信忠保, 余新晓, 张满良, 等. 黄土高原丘陵沟壑区不同土地利用的土壤养分特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2012, 29(3):379-384.
|
| [20] |
Xin Z B, Yu X X, Zhang M L, et al. Soil nutrient characteristics under different land use types in a gully-hilly region of the Loess Plateau[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2012, 29(3):379-384.
|
| [21] |
雷志栋, 杨诗秀, 谢森传. 土壤水动力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社,1988.
|
| [21] |
Lei Z D, Yang S X, Xie S C. Soil hydrodynamics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press,1988.
|
| [22] |
Hines J, Pabst S, Mueller K E, et al. Soil-mediated effects of global change on plant communities depend on plant growth form[J]. Ecosphere, 2017, 8(11):e01996.
|
| [23] |
杨红, 徐唱唱, 赛曼, 等. 不同土地利用方式对土壤含水量、pH值及电导率的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(11):1922-1927.
|
| [23] |
Yang H, Xu C C, Sai M, et al. Effects of land use on soil moisture,pH and electrical conductivity[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28(11):1922-1927.
|
| [24] |
于冬雪, 贾小旭, 黄来明, 等. 黄土区不同土层土壤容重空间变异与模拟[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(1):55-64.
|
| [24] |
Yu D X, Jia X X, Huang L M, et al. Spatial variation of soil bulk density in different soil layers in the loess area and simulation[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(1):55-64.
|
| [25] |
杨士凯, 周运超, 黄磊, 等. 杉木成熟林土壤容重空间变异特征[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2020, 40(1):30-38.
|
| [25] |
Yang S K, Zhou Y C, Huang L, et al. Spatial variation characteristics of soil bulk density inmature forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2020, 40(1):30-38.
|
| [26] |
和丽萍, 李贵祥, 孟广涛, 等. 高黎贡山不同森林类型土壤肥力状况研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 2015, 22(6):116-121.
|
| [26] |
He L P, Li G X, Meng G T, et al. Study on soil fertility of different forest types in Gaoligong mountains[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 22(6):116-121.
|
| [27] |
黎宏祥, 王彬, 王玉杰, 等. 不同林分类型对土壤团聚体稳定性及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(5):84-91.
|
| [27] |
Li H X, Wang B, Wang Y J, et al. Impact of different forest types on stability and organic carbon of soil aggregates[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(5):84-91.
|
| [28] |
Attiwill P M, Leeper G W. Forest soils and nutrient cycles[M]. Washington, DC: Independent Publishe,1987.
|
| [29] |
吕瑞恒, 刘勇, 于海群, 等. 北京山区不同林分类型土壤肥力的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2009, 31(06):159-163.
|
| [29] |
Lyu R H, Liu Y, Yu H Q, et al. Soil fertility of different forest types in the mountainous area of Beijing[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2009, 31(06):159-163.
|
| [30] |
杨斌, 王家学, 郭小玮, 等. 景谷县思茅松人工林土壤养分特征与肥力评价[J]. 西部林业科学, 2023, 52(4):7-12.
|
| [30] |
Yang B, Wang J X, Guo X W, et al. Soil nutrient characteristics and fertility evaluation of Pinus Simaoplantations in Jinggu County[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2023, 52(4):7-12.
|
| [31] |
严明书, 吴春梅, 蒙丽, 等. 重庆市黔江猕猴桃果园土壤养分状况分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(5):1123-1130.
|
| [31] |
Yan M S, Wu C M, Meng L, et al. An analysis of soil nutrient status of kiwifruit orchard in Qianjiang,Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5):1123-1130.
|
| [1] |
LI Yu, ZHANG Yu-Han, GUAN Kai-Jiang, BAO Li-Ran. Evaluating the nutritional and safety quality of camellia oil, oil content of camellia oleifera fruits, and site soils in Youyang[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(2): 521-526. |
| [2] |
HU Qing-Hai, LI Jun-Hua, WANG Xue-Qiu, YI Ming-Xuan, WU Hui, TIAN Mi. Evaluation of the primary soil fertility indices for the agricultural area of Yongqing County, Hebei Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1611-1619. |
|
|
|
|

