|
|
|
| An automatic fitting method for a variogram based on deep learning |
ZHAO Li-Fang1,2( ), YU Si-Yu1,2( ), YU Si-Yu1,2( ), LI Shao-Hua1,2 ), LI Shao-Hua1,2 |
1. Key Laboratory of Exploration Technologies for Oil and Gas Resources, Ministry of Education, Yangtze University, Wuhan 430100, China
2. School of Geosciences, Yangtze University, Wuhan 430100, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract A variogram serves as a crucial tool for quantifying spatial correlations. However, existing variogram fitting methods often yield unstable results. This study proposed an automatic variogram fitting method based on deep learning, aiming to enhance the precision and stability of automatic fitting. The fitting of the experimental variogram is essentially a nonlinear optimization problem, which involves optimizing the matching between the experimental and theoretical variograms. The proposed method generated substantial training datasets using several sets of theoretical variograms with varying parameter values for training and learning in deep neural networks. The trained model was then used for the automatic fitting of the experimental variogram. Multiple sets of experimental results demonstrate that based on the robust fitting capability of deep neural networks, the proposed method manifested superior fitting stability and computational efficiency compared to the least squares method, providing a novel approach for automatic variogram fitting in geostatistics.
|
|
Received: 01 December 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
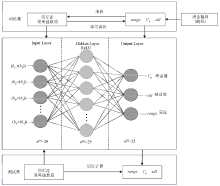
|
Neural network structure
|

| v1 | v2 | v3 | v4 | … | v19 | v20 | C0 | range | sill | | 13.04 | 23.73 | 36.66 | 41.25 | … | 85.43 | 87.01 | 5 | 44.14 | 84.75 | | 6.04 | 16.99 | 43.76 | 45.61 | … | 77.48 | 82.78 | 5 | 35.89 | 79.97 | | 14.45 | 17.54 | 33.05 | 39.66 | … | 78.51 | 76.79 | 5 | 43.64 | 75.19 | | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | | 14.53 | 35.27 | 45.21 | 49.80 | … | 85.18 | 87.15 | 5 | 34.77 | 85.23 | | 21.75 | 40.62 | 51.56 | 68.23 | … | 89.99 | 90.32 | 5 | 28.07 | 87.99 |
|
1 000×20 experimental variational function data
|

| 分组 | C0 | range | sill | | 第一组 | 0 | 20 ~ 45 | 70 ~ 85 | | 第二组 | 10 | 25 ~ 50 | 75 ~ 90 | | 第三组 | 15 | 30 ~ 55 | 80 ~ 95 | | 第四组 | 20 | 35 ~ 60 | 85 ~ 100 |
|
Parameters of each data of the experimental variance function
|
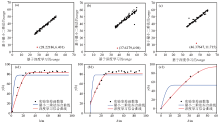
|
Comparison of the fitting effect of the two different methods
a—range mapping relationship between the least squares method and the deep learning method when the variogram function's range is 25~50, with red points indicating outliers; b—range mapping relationship between the least squares method and the deep learning method when the variogram function's range is 35~60, with red points indicating outliers; c—range mapping relationship between the least squares method and the deep learning method when the variogram function's range is 35~60, with red points indicating outliers; a1—the x and y coordinates of the red outliers in a correspond to the values of the least squares fitting curve and the deep learning curve, respectively; b1—the x and y coordinates of the red outliers in b correspond to the range values of the least squares fitting curve and the deep learning curve, respectively; c1—the x and y coordinates of the red outliers in c correspond to the range values of the least squares fitting curve and the deep learning curve, respectively
|

| 参数 | 第一组 | 第二组 | 第三组 | | 理论变差函数 | 最小二乘法 | 深度学习 | 理论变差函数 | 最小二乘法 | 深度学习 | 理论变差函数 | 最小二乘法 | 深度学习 | | C0 | 0 | 0 | -0.13 | 20.00 | 1.67 | 17.97 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | | range | 28.22 | 6.40 | 30.01 | 37.63 | 4.98 | 32.47 | 58.93 | 8.78 | 57.62 | | sill | 84.27 | 78.11 | 83.86 | 85.17 | 78.25 | 81.24 | 96.83 | 53.18 | 94.37 |
|
Comparison of the parameters of the variational functions C0, range, and sill
|
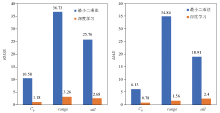
|
Comparison of root mean square error and average error of the two methods
|
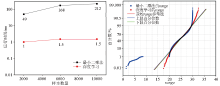
|
Efficiency comparison chart of two methods
|
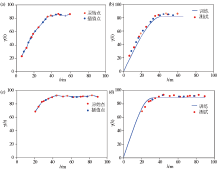
|
Depth learning interpolated fit plot
a—data points of 10 experimental variogram functions interpolated to 20 data points, with red indicating original points and blue indicating interpolated points; b—fitting effect diagram of fig.a interpolated data points; c—data points of 15 experimental variogram functions interpolated to 20 data points, with red indicating original points and blue indicating interpolated points; d—fitting effect diagram of fig.c interpolated data points.
|

| v1 | v2 | … | v10 | C0 | range | sill | | 19.10 | 38.93 | … | 91.27 | 10 | 49.42 | 92.01 | | 17.03 | 27.94 | … | 97.51 | 10 | 54.12 | 88.67 | | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | | 11.36 | 30.05 | … | 94.78 | 10 | 58.91 | 94.25 | | 17.68 | 35.53 | … | 92.45 | 10 | 54.42 | 93.44 |
|
1 000×6 experimental variational function data
|
| [1] |
李正文, 李琼, 吴朝容. 沉积盆地有效储集层综合识别技术[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 2002.
|
| [1] |
Li Z W, Li Q, Wu C R. Comprehensive identification technology of effective reservoirs in sedimentary basins[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 2002.
|
| [2] |
Mardia K V, Marshall R J. Maximum likelihood estimation of models for residual covariance in spatial regression[J]. Biometrika, 1984, 71(1):135-146.
|
| [3] |
李少华, 张昌民, 马玉震. 线性规划法自动拟合变差函数的改进[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 2001, 23(S1):36-37,5.
|
| [3] |
Li S H, Zhang C M, Ma Y Z. Improvement of automatic fit of variation functions in linear programming[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2001, 23(S1):36-37,5.
|
| [4] |
矫希国, 刘超. 变差函数的参数模拟[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 1996, 18(2):157-161.
|
| [4] |
Jiao X G, Liu C. Estimation of variation parameter[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1996, 18(2):157-161.
|
| [5] |
谢源, 李琼, 陈杰, 等. 基于改进的量子粒子群算法的变差函数拟合方法及应用[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 45(3):379-385.
|
| [5] |
Xie Y, Li Q, Chen J, et al. Research on variogram fitting method and its application based on the improved quantum particle swarm algorithm[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science and Technology Edition, 2018, 45(3):379-385.
|
| [6] |
成洪甲, 杨雨, 孙寅萍. 一种基于随机粒子群的变差函数优化方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2012, 12(31):8373-8378.
|
| [6] |
Cheng H J, Yang Y, Sun Y P. Based on the variogram of the random particle swarm optimization method[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2012, 12(31):8373-8378.
|
| [7] |
王一飞, 刘光浚, 刘轩吉, 等. 基于神经网络的脉搏波信号血压检测算法[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2022, 39(8):998-1002.
|
| [7] |
Wang Y F, Liu G J, Liu X J, et al. Neural network-based blood pressure detection algorithms for pulse wave signals[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Physics, 2022, 39(8):998-1002.
|
| [8] |
Yu X, Yu Z D, Ramalingam S. Learning strict identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]// Salt Lake City: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.IEEE,2018: 4432-4440.
|
| [9] |
Yang L, Zhong B R, Xu X H, et al. Application of a semivariogram based on a deep neural network to Ordinary Kriging interpolation of elevation data[J]. PLOS One, 2022, 17(4):e0266942.
|
| [10] |
王仁铎. 用加权多项式回归进行球状模型变差图的最优拟合[J]. 地球科学, 1986, 11(2):143-151.
|
| [10] |
Wang R D. On the best fitting of the spherical model variogram with the weighted polynomial regression[J]. Earth Science, 1986, 11(2):143-151.
|
| [11] |
梅杨, 杨勇, 李浩. 时空理论变异函数模型及其精度影响[J]. 测绘科学, 2017, 42(6):1-5,35.
|
| [11] |
Mei Y, Yang Y, Li H. Study of spatio-temporal theory model and its influence on the sptio-temporal prediction accuracy[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(6):1-5,35.
|
| [12] |
Soltani-Mohammadi S, Safa M. A simulated annealing based optimization algorithm for automatic variogram model fitting[J]. Archives of Mining Sciences, 2016, 61(3):635-649.
|
| [13] |
张磊. 煤矿井下煤质预测及工作面三维可视化研究与实现[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2017.
|
| [13] |
Zhang L. Research and implementation of coal quality prediction and three-dimensional visualization of working face in underground coal mine[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2017.
|
| [14] |
Matheron G. Principles of geostatistics[J]. Economic Geology, 1963, 58(8):1246-1266.
|
| [15] |
Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets[J]. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7):1527-1554.
|
| [16] |
刘梦炀, 武利娟, 梁慧, 等. 一种高精度LSTM-FC大气污染物浓度预测模型[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(S1):184-189.
|
| [16] |
Liu M Y, Wu L J, Liang H, et al. A kind of high-precision LSTM-FC atmospheric contaminant concentrations forecasting model[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(S1):184-189.
|
| [17] |
贺婷, 周宁, 吴啸宇. 基于深度全连接神经网络的储层有效砂体厚度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2023, 53(4):1262-1274.
|
| [17] |
He T, Zhou N, Wu X Y. Thickness prediction of reservoir effective sand body by deep fully connected neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2023, 53(4):1262-1274.
|
| [18] |
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6):84-90.
|
| [19] |
Amari S I. Backpropagation and stochastic gradient descent method[J]. Neurocomputing, 1993, 5(4-5):185-196.
|
| [20] |
Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam:A method for stochastic optimization[C]// Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations(ICLR 2015), 2015.
|
| [21] |
肖克焱. 地质统计学变差函数人机对话拟合[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1994, 24(2):218-221,233.
|
| [21] |
Xiao K Y. The study of variogram model fitting by interactive computer-aided program[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 1994, 24(2):218-221,233.
|
| [22] |
Wackernagel H, Oliveira V D, Kedem B. Multivariate geostatistics[J]. SIAM Review, 1997, 39(2):340-340.
|
| [23] |
Webster R, Oliver M A. Geostatistics for environmental scientists[M]. London: John Wiley Sons, 2007.
|
| [24] |
Minasny B, McBratney A B. The Matérn function as a general model for soil variograms[J]. Geoderma, 2005, 128(3-4):192-207.
|
| [25] |
李长胜, 刘刚. 线性插值算法研究[J]. 机床与液压, 2002, 30(1):107-108.
|
| [25] |
Li C S, Liu G. Research on linear interpolation algorithm[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2002, 30(1):107-108.
|
| [26] |
何定桥, 王鹏军, 杨军. 深度神经网络在EMD虚假分量识别中的应用[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(S1):195-201.
|
| [26] |
He D Q, Wang P J, Yang J. Application of deep neural networks in emd false component identification[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(S1):195-201.
|
| [27] |
樊春玲, 孙四通, 金志华. 贝叶斯神经网络建模预测方法及其应用[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2009, 17(1):85-88.
|
| [27] |
Fan C L, Sun S T, Jin Z H. Modeling & predictive method of Bayesian neural network[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2009, 17(1):85-88.
|
|
|
|

