|
|
|
| Forward modeling of a controllable-source 3D electromagnetic method based on fictitious wave field |
JIANG Zhi-Qiang1( ), LIN Chao2,3( ), LIN Chao2,3( ), YANG Ting-Wei2,3,4, NING Xiao-Bin2 ), YANG Ting-Wei2,3,4, NING Xiao-Bin2 |
1. Guangxi XinFaZhan Communication Group Co.,Ltd.,Nanning 530029,China
2. Guangxi Transportation Science and Technology Group Co.,Ltd.,Nanning 530007,China
3. Guangxi Highway Tunnel Safety Warning Engineering Research Center,Nanning 530007,China
4. Guangxi Key Lab of Road Structure and Materials,Nanning 530007,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study converted the frequency-domain electromagnetic diffusion equation into the wave equation in the fictitious domain based on the transformation relationship between the diffusion field and the fictitious wave field,achieving the numerical calculation of the electromagnetic field in the fictitious wave field.By introducing the complex frequency shifted perfectly matched layer(CFPML) boundary condition,the storage capacity of the computer memory decreased.Furthermore,by encompassing the air layer in the calculation domain,the complex processing of the ground-air interfaces was avoided.Compared to the uniform half-space analytical solution,the algorithm proposed in this study had relative errors of less than 3.5% and thus is effective and correct.Finally,the numerical simulation of a typical geoelectric model indicated that the 3D electromagnetic responses of multiple frequencies can be obtained through single forward modeling,suggesting an elevated calculation efficiency.The numerical simulation results also exhibit that the apparent resistivity calculated based on the fictitious wave field is insensitive to the field source effect and thus can effectively identify anomaly boundaries.
|
|
Received: 27 August 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
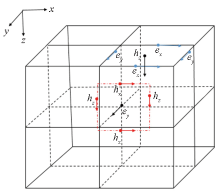
|
Spatial discretization of electromagnetic field in fictitious wave field
|
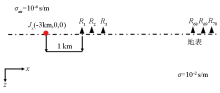
|
Schematic diagram of a uniform half space model
|
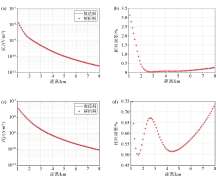
|
Response and relative error plots of the electric field component Ex(a、b) and magnetic field component Hy(c、d) with a frequency of 100 Hz in a uniform half space
|
|
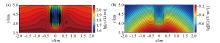
xz surface wave field snapshot of fictitious electric field component E'x at different times in a uniform half space
a—t=0.12 s;b—t=0.16 s;c—t=0.25 s;d—t=0.27 s;e—t=0.28 s;f—t=0.30 s
|
|
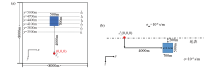
Schematic of low resistance 3D anomalous body model in uniform half space
|
|
xz surface wave field of fictitious electric field component E'x at different times with one low resistance anomalous body
a—t=0.38 s;b—t=0.43 s;c—t=0.44 s;d—t=0.45 s;e—t=0.49 s;f—t=0.50 s
|
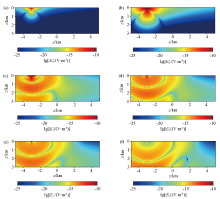
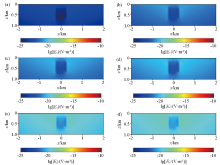
|
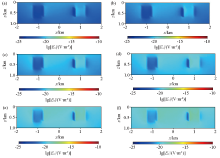
Contour map of electric field component Ex and apparent resistivity of 16 Hz with one low resistance anomalous body
a—apparent resistivity contour line;b—electric field component Ex contour line
|
|
Contour map of electric field component Ex and apparent resistivity of 64 Hz with one low resistance anomalous body
a—apparent resistivity contour line;b—electric field component Ex contour line
|
|
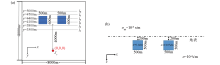
Schematic of a 3D anomalous body model with one low resistance and one high resistance in a uniform half space
a—xy plane cross-section;b—xz plane cross-section
|
|
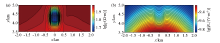
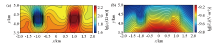
xz surface wave field snapshot of fictitious electric field component E'x at different times with one low resistance and one high resistance anomalous body
a—t=0.43 s;b—t=0.44 s;c—t=0.46 s;d—t=0.47 s;e—t=0.49 s;f—t=0.50 s
|
|
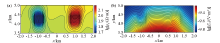
Contour map of electric field component Ex and apparent resistivity of 16 Hz with one low resistance and one high resistance anomalous body
a—apparent resistivity contour line;b—electric field component Ex contour line
|
|
Contour map of electric field component Ex and apparent resistivity of 64 Hz with one low resistance and one high resistance anomalous body
a—apparent resistivity contour line;b—electric field component Ex contour line
|
| [1] |
吴璐苹, 李荫槐. 可控源音频大地电磁法在地下水勘查中的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 1996, 39(5):712-717.
|
| [1] |
Wu L P, Li Y H. Application of controllable source audio frequency magnetotelluric method in groundwater exploration[J]. Journal of Geophysics, 1996, 39(5):712-717.
|
| [2] |
于昌明. CSAMT方法在寻找隐伏金矿中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 1998, 41(1):133-138.
|
| [2] |
Yu C M. Application of CSAMT method in searching for concealed gold deposits[J]. Journal of Geophysics, 1998, 41(1):133-138.
|
| [3] |
黄力军, 陆桂福, 刘瑞德. 可控源音频大地电磁测深法应用实例[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2006, 28(4):337-341.
|
| [3] |
Huang L J, Lu G F, Liu R D. Application example of controllable source audio frequency magnetotelluric sounding[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Prospecting Calculation Technology, 2006, 28(4):337-341.
|
| [4] |
刘瑞德, 黄力军, 孟银生. 可控源音频大地电磁测深法在地热田勘查中应用效果初探[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2007, 4(2):86-89.
|
| [4] |
Liu R D, Huang L J, Meng Y S. Preliminary study on the application effect of controllable source audio frequency magnetotelluric sounding in geothermal field exploration[J]. Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2007, 4(2):86-89.
|
| [5] |
成江明. 可控源音频大地电磁法在隐伏煤矿区的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2008, 23(4):1269-1272.
|
| [5] |
Cheng J M. Application of controllable source audio frequency magnetotelluric method in hidden coal mine area[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2008, 23(4):1269-1272.
|
| [6] |
董泽义, 汤吉, 周志明. 可控源音频大地电磁法在隐伏活动断裂探测中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 2010, 32(3):442-452.
|
| [6] |
Dong Z Y, Tang J, Zhou Z M. Application of controllable source audio frequency magnetotelluric method in detection of concealed active faults[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2010, 32(3):442-452.
|
| [7] |
张国鸿, 李仁和. 可控源音频大地电磁法深部找矿实验效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2010, 34(1):66-70.
|
| [7] |
Zhang G H, Li R H. Experimental results of controlled source audio frequency magnetotelluric method for deep prospecting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 34(1):66-70.
|
| [8] |
Pridmore D F, Hohmann G W, Ward S H, et al. An investigation of finite- element modeling for electrical and electromagnetic data in three dimensions[J]. Geophysics, 1981, 46(7):1009-1024.
|
| [9] |
Mitsuhata Y. 2-D electromagnetic modeling by finite-element method with a dipole source and topography[J]. Geophysics, 2000, 65(2):465-475.
|
| [10] |
顾观文, 吴文鹂, 李桐林. 大地电磁场三维地形影响的矢量有限元数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2014, 44(5):1678-1686.
|
| [10] |
Gu G W, Wu W L, Li T L. Vector finite element numerical simulation of three-dimensional terrain influence of magnetotelluric field[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(5):1678-1686.
|
| [11] |
Raiche A, Coggon J. Analytic Green's tensors for integral equation modelling[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1975, 42(3):1035-1038.
|
| [12] |
鲍光淑, 张碧星, 敬荣中, 等. 三维电磁响应积分方程法数值模拟[J]. 中南工业大学学报:自然科学版, 1999, 30(5):35-37.
|
| [12] |
Bao G S, Zhang B X, Jing R Z, et al. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional electromagnetic response by integral equation method[J]. Journal of Central South University:Natural Science Edition, 1999, 30(5):35-37.
|
| [13] |
陈桂波, 汪宏年, 姚敬金. 用积分方程法模拟各向异性地层中三维电性异常体的电磁响应[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(8):234-241.
|
| [13] |
Chen G B, Wang H N, Yao J J. Using integral equation method to simulate electromagnetic response of three-dimensional electrical anomaly body in anisotropic formation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(8):234-241.
|
| [14] |
彭荣华, 胡祥云, 韩波. 基于拟态有限体积法的频率域可控源三维正演计算[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(10):3927-3939.
|
| [14] |
Peng R H, Hu X Y, Han B. Three-dimensional forward calculation of controllable source in frequency domain based on pseudo-finite volume method[J]. Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(10):3927-3939.
|
| [15] |
Mackie R L. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric modeling using difference equations—Theory and comparisons to integral equation solutions[J]. Geophysics, 1993, 58(2):215-226.
|
| [16] |
沈金松. 用有限差分法计算各向异性介质中多分量感应测井的响应[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2004, 19(1):101-107.
|
| [16] |
Sheng J S. The finite difference method is used to calculate the response of multicomponent induction logging in anisotropic media[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2004, 19(1):101-107.
|
| [17] |
Liu Y H, Yin C C. Electromagnetic divergence correction for 3D anisotropic EM modeling[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2013,96:19-27.
|
| [18] |
朱成. 带地形频率域可控源电磁法三维正反演研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016.
|
| [18] |
Zhu C. Three-dimensional forward and inverse modeling of controllable source electromagnetic method in frequency domain with terrain[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016.
|
| [19] |
Lee K H, Liu G, Morrison H F. A new approach to modeling the electromagnetic response of conductive media[J]. Geophysics, 1989, 54(9):1180-1192.
|
| [20] |
Maaø F. Fast finite-difference time-domain modeling for marine-subsurface electromagnetic problems[J]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 1949, 72(25):35-41.
|
| [21] |
Mittet R. High-order finite-difference simulations of marine CSEM surveys using a correspondence principle for wave and diffusion fields[J]. Geophysics, 2010, 75(1):F33-F50.
|
| [22] |
Berenger J P. A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1994, 114(2):185-200.
|
| [23] |
徐正玉. 地—井瞬变电磁时域有限差分三维数值模拟[D]. 南昌: 东华理工大学, 2016.
|
| [23] |
Xu Z Y. Three-dimensional finite-difference time-domain numerical simulation of surface-well transient electromagnetic[D]. Nanchang: East China University of Technology, 2016.
|
| [24] |
Kuzuoglu M, Mittra R. Frequency dependence of the constitutive parameters of causal perfectly matched anisotropic absorbers[J]. IEEE Microwave & Guided Wave Lett., 1996, 6(12):447-449.
|
| [25] |
Ryhove S K, Mittet R. 3D marine magnetotelluric modeling and inversion with the finite-difference time-domain method[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(6):E269-E286.
|
| [26] |
Li G, Li Y G, Han B, et al. Application of the perfectly matched layer in 3-D marine controlled-source electromagnetic modelling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2018(1):333-344.
|
| [27] |
Du Fort E C, Frankel S P. Stability conditions in the numerical treatment of parabolic differential equations[J]. Mathematical Tables and Other Aids to Computation, 1953, 7(43):135-152.
|
| [28] |
Adhidjaja J I, Hohmann G W. A finite-difference algorithm for the transient electromagnetic response of a three-dimensional body[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1989, 98(2):233-242.
|
| [29] |
葛德彪, 闫玉波. 电磁波时域有限差分方法[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2002.
|
| [29] |
Ge D B, Yan Y B. Finite difference time domain method of electromagnetic wave[M]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Electronic Science and Technology Press, 2002.
|
| [30] |
Adhidjaja J I, Hohmann G W. A finite-difference algorithm for the transient electromagnetic response of a three-dimensional body[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1989, 98(2):233-242.
|
| [31] |
吕英华. 计算电磁学的数值方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006.
|
| [31] |
Lyu Y H. A numerical method for calculating electromagnetism[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2006.
|
| [32] |
Commer M, Newman G A. An accelerated time domain finite difference simulation scheme for three-dimensional transient electromagnetic modeling using geometric multigrid concepts[J]. Radio Science, 2006, 41(3):1-15.
|
| [33] |
辛会翠. 瞬变电磁法2.5维有限差分正演模拟研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013.
|
| [33] |
Xin H C. Research on 2.5D finite-difference forward modeling of transient electromagnetic method[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2013.
|
| [34] |
Hördt A, Dautel S, Tezkan B, et al. Interpretation of long-offset transient electromagnetic data from the Odenwald area,Germany,using two-dimensional modelling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2000, 140(3):577-586.
|
| [35] |
Commer M, Hoversten G M, Um E S. Transient-electromagnetic finite-difference time-domain earth modeling over steel infrastructure[J]. Geophysics, 2015, 80(2):E147-E162.
|
| [36] |
Hu Y, Egbert G, Ji Y, et al. A novel CFS-PML boundary condition for transient electromagnetic simulation using a fictitious wave domain method[J]. Radio Science, 2017, 52(1):118-131.
|
| [1] |
XIAO Shi-Peng, XIONG Gao-Jun, YUAN Meng-Yu, MAO Ming-Qiu, WANG Sheng-Yi, WEI Zeng-Tao. Parameter optimization and imaging of visco-acoustic media using high-order Fourier finite-difference method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1207-1213. |
| [2] |
HE Shuai, YANG Bing-Nan, RUAN Shuai, LI Yong-Gang, HAN Yao-Fei, ZHU Da-Wei. Fine Interpretation of the exploration results of diamond-bearing rock masses in Maping area, Guizhou using the 3D AMT forward modeling and inversion technologies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 618-627. |
|
|
|
|

