|
|
|
| Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in a chemical industry agglomeration area of Yantai City |
HU Sheng-Tao1( ), ZHANG Xiang-Heng2, HAN Ming-Zhi2, TANG Shi-Kai1, YU Lin-Hong1, LI Jin-Peng1, ZHANG Jie1( ), ZHANG Xiang-Heng2, HAN Ming-Zhi2, TANG Shi-Kai1, YU Lin-Hong1, LI Jin-Peng1, ZHANG Jie1( ), ZHAO Guo-Peng1, BAI Ying1 ), ZHAO Guo-Peng1, BAI Ying1 |
1. Shandong No.3 Exploration Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Yantai 264004,China
2. Yantai Ludong Survey and Mapping Co., Ltd., Yantai 264004,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To investigate thehydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in a chemical industrial agglomeration area in Yantai City, this study collected 12 sets of groundwater samples and one set of surface water samples from the study area and its surrounding areas. It analyzed the hydrochemical characteristics ofgroundwater by integrating various methods like mathematical statistics, Piper and Gibbsdiagrams, correlation analysis,the ion ratio method, and principal component analysis. Moreover, it explored the impacts of production activities in thestudy area on the groundwater environment. The results show that:(1) The shallow groundwater in the study area was neutral to slightly alkaline, with the primary hydrochemical type being the SO4-Ca·Na type, followed by the SO4·HCO3-Ca·Mg, HCO3·SO4-Ca·Na, SO4·HCO3·Cl-Ca·Na, SO4·Cl-Ca, SO4·HCO3-Ca, and SO4-Na types;(2) The chemical composition of shallow groundwater originated principally from the combined effects of evaporite and silicate dissolution; (3) Chemical enterprises contributed significantly to groundwater contamination. A nearercontamination source is associated with higher ion concentrations,suggesting more severe groundwater contamination. Along the groundwater flow direction, contaminants in upper reaches are prone to migrate and accumulate toward lower reaches,aggravating groundwater contamination in lower reaches.
|
|
Received: 28 August 2023
Published: 19 September 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
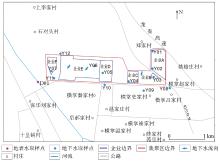
|
The distribution map of groundwater sample collection in the study area
|

| 主要指标 | K+ | Ca2+ | Na+ | Mg2+ | | | Cl- | TDS | pH | | 上游区 | 3.03 | 88.94 | 59.79 | 17.01 | 144.00 | 175.72 | 81.97 | 604.80 | 8.58 | | 内部区 | 平均值 | 2.58 | 332.58 | 190.09 | 71.99 | 243.50 | 1044.19 | 253.31 | 2084.17 | 7.72 | | 变异系数 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.22 | 0.85 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.07 | | 下游区 | 平均值 | 5.94 | 301.89 | 124.88 | 78.55 | 194.80 | 1140.96 | 109.99 | 1908.84 | 7.54 | | 变异系数 | 0.50 | 0.63 | 0.33 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 0.81 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 0.02 | | 总 | 平均值 | 4.01 | 299.49 | 152.06 | 70.14 | 214.92 | 1012.14 | 179.32 | 1887.83 | 7.72 | | 变异系数 | 0.90 | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.81 | 0.26 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.68 | 0.07 |
|
Analysis and statistics of main indexes of groundwater
|
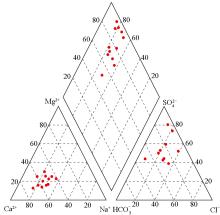
|
Groundwater hydrochemistry Piper trilinear diagram
|
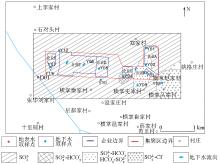
|
Distribution map of anion types in shallow groundwater in the study area
|

| 指标 | K+ | Ca2+ | Na+ | Mg2+ | | | Cl- | pH | TDS | | K+ | 1 | 0.280 | 0.135 | 0.540 | -0.337 | 0.486 | -0.302 | -0.057 | 0.367 | | Ca2+ | | 1 | 0.793** | 0.797** | -0.537 | 0.917** | 0.618* | -0.269 | 0.969** | | Na+ | | | 1 | 0.816** | -0.206 | 0.834** | 0.555 | -0.554 | 0.883** | | Mg2+ | | | | 1 | -0.348 | 0.956** | 0.175 | -0.500 | 0.911** | | | | | | | 1 | -0.494 | -0.151 | -0.301 | -0.474 | | | | | | | | 1 | 0.313 | -0.427 | 0.974** | | Cl- | | | | | | | 1 | -0.008 | 0.515 | | pH | | | | | | | | 1 | -0.390 | | TDS | | | | | | | | | 1 |
|
Correlation coefficient between main ions in shallow groundwater
|
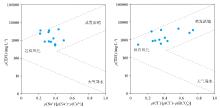
|
Gibbs diagram of shallow groundwater in the study area
|
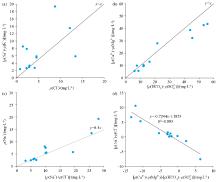
|
Ion ratio diagram of shallow groundwater in the study area
|

|
The ion concentration curve of sampling points in the study area
|

| 主成分 | 特征值 | 主成分贡献率/% | 累积贡献率/% | | 1 | 6.361 | 53.006 | 53.006 | | 2 | 2.179 | 18.155 | 71.161 | | 3 | 1.570 | 13.079 | 84.240 | | 4 | 1.015 | 8.461 | 92.701 | | 5 | 0.448 | 3.736 | 96.437 | | 6 | 0.226 | 1.887 | 98.324 | | 7 | 0.147 | 1.226 | 99.550 | | 8 | 0.049 | 0.407 | 99.957 | | 9 | 0.005 | 0.042 | 99.998 | | 10 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 100.000 | | 11 | 7.863×10-10 | 6.552×10-9 | 100.000 | | 12 | -2.126×10-16 | -1.772×10-15 | 100.000 |
|
Eigenvalue and principal component contribution rate and cumulative contribution rate
|

| 指标 | 起始值 | 提取值 | | K+ | 1.000 | 0.888 | | Ca2+ | 1.000 | 0.960 | | Na+ | 1.000 | 0.915 | | Mg2+ | 1.000 | 0.942 | | | 1.000 | 0.817 | | | 1.000 | 0.994 | | Cl- | 1.000 | 0.980 | | | 1.000 | 0.811 | | pH | 1.000 | 0.861 | | 总硬度 | 1.000 | 0.986 | | 总固体 | 1.000 | 0.997 | | CODMn | 1.000 | 0.973 |
|
Variable commonality
|

| 指标 | 主成分1 | 主成分2 | 主成分3 | 主成分4 | | K+ | 0.066 | -0.166 | -0.418 | 0.382 | | Ca2+ | 0.149 | 0.109 | 0.014 | 0.016 | | Na+ | 0.140 | -0.027 | 0.214 | -0.058 | | Mg2+ | 0.146 | -0.096 | -0.092 | -0.142 | | | -0.073 | -0.211 | 0.398 | 0.029 | | | 0.154 | -0.038 | -0.087 | -0.082 | | Cl- | 0.074 | 0.283 | 0.363 | 0.226 | | | -0.009 | 0.408 | 0.037 | 0.108 | | pH | -0.069 | 0.279 | -0.273 | 0.333 | | 总硬度 | 0.155 | 0.047 | -0.020 | -0.035 | | 总固体 | 0.156 | 0.036 | 0.007 | -0.034 | | CODMn | 0.043 | -0.187 | 0.182 | 0.795 |
|
Principal component score coefficient
|

监测
点位 | y1 | y2 | y3 | y4 | y总 | 排序 | | Y01 | -2.372 | 1.207 | -0.251 | 0.200 | -1.054 | 9 | | Y02 | -2.068 | -0.823 | -0.481 | -0.845 | -1.380 | 11 | | Y03 | -2.848 | -0.552 | -0.997 | -0.766 | -1.805 | 12 | | Y04 | -1.232 | -1.762 | -0.513 | 2.286 | -0.847 | 7 | | Y05 | 0.407 | 3.609 | 0.553 | 0.628 | 0.996 | 4 | | Y06 | 4.294 | -0.567 | 1.348 | -1.297 | 2.240 | 1 | | Y07 | 3.088 | 0.762 | 2.078 | 1.018 | 2.133 | 2 | | Y08 | -2.008 | 1.269 | 0.028 | -0.559 | -0.877 | 8 | | Y09 | -1.604 | -1.243 | -0.179 | -0.050 | -1.103 | 10 | | Y10 | -1.004 | -0.395 | 0.287 | -0.853 | -0.639 | 6 | | Y11 | 3.145 | -0.565 | -0.377 | -0.339 | 1.487 | 3 | | Y12 | 2.200 | -0.939 | -1.495 | 0.577 | 0.849 | 5 |
|
The principal component comprehensive score and ranking of groundwater quality in each sample point of the study area
|
| [1] |
中华人民共和国生态环境部, 国家统计局, 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 第二次全国污染源普查公报[R]. 2020.
|
| [1] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People 's Republic of China,National Bureau of Statistics, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People 's Republic of China. Bulletin of the second national pollution source census[R]. 2020.
|
| [2] |
寇雅威, 徐仲仪, 张恒, 等. 山东泰安大汶口化工集聚区浅层地下水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 山东国土资源, 2023, 39(6):15-25.
|
| [2] |
Kou Y W, Xu Z Y, Zhang H, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater and the origin analysis in Dawenkou chemical industry gathering area in Tai'an City in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2023, 39(6):15-25.
|
| [3] |
成世才, 董妍, 宋永芬, 等. 济南市先行区浅层地下水水文地球化学特征[J]. 人民黄河, 2021, 43(12):86-90,99.
|
| [3] |
Cheng S C, Dong Y, Song Y F, et al. Shallow groundwater hydrogeochemical character of Jinan pioneering zone[J]. Yellow River, 2021, 43(12):86-90,99.
|
| [4] |
张智雄, 许模, 张强, 等. 绵阳红层地区浅层地下水水化学特征、成因及水质分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(3):168-173.
|
| [4] |
Zhang Z X, Xu M, Zhang Q, et al. Hydrogeochemistry,genesis and waterquality analysis of shallow groundwater in red-bed area of the Mianyang City[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(3):168-173.
|
| [5] |
田大永, 张娅, 霍光杰, 等. 郑州市不同埋藏深度地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(7):2776-2786.
|
| [5] |
Tian D Y, Zhang Y, Huo G J, et al. Analysis of the hydro-chemical characteristics of groundwater in Zhengzhou City with different depths and the formation mechanism[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(7):2776-2786.
|
| [6] |
董维红, 孟莹, 王雨山, 等. 三江平原富锦地区浅层地下水水化学特征及其形成作用[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2017, 47(2):542-553.
|
| [6] |
Dong W H, Meng Y, Wang Y S, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation of the shallow groundwater in Fujin,Sanjiang Plain[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2017, 47(2):542-553.
|
| [7] |
於昊天, 马腾, 邓娅敏, 等. 江汉平原东部地区浅层地下水水化学特征[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5):685-692.
|
| [7] |
Yu H T, Ma T, Deng Y M, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in eastern Jianghan Plain[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5):685-692.
|
| [8] |
杨芬, 高柏, 葛勤, 等. 信江流域地下水水化学特征及形成机制[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(9):3505-3512.
|
| [8] |
Yang F, Gao B, Ge Q, et al. Hydro-chemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Xinjiang River Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(9):3505-3512.
|
| [9] |
李玲, 周金龙, 齐万秋, 等. 新疆和田河流域绿洲区浅层地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(3):14-20.
|
| [9] |
Li L, Zhou J L, Qi W Q, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation reasons of shallow groundwater in oasis area of Hotan River Basin,Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2018, 29(3):14-20.
|
| [10] |
秦娜, 成文举, 董方营, 等. 东平湖地区地下水化学特征及质量评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(24):10434-10443.
|
| [10] |
Qin N, Cheng W J, Dong F Y, et al. Chemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in Dongping Lake Area[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(24):10434-10443.
|
| [11] |
冯建国, 鲁统民, 高宗军, 等. 新泰市地下水水化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 山东科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 39(1):11-20.
|
| [11] |
Feng J G, Lu T M, Gao Z J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and causes of groundwater in Xintai City[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology:Natural Science, 2020, 39(1):11-20.
|
| [12] |
王婧, 高世昌, 方媛, 等. 清水河平原地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 人民黄河, 2022, 44(S2):153-156.
|
| [12] |
Wang J, Gao S C, Fang Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of groundwater in Qingshuihe Plain[J]. Yellow River, 2022, 44(S2):153-156.
|
| [13] |
刘元晴, 李伟, 周乐, 等. 牟汶河中上游河水离子组成特征及其影响因素[J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39(2):35-38.
|
| [13] |
Liu Y Q, Li W, Zhou L, et al. Ionic composition characteristics and their controlling factors of river water in the middle and upper reaches of Muwenhe river[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2021, 39(2):35-38.
|
| [14] |
屈吉鸿, 李潇, 张艺锋, 等. 新乡市化工集聚区地下水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(34):95-102.
|
| [14] |
Qu J H, Li X, Zhang Y F, et al. Analysis of groundwater chemical characteristics and cause of formation in chemical agglomeration area of Xinxiang City[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(34):95-102.
|
| [15] |
赵辉. 三江平原蛤蟆通河流域地下水补、径、排特征及水化学演化规律[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.
|
| [15] |
Zhao H. Groundwater recharge,discharge,runoff characteristics and hydrochemical evolution of hamatong river basin in Sanjiang Plain[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017.
|
| [16] |
纪媛媛, 周金龙, 孙英, 等. 新疆昌吉市平原区地下水化学特征及质量评价[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2021, 19(3):551-560.
|
| [16] |
Ji Y Y, Zhou J L, Sun Y, et al. Groundwater chemical characteristics and water quality evaluation for groundwater in plain area of Changji City,Xinjiang[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2021, 19(3):551-560.
|
| [17] |
宫晓艳, 卞建民, 王宇, 等. 松花江吉林段傍河地带地下水化学特征及成因[J]. 人民长江, 2018, 49(11):19-23,28.
|
| [17] |
Gong X Y, Bian J M, Wang Y, et al. Chemical characteristics and causes of riparian groundwater in Jilin section of Songhua River[J]. Yangtze River, 2018, 49(11):19-23,28.
|
| [18] |
覃绍媛, 李泽琴, 许模. 黑龙潭泉域地下水化学特征及补给源识别[J]. 人民黄河, 2020, 42(3):63-67.
|
| [18] |
Qin S Y, Li Z Q, Xu M. Groundwater chemical characteristics and recharge source identification of Heilongtan spring area[J]. Yellow River, 2020, 42(3):63-67.
|
| [1] |
AN Guo-Qiang, LU Bao-Liang, GAO Xin-Yu, ZHU Wu, LI Bo-Sen. 3D correlation tomography inversion of gravity anomalies constrained by edge features and depth weighting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1): 113-124. |
| [2] |
LI Chuan-Jin, WANG Qiang, JIAN Xiang, ZHENG Tao, ZHAN Su-Hua, CHEN Shao-Wei. Microtremor signal simulation and its application in microtremor exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1040-1047. |
|
|
|
|

