|
|
|
| Integrated application of alteration information from Landsat8-OLI remote sensing images and geochemical singularity anomaly information for the Shuiyuesi area of western Hubei Province |
BAO Qi-Bing1,2( ), YANG Peng3( ), YANG Peng3( ), ZHOU Zhou3, LEI Li3, XIA Qing-Lin2, LIU Yin3, GONG Yin3, LU Jin-Xiang3 ), ZHOU Zhou3, LEI Li3, XIA Qing-Lin2, LIU Yin3, GONG Yin3, LU Jin-Xiang3 |
1. Cores and Samples Centre of Natural Resources, China Geological Survey, Langfang 065201, China
2. School of Earth Resources, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan 430084, China
3. The Seventh Geological Brigade of Hubei Geological Bureau, Yichang 443100, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Prolonged intense magmatic-hydrothermal activity and regional metamorphism in western Hubei Province created favorable conditions for the formation of gold deposits. As the Shuiyuesi area witnessed a thorough exploration of surface and outcrop mines, the prospecting of gold deposits in the area has shifted to overburden and deep zones in recent years. However, the prospecting in the Shuiyuesi area becomes gradually complicated due to significant topographic relief, high vegetation coverage, and severe terrain cutting. Hence, efficient prospecting approaches are urgently needed to achieve breakthroughs in ore prospecting. Through geological survey and analysis, this study statistically analyzed the alteration types intimately associated with gold mineralization in nine gold veins of the Shuiyuesi area. It extracted alteration information from Landsat8-OLI remote sensing images using methods like numerical operations, and weak anomaly information of element distribution using methods like multivariate statistical analysis and local singularity analysis. Employing the data integration technology, it integrated the alteration anomaly information from remote sensing images and the singularity anomaly information. Based on comprehensive information, such as geological settings for mineralization and metallogenic regularity, this study identified 19 metallogenic prospect areas and new anomaly clues in the Yangjiatang-Caishenmiao area. The novel approach combining singularity analysis and data integration enhanced the spatial resolution of geochemical anomalies, the spatial details of surface features, and weak anomaly information associated with gold mineralization, thus enabling rapid and efficient identification and extraction of comprehensive anomalies and prediction of metallogenic prospect areas.
|
|
Received: 22 July 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
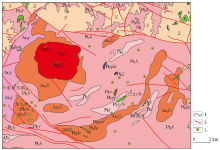
Geological map of Shuiyuesi area
Ar2y—middle Archean Yemadong Formation;Pt1h—early Proterozoic Huanglianghe Formation;Pt2l—middle Proterozoic Lierping Formation; $\epsilon$—Cambrian system;Z—Sinian system;Nh—Nanhua system;Ar3D—Neoarchean Dongchonghe gneiss complex;Pt2v—middle Proterozoic diabase;Pt2Ψlσ—middle Proterozoic pyroxene peridotite;Pt2Σ—middle Proterozoic ultrabasic rocks;Pt3ηγ—Neoproterozoic diorite granite;Pt3βμ—Neoproterozoic gabbro diabase;Pt3ξγ—Neoproterozoic potassium feldspar granite;Pt3γo—Neoproterozoic biotite plagioclase granite;1—geological boundary;2—fault structure;3—gold mineralization points
|

| 金矿脉 | 与金矿化关系密切的蚀变类型 | 可识别离子 | | 罐湾矿脉 | 硅化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化 | Fe3+、 、OH- | | 筲箕湾矿脉 | 硅化、黄铁矿化、绢云母化、褐铁矿化 | Fe2+、Fe3+、OH- | | 何家湾矿脉 | 硅化、黄铁矿化、绢云母化 | Fe2+、OH- | | 祠堂湾矿脉 | 黄铁矿化、碳酸盐化、绿泥石化 | Fe2+、 、OH- | | 庙湾矿脉 | 碳酸盐化、黄铁矿化、绿泥石化 | Fe2+、 、OH- | | 狮子崖矿脉 | 黄铁矿化、褐铁矿化 | Fe2+、Fe3+ | | 天鹅池矿脉 | 黄铁矿化、褐铁矿化 | Fe2+、Fe3+ | | 松树湾矿脉 | 弱黄铁矿化 | Fe2+ | | 宋家湾矿脉 | 黄铁矿化、褐铁矿化 | Fe2+、Fe3+ |
|
The alteration types and identifiable ions closely related to gold mineralization in the Shuiyuesi mining area
|
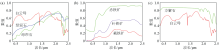
CO 3 2 -(modified according to USGS spectral library)
a—spectral curve of minerals containing OH-;b—spectral curve of minerals containing iron ions;c—spectral curve of minerals containing
">
|
Spectral curves of typical minerals containing OH-, iron ions, and C (modified according to USGS spectral library)
a—spectral curve of minerals containing OH-;b—spectral curve of minerals containing iron ions;c—spectral curve of minerals containing
|
|
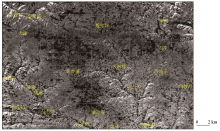
Enhanced image of Landsat8-OLI for alteration information in the research area(OLI6/OLI7)
|

| 变量 | F1 | F2 | | Ag | 0.429 | 0.594 | | Au | 0.819 | 0.083 | | Hg | 0.793 | 0.125 | | Pb | 0.35 | 0.694 | | Zn | -0.126 | 0.857 | | Cu | 0.856 | 0.201 | | 因子方差贡献/% | 46.795 | 19.643 | | 累积方差贡献/% | 46.795 | 66.437 |
|
Orthogonal rotation factor load matrix
|
|
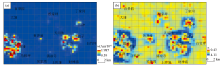
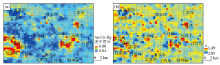
Au element geochemical anomaly map
a—the IDW interpolation results of Au element; b—the singularity analysis results of Au element
|
|
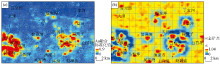
Au-Cu-Hg element combination geochemical anomaly map
a—the IDW interpolation results of Au-Cu-Hg element combination; b—the singularity analysis results of Au-Cu-Hg element combination
|
37])
">
|
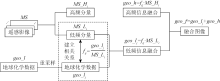
Basic principle of geochemical layer and remote sensing Image fusion technology (modified according to Ding[37])
|
|
The fusion results of geochemical data and remote sensing data in Shuiyuesi research area
a—the fusion result of Au element IDW layer and remote sensing alteration image;b—the fusion results of Au element singularity index layer and remote sensing alteration images
|
|
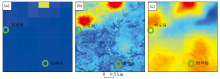
Enlarged comparison map of each layer in the area around Yangjiatang and Caishenmiao (green circle represents the location of the gold mine)
a—the result of zooming in on the local area of the Au element IDW layer; b—the local magnification result after fusing the IDW layer of Au element with the enhanced layer of remote sensing image alteration information;c—the locally magnified result of the fusion of Au element singularity index layer and remote sensing image alteration information enhancement laye
|

| 类别 | 成矿
类型 | 成矿
强度 | 成矿
条件 | 金矿床分布 | 找矿
潜力 | 交通
条件 | | A | 多 | 强 | 十分有利 | 有规模较大金矿 | 大 | 好 | | B | 较多 | 较强 | 有利 | 有小型金矿点 | 较大 | 好 | | C | 一般 | 中等 | 较有利 | 有矿化线索 | 一般 | 较好 |
|
Classification principles of Shuiyuesi research area
|
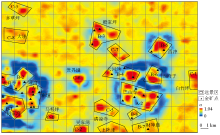
|
Distribution map of metallogenic prospective areas in the Shuiyuesi research area
|
| [1] |
赵鹏大. 地质大数据特点及其合理开发利用[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(4):1-5.
|
| [1] |
Zhao P D. Characteristics and rational utilization of geological big data[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(4):1-5.
|
| [2] |
赵鹏大, 陈永清. 数字地质与数字矿产勘查[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(3):1-5.
|
| [2] |
Zhao P D, Chen Y Q. Digital geology and quantitative mineral exploration[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(3):1-5.
|
| [3] |
陈永清, 赵鹏大. 综合致矿地质异常信息提取与集成[J]. 地球科学, 2009, 34(2):325-335.
|
| [3] |
Chen Y Q, Zhao P D. Extraction and integration of geoanomalies associated with mineralization[J]. Earth Science, 2009, 34(2):325-335.
|
| [4] |
Haghighat M, Abdel-Mottaleb M, Alhalabi W. Discriminant correlation analysis:Real-time feature level fusion for multimodal biometric recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(9):1984-1996.
|
| [5] |
孟小峰, 杜治娟. 大数据融合研究:问题与挑战[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(2):229-246.
|
| [5] |
Meng X F, Du Z J. Research on the big data fusion:Issues and challenges[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(2):229-246.
|
| [6] |
Daily M I, Farr T, Elachi C, et al. Geologic interpretation from composited radar and Landsat imagery[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering &Remote Sensing, 1979,45:1109-1116.
|
| [7] |
Waltz E, Llinas J. Multisensor data fusion[M]. Boston:ArtechHouse,1990.
|
| [8] |
Hall D L. Mathematical techniques in multisensor data fusion[M]. Boston: Artech House, Inc., 2004.
|
| [9] |
董志荣, 申兰. 综合指挥系统情报中心的主要算法——多目标密集环境下的航迹处理方法[R]. 连云港: 国外舰船技术—火控技术类编辑室,1985.
|
| [9] |
Dong Z R, Shen L. The main algorithm of the integrated command system intelligence center-trajectory processing methods in multi-target dense environments[R]. Lianyungang: Foreign Ship Technology-Fire Control Technology Editorial Room,1985.
|
| [10] |
康耀红. 数据融合理论与应用[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社,1997.
|
| [10] |
Kang Y H. Theory and application of data fusion[M]. Xi'an: Xidian University Press,1997.
|
| [11] |
刘福江, 吴信才, 孙华山, 等. 遥感与化探数据融合技术在金矿预测中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2007, 43(3):74-77.
|
| [11] |
Liu F J, Wu X C, Sun H S, et al. Application of fusion techniques of remote sensing and geochemical data in gold ore exploration[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2007, 43(3):74-77.
|
| [12] |
王子烨. 基于测度学习的喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩岩体识别[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020.
|
| [12] |
Wang Z Y. Identification of Himalayanpalegranite rock mass based on measurelearning[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020.
|
| [13] |
赵健铭, 杨长保, 韩立国, 等. 基于岩石光谱吸收特征的白云母含量反演[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2023, 43(1):220-224.
|
| [13] |
Zhao J M, Yang C B, Han L G, et al. The inversion of muscovite content based on spectral absorption characteristics of rocks[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2023, 43(1):220-224.
|
| [14] |
蒋立军, 邢立新, 梁一鸿, 等. 融合化探信息的遥感异常提取[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2011, 41(3):932-936.
|
| [14] |
Jiang L J, Xing L X, Liang Y H, et al. Anomalies information extraction from geochemical dataand remote sensing fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(3):932-936.
|
| [15] |
陈威, 祝明明, 曹晓峰, 等. 遥感—化探信息融合方法在新疆鄯善县大平梁地区找矿靶区预测中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(6):184-193.
|
| [15] |
Chen W, Zhu M M, Cao X F, et al. Application of the remote sensing and geochemical informationfusion method in the prediction of prospecting target in thedapinliang area,Shanshan County,Xinjiang[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(6):184-193.
|
| [16] |
荆林海, 丁海峰, 成秋明, 等. 一种基于遥感蚀变信息的地球化学元素异常来源追踪方法[P]. 中国专利,201810049938.0,2018-01-18.
|
| [16] |
Jing L H, Ding H F, Cheng Q M, et al. A method for tracking the source of geochemical element anomalies based on remote sensing alteration information[P]. Chinese patent,201810049938.0,2018-01-18.
|
| [17] |
Wang Z Y, Zuo R G, Jing L H. Fusion of geochemical and remote-sensing data for lithological mapping using random forest metric learning[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2021, 53(6):1125-1145.
|
| [18] |
黄理善, 李学彪, 荆林海, 等. 基于遥感手段的高寒山区矿产资源远景区快速圈定与综合评价技术集成[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(1):253-270.
|
| [18] |
Huang L S, Li X B, Jing L H, et al. Integration of rapid delineation and comprehensive evaluation technology of mineral resources prospect area in alpine mountainous area based on remote sensing[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(1):253-270.
|
| [19] |
Cheng Q M, Agterberg F P, Ballantyne S B. The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 51(2):109-130.
|
| [20] |
Cheng Q, Xu Y, Grunsky E. Multifractal power spectrum-area method for geochemical anomaly separation[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2000, 9(1):43-51.
|
| [21] |
Cheng Q M. Mapping singularities with stream sediment geochemical data for prediction of undiscovered mineral deposits in Gejiu,Yunnan Province,China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 32(1-2):314-324.
|
| [22] |
成秋明. 多重分形与地质统计学方法用于勘查地球化学异常空间结构和奇异性分析[J]. 地球科学, 2001, 26(2):161-166.
|
| [22] |
Cheng Q M. Multifractal and geostatistic methods for characterizing local structure and singularity properties of exploration geochemical anomalies[J]. Earth Science, 2001, 26(2):161-166.
|
| [23] |
成秋明. 应用复杂性—非线性理论开展成矿预测——奇异性理论—广义自相似性—分形谱系多重分形理论与应用[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(S1):463-466.
|
| [23] |
Cheng Q M. The application of complexity-nonlinear theory to ore prognosis:The singularity theory-generalized self-similarity-fractal lineage multiple fractal theory and its application[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(S1):463-466.
|
| [24] |
陈志军. 多重分形局部奇异性分析方法及其在矿产资源信息提取中的应用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2007.
|
| [24] |
Chen Z J. Multifractal local singularity analysis method and its application in mineralresourcesinformationextraction[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2007.
|
| [25] |
易承生. 湖北省宜昌地区黄陵断穹核北部含石墨地层岩性研究[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2017(4):46-49.
|
| [25] |
Yi C S. Lithology of graphite-bearing strata in the northern part of Huangling fault dome core in Yichang Area,Hubei Province[J]. China Non-metallic Minerals Industry, 2017(4):46-49.
|
| [26] |
周豹, 任八一, 孙腾, 等. 湖北省保康县六冲坪金矿地质特征及成矿作用浅析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4):533-538.
|
| [26] |
Zhou B, Ren B Y, Sun T, et al. Geological characteristics and mineralization of liuchongping gold deposit in Baokang County,Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(4):533-538.
|
| [27] |
向萌, 胡胜华, 聂开红, 等. 鄂西黄陵背斜核部金矿地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2021, 35(6):787-793,874.
|
| [27] |
Xiang M, Hu S H, Nie K H, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of gold deposits in the core ofHuangling anticline,western Hubei[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2021, 35(6):787-793,874.
|
| [28] |
刘继平, 李傲竹, 朱灿豪, 等. 湖北兴山周家湾石墨矿地质特征及找矿前景探讨[J]. 西部资源, 2022(1):146-149.
|
| [28] |
Liu J P, Li A Z, Zhu C H, et al. Geological characteristics and prospectingprospect of Zhoujiawan graphite deposit in Xingshan,Hubei Province[J]. Western Resources, 2022(1):146-149.
|
| [29] |
熊成云, 韦昌山, 金光富, 等. 鄂西黄陵背斜核部中段金矿基本特征及成矿规律[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 1998, 14(1):32-40.
|
| [29] |
Xiong C Y, Wei C S, Jin G F, et al. Basic characteristics and metallogenetic regularity of the gold ore deposits in the middle core of Huangling anticline,western Hubei Province[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 1998, 14(1):32-40.
|
| [30] |
熊成云, 韦昌山, 金光富, 等. 鄂西黄陵背斜地区前南华纪古构造格架及主要地质事件[J]. 地质力学学报, 2004, 10(2):97-112.
|
| [30] |
Xiong C Y, Wei C S, Jin G F, et al. Pre-sinian paleostructural framework and major geological events in the Huangling anticline,western Hubei[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2004, 10(2):97-112.
|
| [31] |
张玉君, 杨建民, 陈薇. ETM+(TM)蚀变遥感异常提取方法研究与应用——地质依据和波谱前提[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2002, 14(4):30-36.
|
| [31] |
Zhang Y J, Yang J M, Chen W. A study of the method for extractioh of alteration anomalies from the ETM+(TM) data and its application:Geologic basis and spectral precondition[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2002, 14(4):30-36.
|
| [32] |
张颖, 王越男, 陈利, 等. 基于Landsat-8影像森林植被信息计算机自动提取研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(28):61-66.
|
| [32] |
Zhang Y, Wang Y N, Chen L, et al. Forest vegetation information computer automatic extraction base on landsat-8[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(28):61-66.
|
| [33] |
Zuo R G. Machine learning of mineralization-related geochemical anomalies:A review of potential methods[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2017, 26(4):457-464.
|
| [34] |
Zuo R G, Xia Q L, Zhang D J. A comparison study of the C-A and S-A models with singularity analysis to identify geochemical anomalies in covered areas[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013,33:165-172.
|
| [35] |
张廷斌. 西藏谢通门县铜金矿带遥感图像蚀变信息提取及多源数据融合在成矿预测中的应用[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2006.
|
| [35] |
Zhang T B. Extractionof alteration information from remote sensing imagesand application of multi-source data fusion inmetallogenic prediction in Xietongmen County copper-gold belt,Tibet[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2006.
|
| [36] |
刘星, 胡光道. 多源数据融合技术在成矿预测中的应用[J]. 地球学报, 2003, 24(5):463-468.
|
| [36] |
Liu X, Hu G D. Multi-source geo-data fusion and its application in metallogenic prognosis[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2003, 24(5):463-468.
|
| [37] |
丁海峰. 一种提升地球化学元素图层分辨率的方法及系统[P]. 中国专利,201811275285.4,2019-2-15.
|
| [37] |
Ding H F. A method and system for improving the resolution of geochemical element layers[P]. China patent,201811275285.4,2019-2-15.
|
| [38] |
向萌, 张权绪, 牟宗玉, 等. 湖北宜昌白竹坪金矿流体包裹体特征及成矿机理探讨[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2019, 33(4):460-463,529.
|
| [38] |
Xiang M, Zhang Q X, Mou Z Y, et al. Fluid inclusion characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of Baizhuping gold deposit in Yichang City,Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2019, 33(4):460-463,529.
|
| [39] |
曹亮, 张利国, 周云, 等. 湖北宜昌白竹坪金矿床的成因:来自流体包裹体及H-O-S-Pb同位素地球化学的证据[J]. 华南地质, 2023(2):387-401.
|
| [39] |
Cao L, Zhang L G, Zhou Y, et al. Genesis of baizhuping gold deposit in Yichang,Hubei:Evidence from fluid inclusion and H-O-S-Pb isotope geochemistry[J]. South China Geology, 2023(2):387-401.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Hong-Yan, LI Cong, CHANG Qiu-Ling, GUAN Xiao-Rong, DU Cheng-Yuan, CHEN Xin, WANG Jing. Data integration based on MapGIS and ASCII code files[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 804-811. |
| [2] |
WAN Tai-Ping, ZHANG Li, LIU Han-Liang. Regional geochemical characteristics and metallogenic prospect area prediction of strategic mineral antimony in the Eerguna block, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1179-1188. |
|
|
|
|

