|
|
|
| Distribution of macroelements in surface sediments and their geological implications from Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi |
WANG Zhi-Jun( ), WANG Jian( ), WANG Jian( ), WANG Ke-Chao, LIU Jian, WANG Yong-Feng, SUN Zhong-Yu ), WANG Ke-Chao, LIU Jian, WANG Yong-Feng, SUN Zhong-Yu |
| Yantai Geological Survey Center of Coastal Zone, China Geological Survey, Yantai 264000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study examined 121 sets of surface sediments collected from Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi, China, determining their grain sizes and macroelement contents and analyzing the characteristics, spatial distribution patterns, and sources of microelement assemblages. The results indicate the presence of eight types of surface sediments in Qinzhou Bay, which are dominated by sands and silty sands in terms of grain size. The surface sediments featured a stable macroelement composition,with SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, and CaO accounting for about 95.54% of the total sediments. Of these, SiO2 and Al2O3 exhibited the highest contents, averaging 73.23% and 8.71%, respectively. Compared to the upper continental crust (UCC), these surface sediments are enriched in SiO2, MnO, and TiO2 but depleted in other elements. These sediments displayed similar spatial distribution patterns of Al2O3, MgO, TiO2, K2O, and Na2O. The significant positive correlations between these oxides indicate similar factors governing their distributions. Using Al as a reference,the enrichment factors (EFs) of nine macroelements in the study area were calculated. The results indicate that these elements largely originated from the UCC, with those from some sites being potentially affected by other factors. A comprehensive analysis of correlation and R factors shows that the ten types of macroelements in the study area can be divided into three categories. The first category consists of SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO, MnO, TiO2, K2O, and Na2O, suggesting a source of terrigenous clastic sediments. The second category is CaO, principally representinga marine biological source. The third type comprises P2O5, representinga mariculture source. The analysis of these sediment sources using the PCA-MLR model reveals that the three sources exhibit relative contribution rates of 46.14%, 15%, and 38.86%, respectively.
|
|
Received: 23 January 2024
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
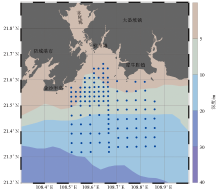
|
Sampling location of surface sediments in Qinzhou Bay
|
|
Percentage content and average particle size distribution of surface sediment particle size components
|

| 元素 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异
系数 | 上地壳
UCC[18] | | SiO2 | 50.74 | 96.29 | 73.23 | 11.56 | 15.78 | 65.90 | | Al2O3 | 1.1 | 19.85 | 8.71 | 5.71 | 65.55 | 15.19 | | Fe2O3 | 0.69 | 13.91 | 3.65 | 1.96 | 53.63 | 5.00 | | CaO | 0.227 | 15.2 | 2.07 | 2.04 | 98.41 | 4.20 | | MgO | 0.23 | 2.47 | 1.16 | 0.61 | 52.20 | 2.21 | | MnO | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.021 | 42.0 | 0.08 | | TiO2 | 0.169 | 1.24 | 0.62 | 0.19 | 30.30 | 0.50 | | P2O5 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 52.84 | 0.16 | | K2O | 0.11 | 2.2 | 1.01 | 0.63 | 61.87 | 3.37 | | Na2O | 0.174 | 3.19 | 1.07 | 0.70 | 65.24 | 3.90 |
|
Statistical of constant element content in surface sediments of the study area %
|
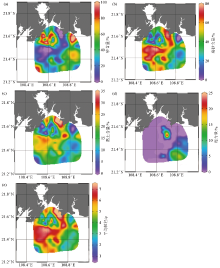
|
Spatial distribution of constant element in surface sediment
|
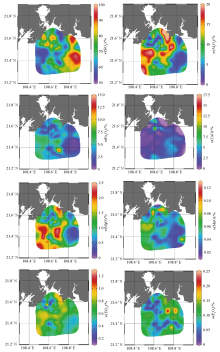
|
Spatial distribution of constant element in surface sediment
|
|
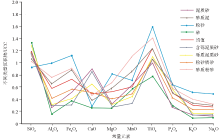
Changes in constant elements in different types of sediments after UCC-normalized
|

| 元素 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准方差 | 变异系数 | | SiO2 | 0.65 | 13.12 | 3.62 | 3.25 | 0.90 | | Fe2O3 | 0.73 | 5.25 | 1.57 | 0.75 | 0.48 | | CaO | 0.11 | 5.46 | 1.21 | 1.29 | 1.07 | | MgO | 0.51 | 3.03 | 1.10 | 0.47 | 0.43 | | MnO | 0.40 | 5.72 | 1.55 | 1.14 | 0.73 | | TiO2 | 1.30 | 10.03 | 3.16 | 2.03 | 0.64 | | P2O5 | 0.21 | 6.83 | 1.28 | 1.21 | 0.95 | | K2O | 0.32 | 0.98 | 0.54 | 0.10 | 0.18 | | Na2O | 0.16 | 1.49 | 0.54 | 0.21 | 0.39 |
|
Major element enrichment factor (EF) statistical parameters of surface sediments in the study area
|
|
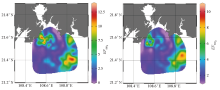
Spatial enrichment characteristics of constant elements SiO2 and TiO2 in surface sediments of the study area
|

| 指标 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | MnO | TiO2 | P2O5 | K2O | Na2O | 砾 | 砂 | 粉砂 | 黏土 | Mz | | SiO2 | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Al2O3 | -0.917** | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Fe2O3 | -0.875** | 0.827** | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | CaO | 0.147 | -0.283** | -0.260** | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | MgO | -0.926** | 0.908** | 0.868** | -0.245** | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | MnO | -0.544** | 0.531** | 0.557** | -0.191* | 0.521** | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | TiO2 | -0.703** | 0.803** | 0.682** | -0.339** | 0.726** | 0.434** | 1 | | | | | | | | | | P2O5 | -0.380** | 0.554** | 0.340** | -0.056 | 0.440** | 0.262** | 0.534** | 1 | | | | | | | | | K2O | -0.926** | 0.987** | 0.848** | -0.285** | 0.931** | 0.514** | 0.795** | 0.516** | 1 | | | | | | | | Na2O | -0.830** | 0.842** | 0.756** | -0.225* | 0.887** | 0.367** | 0.678** | 0.404** | 0.861** | 1 | | | | | | | 砾 | -0.131 | 0.014 | 0.468** | 0.049 | 0.064 | -0.137 | 0.037 | -0.157 | 0.040 | 0.137 | 1 | | | | | | 砂 | -0.250* | 0.125 | 0.245* | -0.221* | 0.201 | 0.225* | 0.113 | -0.148 | 0.124 | 0.137 | 0.034 | 1 | | | | | 粉砂 | 0.262* | -0.131 | -0.265* | 0.247* | -0.209 | -0.227* | -0.109 | 0.162 | -0.130 | -0.149 | -0.162 | -0.983** | 1 | | | | 黏土 | 0.207 | -0.094 | -0.227* | 0.115 | -0.165 | -0.173 | -0.115 | 0.113 | -0.099 | -0.108 | -0.174 | -0.924** | 0.881** | 1 | | | Mz | 0.254* | -0.130 | -0.280** | 0.203 | -0.201 | -0.219* | -0.132 | 0.142 | -0.135 | -0.159 | -0.339** | -0.933** | 0.946** | 0.934** | 1 |
|
Correlation analysis of constant elements, particle size components, and average particle size in the study area
|

| 元素 | F1 | F2 | F3 | | SiO2 | -0.941 | -0.119 | 0.216 | | Al2O3 | 0.972 | 0.037 | 0.052 | | Fe2O3 | 0.893 | -0.033 | -0.218 | | CaO | -0.310 | 0.913 | -0.228 | | MgO | 0.952 | 0.044 | -0.114 | | MnO | 0.586 | -0.117 | -0.227 | | TiO2 | 0.831 | -0.083 | 0.268 | | P2O5 | 0.535 | 0.314 | 0.732 | | K2O | 0.977 | 0.028 | 0.008 | | Na2O | 0.879 | 0.063 | -0.064 | | Mz | 0.822 | 0.013 | -0.058 | | 累积方差/% | 66.863 | 75.732 | 83.270 |
|
Analysis of constant element factors in surface sediment
|
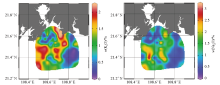
|
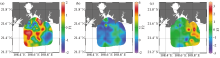
Planar distribution of scores for each factor
|
| [1] |
李梦, 曹庆先, 胡宝清, 等. 近60年广西钦州湾岸线变迁与开发利用空间格局评价[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2022, 41(6):76-86.
|
| [1] |
Li M, Cao Q X, Hu B Q, et al. Spatial pattern change of the coastline development and utilization of Qinzhou Bay in recent 60 years[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2022, 41(6):76-86.
|
| [2] |
张敏, 吴航星, 陆逸彬, 等. 海岸线围垦对广西钦州湾地形演变的影响分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2):124-131.
|
| [2] |
Zhang M, Wu H X, Lu Y B, et al. Impact of the coastal reclamations on topography evolution in the Qinzhou Bay,Guangxi[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2):124-131.
|
| [3] |
冯炳斌, 王日明, 黎树式, 等. 钦州湾人工海滩剖面变化过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4):51-60.
|
| [3] |
Feng B B, Wang R M, Li S S, et al. Changes of the artificial beach profile in the Qinzhou Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4):51-60.
|
| [4] |
劳齐斌, 刘国强, 高劲松, 等. 钦州湾养殖区营养盐分布特征及富营养化状况研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(3):407-416.
|
| [4] |
Lao Q B, Liu G Q, Gao J S, et al. Study on the characteristics and eutrophication of nutrients in the mariculture farms of Qinzhou Bay,South China[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(3):407-416.
|
| [5] |
林红梅, 王伟力, 林彩, 等. 钦州湾及其邻近海域重金属的时空变化特征和影响因素[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2020, 39(4):490-500.
|
| [5] |
Lin H M, Wang W L, Lin C, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of heavy metals and influencing factors in Qinzhou Bay and its adjacent waters in 2013-2014[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2020, 39(4):490-500.
|
| [6] |
阎琨, 庞国涛, 邢新丽, 等. 广西钦州湾表层沉积物中重金属的分布、来源及污染评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2023, 42(2):237-245.
|
| [6] |
Yan K, Pang G T, Xing X L, et al. Distribution,source and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Qinzhou Bay,Guangxi[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2023, 42(2):237-245.
|
| [7] |
Lyu H, Song D H, Zhang S F, et al. Compound effect of land reclamation and land-based pollutant input on water quality in Qinzhou Bay,China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022,826:154183.
|
| [8] |
曹超, 吴承强, 蔡锋, 等. 钦州湾外湾水下地形地貌特征及沉积物来源[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2020, 39(3):378-388.
|
| [8] |
Cao C, Wu C Q, Cai F, et al. Characteristics of submarine topography geomorphology and sediments sources in outer Qinzhou Bay[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2020, 39(3):378-388.
|
| [9] |
夏真, 林进清, 梁开, 等. 广西典型近岸海域表层沉积物碎屑矿物分布及其物源意义[J]. 中国地质调查, 2017, 4(2):66-72.
|
| [9] |
Xia Z, Lin J Q, Liang K, et al. Distribution and provenance significance of detrital minerals in surface sediments under typical coastal water areas,Guangxi[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2017, 4(2):66-72.
|
| [10] |
韩宗珠, 张军强, 邹昊, 等. 渤海湾北部底质沉积物中黏土矿物组成与物源研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2011, 41(11):95-102.
|
| [10] |
Han Z Z, Zhang J Q, Zou H, et al. Characteristics and provenance of clay mineral assemblage of sediments from the northern part of the Bohai Bay[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2011, 41(11):95-102.
|
| [11] |
赵一阳, 鄢明才. 中国浅海沉积物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1994.
|
| [11] |
Zhao Y Y, Yan M C. Geochemistry of sediments of the China shelf sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1994.
|
| [12] |
蓝先洪. 中国陆架的沉积环境地球化学[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2004, 20(9):10-15.
|
| [12] |
Lan X H. Sedimentary and environmental geochemistry of continental shelf in China[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2004, 20(9):10-15.
|
| [13] |
中国海湾志编辑委员会. 中国海湾志第十二分册(广西海湾)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社,1993.
|
| [13] |
Editiorial Committee of Chinese Gulf. Chinese gulf:Vol.12(Guangxi gulf)[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press,1993.
|
| [14] |
张伯虎, 陈沈良, 刘焱雄, 等. 广西钦州湾海域表层沉积物分异特征与规律[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(4):66-70.
|
| [14] |
Zhang B H, Chen S L, Liu Y X, et al. Sediment characteristics and differentiation in the Qinzhou Bay,Guangxi,China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(4):66-70.
|
| [15] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检疫总局. GB/T 12763.8—2007海洋调查规范第8部分:海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.
|
| [15] |
General Administration of Quality Supervision and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 12763.8—2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey Part 8:Marine geology and geophysics survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008.
|
| [16] |
Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River bar-A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1):3-26.
|
| [17] |
虞义勇, 褚宏宪, 杨慧良, 等. 渤海海峡表层沉积物常量元素分布特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(9):52-62.
|
| [17] |
Yu Y Y, Chu H X, Yang H L, et al. Distribution of major elements in surface sediments of Bohai strait and its geological significance[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(9):52-62.
|
| [18] |
Taylor S, McLennan S. The continental crust:Its composition and evolution[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1985, 94(4):57-72.
|
| [19] |
臧金生, 王东晓, 赵瑞强. 化探异常定量评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1114-1118.
|
| [19] |
Zang J S, Wang D X, Zhao R Q. Quantitative evaluation of geochemical anomalies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6):1114-1118.
|
| [20] |
杜德文, 石学法, 孟宪伟, 等. 黄海沉积物地球化学的粒度效应[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(1):78-82.
|
| [20] |
Du D W, Shi X F, Meng X W, et al. Geochemical granularity effect of sediment in the Yellow Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2003, 21(1):78-82.
|
| [21] |
秦蕴珊. 东海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1987.
|
| [21] |
Qin W S. East China Sea geology[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1987.
|
| [22] |
金秉福, 林振宏, 季福武. 海洋沉积环境和物源的元素地球化学记录释读[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(1):99-106.
|
| [22] |
Jin B F, Lin Z H, Ji F W. Interpretation of element geochemical records of marine sedimentary environment and provenance[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2003, 21(1):99-106.
|
| [23] |
梁胜跃, 刘建东, 郭炳跃, 等. 江苏省连云港市前三岛附近海域地球化学特征及风险指标探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(5):963-971,990.
|
| [23] |
Liang S Y, Liu J D, Guo B Y, et al. A comprehensive discussion on the geochemical characteristics and threatening indexes of the marine area around Qiansan Island,Lianyungang,Jiangsu Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(5):963-971,990.
|
| [24] |
杨競红, 王颖, 张振克, 等. 苏北平原2.58 Ma以来的海陆环境演变历史——宝应钻孔沉积物的常量元素记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(3):340-352.
|
| [24] |
Yang J H, Wang Y, Zhang Z K, et al. Major element records of land-sea interaction and evolution in the past 2.58 Ma from the Baoying borehole sediments,northern Jiangsu Plain,China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(3):340-352.
|
| [25] |
石学法, 刘升发, 乔淑卿, 等. 中国东部近海沉积物地球化学:分布特征、控制因素与古气候记录[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(5):883-894.
|
| [25] |
Shi X F, Liu S F, Qiao S Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics,controlling factor and record of paleoclimate in sediments from Eastern China Seas[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(5):883-894.
|
| [26] |
刘广虎, 李军, 陈道华, 等. 台西南海域表层沉积物元素地球化学特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(5):61-68.
|
| [26] |
Liu G H, Li J, Chen D H, et al. Geochemistry of surface sediments in the Taixinan (southwestern Taiwan) sea area in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(5):61-68.
|
| [27] |
黄丽艳, 黄鹄, 廖日权. 钦州湾近岸网箱养殖期磷的分布特征研究[J]. 广西科学, 2023, 30(5):910-921.
|
| [27] |
Huang L Y, Huang H, Liao R Q. Study on distribution characteristics of phosphorus in cage culture stage near Qinzhou Bay,South China[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2023, 30(5):910-921.
|
| [28] |
刘笑天, 刘军, 王以斌, 等. 不同溶解氧条件下沉积物—水体系磷循环[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(12):5571-5584.
|
| [28] |
Liu X T, Liu J, Wang Y B, et al. Phosphorus cycling in a sediment-water system controlled by different dissolved oxygen levels of overlying water[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(12):5571-5584.
|
| [29] |
边璐, 李田, 侯娟. PMF和PCA/MLR法解析上海市高架道路地表径流中多环芳烃的来源[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(10):3840-3846.
|
| [29] |
Bian L, Li T, Hou J. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using two mathematical models for runoff of the Shanghai elevated inner highway,China[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(10):3840-3846.
|
| [1] |
YU Lin-Song, HU Lei, WANG Dong-Ping, LIU Hui, CHEN Zi-Wan, LI Hua-Yong, DENG Huan-Guang. Assessment and trend prediction of the environmental capacity of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Dongping Lake, North China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 1146-1156. |
| [2] |
SONG Yun-Hong, YANG Feng-Chao, LIU Kai, DAI Hui-Min, XU Jiang, HAN Xiao-Meng. Geochemical characteristics of major elements in the black soil profiles of the Hailun area, Heilongjiang Province and their implications for provenance[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1105-1113. |
|
|
|
|

