|
|
|
| Application of audio magnetotellurics in the study of the subsurface water-bearing properties of the Santunhe area, Xinjiang |
YANG Ming-Yuan1( ), ZHANG Han-Xiong2,3( ), ZHANG Han-Xiong2,3( ), MA Chao1, YANG Hai-Lei1, ZHU Wei4 ), MA Chao1, YANG Hai-Lei1, ZHU Wei4 |
1. No.2 Regional Geological Survey Team of Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Changji 831100, China
2. Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Shijiazhuang 050061, China
3. Technology Innovation Center for Geothermal & Hot Dry Rock Exploration and Development, Ministry of Natural Resources, Shijiazhuang 050061, China
4. Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Audio magnetotellurics (AMT) is widely used for energy and mineral explorations because of its high exploration efficiency and high vertical resolution. Using a three-dimensional (3D) inversion algorithm based on data space, this study performed 3D inversion of the AMT data collected from geothermal exploration in the Santunhe area of Xinjiang. As indicated by the inversion results, the 3D inversion avoids the influence of inhomogeneous geobodies on the survey lines in the study area and yielded very rich and intuitive 3D geoelectric anomalies. In combination with the geological data and the 3D inversion results, this study analyzed the subsurface electrical properties of the study area and the formation water-bearing properties related to geothermal reservoirs, and finally inferred several favorable areas for geothermal reservoirs from the geothermal accumulation patterns of the study area.
|
|
Received: 22 November 2022
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
10]
">
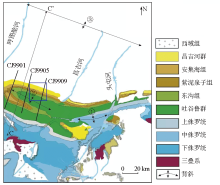
|
The location of the study area and seismic profile positions in the surrounding area(black is seismic profile location, blue is study area range)[10]
|
10]
">
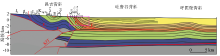
|
C-C’ seismic interpretation profile of Changji anticline[10]
|

| 岩(矿)石名称 | 个
数 | ρs/(Ω·m) | | 最大值 | 最小值 | 几何平均值 | | 呼图壁河组紫红色泥岩 | 30 | 143.00 | 22.38 | 54.35 | | 呼图壁河组灰绿色砂质泥岩 | 24 | 75.91 | 22.47 | 46.61 | | 呼图壁河组灰绿色细砂岩 | 36 | 257.67 | 72.53 | 151.59 | | 呼图壁河组灰绿色粉砂岩 | 24 | 504.14 | 138.26 | 294.01 | | 清水河组灰绿色钙质砾岩 | 36 | 725.02 | 188.20 | 408.32 | | 清水河组紫红色钙质砾岩 | 36 | 347.51 | 100.23 | 255.21 | | 清水河组灰绿色砾岩 | 36 | 855.58 | 221.00 | 455.84 | | 清水河组灰绿色粉砂岩 | 36 | 251.73 | 66.03 | 102.14 | | 齐古组紫红色泥质粉砂岩 | 24 | 22.88 | 5.38 | 12.6 | | 齐古组紫红色砂质泥岩 | 24 | 43.05 | 5.74 | 18.55 |
|
Statistical of rock (ore) physical property parameters in Karaza area around the study area
|
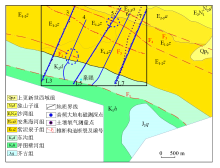
|
The study area geology and AMT survey line position map(black box is the range of three?dimensional inversion of AMT)
|
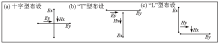
|
AMT data acquisition and distribution mode
|
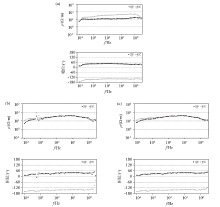
|
Measured apparent resistivity curve of AMT
a—L5-250;b—before de-noising of L7-50;c—after de-noising of L7-50
|
15]
">
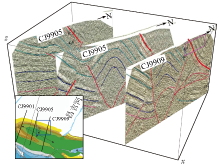
|
Quasi-three-dimensional morphology and distribution characteristics of Changji anticline[15]
|
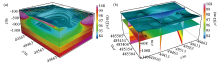
|
AMT 3D inversion results
a—display diagram of AMT-3D inversion results; b—-500 m depth horizontal slice, profile slice and 100 Ω·m isosurface combined graph
|
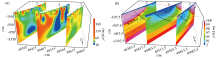
|
Profile inversion results
a—2D inversion results;b—slice of 3D inversion results
|
16]
">
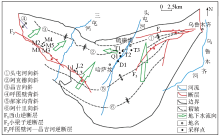
|
Schematic of groundwater flow in the study area[16]
|
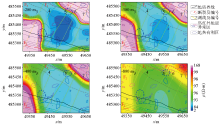
|
Depth slice of AMT 3D inversion results and prediction of geothermal favorable areas
|
| [1] |
徐世光, 郭远生. 地热学基础[M]. 北京: 北京科学出版社, 2009.
|
| [1] |
Xu S G, Guo Y S. Geothermal blood foundation[M]. Beijing: Beijing Science Press, 2009.
|
| [2] |
王佳龙, 邸兵叶, 张宝松, 等. 音频大地电磁法在地热勘查中的应用以福建省宁化县黄泥桥地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3):576-582.
|
| [2] |
Wang J L, Di B Y, Zhang B S, et al. The application of audio frequency magnetotelluric method to the geothermal exploration:A case of Huangniqiao area,Ninghua County,Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3):576-582.
|
| [3] |
魏文博. 我国大地电磁测深新进展及瞻望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(2):245-254.
|
| [3] |
Wei W B. New progress and prospect of magnetotelluric sounding in China[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2002, 17(2):245-254.
|
| [4] |
严良俊, 胡文宝, 杨绍芳, 等. 电磁勘探方法及其在南方碳酸盐岩地区的应用[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001.
|
| [4] |
Yan L J, Hu W B, Yang S F, et al. Electromagnetic prospecting method and its application in carbonate rock areas in the south[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001.
|
| [5] |
冯思臣, 王绪本, 阮帅. 一维大地电磁测深几种反演算法的比较研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2004, 39(5):594-599,498-628.
|
| [5] |
Feng S C, Wang X B, Ruan S. Comparative study of several inversion algorithms for one-dimensional magnetotelluric sounding[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2004, 39(5):594-599,498-628.
|
| [6] |
胡祖志, 胡祥云, 吴文鹂, 等. 大地电磁二维反演方法对比研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2005, 33(1):64-68.
|
| [6] |
Hu Z Z, Hu X Y, Wu W L, et al. Comparative study of two-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion methods[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2005, 33(1):64-68.
|
| [7] |
胡祖志, 胡祥云. 大地电磁三维反演方法综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2005, 20(1):214-220.
|
| [7] |
Hu Z Z, Hu X Y. Review of 3D magnetotelluric inversion methods[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2005, 20(1):214-220.
|
| [8] |
Siripunvaraporn W, Egbert G, Lenbury Y, et al. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion:Data-spale methed[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2005, 150(1/3):3-4.

|
| [9] |
黄登, 胡文宝, 王仁虎, 等. AMT三维反演在浅部岩体勘探中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2015, 12(3):288-293.
|
| [9] |
Huang D, Hu W B, Wang R H, et al. Application of AMT 3D inversion in shallow rock exploration[J]. Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2015, 12(3):288-293.
|
| [10] |
邱建华. 准噶尔南缘新生代逆冲褶皱带构造几何学和运动学[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.
|
| [10] |
Qiu J H. Tectonic geometry and kinematics of the Cenozoic thrust fold belt in the southern margin of Junggar[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017.
|
| [11] |
罗寿兵. 准噶尔盆地南缘昌吉背斜构造建模与构造解释研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油学院, 2004.
|
| [11] |
Luo S B. Structural modeling and interpretation of Changji anticline in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum Institute, 2004.
|
| [12] |
杨景林, 沈一新. 准噶尔盆地南缘紫泥泉子组的时空展布及成因解释[J]. 地层学杂志, 2004, 28(3):215-222.
|
| [12] |
Yang J L, Shen Y X. Temporal and spatial distribution and genetic interpretation of Ziniquanzi Formation in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2004, 28(3):215-222.
|
| [13] |
陈晓冬, 苗辰若, 贾为卫. 可探源音频大地电磁测深在新疆喀拉扎地区含铀砾石层勘探中的应用[J]. 科技视界, 2016(18):237-239.
|
| [13] |
Chen X D, Miao C R, Jia W W. Application of soundable source audio magnetotelluric sounding in the exploration of Uranium-bearing gravel strata in Kalazar,Xinjiang[J]. Scientific and Technological Horizon. 2016(18):237-239.
|
| [14] |
孙洁, 晋光文, 白登海, 等. 大地电磁测深资料的噪声干扰[J]. 物探与化探, 2000, 24(2):119-127.
|
| [14] |
Sun J, Jin G W, Bai D H, et al. The noise interference of magnetotelluric sounding data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2000, 24(2):119-127.
|
| [15] |
王大勇, 朱威, 范翠松, 等. 矿集区大地电磁噪声处理方法及其应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(4) :823-829.
|
| [15] |
Wang D Y, Zhu W, Fan C S, et al. Noise processing methods and application study of MT in the ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39( 4) :823-829.
|
| [16] |
陈伟, 郝晋进, 张健, 等. 昌吉背斜构造浅析[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2010, 33(4):25-28,93.
|
| [16] |
Chen W, Hao J J, Zhang J, et al. Analysis of Changji anticline Structure[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2010, 33(4):25-28,93.
|
| [17] |
谷阳, 丁文龙, 陈伟. 准噶尔盆地南缘齐古背斜构造分析及三维建模[J]. 科技通报, 2017, 33(12):60-64.
|
| [17] |
Gu Y, Ding W L, Chen W. Structural analysis and 3D modeling of Qigu anticline in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Science and Technology Bulletin, 2017, 33(12):60-64.
|
| [18] |
张开军, 张强, 魏迎春, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘硫磺沟地区水文地质特征及其对煤层气富集的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(1):61-65.
|
| [18] |
Zhang K J, Zhang Q, Wei Y C, et al. Hydrogeological characteristics and its influence on coalbed methane enrichment in the southern margin of the the Junggar Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(1):61-65.
|
| [19] |
魏迎春, 张强, 王安民, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘煤系水矿化度对低煤阶煤层气的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2016, 44(1):31-37.
|
| [19] |
Wei Y C, Zhang Q, Wang A M, et al. The influence of the salinity of groundwater in coal measures on low rank coalbed methane in the south margin of Junggar basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2016, 44(1):31-37.
|
| [20] |
周三栋, 刘大锰, 孙邵华, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘硫磺沟煤层气富集主控地质因素及有利区优选[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(1): 179-189.
|
| [20] |
Zhou S D, Liu D M, Sun S H, et al. Factors affecting coalbed methane enrichment and CBM favorable area of Liuhuanggou area in the southern Jungger basin[J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(1):179-189.
|
| [21] |
张岩, 董维红, 李满洲, 等. 河南平原浅层地下水总溶解固体和水化学类型的分布特征[J]. 水文, 2011, 31(2):79-83.
|
| [21] |
Zhang Y, Dong W H, Li M Z, et al. Study on distribution characteristics of TDS and hydrochemical type of shallow groundwater in Henan plain[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2011, 31(2):79-83.
|
| [22] |
陈锋, 刘涛, 顾新鲁, 等. 新疆地热水分布与地质构造的关系[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2016, 28(2):144-148.
|
| [22] |
Chen F, Liu T, Gu X L, et al. Relationship between geothermal water distribution and geological structure in Xinjiang[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2016, 28(2):144-148.
|
| [23] |
陈锋. 新疆维吾尔自治区地热资源调查与评价报告[R]. 新疆地矿局第二水文工程地质大队, 2011.
|
| [23] |
Chen F. Investigation and evaluation report on geothermal resources in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region[R] .The Second Hydrogeological Engineering Geological Brigade of Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, 2011.
|
| [24] |
徐世光, 郭远生. 地热学基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009:103-113.
|
| [24] |
Xu S G, Guo Y S. Fundamentals of geothermal science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009:103-113.
|
| [1] |
Cheng Zheng-Pu, Lian Sheng, Wei Qiang, Hu Wen-Guang, Lei Ming, Li Shu. Research on time-frequency electromagnetic method detection of Wumishan Formation thermal reservoir in deep Xiong’an New Area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1400-1409. |
| [2] |
ZHAO Bao-Feng, WANG Qi-Nian, GUO Xin, GUAN Da-Wei, CHEN Tong-Gang, FANG Wen. Gravity survey and audio magnetotellurics-based insights into the deep structures and geothermal resource potential of the Rucheng Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1147-1156. |
|
|
|
|

