|
|
|
| Application of the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in urban geological surveys |
HE Sheng1,2,3,4( ), WANG Wan-Ping5, DONG Gao-Feng1,2, NAN Xiu-Jia3, WEI Feng-Feng3, BAI Yong-Yong3 ), WANG Wan-Ping5, DONG Gao-Feng1,2, NAN Xiu-Jia3, WEI Feng-Feng3, BAI Yong-Yong3 |
1. Qinghai Bureau of Environmental Geology Exploration,Xining 810008,China
2. Key Laboratory of Environmental Geology of Qinghai Province,Xining 810008,China
3. Qinghai 906 Engineering Survey and Design Institute Co.,Ltd.,Xining 810007,China
4. Qinghai Institute of Geological Environment Survey,Xining 810008,China
5. Qinghai Provincial Land Remediation and Ecological Restoration Center,Xining 810008,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract With the rapid development of urban infrastructure,the demand for urban geological work is increasing,and urban geological surveys become particularly important.Urban geophysical exploration has different exploration purposes and working environments from conventional geophysical exploration.Accordingly,compared with conventional geophysical exploration methods,the geophysical exploration methods for urban geological surveys face the challenges of many interference factors,limited construction sites and time,and high requirements for exploration accuracy.The opposing-coils transient electromagnetic(OCTEM) method enjoys a strong anti-interference ability,convenient and efficient construction,and high resolution.Therefore,this study employed the OCTEM method to investigate the test profile in the urban geological survey and evaluation of Haidong City.This test profile was subjected to numerous interference sources since it crossed 11 highways and railways and passed through factories,schools,logistics parks,villages,living quarters,and rivers.Consequently,the OCTEM results agree well with the results of single-point resistivity sounding and drilling results.Therefore,the OCTEM method proposed in this study is effective for urban geological surveys.
|
|
Received: 24 November 2022
Published: 27 October 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
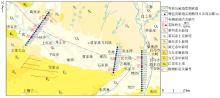
Schematic diagram of geophysical prospecting work layout
|

| 序号 | 地层 | 岩性 | 电阻率/
(Ω·m) | 常见值/
(Ω·m) | | 1 | Q | 黄土状土 | 45~90 | 55 | | 2 | 卵石、碎石 | 80~260 | 150 | | 3 | N | 泥岩 | 5~90 | 15 | | 4 | 砂岩 | 80~150 | 110 |
|
Statistical of formation electrical and physical properties in the study area
|
|
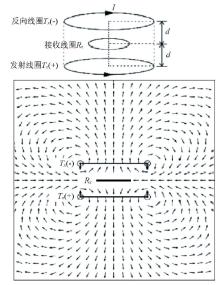
OCTEM coils and its primary magnetic field line on the diametric plane
|
|
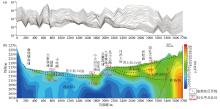
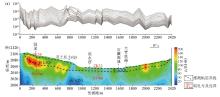
Original secondary field profile(a) and comprehensive result map(b) of OCTEM W1 section
|
|
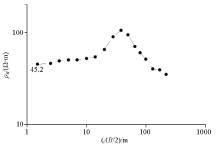
Resistivity sounding D1(ZK6) single point curve
|
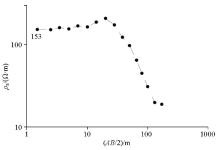
|
Resistivity sounding D2(ZK4) single point curve
|
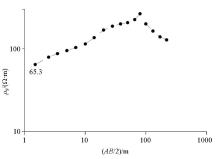
|
Resistivity sounding D3(ZK3) single point curve
|
|
Original secondary field profile(a) and comprehensive result map(b) of OCTEM W2 section
|
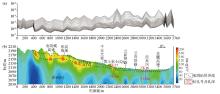
|
Original secondary field profile(a) and comprehensive result map(b) of OCTEM W3 section
|
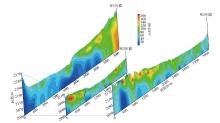
|
Three-dimensional slice result of OCTEM
|

| 序号 | 钻孔编号 | 孔深/m | 地层埋深/m | 岩性 | 地下水位/m | | 1 | ZK3 | 45.1 | 0~3.0 | 黄土状土:灰黄色、黄褐色,稍湿稍密—中密,主要成分为粉土,手搓着砂感,干强度低韧性低,可搓成2~3 mm的土体 | 11.4 | | 3.0~9.0 | 碎石:灰白色,稍湿,稍密,一般粒径30~40 mm,碎成分主要为石英岩、砂岩、花岗岩及少量浅色变质岩等 | | 9.0~33.7 | 卵石:青灰色、灰白色,稍湿—湿,中密,一般粒径20~30 mm,成分主要为石英岩、砂岩、花岗岩及少量浅色变质岩等 | | 33.7~45.1 | 砂岩:33.7~36.4 m为强风化砂岩,36.4~41.4 m为中风化砂岩,41.4~45.1 m为微风化砂岩 | | 2 | ZK4 | 22.5 | 0~9.8 | 卵石:青灰色、灰黄色,稍湿,松散,一般粒径0.2~6 cm,最大7 cm,成分以石英岩、花岗岩为主 | 2.1 | | 9.8~22.5 | 泥岩:9.8~12.5 m为强风化泥岩,12.5~20.2 m为中风化泥岩,20.2~22.5 m为微风化泥岩 | | 3 | ZK5 | 31.2 | 0~13.5 | 卵石:青灰色,稍湿—饱水,稍密—中密,砾石约占20%,卵石约占70%,余为中粗砂,成分以砂岩、石英岩、花岗岩为主 | 无 | | 13.5~31.2 | 泥岩:13.5~19.4 m为强风化泥岩,19.4~27.7 m为中风化砂岩,27.7~31.2 m为微风化泥岩 | | 4 | ZK6 | 30.1 | 0~6.6 | 黄土状土:黄褐色,稍湿,稍密,手搓有砂感,刀切面粗糙,无光泽反应,强度低,手掰易碎,成分以粉土为主 | 11.1 | | 6.6~15.2 | 卵石:青灰色,湿,密实,一般粒径0.2~4 cm,最大5 cm,卵砾石成分以石英岩、花岗岩为主 | | 15.2~30.1 | 泥岩:15.2~18.1 m为强风化泥岩,18.1~24.5 m为中风化泥岩,24.5~30.1 m为微风化泥岩 | | 5 | ZK16 | 31.0 | 0~5.4 | 黄土状土:黄褐色,稍湿,松散,手版易碎,干强度低,成分以粉土为主 | | | 5.4~10.5 | 卵石:青灰色,稍湿,稍密—密实,含砂及圆砾,一般粒径0.5~8 cm,最大11 cm | | 10.5~31.0 | 泥岩:10.5~12.3 m为强风化,12.3~27.5 m为中风化,27.5~31.0 m为微风化 | | 6 | ZK17 | 33.4 | 0~2.0 | 黄土状土:黄褐色,稍湿,稍密,成分主要为粉土,具孔隙,土质较均匀 | | | 2.0~10.8 | 卵石:青灰色、灰白色,稍湿—饱和,稍密—密实,最大粒径110 mm,分选性一般 | | 10.8~33.4 | 泥岩:10.8~15.2 m为强风化,15.2~27.3 m为中风化,27.3~33.4 m为微风化 | | 7 | ZK33 | 24.4 | 0~2.4 | 黄土状土:红褐色,稍湿,松散,成分以粉土为主 | | | 2.4~10.0 | 卵石:青灰色,稍湿,稍密—密实,含砂及圆砾,一般粒径0.5~8 cm,卵石磨圆度一般 | | 10.0~24.4 | 泥岩:10.0~18.1 m为强风化,18.1~22.3 m为中风化,22.3~24.4 m为微风化 | | 8 | ZK34 | 49.95 | 0~5.3 | 黄土状土:灰黄色、黄褐色,稍湿,主要成分为粉土 | | | 5.3~34.0 | 卵石:青灰色,稍湿—饱水,主要成分为石英、长石 | | 34.0~49.95 | 泥岩:34.0~41.6 m为强风化,41.6~47.3 m为中风化,47.3~49.95 m为微风化 |
|
Statistical of geological drilling well data in study area
|
| [1] |
孙怀凤, 李凯, 陈儒军, 等. 浅层岩溶瞬变电磁响应规律试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(3):652-661.
|
| [1] |
Sun H F, Li K, Chen R J, et al. Experimental study on transientelectromagnetic responses to shallow karst[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(3):652-661.
|
| [2] |
李才明, 王良书, 徐鸣洁, 等. 基于小波能谱分析的岩溶区探地雷达目标识别[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006, 49(5):1499-1504.
|
| [2] |
Li C M, Wang L S, Xu M J, et al. Objects recognition of groundpenetrat ing radar in karst regions using wavelet energy spectrum analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006, 49(5):1499-1504.
|
| [3] |
王亮, 龙霞, 王婷婷, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在城市浅层空洞探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5):1289-1295.
|
| [3] |
Wang L, Long X, Wang T T, et al. Application od the opposing-coils transient electromeanetie method in detetion of urbran shallow cavities[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5):1289-1295.
|
| [4] |
席振铢, 刘剑, 龙霞, 等. 瞬变电磁法三分量测量方法研究[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 41(1):272-276.
|
| [4] |
Xi Z Z, Liu J, Long X, et al. Three-component measurement in transient electromagnetic method[J]. Journal of Central South Universily:Science and Technology, 2010, 41(1):272-276.
|
| [5] |
席振铢, 龙霞, 周胜, 等. 基于等值反磁通原理的浅层瞬变电磁法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(9):3428-3435.
|
| [5] |
Xi Z Z, Long X, Zhou S, et al. Opposing coils transient electromagnetic method for shallow subsuface detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(9):3428-3435.
|
| [6] |
王银, 席振铢, 蒋欢, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在探测岩溶病害中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(2):360-363.
|
| [6] |
Wang Y, Xi Z Z, Jiang H, et al. The application research on thedetection of karst disease of airport runway based on OCTEM[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(2):360-363.
|
| [7] |
高远. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在城镇地质灾害调查中的应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(3):152-156.
|
| [7] |
Gao Y. The application of opposing coils transient electromagnetics method in geological hazard investigation of town[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(3):152-156.
|
| [8] |
赵杨杉. 高密度电法与等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在法泗岩溶塌陷精细探测中的联合应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2022, 19(3):348-355.
|
| [8] |
Zhao Y S. Combined application of high density electrical method and opposing coils transient electromagnetic method in fine detection of karst collapse in Fasi[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2022, 19(3):348-355.
|
| [9] |
余涛, 王小龙, 王俊超. 综合物探方法在城市地铁岩溶勘察中的应用[J]. CT理论与应用研究, 2022, 31(5):587-596.
|
| [9] |
Yu T, Wang X L, Wang J C. Application of camprehensive geophysical prospecting method in Karst exploration of urbansubway[J]. CT Theory and Applications, 2022, 31(5):587-596.
|
| [10] |
黄锦捷, 李世平. 物探技术在城市地质调查中的应用[J]. 低碳技术, 2018(6):56-57.
|
| [10] |
Huang J J, Li S P. Application of geophysical prospecting technology in urban geological survey[J]. Low Carbon Technology, 2018(6):56-57.
|
| [11] |
蒋波, 黄敬军, 姜国庆, 等. 物探技术在徐州城市地质调查中的应用[J]. 城市地质, 2019, 14(3):105-112.
|
| [11] |
Jiang B, Huang J J, Jiang G Q, et al. Application of geophysical prospecting technology in urban geological survey of Xuzhou[J]. Urban Geology, 2019, 14(3):105-112.
|
| [12] |
刘杰, 段炜, 王俊, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在公路隧道塌陷区的探测应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(6):1470-1475.
|
| [12] |
Liu J, Duan W, Wang J, et al. The application of oppesing coils trunsient lectmmaguetic method to the detection of undeargnounad ollape in hieghway tumelunder coustruction[J]. Ceophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(6):1470-1475.
|
| [13] |
辛静. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在浅部采空区探测中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2019, 16(5):718-722.
|
| [13] |
Xin J. The application of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method to detect shallow goaf[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2019, 16(5):718-722.
|
| [1] |
WANG Liang, LONG Xia, WANG Ting-Ting, XI Zhen-Zhu, CHEN Xing-Pen, ZHONG Ming-Feng, DONG Zhi-Qiang. Application of the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in detection of urban shallow cavities[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1289-1295. |
| [2] |
LONG Hui, XIE Xing-Long, LI Feng-Zhe, REN Zheng-Wei, WANG Chun-Hui, GUO Shu-Jun. 2D seismic and high-density resistivity sounding reveal the shallow three-dimensional geological structure characteristics of Xiong'an New Area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4): 808-815. |
|
|
|
|

