|
|
|
| One-dimensional focusing inversion of the semi-airborne transient electromagnetic method and its application |
WANG Shi-Xing1( ), HE Ke2,3( ), HE Ke2,3( ), YIN Xiao-Kang1, WEI Dong-Hua1, ZHAO Si-Wei1, GUO Ming3 ), YIN Xiao-Kang1, WEI Dong-Hua1, ZHAO Si-Wei1, GUO Ming3 |
1. China Railway Eryuan Engineering Group Co., Ltd., Chengdu 610031, China
2. Education Information Technology Center, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637002, China
3. College of Geophysics, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The semi-airborne transient electromagnetic method (SATEM) is an emerging flexible and efficient geophysical exploration method using ground launch and air reception. The present inversion methods applied to the SATEM produce very smooth inversion results since they apply the maximum smoothing criterion, thus failing to effectively identify the information of specific layer interfaces. This study introduced the focusing inversion theory to the one-dimensional inversion of the SATEM. First, a focusing inversion stabilizer was determined by selecting appropriate focusing and regularization factors. Then, the inversion objective function including the focusing inversion stabilizer was solved to allow the inversion results to effectively identify the abrupt interfaces of layered strata. Furthermore, multiple layered geoelectric models were built to verify the reliability of the focusing inversion. Moreover, the focusing inversion results were compared with the Occam inversion results to highlight the advantages of the focusing inversion in interface identification. This study conducted the focusing inversion calculation of actual data on groundwater detection of a certain area. The calculation results were then combined with the hydrogeological and logging data for comprehensive analysis. Finally, this study determined the locations and spatial distribution of underground aquifers in the area, verifying the feasibility of the SATEM for groundwater detection.
|
|
Received: 13 July 2022
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
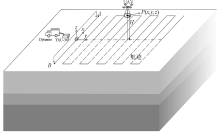
|
Schematic diagram of the working mode of semi-airborne transient electromagnetic method
|
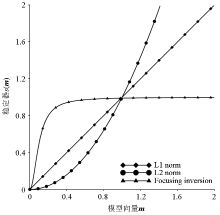
|
Variation of different stabilizers with the gradient of model parameters
|
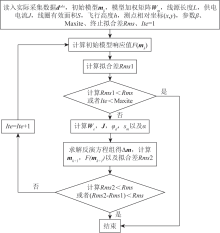
|
Focused inversion flowchart
|

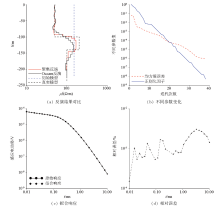
| 地电模型 | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | 层厚/m | H型
K型 | ρ1=300、ρ2=50、ρ3=100
ρ1=50、ρ2=200、ρ3=100 | h1=100、h2=40、h3=∞
h1=100、h2=40、h3=∞ |
|
Three-layer geoelectric model parameters
|
|
Inversion results of H-type geoelectric model
|
|
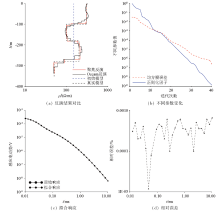
Inversion results of K-type geoelectric model
|

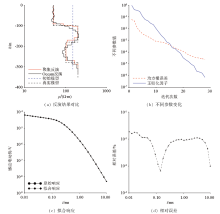
| 地电模型 | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | 层厚/m | | HK型 | ρ1=300、ρ2=100、
ρ3=200、ρ4=50 | h1=100、h2=80、
h3=100、h4=∞ | | KH型 | ρ1=50、ρ2=200、
ρ3=100、ρ4=200 | h1=100、h2=80、
h3=100、h4=∞ |
|
Four-layer geoelectric model parameters
|
|
Inversion results of HK-type geoelectric model
|
|
Inversion results of KH-type geoelectric model
|
|
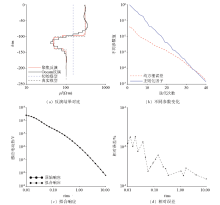
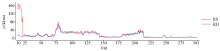
Depth lateral resistivity logging curve
|
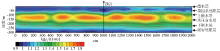
|
Measured data resistivity inversion results
|
| [1] |
林君, 薛国强, 李貅. 半航空电磁探测方法技术创新思考[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(9):2995-3004.
|
| [1] |
Lin J, Xue G Q, Li X. Technological innovation of semi-airborne electromagnetic detection method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(9):2995-3004.
|
| [2] |
王绪本, 张赛民, 高嵩, 等. 无人机半航空瞬变电磁探测技术及其应用[C]// 中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集(二十四), 2019.
|
| [2] |
Wang X B, Zhang S M, Gao S, et al. Semi-airborne transient electromagnetic detection technology and its application[C]// Chinese Joint Annual Conference on Earth Sciences (24), 2019.
|
| [3] |
王仕兴, 易国财, 王绪本, 等. 基于分段二分搜索算法的半航空瞬变电磁电导率深度快速成像方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(3):1317-1324.
|
| [3] |
Wang S X, Yi G C, Wang X B, et al. Research on the Semi-airborne transient electromagnetic conductivity depth rapid imaging method based on segmented binary search algorithm[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(3):1317-1324.
|
| [4] |
张振雄, 易国财, 王仕兴, 等. 基于最小构造模型的地空瞬变电磁一维正反演技术研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2021, 43(3):352-359.
|
| [4] |
Zhang Z X, Yi G C, Wang S X, et al. Research on 1D forward modeling and inversion of ground-airborne transient electromagnetic method based on minimum structural model[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 43(3):352-359.
|
| [5] |
许洋. 半航空电磁一维正反演研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014.
|
| [5] |
Xu Y. Study about 1D forward and inversion of SATEM[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014.
|
| [6] |
张澎, 余小东, 许洋, 等. 半航空时间域电磁数据一维自适应正则化反演[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2017, 39(1):1-8.
|
| [6] |
Zhang P, Yu X D, Xu Y, et al. An adaptive regularized inversion of 1D semi-airborne time-domain electromagnetic data[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 39(1):1-8.
|
| [7] |
赵涵, 景旭, 李貅, 等. 多辐射场源地空瞬变电磁一维反演方法研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(1):132-142.
|
| [7] |
Zhao H, Jing X, Li X, et al. A study of 1D inversion of multi-source ground-airborne transient electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(1):132-142.
|
| [8] |
杨聪, 毛立峰, 毛鑫鑫, 等. 半航空瞬变电磁自适应正则化-阻尼最小二乘算法研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(1):137-146.
|
| [8] |
Yang C, Mao L F, Mao X X, et al. Study on the semi-aerospace transient electromagnetic adaptive regularization-damped least squares algorithm[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(1):137-146.
|
| [9] |
马振军, 底青云, 薛国强, 等. 地—空瞬变电磁法电阻率成像研究与应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(3):1090-1105.
|
| [9] |
Ma Z J, Di Q Y, Xue G Q, et al. The research and application of resistivity imaging of semi-airborne transient electromagnetic method[J]. Chinese J.Geophys., 64(3):1090-1105.
|
| [10] |
何可, 郭明, 胡章荣, 等. 半航空瞬变电磁L1范数自适应正则化反演[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1338-1346.
|
| [10] |
He K, Guo M, Hu Z R, et al. Semi-airborne transient electromagnetic inversion based on L1-norm adaptive regularization[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1338-1346.
|
| [11] |
He K, Wang X B, Guo M, et al. Spatially constrained inversion of semi-airborne transient electromagnetic data based on a mixed norm[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2022, 200:104616.

|
| [12] |
Portniaguine O, Zhdanov M S. Focusing geophysical inversion images[J]. Geophysics, 1999, 64(3):874-887.

|
| [13] |
刘小平. 大地电磁聚焦反演成像方法研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2007.
|
| [13] |
Liu X P. Focusing inversion images of magnetotelluric data[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2007.
|
| [14] |
白宁波, 周君君, 胡祥云. 优化策略的二维大地电磁光滑聚焦反演研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(4):902-909.
|
| [14] |
Bai N B, Zhou Z Z, Hu X Y. Two-dimensional magnetotelluric smooth focusing inversion based on optimization strategy[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(4):902-909.
|
| [15] |
Zhang L L, Yu P, Wang J L, et al. A study on 2D magnetotelluric sharp boundary inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(3):631-637.
|
| [16] |
秦朋波, 黄大年. 重力和重力梯度数据联合聚焦反演方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(6):2203-2224.
|
| [16] |
Qin P B, Huang D N. Integrated gravity and gravity gradient data focusing inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(6):2203-2224.
|
| [17] |
陈闫, 李桐林, 范翠松, 等. 重力梯度全张量数据三维共轭梯度聚焦反演[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(3):1133-1142.
|
| [17] |
Chen Y, Li T L, Fan C S, et al. The 3D focusing inversion of full tensor gravity gradient data based on conjugate gradient[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(3):1133-1142.
|
| [18] |
米萨克·纳比吉安. 应用地球物理学中的电磁方法[M].赵经祥,王彦军,译. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992: 226-231.
|
| [18] |
Misac N N. Electromagnetic methods in applied geophysics[M].Translated by ZhaoX, WangY J. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992: 226-231.
|
| [19] |
甘露, 唐荣江, 王绪本. 瞬变电磁频—时转换混合优化算法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(2): 596-602.
|
| [19] |
Gan L, Tang R J, Wang X B. Hybrid optimization algorithm of transient electromagnetic time-frequency conversion[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(2):596-602.
|
| [20] |
Last B J, Kubik K. Compact gravity inversion[J]. Geophysics, 1983, 48(6):713-721.

|
| [21] |
陈小斌, 赵国泽, 汤吉, 等. 大地电磁自适应正则化反演算法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2005, 48(4):937-946.
|
| [21] |
Chen X B, Zhao G Z, Tang J, et al. An adaptive regularized inversion algorithm for magnetotelluric data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(4):937-946.
|
|
|
|

