|
|
|
| The application of an integrated geogas prospecting for exploring rare metal deposits in the periphery of the Renli mining area, southern Hunan Province |
GAN Xue-Jun1( ), ZHOU Si-Chun1( ), ZHOU Si-Chun1( ), LIU Xiao-Hui1, WANG Deng-Hong2, WEN Chun-Hua3 ), LIU Xiao-Hui1, WANG Deng-Hong2, WEN Chun-Hua3 |
1. Applied Nuclear Technology in Geosciences Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China
2. Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037, China
3. Geological Survey Institute of Hunan Province, Changsha 410083, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In this study, six survey lines were deployed in the Huangbaishan survey area in the periphery of the Renli mining area in southern Hunan Province. An integrated geogas prospecting was applied to explore granite pegmatite-type rare metal deposits in the study area. Based on the characteristics of soil X-ray fluorescence and geogas anomalies above the known pegmatite veins in the mining area, this study captured five soil X-ray fluorescence anomaly zones aligning with the formation trend, with the (Nb+Ta+Rb) cumulative value obtained from X-ray fluorescence measurements as the primary prospecting indicator. The Nos. 1~4 anomaly zones exhibit consistent spatial positions with the known pegmatite veins. Accordingly, this study inferred the positions, trends, and lengths of possible pegmatite veins, and a possibility of extension for the known veins based on the anomaly length. The No. 5 anomaly zone discovered on the south side of the survey area, with a length exceeding 1 000 m, serves as a new prospecting target. Geogas prospecting was conducted along the No. 11 survey line in the middle of the No. 4 anomaly zone with a length of over 1 500 m, capturing the geogas anomalies of elements Li, Be, and Nb that reflect the deep mineralization information of pegmatite veins. This confirms that pegmatite veins in the survey area have significant extensions towards the deep part.
|
|
Received: 25 July 2023
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
3-4]
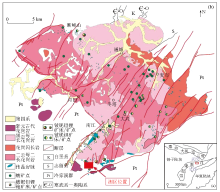
a—geotectonic location of Mufushan mining agglomeration area; b—geology and mineral distribution in Mufushan mining agglomeration area
">
|
Simplified map of geology and minerals in Mufushan rare metal mining area[3-4]
a—geotectonic location of Mufushan mining agglomeration area; b—geology and mineral distribution in Mufushan mining agglomeration area
|
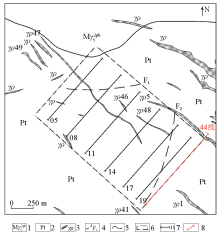
|
Geological sketch and engineering deployment map of Renli mining area and peripheral
1—medium-grained porphyry-like biotite monzonitic granite; 2—Lengjiaxi schist; 3—pegmatite vein and number; 4—speculative faults; 5—geological boundaries; 6—X-ray fluorescence measurement area; 7—X-ray survey line and number; 8—geogas survey line and number
|

| 分析方法 | 分析元素 | 测量元素种类 | | XRF | K、Ca、Cr、Mn、Fe、Ni、Zn、
Pb、Rb、Sr、Zr、Ta、Y、Nb | 14 |
|
X-ray fluorescence measurement elements of Renli mining area and peripheral soil samples in Pingjiang County, Hunan Province
|

| 分析方法 | 分析元素 | 分析元素种类 | | ICP-MS | Li、Be、Sc、Ti、V、Mn、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Ga、Rb、Y、Nb、Ta、Mo、Cd、Sb、Cs、Ba、La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Sm、Eu、Gd、Tb、Dy、Ho、Er、Tm、Yb、Lu、W、Tl、Pb、Bi、Th、U、Sr、In、Zr、Hf、Fe、Au、As | 48 |
|
Analysis elements of Renli mining area and peripheral ground gas samples in Pingjiang County, Hunan Province
|

| 元素 | 检出限/(μg·L-1) | 空白样/(μg·L-1) | 实测含量范围/(μg·L-1) | 平均值/(μg·L-1) | 平均值/空白样 | | Be | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.019~4.700 | 0.3114 | 103.8 | | Li | 0.100 | 0.175 | 1.700~38.60 | 4.504 | 25.7 | | Nb | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.010~0.096 | 0.028 | 14.0 | | Ta | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002~0.049 | 0.007 | 3.5 |
|
Main element analysis results of Renli mining area and peripheral geogas samples in Pingjiang County, Hunan Province
|
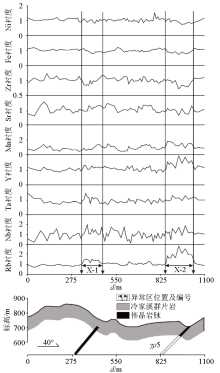
|
Comprehensive profile of soil X-ray fluorescence multi-element measurement of 44 line in Renli mining area
|
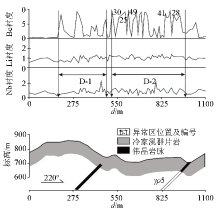
|
Comprehensive profile of geogas survey of 44 line in Renli mining area
|
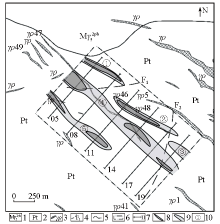
|
Measurement area (Nb+Ta+Rb)/Zr normalized accumulation ratio plane isometric map in Huangboshan area
1—medium-grained porphyry-like biotite monzonitic granite; 2—Lengjiaxi schist; 3—pegmatite vein and number; 4—speculative faults; 5—geological boundaries; 6—X-ray fluorescence measurement area; 7—survey line and number; 8—the abnormal area defined by the mean value plus 5 times standard deviation; 9—the abnormal area defined by the mean value plus 2 times standard deviation;10—X-ray fluorescence anomaly number
|

|
Comprehensive profile of geogas survey of line 11 outside the Renli mining area
|
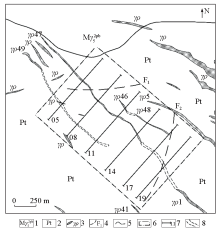
|
Interpretation of the inference of predicted veins in Huangboshan area
1—medium-grained porphyry-like biotite monzonitic granite; 2—Lengjiaxi schist; 3—pegmatite dikes and number; 4—speculative faults; 5—geological boundaries; 6—X-ray fluorescence measurement area; 7—survey line and number; 8—speculative veins
|
| [11] |
Liu Y J, Cao L M. Introduction to elemental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: The Geological Publishing House,1987.
|
| [12] |
周四春, 刘晓辉, 胡波, 等. 南岭重点矿集区深部成矿信息的地气、放射性探测技术与实验[M]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社, 2018.
|
| [12] |
Zhou S C, Liu X H, Hu B, et al. Geogas and radioactivity detection technology and experiment of deep mineralization information in key mineral agglomeration area of Nanling[M]. Beijing: China Atomic Energy Press, 2018.
|
| [1] |
刘翔, 周芳春, 黄志飚, 等. 湖南平江县仁里超大型伟晶岩型铌钽多金属矿床的发现及其意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(2):235-243.
|
| [1] |
Liu X, Zhou F C, Huang Z B, et al. Discovery of Renli superlarge pegmatite-type Nb-Ta polymetallic deposit in Pingjiang,Hunan Province and its significances[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2018, 42(2):235-243.
|
| [2] |
文春华, 罗小亚, 陈剑锋, 等. 湘东北幕阜山地区燕山期岩浆演化与稀有金属成矿的关系[J]. 中国地质调查, 2019, 6(6):19-28.
|
| [2] |
Wen C H, Luo X Y, Chen J F, et al. Relationship between Yanshanian magmatic activity and rare metal mineralization in Mufushan area of Northeast Hunan[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2019, 6(6):19-28.
|
| [3] |
陈剑锋, 文春华, 黄建中, 等. 幕阜山南缘仁里稀有金属矿区7号伟晶岩脉、辉石闪长岩脉特征及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2022, 46(5):951-967.
|
| [3] |
Chen J F, Wen C H, Huang J Z, et al. Characteristics of No.7 pegmatite vein and pyroxene diorite in Renli rare metal deposit,south margin of Mufushan batholiths and its geological implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2022, 46(5):951-967.
|
| [4] |
李鹏, 李建康, 裴荣富, 等. 幕阜山复式花岗岩体多期次演化与白垩纪稀有金属成矿高峰:年代学依据[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(10):1684-1696.
|
| [4] |
Li P, Li J K, Pei R F, et al. Multistage magmatic evolution and cretaceous peak metallogenic epochs of Mufushan composite granite mass:constrains from geochronological evidence[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(10):1684-1696.
|
| [5] |
李鹏, 李建康, 张立平, 等. 幕阜山西南缘黄柏山稀有金属伟晶岩密集区的发现及意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(5):1069-1076.
|
| [5] |
Li P, Li J K, Zhang L P, et al. Discovery and significance of Huangbaishan rare metal pegmatite concentration area on southern margin of Mufushan[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(5):1069-1076.
|
| [6] |
曹创华, 张利军, 刘钧, 等. 华南植被覆盖稀有金属矿集区快速探测评价体系的建立与应用[J]. 矿床地质, 2022, 41(2):225-240.
|
| [6] |
Cao C H, Zhang L J, Liu J, et al. Establishment and application of rapid detection and evaluation system for rare metal ore clusters in vegetation coverage area of South China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2022, 41(2):225-240.
|
| [7] |
黄建中, 陈剑锋, 文春华, 等. 湘东北地区伟晶岩型锂矿成矿模型及找矿潜力分析[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 43(4):527-541.
|
| [7] |
Huang J Z, Chen J F, Wen C H, et al. The metallogenic model and prospecting potentiality of the pegmatite type Li deposit in northwestern Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 43(4):527-541.
|
| [8] |
张龙. 伟晶岩稀有金属矿综合地气异常特征及勘查技术研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2021.
|
| [8] |
Zhang L. Study on comprehensive geogas anomaly characteristics and exploration technology of pegmatite rare metal ore[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2021.
|
| [9] |
周四春, 刘晓辉, 曾国强, 等. X射线荧光勘查技术及其在地质找矿中的应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020.
|
| [9] |
Zhou S C, Liu X H, Zeng G Q, et al. X-ray fluorescence exploration technology and its application in geological prospecting[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020.
|
| [10] |
刘晓辉, 周四春, 童纯菡, 等. 提高地气探测灵敏度的方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(6):1064-1067.
|
| [10] |
Liu X H, Zhou S C, Tong C H, et al. The method and technique for improving the detection sensitivity of dynamic geogas survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(6):1064-1067.
|
| [11] |
刘英俊, 曹励明. 元素地球化学导论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社,1987.
|
| [1] |
WANG Ya-Dong, ZHOU Si-Chun, LIU Xiao-Hui, HU Bo, WANG Guang-Xi, XU Yun-Fu, CAO Hong-Liang, FAN Xin-Sheng, HAN Ruo-Pu. X-ray fluorescence anomalies in the Chakabeishan exploration area for lithium-beryllium deposits, Qinghai Province:Characteristics and implications for prospecting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1635-1642. |
| [2] |
Liu Xiao-Hui, Zhou Si-Chun, Wang Ya-Dong, Han Ruo-Pu, Fan Xin-Sheng. Application of geogas prospecting in the prediction of deep ore-bearing properties in the Chakabeishan exploration area for lithium-beryllium deposits[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1643-1648. |
|
|
|
|

