|
|
|
| Application of geogas prospecting in the prediction of deep ore-bearing properties in the Chakabeishan exploration area for lithium-beryllium deposits |
Liu Xiao-Hui1( ), Zhou Si-Chun1, Wang Ya-Dong2, Han Ruo-Pu1, Fan Xin-Sheng1 ), Zhou Si-Chun1, Wang Ya-Dong2, Han Ruo-Pu1, Fan Xin-Sheng1 |
1. Applied Nuclear Technology in Geosciences Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China
2. Qinghai Geological Survey Institute, Xining 810012, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To provide deep prospecting support for the exploration of lithium-beryllium deposits in the Chakabeishan area, two geogas prospecting profiles each with a length of 800 m were laid out in the exploration area, obtaining the content information of over 30 elements such as Li, Be, Cs, Nb, Rb, Ti, and rare earth elements in the geogas samples from 162 measuring points. Combined with the existing exploration results, the characteristics of local geogas anomalies were investigated in this study. The results are as follows: (1) Significant geogas anomalies of various elements can be detected above the concealed sections of pegmatite veins and beryllium ore bodies; (2) The combined anomalies of elements Li, Rb, Th, Cs, Pb, Nb, Ti, La, and Ce in geogas can indicate pegmatite veins, while the combined anomalies of elements Be, Rb, Nb, Cs, Pb, Ti, and Cu can directly indicate concealed beryllium ore bodies; (3) Be anomalies can indicate beryllium ore bodies within a burial depth of 480 m. This study demonstrates that geogas prospecting can be used to predict the ore-bearing properties of concealed pegmatite veins in the Quaternary coverage area.
|
|
Received: 05 July 2023
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
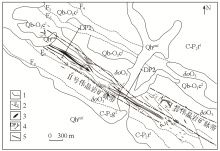
|
Schematic diagram of geogas survey profile layout in Chakabeishan lithium beryllium deposit exploration area
1—measured geological boundaries;2—measured faults;3—pegmatite vein;4—geogas line and number;5—pegmatite vein belt;Qb-O3c—Chakabeishan schist formation;C-P2g—Permo-Carboniferous Guokeshan formation;δoO3—Ordovician quartz diorite;C-P2t—Permo-Carboniferous Tu'ergendaban formation;Qhpal—Holocene alluvial deposits
|

| 元素 | 含量范围/
(μg·L-1) | 平均值/
(μg·L-1) | 空白/
(μg·L-1) | 标准差/
(μg·L-1) | 异常下限/
(μg·L-1) | DP1测线
异常点数量 | DP2测线
异常点数量 | 分析方法检
出限/(μg·L-1) | | Be | 0.001~0.111 | 0.013 | <0.002 | 0.009 | 0.031 | 11 | 8 | 0.002 | | Li | 1.27~3.96 | 1.65 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 2.01 | 5 | 2 | 0.1 | | Nb | 0.001~0.050 | 0.011 | <0.002 | 0.005 | 0.021 | 10 | 8 | 0.002 | | Rb | 0.220~2.670 | 0.522 | 0.036 | 0.257 | 1.040 | 13 | 3 | 0.01 | | Cs | 0.010~0.197 | 0.036 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 0.074 | 13 | 3 | 0.002 | | Th | 0~0.319 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.036 | 7 | 6 | 0.002 | | La | 0.020~3.550 | 0.110 | 0.003 | 0.080 | 0.270 | 11 | 4 | 0.002 | | Ce | 0.030~4.630 | 0.220 | 0.007 | 0.160 | 0.540 | 7 | 5 | 0.002 | | W | 0~0.329 | 0.020 | 0.012 | 0.022 | 0.064 | 8 | 9 | 0.010 | | Ti | 1.46~39.40 | 4.58 | 0.13 | 2.56 | 9.70 | 14 | 5 | 0.10 | | Pb | 0.56~29.70 | 2.65 | 0.10 | 1.91 | 6.47 | 7 | 7 | 0.01 | | Cu | 3.12~397.00 | 11.5 | 0.16 | 6.02 | 23.50 | 4 | 11 | 0.02 |
|
Geogas survey results (some elements) statistics
|
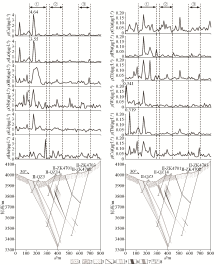
|
DP1 line geogas survey comprehensive profile
1—Quaternary residual-slope sediment; 2—quartzdiorite; 3—two-mica quartz schist; 4—fault; 5—pegmatite vein; 6—beryllium ore body; 7—beryllium mineralized body; 8—drilling and its number
|
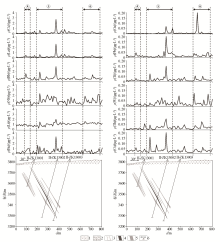
|
DP2 line geogas survey comprehensive profile
1—Quaternary residual-slope sediment; 2—two-mica quartz schist; 3—pegmatite vein; 4—beryllium ore body; 5—beryllium mineralized body; 6—drilling and its number
|
| [1] |
王登红, 王成辉, 孙艳, 等. 我国锂铍钽矿床调查研究进展及相关问题简述[J]. 中国地质调查, 2017, 4(5):1-8.
|
| [1] |
Wang D H, Wang C H, Sun Y, et al. New progresses and discussion on the survey and research of Li,Be,Ta ore deposits in China[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2017, 4(5):1-8.
|
| [2] |
王登红. 关键矿产的研究意义、矿种厘定、资源属性、找矿进展、 存在问题及主攻方向[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(6):1189-1209.
|
| [2] |
Wang D H. Study on critical mineral resources:Significance of research,determination of types,attributes of resources,progress of prospecting,problems of utilization,and direction of exploitation[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2019, 93(6):1189-1209.
|
| [3] |
毛景文, 袁顺达, 谢桂青, 等. 21世纪以来中国关键金属矿产找矿勘查与研究新进展[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(5):935-969.
|
| [3] |
Mao J W, Yuan S D, Xie G Q, et al. New advances on metallogenic studies and exploration on critical minerals of China in 21st century[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(5):935-969.
|
| [4] |
李建武, 李天骄, 贾宏翔, 等. 中国战略性关键矿产目录厘定[J]. 地球学报, 2023, 44(2):261-270.
|
| [4] |
Li J W, Li T J, Jia H X, et al. Determination of China’s strategic and critical minerals list[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2023, 44(2):261-270.
|
| [5] |
苏慧敏, 车玉滢, 尹燕梁, 等. 战略性关键矿产勘查现状与对策:以青海省为例[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(4):1543-1550.
|
| [5] |
Su H M, Che Y Y, Yin Y L, et al. Present situation and research direction of strategic critical mineral exploration:Taking Qinghai province as an example[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(4):1543-1550.
|
| [6] |
周四春, 刘晓辉, 胡波. 地气场信息的地质学意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(6):1044-1049.
|
| [6] |
Zhou S C, Liu X H, Hu B. Geological significance of geogas field information[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(6):1044-1049.
|
| [7] |
周四春, 刘晓辉, 胡波, 等. 滇西某铅锌矿整装勘查区地气、X荧光测量找矿应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(6):1040-1043.
|
| [7] |
Zhou S C, Liu X H, Hu B, et al. The application of geogas and X-ray fluorescence survey to ore prospecring in an integrated exploration area of a certain lead-zine deposit in western Yunnan provinc[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(6):1040-1043.
|
| [8] |
周四春, 刘晓辉, 童纯菡, 等. 地气测量技术及在隐伏矿找矿中的应用研究[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(4):736-754.
|
| [8] |
Zhou S C, Liu X H, Tong C H, et al. Application research of geogas survey in prospecting concealed ore[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2014, 88(4):736-754.
|
| [9] |
周四春, 刘晓辉, 胡波, 等. 南岭重点矿集区深部成矿信息的地气、放射性探测技术与实验[M]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社, 2018.
|
| [9] |
Zhou S C, Liu X H, Hu B, et al. Geogas and radioactive detection technology and experiment of deep mineralization information in Nanling key ore concentration area[M]. Beijing: China Atomic Energy Press, 2018.
|
| [10] |
王勇, 王东升, 吴国东, 等. 地气测量方法在粤北长排花岗岩型铀矿勘查中的应用[J]. 铀矿地质, 2020, 36(4):302-310.
|
| [10] |
Wang Y, Wang D S, Wu G D, et al. Application of geogas method in the exploration of granite-type uranium deposit in Changpai area of northern Guangdong[J]. Uranium Geology, 2020, 36(4):302-310.
|
| [11] |
杨吉成, 周四春, 刘晓辉, 等. 卡鲁安伟晶岩锂矿的地气场特征及找矿意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2019, 38(4):570-578.
|
| [11] |
Yang J C, Zhou S C, Liu X H, et al. Geogas field characteristics of the Kalu’an pegmatite lithium deposit and its prospecting significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2019, 38(4):570-578.
|
| [12] |
刘晓辉, 周四春, 童纯菡, 等. 提高地气探测灵敏度的方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(6):1064-1067.
|
| [12] |
Liu X H, Zhou S C, Tong C H, et al. The method and technique for improving the detection sensitivity of dynamic geogas survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(6):1064-1067.
|
| [13] |
李善平, 潘彤, 严兴鹏, 等. 柴北缘东段茶卡北山伟晶岩稀土元素地球化学特征及物源分析[J]. 稀土, 2022, 43(4):88-99.
|
| [13] |
Li S P, Pan T, Yan X P, et al. REE geochemical characteristics and provenance analysis of Chaka north mountain pegmatite in the eastern part of the northern margin of Qaidam basin,Qinghai province[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2022, 43(4):88-99.
|
| [14] |
王建国, 张世珍, 邢佳, 等. 乌兰茶卡北山含矿伟晶岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2022, 30(6):809-821.
|
| [14] |
Wang J G, Zhang S Z, Xing J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of ore-bearing pegmatites in the Wulan Chakabeishan area[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2022, 30(6):809-821.
|
| [1] |
GAN Xue-Jun, ZHOU Si-Chun, LIU Xiao-Hui, WANG Deng-Hong, WEN Chun-Hua. The application of an integrated geogas prospecting for exploring rare metal deposits in the periphery of the Renli mining area, southern Hunan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1649-1656. |
| [2] |
HAN Ruo-Pu, ZHOU Si-Chun, WANG Deng-Hong, LIU Xiao-Hui, CHEN Shou-Bo, WU Jian-Xin. Comprehensive geogas anomalies in the Hongling area of Hami, Xinjiang: Characteristics and implications for prospecting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1657-1664. |
|
|
|
|

