|
|
|
| Technology for suppressing "black triangle" high-energy noise in vibroseis seismic data acquisition in a desert area |
SU Yun1( ), YOU Hong-Wen1, LI Ling-Xi2, MENG Fan-Bing1, LI Min-Jie1, TANG Juan1, XIE Jin-Li1 ), YOU Hong-Wen1, LI Ling-Xi2, MENG Fan-Bing1, LI Min-Jie1, TANG Juan1, XIE Jin-Li1 |
1. Geophysical Research Institute of Geophysical Research Institute,Zhongyuan Oilfield Company,SINPEC,Zhengzhou 450000,China
2. Zhongyuan Oilfield Company,SINPEC,Puyang 457001,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The special topographic and geomorphic conditions in the desert exploration area of the Guaizihu sag in the Yin'e Basin produce adverse effects on the excitation and reception of seismic data.The surface of the area is covered by hugely thick loose sand,with the thickness of the sand dunes varying in the range of 50~100 m.In the process of vibroseis data acquisition in this area,"black triangle" noise is formed in the near-trace scope due to the dual effects of the mechanical characteristics of the vibroseis and the near-surface structure,resulting in a low signal-to-noise ratio of seismic records.Since the "black triangle" noise features high energy,wide frequency range,wide distribution,and great morphological difference,it is difficult to make accurate statistics of its amplitude (intensity) in a single arrangement of the common shot domain and the common receiver domain,thus resulting in too much residual noise after the suppression of the "black triangle" noise.Given this,this paper proposes a method,in which data rearrangement is firstly conducted based on the shot-offset domain and then denoising is performed.As verified by the application of actual vibroseis data of the Guaizihu area in the Yin'e Basin,this method can effectively protect the near-trace reflection signals(especially the deep weak reflection information) while effectively suppressing the "black triangle" noise and it is effective in improving the signal-to-noise ratio of seismic data.
|
|
Received: 14 October 2020
Published: 28 June 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
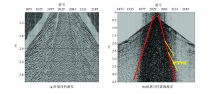
|
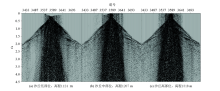
The original single shot records of Guaizihu sag
|
|
The original one shot records of Guaizihu Sag
|
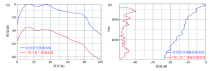
|
Comparison of spectrum curve(a) and amplitude attenuation curve(b) of “black triangle” noise and effective signal
|
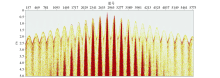
|
Frequency division scanning results of vibroseis “black triangle”
|
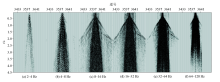
|
Comparison of “black triangle”noise in the different parts of sand dune
|
|
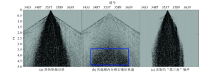
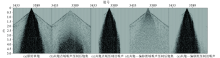
The test of “black triangle” noise suppression in common shot domain
|
|
Seismic trace arrangement of common shot area(a) and common shot offset domain(b)
|
|
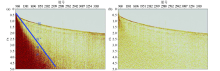
Original record(a) and denoised record(b) in common shot-offset domain
|
|
Comparison of noise attenuation methods of vibroseis “black triangle”
|
|
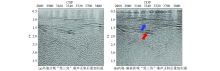
Comparison of stack profile after “black triangle” noise suppression in different domain
|
|
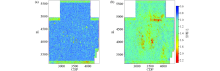
Comparison of signal to noise ratio of Cretaceous layer before(a) and after(b) of “black triangle” noise suppression
|
|
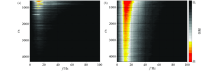
Comparison of statistical time-frequency spectrum before(a) and after(b) of “black triangle” noise suppression
|
| [1] |
王学军, 于宝利, 赵小辉, 等. 油气勘探中“两宽一高”技术问题的探讨与应用[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2015, 20(5):41-53.
|
| [1] |
Wang X J, Yu B L, Zhao X H, et al. Development and application of “two wide and one high” technical problems in oil and gas exploration[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2015, 20(5):41-53.
|
| [2] |
汪恩华, 赵邦六, 王喜双, 等. 中国石油可控震源高效地震采集技术应用与展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2013, 18(5):24-34.
|
| [2] |
Wang E H, Zhao B L, Wang X S, et al. Application and outlook of vibroseis acquisition techniques with high efficiency of CNPC[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2013, 18(5):24-34.
|
| [3] |
王西文, 赵邦六, 吕焕通, 等. 地震资料采集方式对地震处理的影响研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(3):810-852.
|
| [3] |
Wang X W, Zhao B L, Lyu H T, et al. Study on the influence of seismic data acquisition methods on earthquake treatment[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(3):810-852.
|
| [4] |
叶秋焱, 王彦仓, 张登毫, 等. 宽频激发技术在苏里格地区采集中的应用[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2010, 15(2):74-77.
|
| [4] |
Ye Q Y, Wang Y C, Zhang D H, et al. Application of broadband excitation to seismic data acquisition in Sulige area[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2010, 15(2):74-77.
|
| [5] |
张军华, 朱焕, 郑旭刚, 等. 宽方位角地震勘探技术评述[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2007, 42(5):603-609.
|
| [5] |
Zhang J H, Zhu H, Zheng X G, et al. Summary of wild azimuth seismic exploration technique[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 42(5):603-609.
|
| [6] |
王兆磊, 公亭, 李隆梅, 等. 高密度宽方位地震资料处理技术研究进展[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2015, 37(4):465-471.
|
| [6] |
Wang Z L, Gong T, Li L M, et al. Research progress in high-density and wide-azimuth seismic data processing technology[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 37(4):465-471.
|
| [7] |
王汉闯, 陶春辉, 陈生昌, 等. 基于稀疏约束的地震数据高效采集方法理论研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(11):4246-4265.
|
| [7] |
Wang H C, Tao C H, Chen S C, et al. Study on highly efficient seismic data acquisition method and theory based on sparsity constraint[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(11):4246-4265.
|
| [8] |
陈祖斌, 腾吉文, 林君, 等. BSR-2宽频带地震记录仪的研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006, 49(5):1475-1481.
|
| [8] |
Chen Z B, Teng J W, Lin J, et al. Design of BSR-2 broad band seismic recorder[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006, 49(5):1475-1481.

|
| [9] |
佟训乾, 林君, 姜弢, 等. 陆地可控震源发展综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2012, 27(5):1912-1921.
|
| [9] |
Tong X Q, Lin J, Jiang T, et al. Summary of development of land vibrator[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012, 27(5):1912-1921.
|
| [10] |
周锦钟, 张金海, 牛全兵, 等. 柴达木盆地顶山地区低频可控震源“两宽一高”地震资料处理关键技术应用研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(2):313-320.
|
| [10] |
Zhou J Z, Zhang J H, Niu Q B, et al. The key technique application research on low frequency vibrator "two-wide and one-high" seismic data processing in Jiandingshan area of Qaidam Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(2):313-320.
|
| [11] |
丁伟, 胡立新, 何京国, 等. 可控震源高效地震采集技术研究及应用[J]. 石油物探, 2014, 53(3):338-343.
|
| [11] |
Ding W, Hu L X, He J G, et al. The research on vibrator high efficient simulation technology and its application[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2014, 53(3):338-343.
|
| [12] |
瞿长青, 段伟伟. 沙漠区可控震源“黑三角”强能量干扰形成原因研究[C]// 中国石油学会2019年物探技术研讨会论文集, 2019.
|
| [12] |
Qu C Q, Duan W W. Research on the cause of strong enengy interference of vibroseis “black triangle” in desert area[C]// Proceedings of annual meeting of geophysical of SPG, 2019.
|
| [13] |
曲英铭, 李金丽, 李振春, 等. 可控震源相关数据谐波干扰联合压制方法[J]. 石油物探, 2018, 57(2):237-247.
|
| [13] |
Qu Y M, Li J L, Li Z C, et al. Joint suppression of two types of vibroseis noise on correlated data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018, 57(2):237-247.
|
| [14] |
夏洪瑞, 葛川庆, 彭涛. 小波时空变阈值去噪方法在可控震源资料处理中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2010, 45(1):23-57.
|
| [14] |
Xian H R, Ge C Q, Peng T. Application of wavelet time-space-varying threshold denoising method in vibroseis seismic data processing[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 45(1):23-57.
|
| [15] |
刘喜恒, 张红文, 崔永谦, 等. 可控震源三角区噪音压制方法的研究应用[C]// 2019年油气地球物理学术年会论文集, 2019.
|
| [15] |
Liu X H, Zhang H W, Cui Y Q, et al. Research and application of noise suppression method in vibroseis triangle area[C]// Proceedings of annual meeting of Petroleum Geophysics, 2019.
|
| [16] |
张宏, 刘兵, 刘炎坤, 等. 辽河坳陷低频可控震源地震采集技术应用[J]. 长大大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 13(31):41-45.
|
| [16] |
Zhang H, Liu B, Liu Y K, et al. The application of seismic acquisition technology based on low-frequency vibrator in Liaohe Depression[J]. Journal of Yangtze University:Natural Science Edition, 2016, 13(31):41-45.
|
| [17] |
秦婕, 李辉峰, 王宏伟, 等. 叠前去噪技术在鄂尔多斯黄土塬区地震资料的应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2015, 37(5):644-650.
|
| [17] |
Qin J, Li H F, Wang H W, et al. The application of pre-stack noise attenuation technology for seismic data of Soil Yuan area in Ordos basin[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 37(5):644-650.
|
| [18] |
尹思, 王传武, 董永苍, 等. 利用振幅去噪技术提高地震资料分辨率——以柴达木盆地尖顶山地区为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018, 53(S2):7-12.
|
| [18] |
Yin S, Wang C W, Dong Y C, et al. Preserved-amplitude denoising for seismic resolution improvement:An example of Jiandingshan Area in Qaidam Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 53(S2):7-12.
|
| [1] |
XIE Xing-Long, MA Xue-Mei, LONG Hui, LI Qiu-Chen, GUO Shu-Jun, CHENG Zheng-Pu. The parameter selection of middle and shallow seismic exploration based on vibrator[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4): 1004-1013. |
| [2] |
Tong CHAI, Wen-Gong HAN, Ming-Bo BI. A vibrator nonlinear sweeping signal design method and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(4): 753-758. |
|
|
|
|

