|
|
|
| Impacts of human activities on the land quality of Jianghan Plain: A case study of Honghu City |
ZHENG Xiong-Wei1,2( ), TAO Meng-Jun3( ), TAO Meng-Jun3( ), ZHANG Zhi-Yi4, CHA Ya5, WANG Ya-Feng6, ZHANG Xiang-Rong7 ), ZHANG Zhi-Yi4, CHA Ya5, WANG Ya-Feng6, ZHANG Xiang-Rong7 |
1. School of Geosciences, Yangtze University, Wuhan 430100, China
2. Geophysical Exploration Brigade, Hubei Geological Bureau, Wuhan 430056,China
3. Information and Communication College of National University of Defense Technology,Wuhan 430030,China
4. School of Economics and management of Hubei University of Technology,Wuhan 430068,China
5. Jiangsu East China 814 Geophysical Exploration Co.,Ltd.,Nanjing 210000,China
6. Fifth Geological Brigade of Hubei Geological Bureaun,Ezhou 436000,China
7. Hubei Geological Research Laboratory,Wuhan 430034,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to further understand different input ways of heavy metal elements into the agroecosystem and resultant soil pollution and to promote the sustainable development of agriculture in the Jianghan Plain. To this end, data were collected from the geochemical assessment project on the land quality of Honghu City from 2014 to 2019 and were studied as a whole. Then, this study conducted geochemical analyses of heavy metal elements such as Cr and Hg input via three ways, namely atmospheric dry and wet subsidence, irrigation water, and chemical fertilizers, and calculated the input amount of the heavy metal elements via each way. Based on these, this study explored the impacts of the three ways on land quality. The results are as follows:①The land quality in Honghu City is slightly affected by human activities; ②The total input flux of different elements differs greatly with the input ways, reflecting the differences in the heavy metal elements input via local agricultural activities; ③The annual input flux of heavy metal elements via irrigation water is relatively high, and irrigation water contributes the most to the heavy metal elements (except for Zn, Cr, and Pb) input to soil.
|
|
Received: 20 December 2021
Published: 03 January 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
TAO Meng-Jun
E-mail: 493928635@qq.com;113851719@qq.com
|
|
|
|

| 地层 | 代号 | 岩性特征 | | 系 | 统 | 组 | | 第四系 | 全新统 | | Qhal | 冲积层:黄褐色黏土、亚砂土、砂砾石层 | | Qhl | 湖积层:黑—灰黑色淤泥、黏土 | | Qhlal | 湖冲积层:灰黄色黏土、亚黏土 | | Qhf | 沼泽沉积层:青灰色淤泥质亚黏土、亚砂土、淤泥 | | 侏罗系 | 下统 | 桐竹园组 | J1t | 以黄、黄绿、灰黄色砂质页岩、粉砂岩及长石石英细砂岩为主,夹炭质页岩及
薄煤层或煤线 | | 三叠—侏罗系 | | 王龙滩组 | T3J1w | 厚层长石石英砂岩、岩屑砂岩夹粉砂岩、泥岩、煤层和炭质页岩 |
|
Brief table of stratigraphic unit division of the study area
|
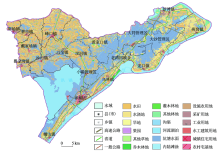
|
Current situation of land use of the study area
|
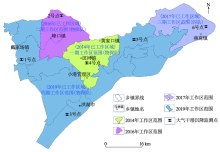
|
The work scope of 2014~2019 and the sample localities of atmospheric dry and wet deposition
|

| 样品类型 | 计量单位 | 2014年 | 2016年 | 2017年 | 2019年 | 累计完成工作量/件 | | 灌溉水样 | 件 | 20 | 20 | 25 | 27 | 92 | | 大气降尘监测样 | 件 | 24 | 24 | 14 | 24 | 86 | | 肥料样 | 件 | 31 | 17 | 20 | 27 | 95 |
|
Sample type workload statistics of the study area
|

| 元素 | 样品数 | 平均值/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 变异系数 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 中位值/10-6 | | Se | 84 | 3.886 | 6.101 | 1.570 | 0.03116 | 25.810 | 0.3381 | | As | 84 | 9.662 | 15.289 | 1.582 | 0.07188 | 64.010 | 2.3249 | | Sb | 24 | 0.812 | 0.454 | 0.559 | 0.10964 | 2.099 | 0.6907 | | Hg | 84 | 0.097 | 0.134 | 1.383 | 0.0026 | 0.476 | 0.0137 | | Cr | 84 | 50.190 | 82.275 | 1.639 | 3.1040 | 473.040 | 12.4900 | | Ni | 84 | 24.522 | 41.085 | 1.675 | 0.6489 | 224.548 | 4.6900 | | Cu | 84 | 60.275 | 97.190 | 1.612 | 1.922 | 426.960 | 9.6400 | | Zn | 84 | 413.956 | 704.202 | 1.701 | 4.78 | 4219.160 | 74.3200 | | Cd | 84 | 3.430 | 5.915 | 1.724 | 0.0426 | 34.000 | 0.4837 | | Pb | 84 | 111.835 | 171.899 | 1.537 | 3.092 | 986.120 | 27.6600 | | Fe | 24 | 6383.300 | 5595.869 | 0.877 | 446.147 | 20345.500 | 4134.1500 | | Al | 24 | 1270.960 | 1758.884 | 1.384 | 0.0000043 | 6621.540 | 0.0003 | | Ca | 24 | 1058.620 | 677.224 | 0.640 | 328.762 | 3502.030 | 937.6860 | | Mg | 24 | 603.060 | 495.509 | 0.822 | 73.9278 | 2049.600 | 489.3350 | | K | 24 | 1057.820 | 888.147 | 0.840 | 94.6428 | 3890.320 | 872.5400 | | Mn | 24 | 28.880 | 29.608 | 1.025 | 0.01 | 102.700 | 22.6500 | | P | 24 | 192.784 | 116.188 | 0.603 | 19.95 | 525.900 | 179.0500 | | Co | 24 | 0.901 | 0.742 | 0.823 | 0.1309 | 3.501 | 0.7321 | | Mo | 24 | 0.240 | 0.152 | 0.634 | 0.0309 | 0.660 | 0.2042 |
|
Characteristic value of geochemical index of atmospheric dust fall of the study area
|

| 指标 | 样品数 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位值 | | As | 84 | 0.629 | 0.46 | 0.7 | 0.075 | 1.608 | 0.567 | | Hg | 84 | 0.018 | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.013 | 0.060 | 0.015 | | Se | 84 | 0.761 | 0.63 | 0.8 | 0.075 | 2.882 | 0.625 | | Cu | 84 | 1.535 | 0.97 | 0.6 | 0.100 | 4.096 | 1.417 | | Zn | 84 | 18.603 | 18.42 | 1.0 | 0.100 | 72.960 | 11.990 | | Mo | 72 | 0.171 | 0.17 | 1.0 | 0.050 | 0.934 | 0.127 | | Cd | 84 | 0.154 | 0.14 | 0.9 | 0.025 | 0.661 | 0.108 | | Pb | 84 | 0.467 | 0.62 | 1.3 | 0.050 | 4.185 | 0.311 | | Ba | 72 | 0.031 | 0.03 | 1.1 | 0.001 | 0.075 | 0.010 | | Fe | 84 | 0.043 | 0.07 | 1.6 | 0.005 | 0.396 | 0.017 | | K | 72 | 0.246 | 0.20 | 0.8 | 0.001 | 0.759 | 0.177 | | Mn | 84 | 0.012 | 0.02 | 1.4 | 0.002 | 0.090 | 0.004 | | P | 84 | 0.016 | 0.02 | 1.1 | 0.003 | 0.070 | 0.010 | | 凯氏N | 84 | 2.199 | 1.16 | 0.5 | 0.438 | 5.210 | 1.930 | | Cr6+ | 84 | 0.025 | 0.17 | 7.0 | 0.001 | 1.400 | 0.004 | | 溶解性总固体 | 84 | 35.738 | 22.24 | 0.6 | 4.000 | 126.000 | 34.000 | | F | 84 | 0.098 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0.025 | 0.248 | 0.098 | | Cl- | 84 | 1.904 | 3.04 | 1.6 | 0.143 | 17.860 | 0.844 | | | 84 | 1.570 | 1.89 | 1.2 | 0.075 | 6.930 | 0.540 | | | 84 | 5.365 | 2.84 | 0.5 | 0.459 | 14.240 | 4.789 | | 总硬度 | 84 | 12.246 | 9.71 | 0.8 | 1.025 | 44.130 | 8.980 | | 高锰酸钾指数 | 84 | 6.588 | 4.08 | 0.6 | 1.540 | 18.200 | 5.480 | | B | 12 | 7.472 | 3.27 | 0.4 | 3.962 | 15.210 | 6.751 | | Sr | 12 | 0.020 | 0.00 | 0.1 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.020 | | V | 12 | 0.020 | 0.00 | 0.0 | 0.020 | 0.021 | 0.020 | | 硫化物 | 12 | 0.062 | 0.02 | 0.4 | 0.030 | 0.090 | 0.060 | | pH | 84 | 6.592 | 0.51 | 0.1 | 5.510 | 8.600 | 6.610 |
|
Characteristic values of geochemical indexes of atmospheric precipitation of the study area
|

| 元素 | 湿沉降元素含量/(μg·L-1) | 干沉降元素含量/10-6 | | 1号点 | 2号点 | 3号点 | 4号点 | 5号点 | 6号点 | 1号点 | 2号点 | 3号点 | 4号点 | 5号点 | 6号点 | | As | 0.77 | 11.65 | 0.7 | 2.35 | 2.18 | 0.58 | 1.32 | 21.92 | 9.07 | 8.26 | 12.38 | 2.39 | | Hg | 0.02 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.92 | 8.04 | 1.03 | 7.05 | 5.03 | 0.49 | | Cu | 1.12 | 4.13 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 7.69 | 24.36 | 1.92 | 15.36 | 19.87 | 2.46 | | Zn | 246.8 | 949.4 | 850.5 | 68 | 899 | 255 | 1032.35 | 8110.18 | 4008.78 | 386.39 | 5645.89 | 5312.12 | | Cd | 0.15 | 3.24 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.87 | 0.33 | 208.47 | 3.04 | 90.36 | 10.89 | 2.56 | | Pb | 0.34 | 8.38 | 3.15 | 1.36 | 4.59 | 0.39 | 27.96 | 106.97 | 13.07 | 2.36 | 45.36 | 36.98 | | Cr | 0.28 | 5.57 | 1.36 | 1.34 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 11.46 | 117.2 | 3.1 | 5.65 | 96.36 | 45.37 | | Ni | 8.1 | 212.3 | 92.1 | 1.5 | 6.6 | 3.4 | 25.19 | 827.35 | 354.65 | 8.62 | 45.23 | 78.35 |
|
Content of heavy metals in dry and wet atmospheric deposition of the study area
|

| 年通量 | Se | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Pb | Zn | | 湿沉降年通量 | 4.157 | 4.877 | 0.537 | 17.171 | 13.294 | 0.106 | 14.513 | 106.789 | | 干沉降年通量 | 0.801 | 5.166 | 0.793 | 19.909 | 16.766 | 0.049 | 37.534 | 138.381 | | 年干湿沉降总通量 | 4.959 | 10.043 | 1.330 | 37.080 | 30.060 | 0.154 | 52.047 | 245.170 |
|
Annual flux of atmospheric dry and wet deposition of the study areakg·km-2·q-1
|
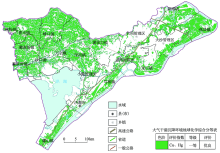
|
Comprehensive grade map of annual flux of atmospheric dry and wet deposition
|

| 参数 | As | Hg | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Cr6+ | pH | | 最大值 | 17.99 | 0.208 | 3.17 | 45.73 | 0.058 | 2.25 | 4.2 | 8.49 | | 最小值 | 2.019 | <0.015 | 0.381 | 0.388 | <0.025 | 0.087 | 1.7 | 6.96 | | 平均值 | 5.354 | 0.066 | 1.2 | 3.83 | 0.037 | 0.63 | 3 | 7.43 | 农田灌溉水标准
(GB 5084—2005) | 50 | 1 | 500 | 2000 | 10 | 200 | 100 | 5.5~8.5 | | 年均输入通量 | 28.57 | 0.35 | 6.40 | 20.44 | 0.20 | 3.36 | 16.01 | |
|
Heavy metal content and annual average input flux in irrigation water of the study area
|

| 肥料种类 | 参数 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 平均值 | 0.2194 | 0.0257 | 3.116 | 0.1246 | 0.001 | 0.3365 | 0.462 | 1.46 | | 复合肥 | 最大值 | 0.4581 | 0.1 | 3.895 | 0.25 | 0.003 | 1.2405 | 0.908 | 4.24 | | 最小值 | 0.0594 | 0.02 | 2.277 | 0.1 | 0.0005 | 0.1165 | 0.183 | 0.1 | | 平均值 | 7.1178 | 0.1372 | 14.36 | 2.0352 | 0.021 | 3.3277 | 2.199 | 56.74 | | 氮肥 | 最大值 | 28.7884 | 1.08 | 35.12 | 26.34 | 0.36 | 14.065 | 13.745 | 1250.5 | | 最小值 | 0.13 | 0.024 | 1.38 | 0.2005 | 0.0005 | 0.21 | 0.1 | 0.1 | | 化肥年均输入通量 | 5.733 | 0.149 | 16.376 | 1.751 | 0.018 | 3.101 | 2.480 | 45.182 |
|
Contents of heavy metals in chemical fertilizers and annual average input fluxes
|

| 元素 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Pb | Zn | | 化肥 | 5.73 | 0.15 | 16.38 | 1.75 | 0.02 | 2.48 | 45.18 | | 灌溉水 | 28.57 | 0.20 | 16.01 | 6.40 | 0.35 | 3.36 | 20.44 | | 干湿沉降 | 1.004 | 0.133 | 3.708 | 3.006 | 0.015 | 5.205 | 24.517 | | 合计 | 35.304 | 0.483 | 36.098 | 11.156 | 0.385 | 11.045 | 90.137 | | 年增加量/10-6 | 0.0097 | 0.0001 | 0.0099 | 0.0031 | 0.0001 | 0.0030 | 0.0248 | | 土壤风险筛选值/10-6 | 25 | 0.6 | 300 | 200 | 0.6 | 140 | 250 | | (年增加量/风险筛选值)/% | 0.0388 | 0.0167 | 0.0033 | 0.0016 | 0.0167 | 0.0021 | 0.0099 |
|
Annual fluxes of heavy metals from different sourcesg·(hm2·a)-1
|
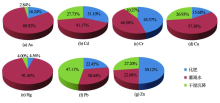
|
Distribution of annual heavy metal input fluxes in different ways
|
| [1] |
熊建华. 土地生态安全评价研究回顾、难点与思考[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2018, 34(6) : 71-76.
|
| [1] |
Xiong J H. Review, difficulty and consideration of land ecological security assessment[J]. Geography and Geographic Information Science, 2018, 34(6) : 71-76.
|
| [2] |
刘明达. 基于土地利用变化的区域生态安全评价——以鄂尔多斯市为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2011, 21(4) :578-590.
|
| [2] |
Liu M D. Assessment of regional ecological security based on land use change:A case study of Ordos City[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2011, 21(4) :578-590.
|
| [3] |
王长松, 陈莉萍, 孔祥英, 等. 仪征市 30 多年来土壤 pH 值时空变化趋势及原因分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2007, 22(3):223-224.
|
| [3] |
Wang C S, Chen L P, Kong X Y, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of soil pH in Yizheng in recent 30 years[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2007, 22(3):223-224.
|
| [4] |
邵学新, 黄标, 顾志权, 等. 长江三角经济迅速发展地区土壤pH 时空变化及影响因素[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 12 (2):143-149.
|
| [4] |
Shao X X, Huang B, Gu Z Q, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of soil pH and its influencing factors in the Yangtze River Delta with rapid economic development[J]. Mineral and Rock Geochemistry, 2006, 12 (2):143-149.
|
| [5] |
张元培, 吴颖, 郑雄伟, 等. 湖北省土壤酸碱度趋势分析及影响因素[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4):30-34.
|
| [5] |
Zhang Y P, Wu Y, Zheng X W, et al. Trend analysis and influencing factors of soil pH in Hubei Province[J]. Resource Environment and Engineering, 2018, 32(4):30-34.
|
| [6] |
浙江省地质调查院. 浙江省基本农田质量调查试点工作报告[R]. 2010.
|
| [6] |
Zhejiang Geological Survey Institute. Report on the pilot project of basic farmland quality investigation in Zhejiang Province[R]. 2010.
|
| [7] |
杨胜科, 王文科, 张威, 等. 砷污染生态效应及水土体系中砷的治理对策研究[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2004, 26(3):69-73.
|
| [7] |
Yang S K, Wang W K, Zhang W, et al. Study on the ecological effects of arsenic pollution and the control measures of arsenic in soil and water system[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Environment, 2004, 26(3):69-73.
|
| [8] |
李启权, 王昌全, 李冰, 等. 成都平原土壤中砷的空间分布及污染评价[J]. 土壤通报, 2007, 25(2):357-360.
|
| [8] |
Li Q Q, Wang C Q, Li B, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of arsenic in soils in Chengdu Plain, China[J]. Soil Notification, 2007, 25(2):357-360.
|
| [9] |
王济, 曾希柏, 王世杰, 等. 贵阳市表层土壤中砷的地球化学基线及污染状况研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(6):1159-1163.
|
| [9] |
Wang J, Zeng X B, Wang S J, et al. Baseline geochemistry and contamination status of arsenic in surface soils in Guiyang, China[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 45(6):1159-1163.
|
| [10] |
杜习乐, 马诗院, 楚纯洁, 等. 郑州市城市土壤砷含量的分布特征及其成因探讨[J]. 土壤, 2008, 40(4):635-639.
|
| [10] |
Du X L, Ma S Y, Chu C J, et al. Distribution of arsenic in urban soils of Zhengzhou and its causes[J]. Soil, 2008, 40(4):635-639.
|
| [11] |
卢新卫, 王五一, 解庆林, 等. 湘西表生环境中的砷及其生态健康效应[J]. 地质科技情报, 2000, 19(4):80-83.
|
| [11] |
Lu X W, Wang W Y, Xie Q L, et al. Arsenic and its ecological health effects in the epiphytic environment of western Hunan[J]. Geo-Technical Information, 2000, 19(4):80-83.
|
| [12] |
朱静, 黄标, 孙维侠, 等. 长江三角洲典型地区农田土壤有机质的时空变异特征及其影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2006, 38(2):158-165.
|
| [12] |
Zhu J, Huang B, Sun W X, et al. Spatio-temporal variability of soil organic matter and its influencing factors in typical agricultural Yangtze River Delta[J]. Soil, 2006, 38(2):158-165.
|
| [1] |
WU Song, CHEN Zheng, LI Yuan-Bin, HUANG Zhao, ZHANG Lin, XU Sheng-Chao, WANG Kai-Gui. Cr and Ni geochemistry and some suggestions on soil pollution risk prevention control in the Zhelong-Gasa area, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 517-527. |
| [2] |
Guo-Guang CHEN, Xiao-Hong LIANG, Jie ZHANG, Zhong-Fang YANG. Geochemical survey method of land quality in hilly areas:A case study of the geochemical survey of land quality in Ganzhou[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3): 463-469. |
|
|
|
|

