|
|
|
| Application of the multi-excitation source transient electromagnetic method in the coal mine goaves |
SUN Hai-Chuan( ), WANG Wen-Zhong, LI Zhi-Zhong, LIU Yong-Liang ), WANG Wen-Zhong, LI Zhi-Zhong, LIU Yong-Liang |
| Gansu Coal Geological Prospecting Institute, Lanzhou 730000,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The large fixed-source loop is a commonly used device in the transient electromagnetic method (TEM). However, moving its transmitter requires a lot of manpower and time, greatly reducing the efficiency of the method. The electrical source TEM enjoys the advantages of large detection depth, less terrain restriction, and high efficiency. However, its signal intensity severely attenuated and it has a low signal-to-noise ratio in the case of a large offset, which limit its detection precision to a certain extent. To achieve high-precise geological exploration, this study built a forward model using the multi-excitation source TEM. With the detection of a water-bearing goaf of the Weijiadi coal mine in Gansu Province as a case study, this study compared the exploration performance of the multi-excitation source TEM with that of the conventional large fixed-source loop and the single-excitation source TEM. As verified by drilling, the multi-excitation source TEM can deliver better exploration performance in the study area. The results of this study can provide technical support and a reference for goaf detection in adjacent and similar areas.
|
|
Received: 19 November 2021
Published: 03 January 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
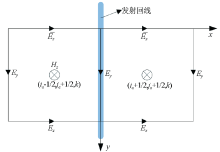
|
Schematic diagram of load mode of Yee unit cell with multiple excitation sources
|
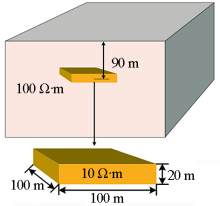
|
Model Sketch
|
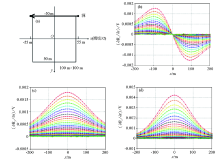
|
Multi-trace map of line 32 under single excitation field source
|
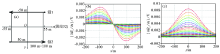
|
Multi-xcitation field source (opposite current direction) line 32 multi-omponent trace
|
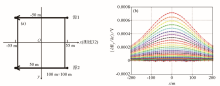
|
Multi-xcitation field source (same current direction) line 32 multi-omponent trace map
|
|
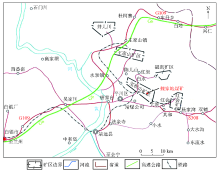
Sketch map of study area location
|
|
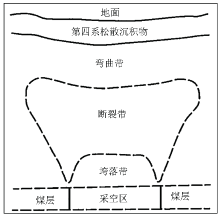
Sketch map of vertical “three zones”for collapse of mined-out area
|

| 地层 | 岩性 | 视电阻率/(Ω·m) | | 第四系 | 黄土、砂质黏土、砂砾石 | >60 | | 侏罗系 | 泥岩、粗砂岩、砂砾岩及煤层 | 10~60 | | 三叠系 | 中、粗砾砂岩,局部含砾 | >150 |
|
Characteristics of formation resistivity
|
|
Geophysical engineering layout drawing
|
|
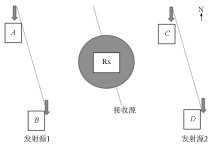
Schematic diagram of emission source and survey area location
|

| 工作装置 | 发射
边长/m | 发射
电流/A | 发射
频率/Hz | 偏移距/m | | 大定源回线 | 600×600 | 15 | 8.333 | ≤200 | | 单激励源 | AB:1500 | 15 | 8.333 | 1000 | | 多激励源 | AB:1500
CD:1500 | 15 | 8.333 | 1000 |
|
Observation parameters of different emission sources
|
|
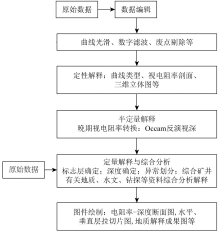
Data processing flowchart
|
|
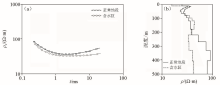
Plot of measured apparent resistivity (a) and plot of inversion depth model (b)
|
|
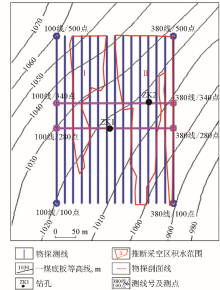
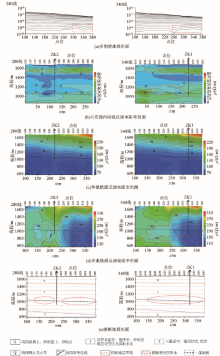
Comprehensive geophysical profile of line 280 (left) and line 340 (right)
|
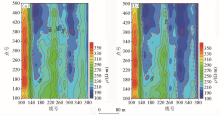
|
Elevation 1 000 m (a) and 1 050 m (b) resistivity contour plan
|
| [1] |
钟声, 王士党. 地面与井下瞬变电磁法联合探测煤矿富水区域[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(3):635-638.
|
| [1] |
Zhong S, Wang S D. The application of combined ground and underground coal mine transient electronmagnetic methods to the exploration of water-rich area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(3):635-638.
|
| [2] |
郭伟立, 薛国强, 周楠楠, 等. 利用瞬变电磁法监测煤矿含水采空区[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(S):114-118.
|
| [2] |
Guo W L, Xue G Q, Zhou N N, et al. Monitoring water-filled goaf by using TEM technology[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(S):114-118.
|
| [3] |
郭文波, 宋建平, 曹捷, 等. 回线源瞬变电磁法在地质灾害调查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2006, 30(4):327-329.
|
| [3] |
Guo W B, Song J P, Cao J, et al. Application of loop source transient electromagnetic method in geological hazard investigation[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 30(4):327-329.
|
| [4] |
黄立军, 陆桂福, 刘瑞德. 电性源瞬变电磁法在油田上的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2005, 29(4):316-318.
|
| [4] |
Huang L J, Lu G F, Liu R D. The application of grounded source transient electromagnetic method to the oil field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2005, 29(4):316-318.
|
| [5] |
薛国强, 闫述, 底青云, 等. 多道瞬变电磁法(MTEM)技术分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2015, 37(1):94-100.
|
| [5] |
Xue G Q, Yan S, Di Q Y, et al. Technical analysis of multi-transient electromagnetic method[J]. Journal of Science and Envirorment, 2015, 37(1):94-100.
|
| [6] |
薛国强, 武欣, 李海, 等. 多道瞬变电磁法(MTEM)国外研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016, 31(5):2187-2191.
|
| [6] |
Xue G Q, Wu X, Li H, et al. Progress of multi-transient electromagnetic method in abroad[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2016, 31(5):2187-2191.
|
| [7] |
薛国强, 底青云, 王若, 等. 多道瞬变电磁法资料处理方法技术综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(1):211-215.
|
| [7] |
Xue G Q, Di Q Y, Wang R, et al. Overview on data progressing methods of multi-transient electromagnetic method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(1):211-215.
|
| [8] |
张莹莹. 电性源瞬变电磁法综述[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):809-823.
|
| [8] |
Zhang Y Y. Review on the study of grounded-source transient electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4):809-823.
|
| [9] |
张莹莹, 李貅, 姚伟华, 等. 多辐射场源地空瞬变电磁法多分量全域视电阻率定义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8):2745-2758.
|
| [9] |
Zhang Y Y, Li X, Yao W H, et al. Multi-component full field apparent resistivity definition of multi-source ground-airborne transient electronmagnetic method with galvanic sources[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2015, 58(8):2745-2758.
|
| [10] |
李貅, 胡伟明, 薛国强. 多辐射源地空瞬变电磁响应三维数值模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(2):716-723.
|
| [10] |
Li X, Hu W M, Xue G Q. 3D modeling of multi-radiation source semi-airborne transient electromagnetic response[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2021, 64(2):716-723.
|
| [11] |
张莹莹. 地空瞬变电磁法逆合成孔径成像方法研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016.
|
| [11] |
Zhang Y Y. Study on inverse synthetic aperture imaging ground-airborne transient electromagnetic method[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2016.
|
| [12] |
王文忠. 多激励源瞬变电磁法方法技术在精细地质调查中的应用研究报告[R]. 甘肃煤炭地质勘查院, 2020.
|
| [12] |
Wang W Z. Research report on application of multi-excitation source transient electromagnetic method technique in fine geological survey[R]. Gansu Coal Geological Prospecting Institute, 2020.
|
| [13] |
周建美, 刘文韬, 李貅, 等. 双轴各向异性介质中回线源瞬变电磁三维拟态有限体积正演算法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 63(1):368-378.
|
| [13] |
Zhou J M, Liu W T, Li X, et al. Research on the 3D mimetic finite volume method for loop-source TEM response in biaxial anisotropic formation[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2018, 63(1):368-378.
|
| [14] |
何俊林. 魏家地煤矿小窑采空区及水文地质普查电法勘探报告[R]. 甘肃煤田地质局一四九队, 2015.
|
| [14] |
He J L. Electrical exploration report of small mine goaf and hydrogeological survey in Weijiadi coal mine[R]. Team 149, Gansu Coal Geology Bureau, 2015.
|
| [15] |
张淑婷. 地球物理勘查技术在探测煤矿采空区中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(S):83-87.
|
| [15] |
Zhang S T. The application of geophysical exploration technology to the detection of coal mine goaf[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(S):83-87.
|
| [16] |
薛永军, 武秀芳, 仲丛明, 等. 煤矿小窑采空区及塌陷区的地球物理勘查[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(S):111-113.
|
| [16] |
Xue Y J, Wu X F, Zhong C M, et al. Geophysical exploration in goaf and collapse areas in small coal pits[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(S): 111-113.
|
| [17] |
陈卫营, 薛国强. 电性源瞬变电磁对薄层的探测能力[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(4):775-779.
|
| [17] |
Chen W Y, Xue G Q. Detection capability of grounded electric source TEM for thin layer[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(4):775-779.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Fan, FENG Guo-Rui, QI Ting-Ye, YU Chuan-Tao, ZHANG Xin-Jun, WANG Chao-Yu, DU Sun-Wen, ZHAO De-Kang. Feasibility of the transient electromagnetic method in the exploration of double-layer waterlogged goafs with different layer spacings in coal mines[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1215-1225. |
| [2] |
ZHOU Zhong-Hang, ZHANG Ying-Ying. Correction of the influence of mountains on grounded-source transient electromagnetic responses[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1236-1249. |
|
|
|
|

