|
|
|
| Sentinel-2A based inversion of the organic matter content of soil in the Sunwu area |
CHEN Chao-Qun1,2,3( ), DAI Hui-Min1,2,3, FENG Yu-Lin1, YANG Ze1,2,3, YANG Jia-Jia1( ), DAI Hui-Min1,2,3, FENG Yu-Lin1, YANG Ze1,2,3, YANG Jia-Jia1( ) ) |
1. Shenyang Center of China Geological Survey, Shenyang 110034, China
2. Key Laboratory of Black Soil Evolution and Ecological Effect, Ministry of Natural Resources, Shenyang 110034, China
3. Key Laboratory of Black Soil Evolution and Ecological Effect, Liaoning Province, Shenyang 110034, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study conducted the inversion of the organic matter content in the soil of the black soil area in Sunwu County, Heilongjiang Province using the Sentinel-2A multispectral remote sensing images and the surveyed soil data. After preprocessing the images, the characteristic bands were selected through correlation analysis and using the random forest (RF) method. Subsequently, a multispectral inversion model for the organic matter content of the soil was built using the partial least square method and the BP neural network, and the inversion of the organic matter content of the soil in the Hongqi Forest Farm was conducted. According to the obtained results, the bands selected based on the reciprocal of the logarithm of the first-order differential of reflectance through the correlation analysis and the combined bands selected using the RF method can effectively improve the inversion precision of the organic matter content in the soil, and the RF-BP neural network model for the combined bands yielded the optimal inversion performance (R2=0.7245 and RMSE=1.3127%). The results of this study will provide technical support and reference for the dynamic monitoring of the organic matter content in soils.
|
|
Received: 25 January 2022
Published: 03 January 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
YANG Jia-Jia
E-mail: 522110156@qq.com;haixianxiaomei@163.com
|
|
|
|
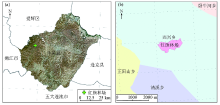
|
Remote sensing image of Sunwu County(a)and the location of Hongqi Forest Farm(b)
|

| 个数 | 最小值/% | 最大值/% | 均值/% | 标准差/% | | 建模集 | 564 | 0.8620 | 11.8266 | 5.7226 | 2.0316 | | 测试集 | 242 | 1.1896 | 11.9128 | 5.8393 | 2.1074 |
|
Statistical information of organic matter content in soil samples
|
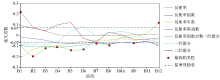
|
Correlation between band reflectivity and transformations and soil organic matter content
|

| 数学变换 | 波段 | | R | B1、B2、B3、B4、B5、B6、B7、B8、B9、B12 | | 1/R | B1、B2 | | lgR | B1、B2、B3、B4、B5、B12 | | Ra | B4、B5、B6、B7、B8、 B9、B12 | | FDR | B1、B2、B3、B4、B5、B6 | | SDR | B1、B4、B5 | | FDLR | B1、B2、B3、B4、B5、B6、B8、B12 | | 组合波段 | 1/B1、FDL(B2)、lg (B3)、B4、FDL(B5)、FDL(B6)、B7、FDL(B8)、(B9)a、FDL(B12) |
|
Feature bands selected by correlation analysis
|
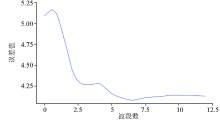
|
Cross validation curve of lgR
|
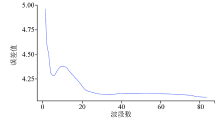
|
Cross validation curve of all bands
|

| 数学变换 | 波段 | | R | B1、B2、B3、B5、B7、B8A | | 1/R | B1、B2、B3、B5、B7、B8A | | lgR | B1、B2、B3、B5、B6、B7 | | Ra | B2、B3、B5、B6、B7、 B8A | | FDR | B1、B2、B3、B4、B6、B12 | | SDR | B1、B3、B4、B5、B11、B12 | | FDLR | B1、B2、B3、B4、B8、B12 | | 组合波段 | B1、B7、B11、1/B1、1/B2、1/B3、1/B11、1/B1、lg(B2)、FDL (B1)、FDL (B2)、FDL (B3)、FDL (B5)、FDL (B6)、FDL (B8)、FD (B1)、FD (B5)、FD (B6)、FD (B12)、SD(B1)、SD(B2)、SD(B3)、SD(B5)、SD(B8)、SD(B11)、SD(B12) |
|
Important bands of RF
|

| 数学
变换 | 拟合模型 | 建模集 | 测试集 | | R2 | RMSE/% | R2 | RMSE/% | 相
关
性 | R | | 0.0275 | 2.0263 | 0.0155 | 2.0925 | | 1/R | | 0.0439 | 1.9847 | 0.0657 | 2.0375 | | lgR | | 0.0525 | 1.9757 | 0.0609 | 2.0406 | | Ra | | 0.0159 | 2.0136 | 0.0121 | 2.0917 | | FDR | y=5.8376-23.9683x1+67.1411x2-63.9701x3+44.2371x4 | 0.0223 | 2.0071 | 0.0409 | 2.0632 | | SDR | | 0.0200 | 2.0093 | 0.0238 | 2.0800 | | FDLR | | 0.0524 | 1.9779 | 0.071 | 2.0366 | | 组合 | | 0.0434 | 1.9852 | 0.0400 | 1.9933 | 随
机
森
林 | R | | 0.0203 | 2.0318 | 0.0035 | 2.0539 | | 1/R | | 0.0234 | 2.2798 | 0.09 | 2.0390 | | lgR | | 0.0480 | 2.0029 | 0.0408 | 2.0124 | | Ra | | 0.0051 | 2.0475 | 0.0023 | 2.0525 | | FDR | | 0.0365 | 2.0149 | 0.0207 | 2.0356 | | SDR | | 0.0331 | 2.0496 | 0.0200 | 2.0520 | | FDLR | | 0.0463 | 2.0046 | 0.0418 | 2.0118 | | 组合 | | 0.0760 | 1.9518 | 0.0363 | 2.0183 |
|
Inversion of soil organic matter by PLSR
|

| 数学变换 | 隐藏层个数 | 建模集 | 测试集 | | R2 | RMSE/% | R2 | RMSE/% | 相
关
性 | R | 5 | 0.3635 | 1.3998 | 0.2711 | 1.4472 | | 1/R | 11 | 0.2816 | 1.4057 | 0.2291 | 1.4283 | | lgR | 6 | 0.3392 | 1.3967 | 0.2818 | 1.4207 | | Ra | 11 | 0.2726 | 1.4041 | 0.2388 | 1.4555 | | FDR | 10 | 0.2074 | 1.4149 | 0.1697 | 1.4368 | | SDR | 9 | 0.2005 | 1.4106 | 0.1977 | 1.4388 | | FDLR | 6 | 0.6237 | 1.3548 | 0.4446 | 1.2664 | | 组合 | 16 | 0.5637 | 1.3548 | 0.4305 | 1.3659 | 随
机
森
林 | R | 7 | 0.2906 | 1.4000 | 0.2601 | 1.4362 | | 1/R | 7 | 0.2603 | 1.4068 | 0.2241 | 1.4262 | | lgR | 14 | 0.2883 | 1.4068 | 0.2664 | 1.4231 | | Ra | 14 | 0.1663 | 1.4152 | 0.2499 | 1.4200 | | FDR | 7 | 0.3751 | 1.3980 | 0.2860 | 1.4090 | | SDR | 11 | 0.2783 | 1.4107 | 0.2057 | 1.4520 | | FDLR | 13 | 0.4544 | 1.3750 | 0.3653 | 1.2420 | | 组合 | 16 | 0.7245 | 1.3127 | 0.5418 | 1.3722 |
|
Inversion of soil organic matter by BP neural network
|
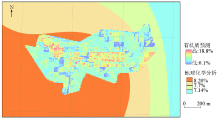
|
Distribution of soil organic matter in Hongqi Forest Farm
|
| [1] |
孔牧, 杨少平. 森林沼泽景观区有机质对元素表生地球化学特征的影响机制[J]. 物探与化探, 2008, 32(1):31-32,74.
|
| [1] |
Kong M, Yang S P. Preliminary research into the disturbed principle of organic material to character of supergene-geochemistry in forest marsh landscape andscape area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(1):31-32,74.
|
| [2] |
Rasmussen C, Heckman K, Wieder W R, et al. Beyond clay:Towards an improved set of variables for predicting soil organic matter content[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2018, 137(5):297-306.

|
| [3] |
戴慧敏, 刘凯, 宋运红, 等. 东北地区黑土退化地球化学指示与退化强度[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6):510-517.DOI:10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2020.06.002.
|
| [3] |
Dai H M, Liu K, Song Y H, et al. Black soil degradation and intensity in northeast China: Geochemical indication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6):510-517.DOI:10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2020.06.002.
|
| [4] |
刘焕军, 张美薇, 杨昊轩, 等. 多光谱遥感结合随机森林算法反演耕作土壤有机质含量[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(10):134-140.
|
| [4] |
Liu H J, Zhang M W, Yang H X, et al. Invertion of cultivated soil organic matter content combining multi-spectral remote sensing and random forest algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(10):134-140.
|
| [5] |
屈冉, 张雅琼, 聂忆黄, 等. 基于多光谱遥感影像的富川县表层土壤有机质含量反演[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2019, 44(1):154-157.
|
| [5] |
Qu R, Zhang Y Q, Nie Y H, et al. Inversion of surface soil organic matter content in Fuchuan county based on multi spectral remote sensing image[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2019, 44(1):154-157.
|
| [6] |
陈德宝, 陈桂芬. 基于Landsat8遥感图像的黑土区土壤有机质含量反演研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2020, 41(6):194-198.
|
| [6] |
Chen D B, Chen G F. Inversion of soil organic matter content in black soil region based on landsat8 remote sensing image[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2020, 41(6):194-198.
|
| [7] |
陈思明, 邹双全, 毛艳玲, 等. 土壤光谱重建的湿地土壤有机质含量多光谱反演[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(3):912-917.
|
| [7] |
Chen S M, Zou S Q, Mao Y L, et al. Inversion of soil organic matter content in wetland using multispectral data based on soil spectral reconstruction[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(3):912-917.
|
| [8] |
Dhawale N M, Adamchuk V I, Prasher S O, et al. Proximal soil sensing of soil texture and organic matter with a prototype portable mid-infrared spectrometer[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2015, 66(4): 661-669.

|
| [9] |
马驰. 基于Sentinel-2A遥感影像土壤有机质含量的反演研究[J]. 北方园艺, 2020(2):94-100.
|
| [9] |
Ma C. Inversion of soil organic matter content based on sentinel-2A remote sensing image[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020(2):94-100.
|
| [10] |
刘鹏. 孙吴县耕地质量评价[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2020.
|
| [10] |
Liu P. Evaluation of cultivated land quality in Sunwu County[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2020.
|
| [11] |
李丹丹. 黑河市耕地地力评价与土壤改良对策研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2018.
|
| [11] |
Li D D. Investigation and evaluation on cultivated land fertility of Heihe City[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2018.
|
| [12] |
Breiman L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1):5-32.

|
| [13] |
彭刘亚, 解惠婷, 冯伟栋. 基于随机森林算法的砂土液化预测方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(6):1429-1434.
|
| [13] |
Peng L Y, Xie H T, Feng W D. The method of predict sand liquefaction based on random forest algorithm[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(6):1429-1434.
|
| [14] |
王琨, 肖克炎, 丛源. 对数比变换和偏最小二乘法在地球化学组合异常提取中的应用——以湘西北铅锌矿为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(1):141-148.
|
| [14] |
Wang K, Xiao K Y, Cong Y. Log-ratio transformation and PLS methods for identifying integrated geochemical anomalies: A case study of lead-zinc mineralization in northwestern Hunan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(1):141-148.
|
| [15] |
陈昊宇, 杨光, 韩雪莹, 等. 基于连续小波变换的土壤有机质含量高光谱反演[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5):132-142.DOI:10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0742.
|
| [15] |
Chen H Y, Yang G, Han X Y, et al. Hyperspectral inversion of soil organic matter content based on continuous wavelet transform journal of agricultural science and technology[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(5):132-142.DOI:10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0742.
|
| [16] |
叶勤, 姜雪芹, 李西灿, 等. 基于高光谱数据的土壤有机质含量反演模型比较[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(3):164-172.
|
| [16] |
Ye Q, Jiang X Q, Li X C, et al. Comparison on inversion model of soil organic matter content based on hyperspectral data[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(3):164-172.
|
| [17] |
王启元, 赵艳玲, 房铄东, 等. 基于多光谱遥感的裸土土壤含水量反演研究[J]. 矿业科学学报, 2020, 5(6):608-615.
|
| [17] |
Wang Q Y, Zhao Y L, Fang S D, et al. Inversion of soil moisture in bare soil based on multi-spectral remote sensing[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2020, 5(6): 608-615.
|
| [18] |
汤超. 淮北矿区有机质含量反演[J]. 农业与技术, 2021, 41(13):123-128.DOI:10.19754/j.nyyjs.20210715035.
|
| [18] |
Tang C. Inversion of organic matter content in Huaibei mining area[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2021, 41(13):123-128.DOI:10.19754/j.nyyjs.20210715035.
|
| [19] |
谢树刚. 基于高光谱的黄河三角洲土壤有机质含量估测模型研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2021.DOI:10.27277/d.cnki.gsdnu.2021.000631.
|
| [19] |
Xie S G. Research on estimation model of soil organic matter content in Yellow River Delta based on hyperspectral[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2021.DOI: 10.27277/d.cnki.gsdnu.2021.000631.
|
| [20] |
陶培峰, 王建华, 李志忠, 等. 基于高光谱的土壤养分含量反演模型研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(1):68-75,84.DOI:10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2020.01.006.
|
| [20] |
Tao P F, Wang J H, Li Z Z, et al. Research of soil nutrient content inversion model based on hyperspectral data[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(1):68-75,84.DOI:10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2020.01.006.
|
| [1] |
LI Peng-Fei, GUAN Hou-Chun, WANG Xiang, Chen Yan-Bin, WANG Yao, WU Heng, SHI Chun-Hong. The distribution and influencing factors of zinc in the fluvo-aquic soil and the lime concretion black soil in northern Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(6): 1545-1554. |
| [2] |
XIAO Hong-Ye, LIU Guo-Dong, YANG Ze, FANG Na-Na, DAI Hui-Min, LIU Kai, HAN Xiao-Meng, ZHU Heng. Spatio-temporal change in land uses of the black soil area in northeast China over the past half century[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1037-1049. |
|
|
|
|

