|
|
|
| Evaluation of the soil quality and the suitability for green food-producing areas in the Xunke Plain, Heilongjiang Province |
ZHANG Zhe-Huan1,2,3( ), LIU Kai1,2,3, ZHAO Jun4, LIANG Shuai1,2,3, WEI Ming-Hui1,2,3, LIU Yang1,2,3 ), LIU Kai1,2,3, ZHAO Jun4, LIANG Shuai1,2,3, WEI Ming-Hui1,2,3, LIU Yang1,2,3 |
1. Shenyang Center of China Geological Survey, Shenyang 110034, China
2. Key Laboratory for Evolution and Ecological Effect in Black Land, Ministry of Natural Resources, Shenyang 110034, China
3. Key Laboratory for Evolution and Ecological Effect in Black Land of Liaoning Province, Shenyang 110034, China
4. Xi'an Center of Geological Survey, CGS, Xi'an 710054, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract As per the Specification of Land Quality Geochemical Assessment and the Soil Environment Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (Trial), this study evaluated the soil quality of the Xunke Plain and the soil environmental quality of the plain as green food-producing areas using the 1:250 000 geochemical survey data of land quality. The results show that the Xunke Plain has fertile land and an excellent environment and is suitable for the development of green agriculture. ①The Xunke Plain is rich or highly rich in 16 soil nutrients (i.e., N, P, K, organic matter, CaO, MgO, Fe2O3, S, B, Zn, Mn, Cu, Mo, Co, Ge, and V) except for CaO, MgO, Cu, and Zn, which are deficient, and Ge and B, which are highly deficient. This plain mainly has soil nutrients of highly rich and rich comprehensive grades, which cover an area of 6,088 km2 and 4,984 km2, respectively, accounting for 44.58% and 36.5% of the total area of the plain, respectively. ②This plain mainly has the soil environmental quality of risk-free comprehensive grade, which covers an area of 13,600 km2, accounting for 99.59% of the total area of the plain. The portion with controllable risk covers an area of 56 km2, accounting for 0.41%. ③This plain mainly has soil quality of excellent comprehensive grade, which covers an area of 11,028 km2, accounting for 80.76% of the total area of the plain. The land portion with high-quality soil quality has an area of 2,072 km2, accounting for 15.17%, and that with moderate soil quality covers an area of 556 km2, accounting for 4.07%. There is no poor (fourth grade) or inferior (fifth grade) soil in the plain. ④The soil of the Xunke Plain meeting the requirements of Class-I (AA) and Class-II (A) green food-producing areas has an area of 13,396.45 km2 and 148 km2, respectively, accounting for 98.1% and 1.1% of the total area of the plain, respectively. The soil that is unsuitable to be used as green food-producing areas has an area of 112 km2, accounting for 0.8% of the total area of the plain. Overall, the Xunke Plain enjoys sufficient soil nutrients and a clean environment and has great potential for developing as green food-producing areas.
|
|
Received: 25 January 2022
Published: 03 January 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
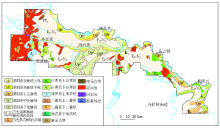
|
Geological map of the study area
|

| 指标 | 检出限 | 分析方法 | | 指标 | 检出限 | 分析方法 | | Cr | 1.8 | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | | Zn | 0.3 | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | | Cu | 0.9 | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | | TFe2O3 | 0.01 | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | | P | 6 | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | | CaO | 0.02 | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | | Pb | 1 | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | | MgO | 0.02 | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | | V | 4 | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | | Co | 0.6 | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | | K2O | 0.02 | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | | Mn | 0.3 | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | | Cu | 0.9 | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | | Ni | 1.5 | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | | As | 0.5 | 原子荧光光度法(AFS) | | S | 18 | 高频燃烧红外吸收法(CS) | | Hg | 0.0003 | 原子荧光光度法(AFS) | | Cd | 0.02 | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | | B | 1 | 发射光谱法(AES) | | Ge | 0.09 | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | | Corg | 0.03 | 容量法(VOL) | | Mo | 0.06 | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | | N | 19 | 凯氏定氮法 | | | | |
|
Analysis methods and detection limits of soil elements
|

| 等级 | 一级
(丰富) | 二级
(较丰富) | 三级
(中等) | 四级
(较缺乏) | 五级
(缺乏) | | ?养综 | ≥4.5 | <3.5~4.5 | <3.5~2.5 | <2.5~1.5 | <1.5 |
|
Comprehensive geochemical classification of soil nutrients
|

| 环境等级 | 一等(无风险) | 二等(风险可控) | 三等(风险较高) | | 污染风险 | 无风险 | 风险可控 | 风险较高 | | 划分方法 | Ci≤Si | Si﹤Ci≤Gi | Ci>Gi |
|
Standard for risk classification of single element pollution of heavy metals
|

| 土壤质量 | 环境综合等级 | 一等
(无风险) | 二等
(风险可控) | 三等
(风险较高) | 养分
综合
等级 | 一等(丰富) | 一等 | 三等 | 五等 | | 二等(较丰富) | 一等 | 三等 | 五等 | | 三等(中等) | 二等 | 三等 | 五等 | | 四等(较缺乏) | 三等 | 三等 | 五等 | | 五等(缺乏) | 四等 | 四等 | 五等 |
|
Comprehensive geochemical grade of soil quality
|

| 项目 | 旱田 | 水田 | pH<
6.5 | 6.5≤pH
≤7.5 | pH>
7.5 | pH<
6.5 | 6.5≤pH
≤7.5 | pH>
7.5 | | 镉 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.40 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.40 | | 汞 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.35 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.40 | ≤0.40 | | 砷 | ≤25 | ≤20 | ≤20 | ≤20 | ≤20 | ≤15 | | 铅 | ≤50 | ≤50 | ≤50 | ≤50 | ≤50 | ≤50 | | 铬 | ≤120 | ≤120 | ≤120 | ≤120 | ≤120 | ≤120 | | 铜 | ≤50 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤50 | ≤60 | ≤60 |
|
Envionmental quality limits for soil in green food production areas 10-6
|

| 项目 | 级别 | 旱田 | 水田 | | Ⅰ | >15 | >25 | | 有机质/10-3 | Ⅱ | 10~15 | 20~25 | | Ⅲ | <10 | <20 | | Ⅰ | >1.0 | >1.2 | | 全氮/10-3 | Ⅱ | 0.8~1.0 | 1.0~1.2 | | Ⅲ | <0.8 | <1.0 |
|
Classification of soil fertility grade
|

| 指标 | 含量 | 土壤质量 | | 范围值/10-3 | 平均值/10-3 | 等级
含义 | 一等
丰富 | 二等
较丰富 | 三等
中等 | 四等
较缺乏 | 五等
缺乏 | | N | 0.29~4.75 | 2.31 | 面积/km2 | 8460 | 3032 | 1684 | 380 | 100 | | 比例/% | 61.95 | 22.2 | 12.33 | 2.78 | 0.73 | | P | 0.20~1.91 | 0.98 | 面积/km2 | 6604 | 3112 | 2188 | 1408 | 344 | | 比例/% | 48.36 | 22.79 | 16.02 | 10.31 | 2.52 | | K | 15.85~24.64 | 20.26 | 面积/km2 | 228 | 7300 | 6108 | 20 | 0 | | 比例/% | 1.67 | 53.46 | 44.73 | 0.15 | 0 | | 有机质 | 1.16~103.96 | 47.37 | 面积/km2 | 8424 | 2832 | 1792 | 544 | 64 | | 比例/% | 61.69 | 20.74 | 13.12 | 3.98 | 0.47 |
|
Statistical table of content and evaluation results of soil macronutrient elements (indicators)
|

| 指标 | 含量 | 土壤质量 | | 范围值 | 平均值 | 等级
含义 | 一等
丰富 | 二等
较丰富 | 三等
中等 | 四等
较缺乏 | 五等
缺乏 | | CaO | 0.30~1.74 | 0.95 | 面积/km2 | 0 | 0 | 2880 | 10684 | 92 | | 比例/% | 0 | 0 | 21.09 | 78.24 | 0.67 | | MgO | 0.30~1.49 | 0.89 | 面积/km2 | 0 | 20 | 608 | 10344 | 2684 | | 比例/% | 0 | 0.15 | 4.45 | 75.75 | 19.65 | | S | 44~551.5 | 270.93 | 面积/ km2 | 3224 | 3392 | 2764 | 2200 | 2076 | | 比例/% | 23.61 | 24.84 | 20.24 | 16.11 | 15.2 |
|
Statistical table of content of nutrient elements in soil and evaluation results
|

| 指标 | 含量 | 土壤质量 | 超出上限 | | 范围值 | 平均值 | 等级
含义 | 一等
丰富 | 二等
较丰富 | 三等
中等 | 四等
较缺乏 | 五等
缺乏 | | Fe2O3 | 1.41~6.57 | 4.12 | 面积/km2 | 852 | 3965 | 2680 | 3108 | 3052 | | | 比例/% | 6.24 | 29.03 | 19.63 | 22.76 | 22.35 | | | Mn | 180.78~1834 | 998.27 | 面积/km2 | 11004 | 852 | 540 | 284 | 104 | 872 | | 比例/% | 80.58 | 6.24 | 3.95 | 2.08 | 0.76 | 6.39 | | Cu | 5.1~28.6 | 16.53 | 面积/km2 | 45 | 236 | 1692 | 5951 | 5728 | 4 | | 比例/% | 0.32 | 1.73 | 12.39 | 43.59 | 41.94 | 0.03 | | Zn | 25.21~104.76 | 63.45 | 面积/km2 | 1348 | 2492 | 3300 | 4316 | 2180 | 20 | | 比例/% | 9.87 | 18.25 | 24.17 | 31.61 | 15.96 | 0.15 | | B | 12.7~46.21 | 29.03 | 面积 | 4 | 0 | 72 | 5380 | 8200 | | | 比例% | 0.03 | 0 | 0.53 | 39.40 | 60.05 | | | Mo | 0.29~1.61 | 0.91 | 面积/km2 | 8028 | 4100 | 1040 | 380 | 68 | 40 | | 比例/% | 58.79 | 30.02 | 7.62 | 2.78 | 0.50 | 0.29 | | Co | 5.47~19.36 | 12.34 | 面积/km2 | 1676 | 4000 | 4428 | 2956 | 0.50 | | | 比例/% | 12.27 | 29.29 | 32.43 | 21.65 | 4.36 | | | V | 37.8~118.5 | 78.29 | 面积/km2 | 1648 | 3416 | 3088 | 3340 | 2164 | | | 比例/% | 12.07 | 25.01 | 22.61 | 24.46 | 15.85 | | | Ge | 0.92~1.57 | 1.25 | 面积/km2 | 212 | 876 | 3104 | 4840 | 4624 | | | 比例/% | 1.55 | 6.41 | 22.73 | 35.44 | 33.86 | |
|
Content and evaluation results of soil micronutrients
|

| 等级 | 一等 | 二等 | 三等 | 四等 | 五等 | | 含义 | 丰富 | 较丰富 | 中等 | 较缺乏 | 缺乏 | | 面积/ km2 | 6088 | 4984 | 2084 | 500 | 0 | | 比例/% | 44.58 | 36.5 | 15.26 | 3.66 | 0 |
|
Comprehensive evaluation results of surface soil nutrients
|
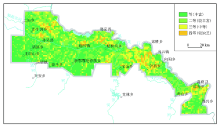
|
Comprehensive grade evaluation map of soil nutrients in Xunke Plain
|

| 元素 | 一等(无风险) | 二等(风险可控) | | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | | Ni | 13652 | 99.97 | 4 | 0.03 | | Hg | 13656 | 100 | | | | As | 13632 | 99.82 | 24 | 0.18 | | Pb | 13656 | 100 | | | | Cr | 13652 | 99.97 | 4 | 0.03 | | Cu | 13652 | 99.97 | 4 | 0.03 | | Cd | 13636 | 99.85 | 20 | 0.15 | | Zn | 13636 | 99.85 | 20 | 0.15 | | 环境综合 | 13600 | 99.59 | 56 | 0.41 |
|
Single index evaluation results of soil environment
|
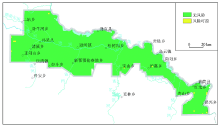
|
Comprehensive grade evaluation map of soil environment in Xunke plain
|
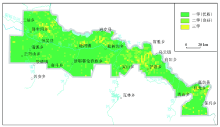
|
Comprehensive grade evaluation map of soil quality in Xunke plain
|
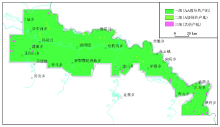
|
Environmental quality assessment map of green producing areas in Xunke plain
|
| [1] |
倪绍祥. 土地类型与土地评价概论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1999:56-307.
|
| [1] |
Ni S X. Introduction to land types and land evaluation[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1999:56-307.
|
| [2] |
任家强, 汪景宽, 杨晓波, 等. 辽河中下游平原土地质量地球化学评价及空间分布研究[J]. 沈阳大学学报, 2011, 37(4):208-211.
|
| [2] |
Ren J Q, Wang J K, Yang X B, et al. Geochemical evaluation and spatial distribution of land quality in the middle and lower reaches of Liaohe Plain[J]. Journal of Shenyang University, 2011, 37(4): 208-211.
|
| [3] |
潘志恒, 李鑫, 白荣杰, 等. 长春经济区土壤地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6):564-569.
|
| [3] |
Pan Z H, Li X, Bai R J. Geochemical characteristics of soil in Changchun Economic Zone[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6):564-569.
|
| [4] |
杨忠芳. 现代环境地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社,1999.
|
| [4] |
Yang Z F. Modern environmental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999.
|
| [5] |
孙淑梅, 张连志, 闰冬. 吉林省德惠—农安地区土地质量地球化学评估[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(6):998-1002.
|
| [5] |
Sun S M, Zhang L Z, Run D. Geochemical evaluation of land quality in Dehui-Nong'an area of Jilin Province[J]. Modern Geology, 2008, 22(6):998-1002.
|
| [6] |
刘国栋, 崔玉军, 刘立芬, 等. 土地质量地球化学评价方法研究与应用:以黑龙江省宏胜镇为例[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(1):167-176.
|
| [6] |
Liu G D, Cui Y J, Liu L F, et al. Research and application of geochemical evaluation method of land quality:A case study of Hongsheng Town, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Modern Geology, 2017, 31(1):167-176.
|
| [7] |
梁红霞, 史春鸿. 当涂县土地质量地球化学评估[J]. 安徽地质, 2014, 24(2):122-126.
|
| [7] |
Liang H X, Shi C H. Geochemical evaluation of land quality in Dangtu County[J]. Geology of Anhui, 2014, 24(2):122-126.
|
| [8] |
于成广, 杨忠芳, 杨晓波, 等. 土地质量评估方法研究与应用:以盘锦市为例[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):873-878.
|
| [8] |
Yu C G, Yang Z F, Yang X B, et al. Research and application of land quality evaluation method:A case study of Panjin City[J]. Modern Geology, 2012, 26(5):873-878.
|
| [9] |
刘军保, 黄春雷, 岑静. 土地质量地球化学评估方法研究:以慈溪市为例[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2010, 21(1):50-59.
|
| [9] |
Liu J B, Huang C L, Cen J. Study on geochemical evaluation method of land quality:A case study of Cixi City[J]. Resource Survey and Environment, 2010, 21(1):50-59.
|
| [10] |
王增辉, 王存龙, 赵西强, 等. 山东省黄河下游流域土地质量地球化学评估及方法研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(4):743-748.
|
| [10] |
Wang Z H, Wang C L, Zhao X Q, et al. Geochemical evaluation and method of land quality in the lower Yellow River Basin of Shandong Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(4):743-748.
|
| [11] |
戴慧敏, 刘凯, 宋运红, 等. 东北地区黑土退化地球化学指示与退化强度[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6):510-517.
|
| [11] |
Dai H M, Liu K, Song Y H, et al. Geochemical indicators and degradation intensity of black soil degradation in Northeast China[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6):510-517.
|
| [12] |
NY/T 391—2021绿色食品产地环境质量[S].
|
| [12] |
NY/T 391—2021 Environmental quality of green food producing areas[S].
|
| [13] |
NY/T 1054—2021绿色食品产地环境调查、监测与评价规范[S].
|
| [13] |
NY/T 1054—2021 Code for environmental investigation, monitoring and evaluation of green food producing areas[S].
|
| [14] |
NY/T 5295—2015 无公害农产品产地环境评价准则[S].
|
| [14] |
NY/T 5295—2015 Environmental assessment criteria for producing areas of pollution-free agricultural products[S].
|
| [15] |
耿增超, 戴伟. 土壤学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011:146.
|
| [15] |
Geng Z C, Dai W. Soil science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011:146.
|
| [16] |
全国农业技术推广中心. 东北玉米优势区耕地质量专题评价[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2017:129.
|
| [16] |
National Agricultural Technology Extension Center. Special evaluation of cultivated land quality in maize dominant areas of Northeast China[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2017:129.
|
| [17] |
浙江农业大学. 植物营养与肥料[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1991:123-130.
|
| [17] |
Zhejiang Agriculture University. Plants nutrition and fertilizer[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 1991:123-130.
|
| [18] |
张俊伶, 张福锁, 廖红, 等. 植物营养学[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2021:112.
|
| [18] |
Zhang J L, Zhang F S, Liao H, et al. Plantsnutrition[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture University Press, 2021:112.
|
| [19] |
蔡庆生. 植物生理学[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2014:121-122.
|
| [19] |
Cai Q S. Plant physiology[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2014:121-122.
|
| [20] |
刘万华, 邵凤城, 刘淑君, 等. 武清区农田土壤缺硼现状与补硼措施[J]. 天津农业科学, 2009, 15(增刊):5-7.
|
| [20] |
Liu W H, Shao F C, Liu S J, et al. Current situation of boron deficiency in farmland soil and boron supplement measures in Wuqing District[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Science, 2009, 15(S):5-7.
|
| [21] |
蒋德安. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社, 1999:22-23.
|
| [21] |
Jiang D A. Experimental guidance of plant physiology[M]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press, 1999:22-23.
|
| [22] |
唐明灯, 吴龙华, 李宁, 等. 修复植物薷堆肥对缺铜土壤上冬小麦生长和铜胡收的初步研究[J]. 土壤, 2006, 38(5):614-618.
|
| [22] |
Tang M D, Wu L H, Li N, et al. Preliminary study on the effects of Repairing Plant Elsholtzia compost on the growth and copper harvest of Winter Wheat in copper deficient soil[J]. Soil, 2006, 38(5):614-618.
|
| [23] |
郑利伟. 土壤缺锌作物典型症状及综合防治措施[J]. 现代农业科技, 2009(7):185.
|
| [23] |
Zheng L W. Typical symptoms and comprehensive control measures of soil zinc deficiency crops[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and technology, 2009(7):185.
|
| [24] |
徐德海. 化学元素知识简明手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2012.
|
| [24] |
Xu D H. Concise handbook of chemical element knowledge[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2012.
|
| [25] |
叶铁林, 徐宝财. 化学元素的奇妙世界[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2016.
|
| [25] |
Ye T L, Xu B C. The wonderful world of chemical elements[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2016.
|
| [26] |
袁宏, 赵利, 王茂丽, 等. 西藏拉萨至曲水拉萨河沿岸农用地土壤硒锗空间分布与评价[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(2):427-432.
|
| [26] |
Yuan H, Zhao L, Wang M L, et al. Spatial distribution and evaluation of selenium and germanium in agricultural soil along Lhasa River from Lhasa to Qushui, Tibet[J]. Soil, 2020, 52(2):427-432.
|
| [1] |
SHU Zhi-Ming, WANG Xiong-Jun, LAI Jian-Qing, HU Rong-Guo. THE APPLICATION OF FRACTAL THEORY TO SOIL HEAVY TRACE METAL ANALYSIS IN TAIYUAN BASIN, SHANXI PROVINCE[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(2): 157-160. |
| [2] |
CAI Zhao-Yang, SUN De-You, WU Guo-Hua. THE APPLICATION OF COMBINED MapGIS AND Surfer IN GEOCHEMICAL EXPLORATION: A CASE STUDY IN BACHELI AREA OF HEIHE CITY, HEILONGJIANG PROVINCE[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(2): 220-223. |
|
|
|
|

