|
|
|
| The prediction of electrochemical prospecting in Youfang area of the Xiangshan orefield |
TANG Rui1( ), OUYANG Fei1( ), OUYANG Fei1( ), LUO Xian-Rong1, ZHENG Chao-Jie1, TANG Guo-Dong1, LIU Pan-Feng1, CAI Ye-Lei1, YANG Xiao-Xiao2 ), LUO Xian-Rong1, ZHENG Chao-Jie1, TANG Guo-Dong1, LIU Pan-Feng1, CAI Ye-Lei1, YANG Xiao-Xiao2 |
1. Institute for Prediction of Hidden Deposits, School of Geosciences, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541004,China
2. No.310 Geological Party of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region,Guilin 541000,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In order to make a breakthrough in prospecting in the Youfang area of the Xiangshan ore field, the authors carried out geoelectric extraction and surveying in this area for deep prospecting prediction. It is found that the anomalies are obviously controlled by the faults, and are mainly distributed along the ore-controlling faults and the intersection of the faults. Cluster analysis and factor analysis reveal that there is a significant correlation between the trace elements, thus forming the corresponding element combinations: F1 factor (Ti、V、Mo、Th、U), F2 factor (As、Pb、Sb), and F3 factor (Co、Ni). The spatial distribution of uranium-thorium ratios shows a significant positive correlation with the estimated base depth of AMT, controlled by volcanic rock thickness. The authors synthesized the abnormal features of geoelectrically extracted elements and the mineralization regularity of the Xiangshan ore field, established a comprehensive geological-geoelectrochemical prospecting model, and delineated two corresponding targets in the study area, of which No.1 target area has good prospecting prospect.
|
|
Received: 23 September 2020
Published: 21 December 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
OUYANG Fei
E-mail: 945087837@qq.com;ouyfglut@qq.com
|
|
|
|
25])
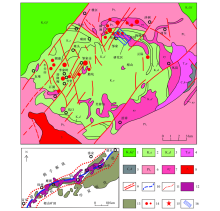
1—upper Cretaceous Guifeng group; 2—lower Cretaceous Ehuling formation; 3—lower Cretaceous Daguding formation; 4—upper Triassic Anyuan formation; 5—lower Carboniferous Huashanling formation; 6—Neoproterozoic; 7—subporphyritic granite; 8—granite; 9—real and inferred faults; 10—Gan-Hang fault zone; 11—Gan-Hang structural belt range; 12—red fault basin; 13—volcanic basin; 14—uranium deposit; 15—Xiangshan ore field; 16—research area
">
|
Outline of geological structure in Xiangshan basin(revised according to Dong Bao-ping[25])
1—upper Cretaceous Guifeng group; 2—lower Cretaceous Ehuling formation; 3—lower Cretaceous Daguding formation; 4—upper Triassic Anyuan formation; 5—lower Carboniferous Huashanling formation; 6—Neoproterozoic; 7—subporphyritic granite; 8—granite; 9—real and inferred faults; 10—Gan-Hang fault zone; 11—Gan-Hang structural belt range; 12—red fault basin; 13—volcanic basin; 14—uranium deposit; 15—Xiangshan ore field; 16—research area
|
|
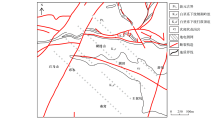
Geological map of Youfang study area
|
27])
">
|
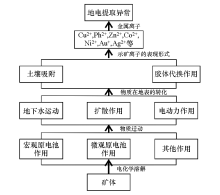
The brief diagram of the geochemical extraction migration model(revised according to Luo Xian-rong[27])
|
29])
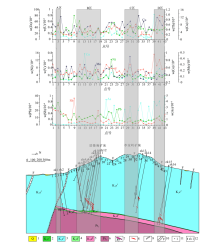
1—Quaternary; 2—lower Cretaceous lower Ehuling; 3—upper Cretaceous lower Ehuling; 4—lower Cretaceous lower Daguding formation; 5—upper Cretaceous lower Daguding formation; 6—Neoproterozoic; 7—subporphyritic granite; 8—uranium ore body; 9—void; 10—fault; 11—point and point number; 12—borehole and number
">
|
The comprehensive geological geodesic anomaly profile of Line 64(Revised according to Wang dong[29])
1—Quaternary; 2—lower Cretaceous lower Ehuling; 3—upper Cretaceous lower Ehuling; 4—lower Cretaceous lower Daguding formation; 5—upper Cretaceous lower Daguding formation; 6—Neoproterozoic; 7—subporphyritic granite; 8—uranium ore body; 9—void; 10—fault; 11—point and point number; 12—borehole and number
|

| 指标 | Ti | V | Co | Ni | As | Cu | Zn | Mo | Sb | Pb | Th | U | | 算数平均值 | 4.69 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.63 | 2.41 | 19.33 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 3.18 | 0.20 | 0.10 | | 中值 | 3.53 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.41 | 1.06 | 7.86 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.53 | 0.17 | 0.06 | | 众数 | 2.24 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 0.58 | 4.76 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.50 | 0.15 | 0.04 | | 标准差 | 5.20 | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 6.38 | 42.94 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 15.28 | 0.28 | 0.26 | | 最小值 | 1.16 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.41 | 2.06 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.85 | 0.04 | 0.01 | | 最大值 | 76.36 | 7.08 | 5.73 | 6.77 | 98.49 | 499.75 | 4.18 | 0.13 | 0.73 | 289.74 | 5.29 | 4.76 | | 偏度 | 8.70 | 12.81 | 5.95 | 4.48 | 10.71 | 7.01 | 12.26 | 6.70 | 8.97 | 17.23 | 15.76 | 14.77 | | 峰度 | 103.25 | 205.89 | 43.46 | 27.03 | 142.63 | 60.77 | 168.01 | 66.67 | 101.71 | 318.10 | 285.21 | 255.09 | | 变异系数 | 1.11 | 1.07 | 1.98 | 1.08 | 1.70 | 2.65 | 2.22 | 0.86 | 1.28 | 4.80 | 1.38 | 2.52 |
|
Statistical parameters of geo-electric chemistry elements content
|
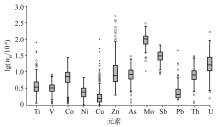
|
Box diagram of element content after logarithmic conversion
|
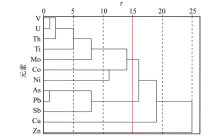
|
Cluster analysis tree
|

| 元素 | Ti | V | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Mo | Sb | Pb | Th | U | | Ti | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | V | 0.840 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | Co | 0.533 | 0.570 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | Ni | 0.562 | 0.501 | 0.563 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | Cu | 0.332 | 0.397 | 0.248 | 0.341 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | Zn | 0.074 | 0.107 | 0.047 | 0.101 | 0.116 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | As | 0.743 | 0.658 | 0.366 | 0.413 | 0.325 | 0.068 | 1.000 | | | | | | | Mo | 0.674 | 0.720 | 0.342 | 0.452 | 0.327 | 0.107 | 0.718 | 1.000 | | | | | | Sb | 0.312 | 0.261 | 0.111 | 0.294 | 0.164 | -0.002 | 0.664 | 0.590 | 1.000 | | | | | Pb | 0.542 | 0.356 | 0.183 | 0.234 | 0.183 | 0.039 | 0.904 | 0.469 | 0.661 | 1.000 | | | | Th | 0.810 | 0.891 | 0.488 | 0.406 | 0.366 | 0.122 | 0.642 | 0.660 | 0.139 | 0.368 | 1.000 | | | U | 0.715 | 0.923 | 0.527 | 0.422 | 0.411 | 0.111 | 0.619 | 0.688 | 0.202 | 0.307 | 0.887 | 1.000 |
|
Variable correlation coefficient matrix of factor analysis
|

| 元素 | F1 | F2 | F3 | | Ti | | 0.363 | 0.371 | | V | | 0.193 | 0.318 | | Co | 0.378 | 0.005 | | | Ni | 0.205 | 0.220 | | | As | 0.529 | | 0.161 | | Mo | | 0.539 | 0.209 | | Sb | -0.003 | | 0.143 | | Pb | 0.234 | | 0.022 | | Th | | 0.140 | 0.185 | | U | | 0.132 | 0.231 | | 方差贡献率/% | 39.579 | 27.690 | 17.746 | | 累计方差贡献率/% | 39.579 | 67.268 | 85.015 |
|
Rotated orthogonal factors and cumulative variance contributions
|

| 元素 | 背景值 | 标准差 | 外带下限 | 中带下限 | 内带下限 | | Ti | 3.576 | 1.367 | 4.942 | 6.309 | 9.043 | | V | 0.302 | 0.081 | 0.383 | 0.464 | 0.627 | | Co | 0.127 | 0.046 | 0.172 | 0.218 | 0.309 | | Ni | 0.384 | 0.119 | 0.503 | 0.622 | 0.860 | | As | 0.121 | 0.044 | 0.164 | 0.208 | 0.296 | | Mo | 0.010 | 0.004 | 0.014 | 0.019 | 0.028 | | Sb | 0.035 | 0.017 | 0.052 | 0.069 | 0.103 | | Pb | 1.511 | 0.380 | 1.891 | 2.271 | 3.031 | | Th | 0.169 | 0.063 | 0.232 | 0.295 | 0.422 | | U | 0.060 | 0.024 | 0.084 | 0.108 | 0.156 |
|
Contents of various elements for classifying various abnormal zones in the xiangshan,Jiangxi Province
|
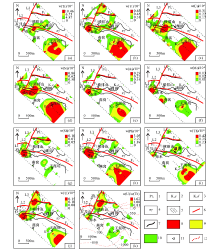
|
Anomaly plan of single element extraction and w(U)/w(Th) ratio plan of geoelectricity extraction in Youfang area
1—Neoproterozoic; 2—lower Cretaceous Ehuling formation; 3—lower Cretaceous Daguding formation; 4—subporphyritic granite; 5—geoelectric survey network; 6—fault structure; 7—geological boundary; 8—anomaly inner zone; 9—anomaly middle zone; 10—anomaly outer zone; 11—place name; 12—AMT inferred basement depth
|
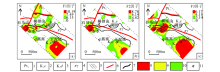
|
The combination of elements in the youfang area
1—Neoproterozoic; 2—lower Cretaceous Ehuling formation; 3—lower Cretaceous Daguding formation; 4—subporphyritic granite; 5—geoelectric survey network; 6—fault structure; 7—geological boundary ; 8—anomalous inner zone; 9—anomalous middle zone; 10—anomalous outer zone; 11—place name
|
|
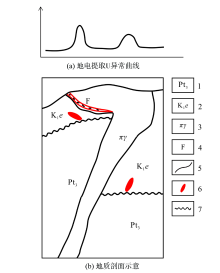
Geological-geoelectrochemical comprehensive prospecting model
1—Neoproterozoic; 2—lower Cretaceous Ehuling formation; 3—secondary porphyritic granite; 4—fault structure; 5—geological boundary; 6—ore body; 7—unconformity contact
|
|
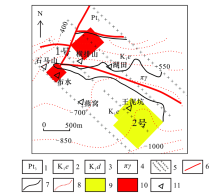
A map showing predicted prospecting targets in the Xiangshan deposit
1—Neoproterozoic; 2—lower Cretaceous Ehuling formation; 3—lower Cretaceous Daguding formation; 4—subporphyritic granite; 5—geoelectric survey network; 6—fault structure; 7—geological boundary; 8—AMT inferred basal depth; 9—No.2 target area; 10—No.1 target area; 11—place name
|
| [1] |
李子颖, 张万良. 江西相山矿田主要铀矿化类型及其地球化学特征对比研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1):1-16.
|
| [1] |
Li Z Y, Zhang W L. Main uranium mineralization types and their comparison of geochemical characteristics in Xiangshan orefield, Jiangxi[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(1):1-16.
|
| [2] |
田明明, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 等. 江西相山铀矿田中西部鹅湖岭组与打鼓顶组碎斑流纹岩特征对比及其成因探讨[J/OL]. 地球科学, 2020:1-35[2020-08-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20200714.0954.004.html.
|
| [2] |
Tian M M, Li Z Y, Nie J T, et al. A comparative study and its genesis of porphyroclastic rhyolite from Ehuling and Daguding formations in the midwest of Xiangshan uranium orefield, Jiangxi Province [J/OL]. Earth Science, 2020:1-35[2020-08-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20200714.0954.004.html.
|
| [3] |
郭建, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 等. 江西相山铀矿田深部多金属矿化中黄铁矿微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2020, 39(3):257-266.
|
| [3] |
Guo J, Li Z Y, Nie J T, et al. Trace-element geochemical characteristics of pyrite in polymetallic mineralization in the depth of the Xiangshan uranium orefield, Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2020, 39(3):257-266.
|
| [4] |
刘斌, 陈卫锋, 高爽, 等. 相山铀矿田黄铁矿微量元素、硫同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(6):1321-1335.
|
| [4] |
Liu B, Chen W F, Gao S, et al. Sulfur isotope and trace element geochemical characteristics of pyrite in Xiangshan uranium orefield and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(6):1321-1335.
|
| [5] |
林锦荣, 胡志华, 王勇剑, 等. 相山铀矿田铀多金属成矿时代与成矿热历史[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(9):2801-2816.
|
| [5] |
Lin J R, Hu Z H, Wang Y J, et al. Ore-forming age and thermal history of uranium-polymetallic mineralization in Xiangshan uranium orefield[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(9):2801-2816.
|
| [6] |
邓康乐. 苏联化探工作进展[J]. 国外地质勘探技术, 1981(3):1-9.
|
| [6] |
Deng K L. Progress in soviet geophysical exploration[J]. Foreign Geoexploration Technology, 1981(3):1-9.
|
| [7] |
罗先熔, 周涛发. 吉林红旗岭铜镍矿床地电化学异常特征、成晕机制及找矿预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2004(2):304-308.
|
| [7] |
Luo X R, Zhou T F. Feature and forming mechanism of geo-electrochemical anomaly of the Hongqiling copper -nickel deposit and its prediction, Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2004(2):304-308.
|
| [8] |
文美兰, 罗先熔, 熊健, 等. 地电化学法在南澳大利亚寻找隐伏金矿的研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2010, 46(1):153-159.
|
| [8] |
Wen M L, Luo X R, Xiong J, et al. Electro-geochemical method in the search of concealed gold deposits in south Australia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2010, 46(1):153-159.
|
| [9] |
王光洪, 罗先熔, 单江涛, 等. 第四纪沉积物覆盖区地电化学法寻找隐伏金矿——以安徽凤阳地区为例[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2010, 30(1):52-55.
|
| [9] |
Wang G H, Luo X R, Shan J, et al. Geoelectro-chemical method for prospecting gold mine in quaternary sediment region—A case from Fengyang, Anhui[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2010, 30(1):52-55.
|
| [10] |
王葆华, 文美兰, 欧阳菲, 等. 草原覆盖区铅锌银矿床地电化学异常特征及找矿预测——以内蒙古哈达特陶勒盖矿区为例[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2011, 31(02):192-197.
|
| [10] |
Wang B H, Wen M L, Ouyang F, et al. Features of geo-electrochemical anomaly and Pb-Zn-Ag exploration forecast in plains—Taking Hardattolgoi lead-zinc-silver polymetallic deposit of Inner Mongolia as an example[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2011, 31(2):192-197.
|
| [11] |
黄学强, 罗先熔, 刘巍, 等. 凹陷盆地铜镍多金属矿床地电化学异常特征及找矿预测[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(2):199-205.
|
| [11] |
Huang X Q, Luo X R, Liu W, et al. Features of geo-electrochemical anomaly and copper-nickel prospecting prognosis in Hollow Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(2):199-205.
|
| [12] |
刘攀峰, 文美兰, 杨龙坤, 等. 高原寒冷区地电化学提取技术试验与找矿预测[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(6):2000-2007.
|
| [12] |
Liu P F, Wen M L, Yang L K, et al. Geo-electrochemical extraction technology test and the prospecting prediction in cold plateau area[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(6):2000-2007.
|
| [13] |
杨笑笑, 罗先熔, 文美兰, 等. 地电化学法在豫西崤山黄土覆盖区找矿中的应用——以洛宁县石龙山预查区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(2):244-256.
|
| [13] |
Yang X X, Luo X R, Wen M L, et al. The application of geo-electrochemical methods to prospecting in the loess-covered Xiaoshan Mountain, western Henan Province: A case study ofthe Shilongshan gold polymetallic ore prospecting area in Luoning County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(2):244-256.
|
| [14] |
文美兰, 罗先熔, 熊健. 江西某地区地电化学法寻找隐伏铀矿研究[J]. 矿产勘查, 2011, 2(4):404-408.
|
| [14] |
Wen M L, Luo X R, Xiong J. Electro-geochemical method in search of concealed uranium deposits in a area of Jiangxi province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2011, 2(4):404-408.
|
| [15] |
李世铸, 罗先熔, 唐志祥, 等. 火山岩地区地电提取法寻找隐伏铀铅锌矿[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(3):441-446.
|
| [15] |
Li S Z, Luo X R, Tang Z X, et al. The application of geological CHIM method to the prospecting for concealed uranium-lead-zinc deposits in vocanic rock areas[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(3):441-446.
|
| [16] |
满荣浩, 罗先熔, 易超. 地电化学法在鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区寻找隐伏铀矿中的应用[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(5):1007-1013.
|
| [16] |
Man R H, Luo X R, Yi C. Application of the geo-electrochemical method on prospecting for concealed uranium deposits in the Dongsheng area of the Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(5):1007-1013.
|
| [17] |
蓝天, 罗先熔, 陈晓青, 等. 地电化学方法在浙江江山——长台地区寻找隐伏铀矿的应用[J]. 世界地质, 2017, 36(3):976-988.
|
| [17] |
Lan T, Luo X R, Chen X Q, et al. Application of geo-electro-chemical methods in searching hidden uranium deposits in Jiangshan-Changtai area of Zhejiang[J]. Global Geology, 2017, 36(3):976-988.
|
| [18] |
黄宁宁, 罗先熔, 易超, 等. 因子分析在内蒙东胜地区寻找隐伏铀矿中的应用[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2019, 39(4):856-862.
|
| [18] |
Huang N N, Luo X R, Yi C, et al. Application of factor analysis in search for concealeduranium deposit in Dongsheng area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2019, 39(4):856-862.
|
| [19] |
侯冬梅, 罗先熔, 王建历, 等. 地球电化学法在中国—澳大利亚两国寻找隐伏铀矿中的对比研究[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(1):126-135.
|
| [19] |
Hou D M, Luo X R, Wang J L, et al. A comparative study of the prospecting for hidden uraniumdeposits by applying geo-electrochemical method in China and Australia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(1):126-135.
|
| [20] |
文雪琴, 罗先熔, 邵飞, 等. 多种新方法寻找隐伏铀矿床的试验研究[J]. 桂林工学院学报, 2003, 23(1):26-30.
|
| [20] |
Wen X Q, Luo X R, Shao F, et al. New method study in search of uranium deposit[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2003, 23(1):26-30.
|
| [21] |
严冰, 胡瑞忠, 周莉, 等. 江西相山铀矿田的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2012, 32(6):48-52.
|
| [21] |
Yan B, Hu R Z, Zhou L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of REE in Xiangshan uranium orefield, Jiangxi Province[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2012, 32(6):48-52.
|
| [22] |
董保平, 吉高萍, 成霖, 等. 相山铀矿田游坊地区地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 东华理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 36(S2):74-79.
|
| [22] |
Dong B P, Ji G P, Cheng L, et al. Geologic feature and prospecting direction of Youfang area in Xiangshan uranium orefield[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology:Natural Science, 2013, 36(S2):74-79.
|
| [23] |
严冰, 严寒, 周莉, 等. 江西相山火山岩型铀矿 C、O、H、S 同位素特征及意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2013, 33(3):47-53.
|
| [23] |
Yan B, Yan H, Zhou L, et al. Isotopic characteristics of C, O, H and S in Xiangshan uranium orefield, Jiangxi Province[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2013, 33(3):47-53.
|
| [24] |
胡志华, 林锦荣, 王勇剑, 等. 相山矿田邹家山铀矿床钛铀矿地球化学特征及其成矿意义探讨[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2018, 35(2):63-70.
|
| [24] |
Hu Z H, Lin J R, Wang Y J, et al. Discussion on geochemical characteristics of the brannerite and its metallogenic significance in Zoujiashan uranium deposit, Xiangshan ore field[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2018, 35(2):63-70.
|
| [25] |
董保平. 相山矿田璜田矿区铀成矿地质条件及找矿远景[C]// 江西省地质学会2020年论文汇编I.:江西省地质学会, 2020:192-204.
|
| [25] |
Dong B P. Geological conditions of uranium mineralization and prospecting prospect of Hangtian area in Xiangshan ore fields[C]// Compilation of 2020 Papers of Jiangxi Geological Society I.:Jiangxi Geological Society, 2020:192-204.
|
| [26] |
曾文乐, 陈荣清, 谢国发, 等. 相山矿田铀矿找矿进展及远景分析[J]. 东华理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 42(2):101-107.
|
| [26] |
Zeng W L, Chen R Q, Xie G F, et al. Prospecting progress and prospective analysis of uranium deposit in Xiangshan ore field[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology:Natural Science, 2019, 42(2):101-107.
|
| [27] |
罗先熔. 地电化学成晕机制、方法技术及找矿研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2005.
|
| [27] |
Luo X R. The mechanism of electrogeochemical halo-formation and the application of electrogeochemical method to exploration of metallic ore deposits[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2005.
|
| [28] |
施意华, 杨仲平, 黄俭惠, 等. ICP-MS测定电吸附找矿泡塑样品中微量元素[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2009, 29(6):1687-1690.
|
| [28] |
Shi Y H, Yang Z P, Huang J H, et al. Determination of trace elements in electrical absorption prospecting polyform sample by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2009, 29(6):1687-1690.
|
| [29] |
王东. 江西相山乐家地区地电提取测量法寻找隐伏铀矿的研究[D]. 桂林:桂林理工大学, 2020.
|
| [29] |
Wang D. Study on searching for concealed uranium deposits by geoelectrochemical survey in Lejia area, Xiangshan, Jiangxi Province[D]. Guilin:Guilin University of Technology, 2020.
|
| [30] |
龚鹏. 地球化学矿致异常空间分析与定量评价[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉), 2014.
|
| [30] |
Gong P. Spatial analysis and quantitative evaluation of geochemical anomalies caused by ore bodies[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2014.
|
| [31] |
侯景儒. 数学地质浅谈[J]. 地质与勘探, 1977, 13(7):12-19.
|
| [31] |
Hou J R. Mathematics geology introduction[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1977, 13(7):12-19.
|
| [32] |
罗先熔, 文美兰, 欧阳菲, 等. 勘查地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007:36-44.
|
| [32] |
Luo X R, Wen M L, Ouyang F, et al. Exploration geochemistry [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007:36-44.
|
| [33] |
刘延斌, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 等. 地电化学集成技术在内蒙古格鲁其堆山矿区及外围寻找隐伏铅锌矿的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(5):1001-1012.
|
| [33] |
Liu Y B, Luo X R, Liu P F, et al. Application of geo-electrochemical integration technology to search for concealed Pb-Zn ore in the Geluqiduishan mining area and its periphery, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(5):1001-1012.
|
| [34] |
魏浩, 徐九华, 刘振刚, 等. 内蒙古凉城县草几坝一带土壤化探的数学地质分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011, 47(3):473-482.
|
| [34] |
Wei H, Xu J H, Liu Z G, et al. Analysis of mathematical geology for soil geochemistry in the Caojiba area of Liangcheng county, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2011, 47(3):473-482.
|
| [35] |
周顶, 庄光军, 张东林, 等. 河南省栾川县红庄—元岭金矿床原生晕轴向分带特征及深部成矿远景评价[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(6):1126-1137.
|
| [35] |
Zhou D, Zhuang G J, Zhang D L, et al. Axial zoning characteristics of primary haloes and evaluation of deep mineralization prospect of the Hongzhuang-Yuanling gold deposit in Luanchuan Couty, Henan Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2015, 51(6):1126-1137.
|
| [36] |
赵少卿, 魏俊浩, 高翔, 等. 因子分析在地球化学分区中的应用:以内蒙古石板井地区1∶5万岩屑地球化学测量数据为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2012, 31(2):27-34.
|
| [36] |
Zhao S Q, Wei J H, Gao X, et al. Factor analysis in the geochemical subdivisions: Taking 1∶50 000 debris geochemical survey in the Shibanjing area of Inner Mongolia as an example[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2012, 31(2):27-34.
|
| [37] |
戎嘉树, 冯明月, 欧振武, 等. 花岗岩中晶质铀矿及其找矿意义[J]. 放射性地质, 1987, 25(5):263-269.
|
| [37] |
Rong J S, Feng M Y, Ou Z W, et al. Granite mesomorphic uranium mine and its prospecting significance[J]. Uranium Geology, 1987, 25(5):263-269.
|
| [38] |
李莲. 因子分析在化探异常评价中的应用[J]. 物化探计算技术, 1986, 8(1):75-81.
|
| [38] |
Li L. Application of factor analysis in evaluation of geochemical anomaly[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1986, 8(1):75-81.
|
| [39] |
刘刚, 罗先熔, 郑超杰, 等. 地电化学集成技术在藏南姐纳各普金多金属矿区的找矿预测研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(5):894-902.
|
| [39] |
Liu G, Luo X R, Zhen C J, et al. A study of geo-electrochemical integration technology for prospecting mineral resources in the Jienagepu Au polymetallic ore field, Shanan City, Tibet, China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2018, 37(5):894-902.
|
| [1] |
CHEN Xiao, ZENG Zhi-Wen, DENG Ju-Zhi, ZHANG Zhi-Yong, CHEN Hui, YU Hui, WANG Yan-Guo. Regularized joint inversion of magnetotelluric and gravity data based on inequality and Gramian constraints[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 575-583. |
| [2] |
ZHU Wei-Ping. Chronological study advances of the granites and uranium mineralization in the Changjiang uranium ore-field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(6): 1327-1337. |
|
|
|
|

