|
|
|
| Exploration and practice of non-uniform time-lapse seismic key technology in Shengli Oilfield |
RUI Yong-Jun( ), SHANG Xin-Min ), SHANG Xin-Min |
| Geophysical Research Institute of Shengli Oilfield Company,Dongying 257022,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Time-lapse seismic survey is an effective technique for reservoir dynamic description,but it has not been widely used since its success in the last century due to the high cost and the limitation of its application range.Since 2007,Shengli Oilfield has put forward the idea of non-uniform time-lapse seismic survey in view of the current situation of the secondary acquisition seismic survey in high mature exploration area.Aiming at tackling a series of technical problems,such as how to evaluate and eliminate the influence of non-uniform acquisition system, how to detect the small difference of monitor changes and how to comprehensively use the time-lapse results,researchers have spent more than ten years to innovate the key technologies,i.e.,the matching technology of non-uniform time-lapse seismic acquisition system,the pre-stack cross equalization technology based on well data,the joint optimization technology of pre-stack and post-stack sensitive attributes,and the comprehensive interpretation technology of time-lapse seismic based on reservoir value.The time-lapse seismic technology of water-drive complex fault block reservoir,small-scale gas reservoir boundary monitoring and steam huff and puff heavy oil reservoir has been formed.The application demonstration of six blocks with an area of 300 square kilometers has been carried out,which shows the broad prospect of the achievements and broadens the ability of reservoir geophysical technology to solve the development problems.
|
|
Received: 11 May 2020
Published: 21 December 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 滨二区三维 | 滨一二区三维 | | 采集年度 | 1991 | 2010 | | 观测系统 | 4L6S | 20L15S | | 道数 | 240道 | 5760道 | | 面元 | 50 m×25 m | 25 m×12.5 m | | 覆盖次数 | 20次 | 240次 | | 横纵比 | 0.2 | 0.5 | | 道距/m | 50 | 25 | | 接收线距/m | 200 | 150 | | 炮点距/m | 100 | 50 | | 炮线距/m | 150 | 150 | | 最大炮检距/m | 3 150 | 4 008 |
|
Parameters of 3D seismic survey in bin2 and bin1-2 district
|
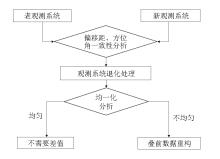
|
Matching technical process of inconsistent acquisition time-lapse seismic geometry system
|
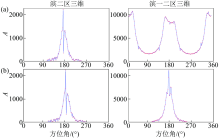
|
Seismic azimuth change before(a) and after(b) match processing
|
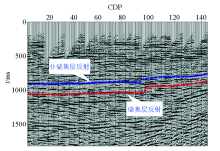
|
Typical seismic profile of block Shan-56
|

|
Amplitude difference between non reservoir(a) and reservoir(b) matching
|
|
Pseudo multi-channel prestack cross equalization technology based on well control
|
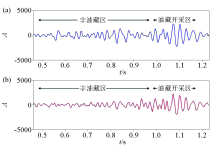
|
Comparison of traditional method(a) and new method(b)
|
|
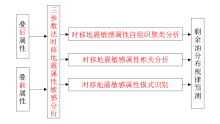
Joint optimization of pre stack and post stack time lapse sensitive attributes
|
|
Comparison of numerical simulation(a) and time-lapse seismic prediction(b)
|
|
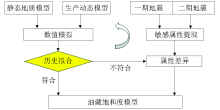
Time-lapse seismic interpretation based on reservoir simulation
|
|
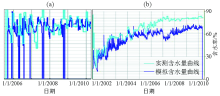
Water saturation fitting between single well(a) and block(b) in block shan56
|
|
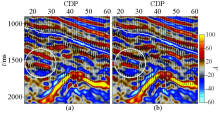
Comparison before(a) and after(b) adjustment based on time-lapse seismic difference attributes
|
|
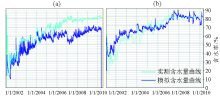
Water saturation of block dan56 before(a) and after(b) reservoir simulation adjustment
|

| 序号 | 区块 | 油藏类型 | 应用效果 | | 1 | 义东 | 复杂岩性 | 预测含油面积2.2 km2,剩余石油地质储量212万t | | 2 | 单56 | 稠油热采 | 发现有利区块2个,预测剩余储量达88万t | | 3 | 永55 | 气藏 | 预测有利范围地质储量30.4亿m3 | | 4 | 高气7 | 气藏 | 预测有利范围地质储量0.25亿m3 | | 5 | 永3 | 复杂断块 | 发现有利区块5个,预测剩余地质储量达26.1万t | | 6 | 高89 | 滩坝砂 | CO2驱波及范围监测 |
|
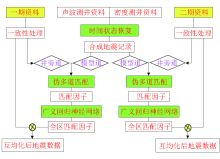
Application of inconsistent time-lapse seismic in Shengli oilfield
|

| 开发阶段 | 时间范围 | 产量/万t | 含水/% | | 产油 | 产液 | | 低速开发 | 1878~1992 | 5.71 | 9.85 | 13.380 | | 高速开发 | 1992~2000 | 27.10 | 67.75 | 80 | | 挖潜增产 | 2000~现今 | 8.85 | 99.53 | 90.1 |
|
Reservoir development history in Yidong area
|

| 三维区块 | 邵义三维 | 四扣三维 | 义东高精度 | | 采集时间 | 1990 | 2000 | 2013 | | 观测系统 | 4L6S | 8L16S | 32L10S | | 接收道数 | 240 | 768 | 10368 | | 面元 | 50 m×25 m | 25 m×25 m | 12.5 m×12.5 m | | 覆盖次数 | 20 | 64 | 216 | | 最大偏移距/m | 3197 | 2510 | 4492 | | 横纵比 | | | |
|
Observation system parameters of the third phase seismic in Yidong area
|
|
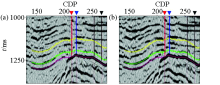
Comparison of two seismic sections after time-lapse seismic processing
a—Shao-Yi 3D in 1990;b—Yidong-high precision 3D in 2013
|
|
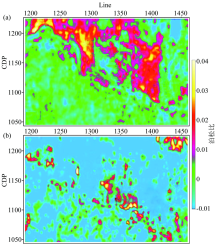
Plane difference of Poisson's ratio of two time-lapse seismic in Yidong area
a—the difference of Poisson's ratio between Shaoyi (1990) and Sikou (2000) in S3;b—the difference of Poisson's ratio between Sikou (2000) and Yidong high precision (2013) in S3
|

| 三维区块 | 樊家三维 | 高89三维 | | 采集时间 | 1992 | 2011 | | 观测系统 | 4L6S | 18L12S | | 面元 | 50 m×25 m | 25 m×25 m | | 覆盖次数 | 20 | 225 | | 最大偏移距/m | 3150 | 5500 |
|
Parameters of two periods of seismic observation system in gao89 area
|
|
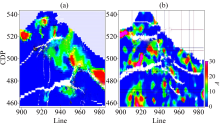
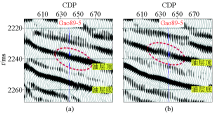
South-North seismic section of gao89-5 well
a—fanjia 3D (1992) section;b—gao89 3D (2011) section
|
|
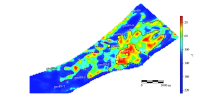
Prediction chatt of amplitude difference attribute of CO2 sweep range in gao89 well block
|
| [1] |
甘利灯, 姚逢昌, 杜文辉, 等. 水驱油藏四维地震技术[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(4):437-444.
|
| [1] |
Gan L D, Yao F C, Du W H, et al. 4D seismic technology for water flooding reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(4):437-444.
|
| [2] |
熊翥. 我国物探技术的进步及展望[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2004, 39(5):618-623.
|
| [2] |
Xiong Z. Progress and prospect of geophysical technology in China[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2004, 39(5):618-623.
|
| [3] |
Waine M W, et al. Seismic monitoring of the Duri steamflood:Application to reservoir management[J]. The Leading Edge, 1997, 16(9):1275-1278.

|
| [4] |
秦绪英, 朱海龙. 时移地震技术及其应用现状分析[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2007, 30(3):219-225.
|
| [4] |
Qin X Y, Zhu H L. Analysis of the current status of time-lapse seismic technology[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2007, 30(3):219-225.
|
| [5] |
云美厚, 丁伟, 杨长春. 油藏水驱开采时移地震监测岩石物理基础测量[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006, 49(6):1813-1818.
|
| [5] |
Yun M H, Ding W, Yang C C. Petrophysical measurements for time-lapse seismic monitoring of reservoir waterflooding recovery[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006, 49(6):1813-1818.
|
| [6] |
曹辉. 油藏监测中的时延地震技术[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2003, 26(5):342-348.
|
| [6] |
Cao H. Time-lapse seismic techniques in reservoir monitoring[J]. Progress Exploration Geophysics, 2003, 26(5):342-348.
|
| [7] |
鲍祥生, 丁建荣, 李红彩. 高集地区时移地震地震可行性研究[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2014, 36(12):81-85.
|
| [7] |
Bao X S, Ding J R, Li H C. Fesibility study of time-lapse seismic technology in Gaoji area[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2014, 36(12):81-85.
|
| [8] |
朱振宇, 王小六, 何洋洋, 等. 海上时移地震关键技术研究与应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(4):76-85.
|
| [8] |
Zhu Z Y, Wang X L, He Y Y, et al. Research and application of key marine time-lapse seismic technologies[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(4):76-85.
|
| [9] |
邬达理, 李宗杰, 蒋波, 等. 陆上非重复性时移地震资料处理存在的问题与策略[J]. 石油物探, 2015, 54(4):427-434.
|
| [9] |
Wu D L, Li Z J, Jiang B, et al. The problems for land non-repeated time-lapse seismic data processing and its countermeasures[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petreleum, 2015, 54(4):427-434.
|
| [10] |
王延光. 胜利油区时移地震技术应用研究与实践[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(1):50-54.
|
| [10] |
Wang Y G. Study and application of time lapse seismic in Shengli oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2012, 19(1):50-54.
|
| [11] |
刘成斋. 胜利探区地震采集技术发展历程回顾与启示[J]. 石油天然气地质, 2008, 29(3):397-403.
|
| [11] |
Liu C Z. Review and enlightment of seismic acquisition technology development in Shengli exportation area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(3):397-403.
|
| [12] |
尚新民, 芮拥军, 石林光, 等. 胜利油田高密度地震探索与实践[J]. 地球物理徐进展, 2018, 33(4):1545-1553.
|
| [12] |
Shang X M, Rui Y J, Shi L G, et al. Exploration and practice of high-density seismic survey in Shengli oilfield[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(4):1545-1553.
|
| [13] |
尹成, 葛子建, 芮拥军, 等. 非一致性采集时移地震油藏监测可行性研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 36(1):170-180.
|
| [13] |
Yin C, Ge Z J, Rui Y J, et al. Feasibility study on non-repeating acquired time-lapse seimic reservoir monitoring[J]. Journal of Southwest Petrelueum University:Science & Technology Edition, 2014, 36(1):170-180.
|
| [14] |
芮拥军. 陆上非一致性采集时延地震处理关键技术[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(4):778-782.
|
| [14] |
Rui Y J. Key processing technique for land non-uniform acquisition of time-lapse seismic[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(4):778-782.
|
| [15] |
石玉梅, 刘雯林, 姚逢昌. 地震资料信噪比对油藏地震监测的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(s1):113-116.
|
| [15] |
Shi Y M, Liu W L, Yao F C. Effects of signal-to-noise ratio on seismic reservoir monitoring[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(s1):113-116.
|
| [16] |
黄旭日. 国外时移地震技术的研究现状[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2003, 26(1):8-12.
|
| [16] |
Huang X R. A review of time-lapse seismic techniques abroad[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2003, 26(1):8-12.
|
| [17] |
李志娜, 张敏, 李振春, 等. 基于伪多道匹配的时移地震互均化方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2015, 50(6):1083-1088.
|
| [17] |
Li Z N, Zhang M, Li Z C, et al. Cross-equalization based on pseudo-multichannel matching in time-lapse seimic[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2015, 50(6):1083-1088.
|
| [18] |
朱焱, 谢进庄, 杨为华, 等. 提高油藏数值模拟历史拟合精度的方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(2):225-229.
|
| [18] |
Zhu Y, Xie J Z, Yang W H, et al. Method for improving history matching precision of reservoir numerical simulation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(2):225-229.
|
| [19] |
李玉梅, 陈开远, 赵玉欣. 提高油藏数值模拟精度的对策研究[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2010, 32(3):350-352.
|
| [19] |
Li Y M, Chen K Y, Zhao Y X. Countermeasures for improving the accuracy Numerical Simulatio[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2010, 32(3):350-352.
|
| [20] |
王厉强, 刘慧卿, 赵丽, 等. 提高精细油藏数值模拟预测精度的前期研究——以流花11-1油藏为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2006, 13(5):69-71.
|
| [20] |
Wang L Q, Liu H Q, Zhao L, et al. Earlier research of enhancing the precision of fine reservoir numerical simulation-taking Liuhua 11-1 oil reservoir as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2006, 13(5):69-71.
|
| [21] |
Whorton L P, Brownscombe E R, Dyes A B. Method for producing oil by means of carbon dioxide: U. S. Patent 2623596[P]. 1952-12-30.
|
| [22] |
朱希安, 汪毓铎. 国内外CO2运移监测技术和方法研究新进展[J]. 中国煤层气, 2011, 8(5):3-7.
|
| [22] |
Zhu X A, Wang Y D. The new progress on movement monitoring technique and method research of CO2 in domestic and abroad[J]. China Coalbeo Methane, 2011, 8(5):3-7.
|
| [23] |
由荣军, 李德春, 武俊文. CO2地质储存的地震监测[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(1):114-116.
|
| [23] |
You R J, Li D C, Wu J W. A preliminary study of seismic monitoring in CO2 Geological Storage[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(1):114-116.
|
| [24] |
秦积舜, 韩海水, 刘晓蕾. 美国CO2驱油技术应用及启示[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(2):209-216.
|
| [24] |
Qin J S, Han H S, Liu X L. Application and enlightenment of carbon dioxide flooding in th United States of America[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(2):209-216.
|
|
|
|

