|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in Chahe area of Sichuan Province |
XU Yun-Feng1,2( ), HAO Xue-Feng1,2( ), HAO Xue-Feng1,2( ), QIN Yu-Long1,2, WANG Xian-Feng1,2, XIONG Chang-Li1,2, LI Ming-Ze1,2, WU Weng-Hui1,2, ZHAN Han-Yu1,2 ), QIN Yu-Long1,2, WANG Xian-Feng1,2, XIONG Chang-Li1,2, LI Ming-Ze1,2, WU Weng-Hui1,2, ZHAN Han-Yu1,2 |
1. Sichuan Geological Survey Institute, Chengdu 610081, China
2. Evaluation and Utilization of Strategic Rare Metals and Rare Earth Resource Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610081, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Chahe deposit is the largest tin deposit in Sichuan Province. In order to gain a prospecting breakthrough, the authors conducted 1:50 000 stream sediment survey, studied the characteristics of element combination of this area by feature analysis and factor analysis of the measuring results. The results show that the three main ore-forming element groups of Ag-Pb-Zn, Bi-F-W-Sn and Cu-Ni have similar enrichment rules, in which the enrichment regularities of W, Sn and other medium and high temperature elements are extremely significant, and the overlapping features of the spatial distribution of the element anomalies are good.The lower limit values were determined by methods of cumulative frequency and iteration. The authors compiled the element anomaly maps and delineated nine comprehensive anomalies. By comprehensive evaluation of the anomalies, the authors consider that the Chahe and Fangjia composite anomalies are the prospective areas. The authors analyzed the geological condition for mineralization, carried out mineral inspection, and discovered a new skarn type tungsten-tin vein in the Chahe prospective area and more than ten new quartz-vein type tungsten veins in the Fangjia prospective area. The Fangjia prospective area, with a certain degree of similarity in geological characteristics with the "five-story+basement" prospecting model for tungsten deposits, has a favorite prospect in the search for polymetallic deposits such as tungsten, copper, lead and molybdenum.
|
|
Received: 22 August 2020
Published: 27 July 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
HAO Xue-Feng
E-mail: 125630276@qq.com;87483931@qq.com
|
|
|
|
9])
">
|
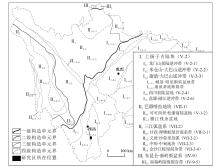
Tectonic map of the Chahe area,Sichuan Province(modified after [9])
|
11])
1—Quaternary; 2—Xiaoba formation; 3—Feitianshan formation; 4—Guangou formation; 5—Niugundang formation; 6—Xincun formation; 7—Yimen formation; 8—Baiguowan formation; 9—mount Emei basalt formation; 10—Hongshiya formation; 11—Erdaoshui formation; 12—Xiwangmiao formation; 13—Qiongzhusi formation; 14—Dengying formation; 15—Guanyinya formation; 16—Lieguliu formation; 17—Tianbaoshan formation; 18—Fengshanying formation; 19—Limahe formation; 20—Tangtang formation; 21—medium grain porphyritic biotite granite; 22—medium grain porphyritic granodiorite; 23—medium grain porphyritic monzogranite; 24—fine grain two mica granite; 25—fine grain porphyritic biotite granite; 26—gneissic granite; 27—granodiorite; 28—metamorphic gabbro; 29—diabase gabbro veins; 30—quartz veins; 31—geological boundaries; 32—measured and inferred sedimentary unconformity boundaries; 33—measured and inferred reverse faults; 34—measured and inferred normal faults; 35—strike-slip faults; 36—undefined faults
">
|
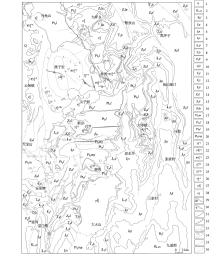
Sketch map of geology and mineral resources of the Chahe area,Sichuan Province (modified after [11])
1—Quaternary; 2—Xiaoba formation; 3—Feitianshan formation; 4—Guangou formation; 5—Niugundang formation; 6—Xincun formation; 7—Yimen formation; 8—Baiguowan formation; 9—mount Emei basalt formation; 10—Hongshiya formation; 11—Erdaoshui formation; 12—Xiwangmiao formation; 13—Qiongzhusi formation; 14—Dengying formation; 15—Guanyinya formation; 16—Lieguliu formation; 17—Tianbaoshan formation; 18—Fengshanying formation; 19—Limahe formation; 20—Tangtang formation; 21—medium grain porphyritic biotite granite; 22—medium grain porphyritic granodiorite; 23—medium grain porphyritic monzogranite; 24—fine grain two mica granite; 25—fine grain porphyritic biotite granite; 26—gneissic granite; 27—granodiorite; 28—metamorphic gabbro; 29—diabase gabbro veins; 30—quartz veins; 31—geological boundaries; 32—measured and inferred sedimentary unconformity boundaries; 33—measured and inferred reverse faults; 34—measured and inferred normal faults; 35—strike-slip faults; 36—undefined faults
|

| 元素 | 均值 | 中值 | 极小值 | 极大值 | 标准差 | 中国高寒山地背景值[13] | 变异系数 | 富集系数 | | Ag | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.50 | 1.16 | | As | 7.99 | 7.14 | 0.94 | 20.87 | 4.32 | 14.20 | 0.54 | 0.56 | | Au | 1.13 | 1.01 | 0.10 | 3.01 | 0.63 | 1.30 | 0.56 | 0.87 | | B | 73.20 | 68.60 | 2.30 | 189.00 | 38.67 | 52.00 | 0.53 | 1.41 | | Bi | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.05 | 1.32 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.43 | 1.81 | | Cd | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.59 | 2.55 | | Co | 19.12 | 18.44 | 1.61 | 44.17 | 8.35 | 10.80 | 0.44 | 1.77 | | Cr | 82.80 | 86.28 | 5.00 | 190.46 | 36.73 | 53.00 | 0.44 | 1.56 | | Cu | 33.78 | 30.78 | 2.68 | 84.10 | 16.84 | 19.20 | 0.50 | 1.76 | | F | 685.9 | 677.9 | 156.1 | 1331.3 | 215.2 | 489.0 | 0.31 | 1.40 | | Hg | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.60 | 2.17 | | Mo | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.10 | 1.62 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.52 | 0.98 | | Ni | 35.18 | 36.36 | 1.83 | 83.62 | 16.16 | 23.90 | 0.46 | 1.47 | | Pb | 31.39 | 30.99 | 2.50 | 62.51 | 10.38 | 22.70 | 0.33 | 1.38 | | Sb | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 1.31 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 0.50 | 0.60 | | Sn | 4.90 | 3.73 | 0.50 | 12.94 | 2.67 | 2.90 | 0.54 | 1.69 | | W | 2.64 | 2.15 | 0.20 | 6.89 | 1.42 | 1.90 | 0.54 | 1.39 | | Zn | 92.30 | 92.41 | 13.97 | 188.38 | 32.12 | 66.00 | 0.35 | 1.40 |
|
Characteristic parameters of element geochemistry after elimination
|

| 元素 | Ag | Au | Bi | Cu | F | Hg | Mo | Ni | Pb | Sb | Sn | W | Zn | | 异常下限 | 0.18 | 3 | 2.5 | 75 | 1000 | 0.11 | 1.2 | 55 | 55 | 1 | 15 | 9 | 150 | | 外带 | 0.18 | 3 | 2.5 | 75 | 1000 | 0.11 | 1.2 | 55 | 55 | 1 | 15 | 9 | 150 | | 中带 | 0.36 | 6 | 5 | 150 | 2000 | 0.22 | 2.4 | 100 | 110 | 2 | 30 | 18 | 300 | | 内带 | 0.72 | 12 | 10 | 300 | 4000 | 0.44 | 4.6 | 200 | 220 | 4 | 60 | 36 | 600 |
|
Values for lower limit and concentration zoning of stream sediment anomalies of major metallogenic elements
|

| 成分 | 初始因子载荷矩阵 | 元素 | 旋转成分矩阵 | | 特征值 | 方差的/% | 累积/% | F1 | F2 | F3 | | F1 | 3.93 | 30.229 | 30.229 | Pb | 0.906 | 0.04 | -0.07 | | F2 | 2.109 | 16.222 | 46.451 | Ag | 0.904 | 0.09 | 0.013 | | F3 | 1.315 | 10.115 | 56.566 | Sb | 0.875 | -0.021 | 0.173 | | F4 | 0.994 | 7.647 | 64.213 | Zn | 0.833 | 0.029 | -0.062 | | F5 | 0.915 | 7.042 | 71.255 | Mo | 0.742 | -0.078 | 0.091 | | F6 | 0.83 | 6.382 | 77.636 | Hg | 0.424 | -0.136 | 0.305 | | F7 | 0.603 | 4.635 | 82.271 | W | -0.035 | 0.759 | -0.027 | | F8 | 0.583 | 4.487 | 86.758 | Bi | -0.022 | 0.747 | 0.071 | | F9 | 0.549 | 4.224 | 90.982 | Sn | -0.042 | 0.733 | 0.017 | | F10 | 0.485 | 3.734 | 94.717 | F | 0.044 | 0.457 | 0.098 | | F11 | 0.352 | 2.705 | 97.422 | Ni | 0.035 | -0.242 | 0.787 | | F12 | 0.202 | 1.551 | 98.972 | Cu | 0.181 | 0.315 | 0.729 | | F13 | 0.134 | 1.028 | 100 | Au | -0.027 | 0.137 | 0.294 |
|
Characteristic parameters of factor analyses
|
|
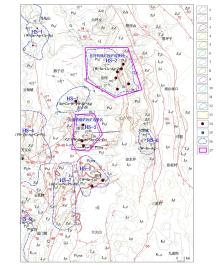
Distribution of the composite anomalies of the major metallogenic elements and prospective areas
1—Au anomaly; 2—Ag anomaly; 3—Bi anomaly; 4—F anomaly; 5—Hg anomaly; 6—Cu anomaly; 7—Mo anomaly; 8—Ni anomaly; 9—Pb anomaly; 10—Zn anomaly; 11—Sb anomaly; 12—Sn anomaly; 13—W anomaly; 14—Tin orebody; 15—Pb-Zn orebody;16—comprehensive anomaly; 17—prospective area
|
12])
1—carbonate of Fengshanying formation; 2—hypabyssal crust-derived granite; 3—metamorphic diabase; 4—sarn; 5—tin orebody; 6—siderite body; 7—fluorite quartz vein; 8—zoning boundary of element combination
">
|
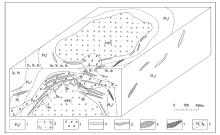
Geological model for Chahe tin deposit (modified after [12])
1—carbonate of Fengshanying formation; 2—hypabyssal crust-derived granite; 3—metamorphic diabase; 4—sarn; 5—tin orebody; 6—siderite body; 7—fluorite quartz vein; 8—zoning boundary of element combination
|
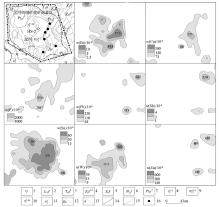
|
Anomaly profile maps of Chahe prospective area
1—Quaternary; 2—first member of Yimen formation; 3—lower member of Baiguowan formation; 4—first member and second member of Dengying formation; 5—Guanyinya formation; 6—Fengshanying formation; 7—first member of Limahe formation; 8—medium grain porphyritic biotite granite; 9—medium grain porphyritic monzogranite; 10—fine grain porphyritic biotite granite; 11—metamorphic gabbro; 12—diabase gabbro veins; 13—quartz veins; 14—geological boundaries; 15—faults; 16—tungsten-tin ores
|
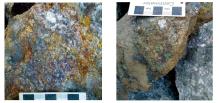
|
Pictures of cassiterite sulfide ore in Chahe mining area
|
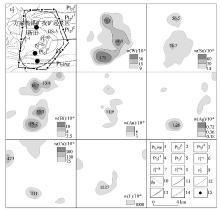
|
Anomaly profile maps of Fangjia prospective area
1—Tangtang formation; 2—third member of Limahe formation; 3—second member of Limahe formation; 4—first member of Limahe formation; 5—Fengshanying formation; 6—gneissic granite; 7—fine grain two mica granite; 8—fine grain porphyritic biotite granite; 9—medium grain porphyritic monzogranite; 10—fine grain porphyritic biotite granite; 11—geological boundaries; 12—faults; 13—anticline; 14—syncline; 15—tungsten-tin ores
|

|
Pictures of tin ore in Fangjia mining area
|
| [1] |
陈毓川, 王登红, 翟裕生, 等. 中国成矿体系与区域成矿评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [1] |
Chen Y C, Wang D H, Zhai Y S, et al. The metallogenic system and regional metallogenic evaluation in Chinese[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
|
| [2] |
彭齐鸣. 四川会理岔河元古宙锡矿床的地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1987, 17(2):177-188.
|
| [2] |
Peng Q M. Geology and genessis of the proterozoic tin deposit at Chahe, Huili, west SiChuan[J], Journal of Changchun College of Geology, 1987, 17(2):177-188.
|
| [3] |
赵一鸣, 吴良士. 中国主要金属矿床成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004.
|
| [3] |
Zhao Y M, Wu L S. Metallogenic regularities of major metal deposits in China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004.
|
| [4] |
李立主. 四川岔河锡矿床地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 云南地质, 1984, 8(1):59-71.
|
| [4] |
Li L Z. Geological characteristics and prospecting criteria of the Chahe tin deposit in Sichuan Province[J]. Yunnan Geology, 1984, 8(1):59-71.
|
| [5] |
谭榜平, 张成江. 四川岔河锡矿地质地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 矿物岩石, 2001, 21(1):67-70.
|
| [5] |
Tan B P, Zhang C J. The characteristics of geology and geochemistry in Chahe tin deposit, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2001, 21(1):67-70.
|
| [6] |
郭春丽, 王登红, 付小方, 等. 四川岔河锡矿区富铟矿石的发现及其找矿意义[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(4):550-556.
|
| [6] |
Guo C L, Wang D H, Fu X F, et al. Discovery of indium-rich ores in Chahe tin deposits, Huili,Sichuan, and its significances[J]. Geological Review, 2006, 52(4):550-556.
|
| [7] |
刘玉红, 周勇. 岔河锡矿外围唐家湾锡多金属矿找矿潜力[J]. 现代矿业, 2016, 562(2):95-97.
|
| [7] |
Liu Y H, Zhou Y. Prospecting potential of Tangjiawan tin polymetallic ore in the periphery of Chahe tin mine[J]. Modern Mining, 2016, 562(2):95-97.
|
| [8] |
程龙. 四川会理县岔河唐家锡多金属矿床地质特征及找矿方向研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017.
|
| [8] |
Cheng L. Geological characteristics and prospecting directions of the Chahe Tangjiawan tin multi-metal deposit in Huili,Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017.
|
| [9] |
张建东, 胡世华, 秦宇龙, 等. 四川省地质构造与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015.
|
| [9] |
Zhang J D, Hu S H, Qin Y L, et al. Geological tectonic and metallogenic in Sichuan Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015.
|
| [10] |
曾云, 贺金良, 王秀京, 等. 四川省成矿区带划分及区域成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015.
|
| [10] |
Zeng Y, He J L, Wang X J, et al. Division of the metallogenic belt and its metallogenic regularity in Sichuan Province [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015.
|
| [11] |
袁兴福, 罗光贵, 杨花明, 等. 1:50000摩挲营幅、益门幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 四川省地矿局攀西地质大队, 1986.
|
| [11] |
Yuan X F, Luo G G, Yang H M, et al. Report of regional geological survey of 1:50000 mosuoying sheet, Yimen sheet[R]. Panxi Geological Team of Sichuan Geological and Mineral Exploration and Development Bureau, 1986.
|
| [12] |
臧兴运, 王建新, 赵利刚, 等. 火山岩区土壤地球化学测量数据的处理与找矿[J]. 黄金, 2007, 28(4):10-13.
|
| [12] |
Zang X Y, Wang J X, Zhao G L, et al. Pedogeochemical survey data processing and ore prospecting in volcanic terrain[J]. Gold, 2007, 28(4):10-13.
|
| [13] |
史长义, 梁萌, 冯斌. 中国水系沉积物39种元素系列背景值[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(2):234-251.
|
| [13] |
Shi C Y, Liang M, Feng B. Average backgound values of 39 chemical elements in stream sediments of China[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(2):234-251.
|
| [14] |
张小静. 西昆仑地区地球化学异常识别及最小预测区划分[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009.
|
| [14] |
Zhang X J. The identification of geochemical anomalies and delineation of prospective mineralization areas in the region of West Kunlun[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology, 2009.
|
| [15] |
师磊. 区域地球化学勘查数据处理方法研究[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2009.
|
| [15] |
Shi L. Study of data processing method in regional geochemical exploration[D]. Jilin: Jilin University, 2009.
|
| [16] |
连盈盈. 盲提取在地球化学异常识别中的应用[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009.
|
| [16] |
Lian Y Y. BSE applied to distinguish geochemical anomaly from background[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology, 2009.
|
| [17] |
王旭辉. 辽宁省义县幅水系沉积物地球化学异常筛选及评价[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2009.
|
| [17] |
Wang X H. Sieving and ealuation of geochemical anomalies of stream sediments in Yixian sheet, Liaoning Province[D]. Jilin: Jilin University, 2009.
|
| [18] |
徐云峰. 西藏甲玛斑岩矿床外围综合信息找矿预测[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014.
|
| [18] |
Xu Y F. Integrated information prospecting prediction of the external of Jiama porphyry deposit, Tibet[D]. Chengdu, Chengdu University of Technology, 2014.
|
| [19] |
刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984.
|
| [19] |
Liu Y J, Cao L M, Li Z L, et al. Elemental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984.
|
| [20] |
翟培英, 刘念池. 蚀变岩型金矿物化探找矿模式初探[J]. 物探与化探, 1987, 11(1):57-63.
|
| [20] |
Zhai P Y, Liu N C. A preliminary discussion on the geophysical and geochemical ore prospecting model for gold deposits of altered rock type[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1987, 11(1):57-63.
|
| [21] |
李连生. 川西锡矿类型的成矿特征及找矿方向[J]. 矿物岩石, 1988(4):1-7.
|
| [21] |
Li L S. Types and minerogenetic features of tin deposits in west Sichuan and their prospecting significance[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 1988(4):1-7.
|
| [22] |
田慧新, 慕纪录, 龚夏生, 等. 四川某锡矿锡石标型特征及矿床成因的初步探讨[J]. 矿物学报, 1981(2):56-66.
|
| [22] |
Tian H X, Mu J L, Gong X S, et al. Typomorphic features of cassiterite and the genesis of a tin deposit in Sichuan Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1981(2):56-66.
|
| [23] |
田慧新, 慕记录, 龚夏生, 等. 四川会理岔河锡矿床锡石标型特征及矿床成因的初步研究[J]. 成都理工大学学报, 1981(1):60-68.
|
| [23] |
Tian H X, Mu J L, Gong X S, et al. Typomorphic features of cassiterite and the genesis of Chahe tin deposit in Huili,Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 1981(1):60-68.
|
| [24] |
许建祥, 曾载淋, 王登红, 等. 赣南钨矿新类型及“五层楼+地下室”找矿模型[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(7):880-887.
|
| [24] |
Xu J X, Zeng Z L, Wang D H, et al. A new type of tungsten deposit in southern Jiangxi and the new model of“five floors +basement” for prospecting[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(7):880-887.
|
| [1] |
JIANG Bing, LIU Yang, WU Zhen, ZHANG De-Ming, SUN Zeng-Bing, MA Jian. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in irrigation water and soils in the Gaomi area, Shandong Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1348-1353. |
| [2] |
NAN Zhe, WANG Lin-Shi, HOU Xu, ZHAI Zheng-Bo, WANG Yang, LIU Yang. Geological and geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of rare element and rare earth element deposits in Saima alkaline complex[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 670-680. |
|
|
|
|

