|
|
|
| Accurate prediction of channel sand based on frequency-divided configuration inversion method:A case study of Zhaohuangzhuang area in Jizhong Sag,Huabei Oilfield |
LIU Hong-Zhou1( ), WANG Meng-Hua1, ZHANG Hao1, PENG Ling-Li1, LI Wen1, ZHANG Jie1, ZHAO Zhi-Peng1, WU Ze-Jing2 ), WANG Meng-Hua1, ZHANG Hao1, PENG Ling-Li1, LI Wen1, ZHANG Jie1, ZHAO Zhi-Peng1, WU Ze-Jing2 |
1. Exploration and Development Research Institute of Huabei Oilfield Company,Renqiu 062552,China
2. New Energy Project of Huabei Oilfield Company,Renqiu 062552,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Channel sand bodies have the characteristics of thin single-layer thickness,small scale,scattered distribution,and strong heterogeneity.In conventional model inversion and prediction,there are problems such as serious modeling,low lateral resolution,and easily damaging the structural morphology of sedimentary bodies,which results in low prediction accuracy.This study uses the frequency-divided configuration inversion method to accurately predict channel sand.This method fully considers the dominant frequency band of logging and seismic and waveform change characteristics,and combines the low,medium and high frequency band models to form the initial model.Then under the framework of Bayesian,the inversion result of the whole frequency band is corrected through the constraints of the seismic synthesis record.In the practice of forecasting thin and small channel sand reservoirs in the Zhaohuangzhuang area,the inversion results have higher vertical and horizontal resolutions,which better support the well placement in this area.The sand body is reasonable and clear for the horizontal stacking relationship and sharp point,and conforms to the distribution characteristics of the sediment body of the meandering river for the plane distribution.Meanwhile,the predicted rate of resolving reservoirs with a thickness of more than 4 m is over 80%.The precise prediction method of thin and small sand bodies based on frequency division configuration inversion has certain guiding significance for the prediction of seismic reservoirs in similar regions or zones.
|
|
Received: 07 June 2020
Published: 15 December 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
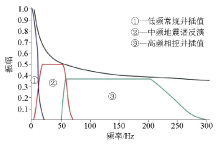
Geological overview map of Zhaohuangzhuang area
|
|
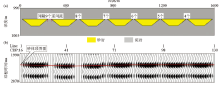
Schematic diagram of frequency division configuration modeling
|
|
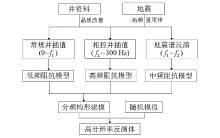
The key technical process of frequency division configuration inversion
|
|
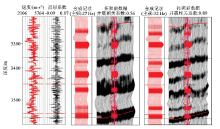
Comparison of seismic profiles before and after frequency extension based on compressed sensing method
a—seismic section before extension frequency;b—seismic spectrum before extension frequency;c—seismic section after extension frequency;d—seismic spectrum after extension frequency
|
|
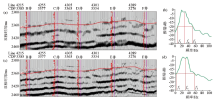
Comparison of well-to-seismic calibration before and after frequency extension
|
|
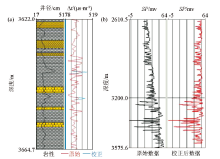
The correction of log curve
a—environmental correction of AC;b—mudstone baseline correction of SP
|
|
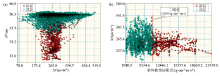
Analysis of rock physical characteristics
a—analysis of AC and SP intersection;b—analysis of reconstructed impedance and AC intersection
|
|
Forward modeling and simulation results
a—analysis of AC and SP intersection;b—analysis of reconstructed impedance and AC intersection
|
|
Comparison of inversion effects of frequency division configuration inversion with different inversion parameters
a—waveform comparison time window 15 ms,waveform similarity degree 0.75;b—waveform comparison time window 30 ms, waveform similarity degree 0.9;c—waveform comparison time window 30 ms,waveform similarity degree 0.5;d—waveform comparison time window 30 ms, waveform similarity degree 0.75
|
|
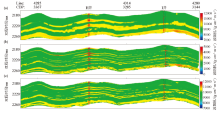
Wave impedance model for different frequency bands
a—mid-low frequency impedance model;b—high frequency impedance model;c—full frequency band impedance model
|
|
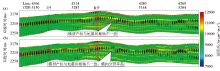
Comparison of initial models of different modeling methods
a—conventional interpolation modeling between wells;b—frequency division configuration modeling
|
|
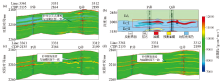
Comparison of different modeling methods and parameter inversion results
a—frequency division configuration inversion(key parameter:30 ms,0.75);b—reservoir profile;c—frequency division configuration inversion(key parameter:30 ms,0.79);d—conventional model inversion
|

| 验证井 | Y1井 | Y2井 | | | 实钻单层砂体厚度/m | 4 | 4.5 | 6 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 3.3 | 1 | 4 | 1.5 | | | 预测单层砂体厚度/m | 4.6 | 5.2 | 6 | 4.5 | 0 | 4.7 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 4.5 | 2 | | | 单层厚度相对误差/% | 15.0 | 15.6 | 0 | 28 | 未识别 | 4.4 | 33.3 | 25.0 | 未识别 | 12.5 | 33.0 | | | 验证井 | Y3井 | Y4井 | | | 实钻单层砂体厚度/m | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 6.5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | | 预测单层砂体厚度/m | 4 | 0 | 4.7 | 2 | 3.5 | 5.8 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 3.5 | 8 | 4.5 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 5.3 | 6 | | 单层厚度相对误差/% | 0 | 未识别 | 17.5 | 0 | -12.5 | -3.3 | 50.0 | 0 | 未识别 | 未识别 | 75.0 | 0 | 12.5 | 7.7 | 0 | 20.0 | 6.0 | 20.0 |
|
Error prediction for thickness of single sand body in target interval
|
|
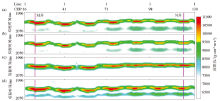
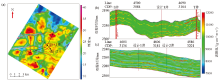
Plan of inversion prediction of sand thickness in target interval
a—sand body thickness of the 1st sand group in the study area;b—inversion profile through well S,design 1 and T;c—inversion profile through well design 1 and design 2
|
| [1] |
姚逢昌, 甘利灯. 地震反演的应用与限制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(2):53-56.
|
| [1] |
Yao F C, Gan L D. Application and restriction of seismic inversion[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(2):53-56.
|
| [2] |
撒利明, 杨午阳, 姚逢昌, 等. 地震反演技术回顾与展望[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2015, 50(1):184-202.
|
| [2] |
Sa L M, Yang W Y, Yao F C, et al. Past present and future of geophysical inversion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2015, 50(1):184-202.
|
| [3] |
王香文, 刘红, 滕彬彬, 等. 地质统计学反演技术在薄储层预测中的应用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(5):730-735.
|
| [3] |
Wang X W, Liu H, Teng B B, et al. Application of geostatistical inversion to thin reservoir prediction[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2012, 33(5):730-735.
|
| [4] |
沈洪涛, 郭乃川, 秦童, 等. 地质统计学反演技术在超薄储层预测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(1):248-253.
|
| [4] |
Shen H T, Guo N C, Qin T, et al. Application of geostatistical inversion for super thin reservoir prediction[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(1):248-253.
|
| [5] |
张国华. 地质统计学反演及其在储层预测中的应用[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学, 2015.
|
| [5] |
Zhang G H. Geostatistical Inversion and its application in reservoir prediction[D]. Qingdao:Ocean University of China, 2015.
|
| [6] |
韩翀, 臧殿光, 李建华. 地质统计学反演在四川盆地L地区储层预测中的应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2010, 32(3):310-315.
|
| [6] |
Han C, Zang D G, Li J H. The application of geostatistical inversion to reservoir prediction of L area in Sichuan basin[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 32(3):310-315.
|
| [7] |
杨涛, 乐友喜, 吴勇. 形指示反演在储层预测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(2):325-332.
|
| [7] |
Yang T, Yue Y X, Wu Y. Application of the waveform inversion in reservoir prediction[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(2):325-332.
|
| [8] |
顾雯, 徐敏, 王铎翰, 等. 地震波形指示反演技术在薄储层预测中的应用——以准噶尔盆地B地区薄层砂岩气藏为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(11):2064-2069.
|
| [8] |
Gu W, Xu M, Wang D H, et al. Application of seismic motion inversion technology in thin reservoir prediction:A case study of the thin sandstone gas reservoir in the B area of Junggar Basion[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(11):2064-2069.
|
| [9] |
韩长城, 林承焰, 任丽华, 等. 地震波形指示反演在东营凹陷王家岗地区沙四上亚段滩坝砂的应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 41(2):60-69.
|
| [9] |
Han C C, Lin C Y, Ren L H, et al. Application of seismic waveform inversion in Es4 beach-bar sandstone in Wangjiagang area,Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum:Science Edition, 2017, 41(2):60-69.
|
| [10] |
高君, 毕建军, 赵海山, 等. 地震波形指示反演薄储层预测技术及其应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 31(1):148-151.
|
| [10] |
Gao J, Bi J J, Zhao H S, et al. Seismic waveform inversion technology and application of thinner reservoir prediction[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 31(1):148-151.
|
| [11] |
郭鹏, 苑益军, 刘喜武, 等. 基于高分辨率波形指示反演方法在“甜点”预测中的应用:以四川盆地焦石坝地区页岩储层为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(2):406-411.
|
| [11] |
Guo P, Yuan Y J, Liu X W, et al. Inversion method based on high-resolution waveform and its application on predicting sweet spots:An example from shale gas reservoirs in Jiaoshiba Area of Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(2):406-414.
|
| [12] |
左兰茹. 高保真高分辨率研究和处理技术[D]. 北京:中国石油勘探开发科学研究院, 2000.
|
| [12] |
Zuo L R. High-fidelity and high-resolution research and processing technology[D]. Beijing:China Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000.
|
| [13] |
韩立国, 张莹, 韩利, 等. 基于压缩感知和稀疏反演的地震数据低频补偿[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(s3):259-264.
|
| [13] |
Han L G, Zhang Y, Han L, et al. Compressed sensing and sparse inversion based low-frequency information compensation of seismic data[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(s3):259-264.
|
| [14] |
江阳. 基于QT的地震谱反演关键技术研究及模块研制[D]. 成都:电子科技大学, 2016.
|
| [14] |
Jiang Y. Key technology research and module development of seismic spectrum inversion based on QT platform[D]. Chengdu:School of Optoelectronic Information, 2016.
|
| [15] |
肖张波. 地震数据约束下的贝叶斯随机反演方法研究[D]. 青岛:中国石油大学(华东), 2013.
|
| [15] |
Xiao Z B. Research on bayesian stochastic inversion constrained by seismic data[D]. Qingdao:China University of Petroleum (East China), 2013.
|
| [1] |
SONG Chen, JIN Ji-Neng, PAN Ren-Fang, ZHU Bo-Yuan, YU Zhi-Hua, TANG Xiao-Ling. Application of frequency division AVO in the gas-bearing analysis of reservoir in the Xu-2 Member of the Anyue gas field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 681-689. |
| [2] |
REN Xian-Jun, LI Zhong, MA Ying-Long, DONG Ping, TIAN Xing-Da. Application of seismic frequency-divided iterative inversion in the prediction of thinly laminated channel sand bodies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 420-428. |
|
|
|
|

