|
|
|
| Gravity characteristics and hydrocarbon prospect of Trinidad Basin |
XING Jin-Cheng1,2( ), YUAN Bing-Qiang1,2, ZHANG Chun-Guan1,2, FENG Xu-Liang1,2, DUAN Rui-Feng1,2, XUE Jian1,2, JIA Hong-Yang1,2, LI Xiang1,2 ), YUAN Bing-Qiang1,2, ZHANG Chun-Guan1,2, FENG Xu-Liang1,2, DUAN Rui-Feng1,2, XUE Jian1,2, JIA Hong-Yang1,2, LI Xiang1,2 |
1. College of Geosciences and Engineering, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an 710065,China
2. ShaanXi Key Lab of Petroleum Accumulation Geology, Xi’an 710065,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Trinidad Basin, which is located in the northern part of Venezuela in South America and the southern margin of the Caribbean Sea has a good prospect for oil and gas resources. The formers have studied the tectonic evolution, sedimentary characteristics of the basin, the work was mainly focused on the southeastern basin, there is lack of research on the characteristics of the structure of the entire basin. In order to study systematically the distribution of faults and basement characteristics of the basin, predict the prospective areas of hydrocarbon, and provide a basis for further hydrocarbon exploration and development in the basin. This paper uses ship log gravity data and satellite gravity data provided by GETECH to analyze and study the characteristics of the gravity field of the basin, infer the fault structure system of the basin. With the constraints of the three existing seismic profiles, the three gravity profiles with the same position as the above seismic profiles were fitted, the basement depth of the basin is calculated combined with correlation analysis and Parker, the structural units and favorable hydrocarbon exploration areas of the basin are predicted. The results show that the structure of Trinidad basin is complex, there are mainly two groups of faults in NE direction and NW direction, the NE-oriented main faults control the scope of the basin and the development of stratum in the basin. The basement of the basin is undulating and can be divided into six structural units: the eastern subbasin, the northern subbasin, the central uplift belt, the central nappe belt, the western subbasin and the western uplift. The eastern sub-basin, the north sub-basin and the western sub-basin are favorable areas for hydrocarbon exploration.
|
|
Received: 13 February 2021
Published: 21 December 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
1],the red line shows the basin area)
">
|
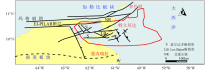
The tectonic sketch of Trinidad (modified after IHS[1],the red line shows the basin area)
|

|
The synthetical stratum histogram of Trinidad Basin
|
|
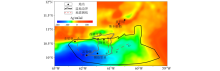
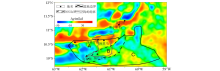
Map of Bouguer gravity anomaly in Trinidad basin and its adjacent areas
|
|
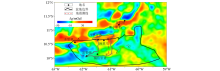
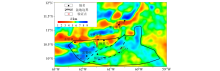
Map of residual gravity anomaly in Trinidad Basin and its adjacent areas
|
|
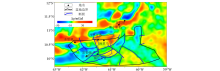
Map of the fault distribution with residual gravity anomaly in Trinidad Basin
|
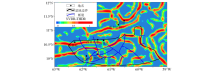
|
Map of the fault distribution with NVDR-THDR of Bouguer gravity anomaly in Trinidad Basin
|
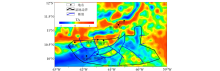
|
Map of the fault distribution with TA of Bouguer gravity anomaly in Trinidad Basin
|
|
2D interpreted and modelled of section AA' (the density unit is 103 kg/m3)
|
|
2D interpreted and modelled of section BB'(the density unit is 103 kg/m3)
|
|
2D interpreted and modelled of section CC' (the density unit is 103 kg/m3)
|
|
Sketch map of basement depth calculation zone
|
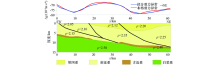
|
Inverse result of basement depth in Trinidad basin by Parker method and location of verification points of inverse result
|

| 点号 | 地震解释深度/m | Parker法反演深度/m | 误差/m | 误差率/% | | A1 | 3894 | 7851 | 3957 | 50.4 | | A2 | 4108 | 6012 | 1905 | 31.7 | | A3 | 3638 | 3461 | -177 | 5.1 | | A4 | 3650 | 1407 | -2242 | 159.3 | | A5 | 2810 | 2154 | -657 | 30.5 | | A6 | 2258 | 1966 | -292 | 14.9 | | B1 | 7930 | 1009 | -6921 | 685.7 | | B2 | 7969 | 1638 | -6331 | 386.5 | | B3 | 8081 | 4062 | -4018 | 98.9 | | B4 | 8137 | 4443 | -3694 | 83.1 | | B5 | 8192 | 4588 | -3604 | 78.5 | | B6 | 8232 | 4734 | -3498 | 73.9 | | B7 | 8264 | 4888 | -3376 | 69.1 | | B8 | 8356 | 5208 | -3148 | 60.4 | | B9 | 8458 | 5217 | -3241 | 62.1 | | B10 | 8555 | 5080 | -3475 | 68.4 | | B11 | 8641 | 5050 | -3591 | 71.1 | | B12 | 8718 | 5368 | -3350 | 62.4 | | B13 | 8786 | 6046 | -2739 | 45.3 | | C1 | 9054 | 7513 | -1541 | 20.5 | | C2 | 9059 | 7493 | -1566 | 20.9 | | C3 | 8876 | 8144 | -732 | 9.0 | | C4 | 8813 | 8797 | -16 | 0.2 | | C5 | 8834 | 9362 | 528 | 5.6 | | C6 | 8893 | 9860 | 967 | 9.8 | | C7 | 9086 | 10414 | 1329 | 12.8 |
|
Comparison table of Parker method inverse results and seismic interpretation depth
|
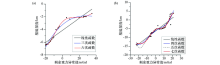
|
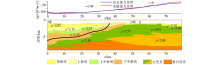
Regression analysis results of residual gravity anomaly and seismic interpretation depth in areas A(a) and B(b)
|
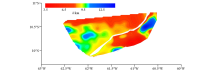
|
Calculated results of basement depth in zone A and B
|

| 点号 | 地震解释深度/m | 相关分析法计算深度/m | 误差/m | 误差率/% | | A1 | 6170 | 7851 | 1681 | 21.4 | | A2 | 6072 | 6012 | -59 | 1.0 | | A3 | 3252 | 3461 | 209 | 6.0 | | A4 | 1350 | 1407 | 58 | 4.1 | | A5 | 2213 | 2154 | -59 | 2.7 | | B1 | 783 | 1009 | 226 | 22.4 | | B2 | 1706 | 1638 | -68 | 4.2 | | B3 | 3517 | 4062 | 546 | 13.4 | | B4 | 4037 | 4443 | 406 | 9.1 | | B5 | 4363 | 4588 | 226 | 4.9 | | B6 | 4497 | 4734 | 237 | 5.0 | | B7 | 4607 | 4888 | 281 | 5.8 | | B8 | 4744 | 5208 | 465 | 8.9 | | B9 | 4806 | 5217 | 411 | 7.9 | | B10 | 4916 | 5080 | 164 | 3.2 | | B11 | 5150 | 5050 | -101 | 2.0 | | B12 | 5530 | 5368 | -163 | 3.0 | | B13 | 6025 | 6046 | 21 | 0.4 |
|
Comparison table of calculation results of correlation-analysis method and seismic interpretation depth
|
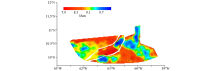
|
Basement depth of Trinidad basin
|

|
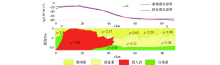
Sketch map of the division of secondary structural units in the Trinidad Basin
|
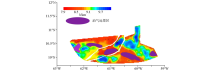
|
Overlay of basement depth calculation results and oil&gas prospects in the Trinidad Basin
|
| [1] |
IHS. Energy and its affiliated and subsidiary companies[R]. Tobago basin, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela, Grenada, Barbados,Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, 2008.
|
| [2] |
袁炳强, 张春灌. 重磁勘探[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2015.
|
| [2] |
Yuan B Q, Zhang C G. Gravity and magnetic prospect [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2015.
|
| [3] |
刘银萍, 王祝文, 杜晓娟, 等. 边界识别技术及其在虎林盆地中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(3):271-278.
|
| [3] |
Liu Y P, Wang Z W, Du X J, et al. Boundary detection method and its application in Hulin Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(3):271-278.
|
| [4] |
杨斯涵. 重磁位场分离及边界识别方法研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2015.
|
| [4] |
Yang S H. Study on the separation of gravity and magnetic potential field and Boundary recognition method[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015.
|
| [5] |
Flinch J F, Rambaran V, Ali W, et al. Chapter 17 Structure of the Gulf of paria pull-apart basin (Eastern Venezuela-Trinidad)[J]. Sedimentary Basins of the World, 1999, 4:477-484.
|
| [6] |
Algar S T, Pindell J L. Structure and deformation history of the northern range of Trinidad and adjacent areas[J]. Tectonics, 1993, 12(4):814-829.

|
| [7] |
Garciacaro E, Mann P, Escalona A. Regional structure and tectonic history of the obliquely colliding Columbus foreland basin, offshore Trinidad and Venezuela[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(1):126-148.
|
| [8] |
Douglas W O. The inversion and interpretation of gravity anomalies[J]. Geophysics, 1974, 39(4):526-536.

|
| [9] |
Robert L P. Best bounds on density and depth from gravity data[J]. Geophysics, 1974, 39(5):644-649.

|
| [10] |
柴玉璞, 贾继军. Parker公式的一系列推广及其在石油重力勘探中的应用前景[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1990, 25(3):321-332.
|
| [10] |
Chai Y P, Jia J J. Parker’s fomulas in different forms and their applications to oil gravity survey[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1990, 25(3):321-332.
|
| [11] |
冯娟, 孟小红, 陈召曦, 等. 三维密度界面的正反演研究和应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(1):287-294.
|
| [11] |
Feng J, Meng X H, Chen Z X, et al. The investigation and application of three-dimensional density interface[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(1):287-294.
|
| [12] |
冯旭亮, 袁炳强, 李玉宏, 等. 渭河盆地基底三维变密度重力反演[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(2):461-471,242.
|
| [12] |
Feng X L, Yuan B Q, Li Y H, et al. Basement depth estimation based on gravity anomalies in Weihe Basin with 3D variable density contrast model[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(2):461-471,242.
|
| [13] |
肖鹏飞, 陈生昌, 孟令顺, 等. 高精度重力资料的密度界面反演[J]. 物探与化探, 2007, 31(1):29-33.
|
| [13] |
Xiao P F, Chen S C, Meng L S, et al. The density interface inversion of high-precision gravity data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 31(1):29-33.
|
| [14] |
Yuan B, Song L, Hang L, et al. Gravity and magnetic field characteristics and hydrocarbon prospects of the Tobago Basin[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2017, 66(8):1586-1601.

|
| [15] |
强洋洋, 袁炳强, 马杰, 等. 利用重力资料研究穆格莱德盆地南部新生界分布[J]. 西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 30(3):18-23.
|
| [15] |
Qiang Y Y, Yuan B Q, Ma J, et al. The study of the distribution of Cenozoic in the southern Muglad Basin based on gravity data[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University:Natural Science Edition, 2015, 30(3):18-23.
|
| [16] |
夏怡凡. SPSS统计分析精要与实例详解[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2010.
|
| [16] |
Xia Y F. SPSS statistical analysis essentials and detailed explanation of examples[D]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2010.
|
| [17] |
Robertson P, Burke K. Evolution of southern Caribbean Plate boundary, vicinity of Trinidad and Tobago[J]. Bulletin American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1989, 73(4):490-509.
|
| [1] |
YANG Rong-Xiang, WANG Wan-Yin, CAI Meng-Ke, WANG Ding-Ding, LUO Xin-Gang. A study of tectonic framework of the Qinnan sag in Bohai Basin and its adjacent areas based on satellite gravity anomalies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 584-596. |
| [2] |
WANG Run-Sheng, WU Bin, ZHANG Hai-Rui, YU Jia-Bin, DONG Yan-Long, GUO Guo-Qiang, KANG Yi-Ming. Gravity field characteristics and boundaries of geotectonic units on the northeastern margin of the Linyi uplift, Shandong Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 279-289. |
|
|
|
|

