|
|
|
| Gravity field characteristics and boundaries of geotectonic units on the northeastern margin of the Linyi uplift, Shandong Province |
WANG Run-Sheng1,2( ), WU Bin3, ZHANG Hai-Rui3, YU Jia-Bin1,2( ), WU Bin3, ZHANG Hai-Rui3, YU Jia-Bin1,2( ), DONG Yan-Long4,5, GUO Guo-Qiang1,2, KANG Yi-Ming1,2 ), DONG Yan-Long4,5, GUO Guo-Qiang1,2, KANG Yi-Ming1,2 |
1. Shandong Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration Institute, Jinan 250013, China
2. Shandong Geological Exploration Engineering Technology Research Center, Jinan 250013,China
3. No. 4 Exploration Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shandong Province, Weifang 261021,China
4. School of Earth Sciences, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),Wuhan 430074, China
5. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China Univesity of Geosciences(Wuhan),Wuhan 430074, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The northeastern margin of the Linyi uplift is located at the eastern end of the Luxi Block and immediately adjacent to the Yishu fault in the east. The main structural framework of the study area is controlled by the NE-trending Tangwu-Gegou fault and the NW-trending Mengshan fault. Covered by the Cenozoic sediments, the boundaries of main tectonic units in the study area are almost all concealed, and it is necessary to further investigate the change in the strike of the eastern end of the Mengshan fault as well as the distribution of the angular unconformity along the northern boundary of the Linyi uplift. Using the latest 1:50,000 high-precision gravity data, this study mainly investigated the positions and intersection relationships of the boundaries of tectonic units based on the qualitative analysis of gravity field, the interpretation of multiple gravity potential field conversion, and the division scheme of geotectonic units in Shandong Province. The analysis results are as follows. The Mengshan fault at the junction of the Mengshan uplift and the Pingyi sag transitions from the NW trending to nearly-EW trending in the east of Bancheng Town, significantly cuts the NE-trending Tangwu-Gegou fault, and shows a NW-trending turn to the east again. The angular unconformity at the junction of the Linyi uplift and the Pingyi sag neither ends in the Mengshan fault in the north nor turns southward but extends to the Tangwu-Gegou fault in the east. This unconformity also controls the southern boundary of the Pingyi sag, making the NW-trending banded gravity anomalies of the sag turn eastward. Consequently, the boot-shaped low-value gravity anomalies were formed in the study area. Based on the high-precision gravity boundary identification, this study determined the fault system and tectonic division of the northeastern margin of the Linyi uplift, providing high-precision gravity data for the basic geological study in the study area and laying a good foundation for further mineral geological survey.
|
|
Received: 29 March 2022
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
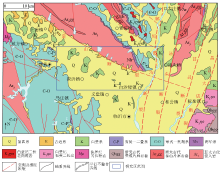
|
Sketch map of regional geological structure
|

| 地质年代 | 地层或序列 | 群或单元 | 岩石名称 | 密度σ/(103kg·m-3) | 密度特征 | | 平均值 | 变化范围 | | 新生代 | 第四系 | | 沙土、黏土 | 1.71 | 1.69~1.78 | 低密度 | | 古近系 | 官庄群 | 泥岩、砾岩 | 2.38 | 2.23~2.43 | | 中生代 | 白垩系 | 青山群 | 潜粗面岩 | 2.51 | 2.40~2.55 | 低密度 | | 莱阳群 | 凝灰岩 | 2.52 | 2.36~2.59 | | 古生代 | 奥陶系 | 马家沟群 | 白云质灰岩 | 2.73 | 2.67~2.82 | 高密度 | | 寒武系 | 九龙群 | 灰岩 | 2.74 | 2.71~2.80 | | 长清群 | 砂岩 | 2.64 | 2.59~2.68 | 中低密度 | | 新元古代 | 南华系 | 土门群 | 砂岩 | 2.68 | 2.63~2.71 | 中等密度 | | 新太古代 | 傲徕山 | 蒋峪单元 | 二长花岗岩 | 2.61 | 2.57~2.65 | 中低密度 |
|
Density characteristics of the study area
|
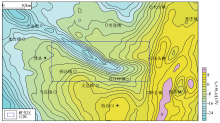
|
Regional bouguer gravity anomaly map
|
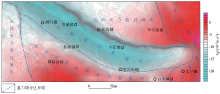
|
Map of bouguer gravity anomaly in the study area
|
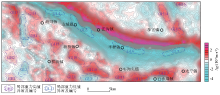
|
Map of residual gravity anomaly in the study area
|
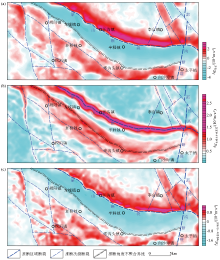
|
Gravity analysis map of fault system division in the study area
a—residual gravity anomaly;b—the horizontal gradient module of Bouguer gravity anomaly;c—the first-order vertical derivatives of Bouguer gravity anomaly
|
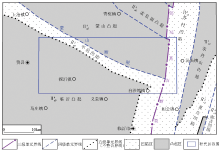
|
Geotectonic background map of the study area
|

| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | | 华北板块 | 鲁西隆起区 | 鲁中隆起 | 蒙山—蒙阴断隆 | 蒙山凸起 | | 尼山—平邑断隆 | 临沂凸起、
平邑凹陷 | | 沂沭断裂带 | 马站—苏村断陷 | 苏村凹陷 |
|
Division of geotectonic units in the study area
|
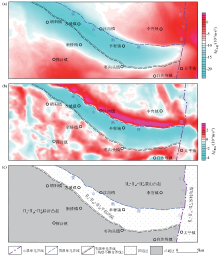
|
Comprehensive schematic diagram of tectonic units division inferred by gravity data
a—bouguer gravity anomaly;b—residual gravity anomaly;c—inferred tectonic units division
|
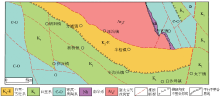
|
Bedrock geological map of pre Neogene inferred by gravity data
|
| [1] |
黄太岭, 高建国. 山东省区域地球物理场[J]. 山东地质, 2002, 18(3/4):88-94.
|
| [1] |
Huang T L, Gao J G. Regional geophysical field in Shandong Province[J]. Geology of Shandong, 2002, 18(3/4):88-94.
|
| [2] |
杜晓娟, 孟令顺, 张凤旭, 等. 利用重磁场研究郯庐断裂及周边构造[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2005, 35(S1):51-56.
|
| [2] |
Du X J, Meng L S, Zhang F X, et al. Study on Tanlu Fault Zone and adjacent area by gravity and magnetic field[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2005, 35(S1):51-56.
|
| [3] |
唐新功, 陈永顺, 唐哲. 应用布格重力异常研究郯庐断裂构造[J]. 地震学报, 2006, 28(6):603-610.
|
| [3] |
Tang X G, Chen Y S, Tang Z. Bouguer gravity study of middle section of Tanlu Fault[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2006, 28(6):603-610.
|
| [4] |
王鑫, 张景发, 付萍杰, 等. 沂沭断裂带重力场及地壳结构特征[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(3):731-747.
|
| [4] |
Wang X, Zhang J F, Fu P J, et al. Deep structures of Yishu Fault Zone derived from gravity data[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2015, 37(3):731-747.
|
| [5] |
于磊, 张健, 高玲举, 等. 鲁西隆起重磁异常特征及其构造活动性分析[J]. 地震学报, 2017, 39(5):694-707.
|
| [5] |
Yu L, Zhang J, Gao L J, et al. Gravity magnetic anomalies and tectonic activities in Luxi uplift[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2017, 39(5):694-707.
|
| [6] |
晁洪太, 崔昭文, 李家灵. 鲁中地区北西向断裂及其第四纪晚期的活动特征[J]. 地震学刊, 1992(2):1-10.
|
| [6] |
Chao H T, Cui Z W, Li J L. The N-W trending faults in middle part of Shandong Province and their activities in the late Quaternary[J]. Journal of Seismology, 1992(2):1-10.
|
| [7] |
王志才, 石荣会, 晁洪太, 等. 鲁中南隆起区第四纪晚期断裂活动特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(4):95-102.
|
| [7] |
Wang Z C, Shi R H, Chao H T, et al. Characteristics of the Quaternary fault activities in the middle and south region of Shandong Province[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(4):95-102.
|
| [8] |
王先美, 钟大赉, 王毅. 鲁西北西向断裂系晚中生代活动的几何学、运动学及年代学研究[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(9):1258-1273.
|
| [8] |
Wang X M, Zhong D L, Wang Y. Geometry,kinematics and thermochronology study of the late Mesozoic movement of NW-trending faults,Western Shandong[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(9):1258-1273.
|
| [9] |
王先美, 钟大赉, 李理, 等. 鲁西北西向断裂系与沂沭断裂带晚中生代演化关系及其动力学背景探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(3):166-190.
|
| [9] |
Wang X M, Zhong D L, Li L, et al. Relationship between NW faults of West Shandong and Yishu fault zone in late Mesozoic and their geotectonic setting operations[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(3):166-190.
|
| [10] |
张鹏, 王良书, 石火生, 等. 郯庐断裂带山东段的中新生代构造演化特征[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(9):1316-1323.
|
| [10] |
Zhang P, Wang L S, Shi H S, et al. The Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Shandong segment of the Tanlu Fault Zone[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(9):1316-1323.
|
| [11] |
谢庆宾, 管守锐, 李熙哲. 山东平邑盆地官中段沉积环境和层序地层特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(1):71-77.
|
| [11] |
Xie Q B, Guan S R, Li X Z. Depositional environment and sequence stratigraphy characteristics of middle member of the Guanzhong Formation in the Pingyi Basin,Shandong[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(1):71-77.
|
| [12] |
宋奠南. 山东中新生代盆地基本特征及演化过程[J]. 山东地质, 2001, 17(5):5-10.
|
| [12] |
Song D N. Basic characteristics and evolution history of Meso-Cenozoic Basins in Shandong Province[J]. Geology of Shandong, 2001, 17(5):5-10.
|
| [13] |
陈华国, 赵艳杰, 甘延景, 等. 平邑盆地古近纪官庄群沉积建造与膏岩富集规律[J]. 山东国土资源, 2008, 24(5):30-32,36.
|
| [13] |
Chen H G, Zhao Y J, Gan Y J, et al. Sedimentary foundation and plaster rock concentration rules of Paleogene Guanzhuang Group in Pingyi Basin[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2008, 24(5):30-32,36.
|
| [14] |
张增奇, 刘书才, 杜圣贤, 等. 山东省地层划分对比厘定意见[J]. 山东国土资源, 2011, 27(9):1-9.
|
| [14] |
Zhang Z Q, Liu S C, Du S X, et al. Determination opinions on stratigraphic division and correlation in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2011, 27(9):1-9.
|
| [15] |
孙天柱, 武斌. 临沂方城盆地中生代青山群火山岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 山东国土资源, 2020, 36(6):14-22.
|
| [15] |
Sun T Z, Wu B. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of volcanic rocks in Mesozoic Qingshan Group in Fangcheng Basin of Linyi City[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2020, 36(6):14-22.
|
| [16] |
晁洪太, 李家灵, 崔昭文, 等. 山东中部一条明显的北西向中强地震带[J]. 华北地震科学, 1998, 16(2):23-29.
|
| [16] |
Chao H T, Li J L, Cui Z W, et al. An evident NW-trending seismic zone of medium-strong earthquake in central Shandong Province[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 1998, 16(2):23-29.
|
| [17] |
牛树银, 胡华斌, 毛景文, 等. 鲁西地区地质构造特征及其形成机制[J]. 中国地质, 2004, 31(1):34-39.
|
| [17] |
Niu S Y, Hu H B, Mao J W, et al. Structure in Western Shandong and its genetic mechanism[J]. Geology in China, 2004, 31(1):34-39.
|
| [18] |
王万银, 张瑾爱, 刘莹, 等. 利用重磁资料研究莺—琼盆地构造分界及其两侧断裂特征[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2013, 28(3):1575-1583.
|
| [18] |
Wang W Y, Zhang J A, Liu Y, et al. Research on the tectonic boundary of Yingqiong Basin and adjacent faults' features based on gravity and magnetic data[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2013, 28(3):1575-1583.
|
| [19] |
曾琴琴, 王永华, 李富, 等. 重力异常垂向二阶导数在攀西裂谷特征分析中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(1):29-33.
|
| [19] |
Zeng Q Q, Wang Y H, Li F, et al. Application of the vertical second derivative of gravity anomaly for characteristics analysis of Panxi Rift[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(1):29-33.
|
| [20] |
马涛, 朱莹洁, 杨永, 等. 基于重磁异常的嘉偕平顶山群构造区划特征研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):938-948.
|
| [20] |
Ma T, Zhu Y J, Yang Y, et al. Research on tectonic division in Jiaxie guyots based on gravity and magnetic anomalies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):938-948.
|
| [21] |
许文强, 袁炳强, 刘必良, 等. 多种重磁位场边缘识别方法及在南黄海北部断裂构造识别中的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):962-974.
|
| [21] |
Xu W Q, Yuan B Q, Liu B L, et al. Multiple gravity and magnetic potential field edge detection methods and their application to the boundary of fault structures in northern South Yellow Sea[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):962-974.
|
| [22] |
张磊, 王万银, 赵修军, 等. 基于重磁场特征的新蔡铁矿区构造单元分布特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):975-984.
|
| [22] |
Zhang L, Wang W Y, Zhao X J, et al. Distribution characteristics of structural units in the Xincai iron ore district based on gravity and magnetic field characteristics[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):975-984.
|
| [23] |
王润生, 郝兴中, 陈大磊, 等. 山东齐河—禹城地区矽卡岩型铁矿成矿地质体边界讨论及深部特征研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(1):59-68.
|
| [23] |
Wang R S, Hao X Z, Chen D L, et al. Discussion on the boundary of metallogenic geological body of skarn type iron deposits and study on its deep characteristics in Qihe-Yucheng area,Shandong Province[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37 (1):59-68.
|
| [24] |
王润生, 郝兴中, 刘洪波, 等. 鲁西齐河地区矽卡岩型铁矿重磁方法找矿规律研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(2):664-677.
|
| [24] |
Wang R S, Hao X Z, Liu H B, et al. Study on prospecting law of skarn type iron deposit by gravity and magnetic method in Qihe area of western Shandong[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(2):664-677.
|
| [25] |
李三忠, 王金铎, 刘建忠, 等. 鲁西地块中生代构造格局及其形成背景[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(4):487-497.
|
| [25] |
Li S Z, Wang J D, Liu J Z, et al. Mesozoic structure and its tectonic setting in the Western Shandong Block[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(4):487-497.
|
| [26] |
宋明春. 山东省大地构造单元组成、背景和演化[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2008, 31(3):165-175.
|
| [26] |
Song M C. The composing,setting and evolution of tectonic units in Shandong Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2008, 31(3):165-175.
|
| [27] |
李洪奎, 杨永波, 耿科, 等. 山东重大基础地质问题研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2):594-606.
|
| [27] |
Li H K, Yang Y B, Geng K, et al. Research progress on major basic geological problems in Shandong Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(2):594-606.
|
| [28] |
张增奇, 张成基, 王世进, 等. 山东省地层侵入岩构造单元划分对比意见[J]. 山东国土资源, 2014, 30(3):1-23.
|
| [28] |
Zhang Z Q, Zhang C J, Wang S J, et al. Views on classification and contrast of tectonic units in strata in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2014, 30(3):1-23.
|
| [1] |
YANG Rong-Xiang, WANG Wan-Yin, CAI Meng-Ke, WANG Ding-Ding, LUO Xin-Gang. A study of tectonic framework of the Qinnan sag in Bohai Basin and its adjacent areas based on satellite gravity anomalies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 584-596. |
| [2] |
SUN Zheng, WANG Jun, DING Peng, TAN Xin. Amethod for determining the optimal height for upward continuation of gravity anomalies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 162-170. |
|
|
|
|

