|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and environmental assessment of heavy metal elements in agricultural soil of Anqiu area, Shandong Province |
ZHAO Xiu-Fang1( ), ZHANG Yong-Shuai1, FENG Ai-Ping1, WANG Yi-Xuan2, XIA Li-Xian1, WANG Hong-Lei1, DU Wei1 ), ZHANG Yong-Shuai1, FENG Ai-Ping1, WANG Yi-Xuan2, XIA Li-Xian1, WANG Hong-Lei1, DU Wei1 |
1. The Seventh Geological and Mineral Exploration Institute, Linyi 276006,China
2. College of Horticulture, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing 210095,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In order to understand the status of soil heavy metal pollution in Anqiu Area, Shandong Province,10 194 soil samples are systematically collected,the contents of 8 heavy metal elements including Cd, Hg, Pb and As are tested and analyzed.The geochemical distribution characteristics of heavy metal elements and their possible sources are discussed by using geostatistical and multivariate statistical methods.The results show that the average contents of Cd, Hg and As in the soil of the study area are similar to the background values of Weifang soil, and the average contents of other elements are slightly higher than the soil background values of Weifang.The average contents of the 8 heavy metal elements are all lower than risk screening values of standard. According to cluster analysis,eight heavy metal elements are mainly divided into four categories.The first category is Cr, Ni, Cu and Zn, whose distributions are mainly affected by natural factors such as the parent material of the soil, while Zn is also affected by human activities.The second category is Cd,Pb and the third category is Hg. The distribution characteristics of these elements are greatly affected by human activities such as metal smelting and processing, transportation, mining, etc.The fourth category is As, which is not only inherited from the the parent material of the soil, but also affected by human activities. The soil environmental quality in the study area is evaluated by Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land(GB 15618—2018),the results show that the soil environment in the study area is mainly safe zone, risk-freeand. Point source pollution only exists in some places.
|
|
Received: 06 November 2019
Published: 29 December 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
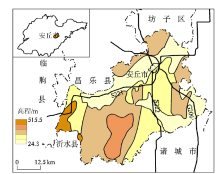
|
Geographical location map of Anqiu City
|
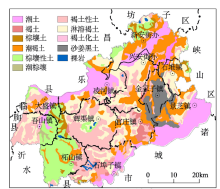
|
Soil type map of Anqiu City
|
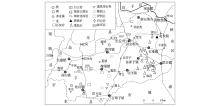
|
Major mineral distribution sketch
|

污染
项目 | 风险筛选值/10-6 | | pH≤5.5 | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | pH>7.5 | | 镉 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.6 | | 汞 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 3.4 | | 砷 | 40 | 40 | 30 | 25 | | 铅 | 70 | 90 | 120 | 170 | | 铬 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 250 | | 铜 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 | | 镍 | 60 | 70 | 100 | 190 | | 锌 | 200 | 200 | 250 | 300 |
|
Risk screening values for soil contamination of agricultural land
|

污染
项目 | 风险管控值/10-6 | | pH≤5.5 | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | pH>7.5 | | 镉 | 1.5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | | 汞 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 4 | 6 | | 砷 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 100 | | 铅 | 400 | 500 | 700 | 1000 | | 铬 | 800 | 850 | 1000 | 1300 |
|
Risk control values for soil contamination of agriculturalland
|

| 等级 | 一等 | 三等 | 三级 | | 污染风险 | 无风险 | 风险可控 | 风险较高 | | 划分方法 | Ci≤Si | Ci<Si≤Gi | Ci>Gi |
|
Geochemical classification for soil environment
|

| 元素 | 最大值/10-6 | 最小值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 中值/10-6 | 标准差 | Cv/% | 偏度 | 峰度 | 潍坊市土壤
背景值[21] | | Cd | 5.96 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 94.90 | 1246.09 | 30.37 | 0.11 | | Hg | 2.290 | 0.001 | 0.033 | 0.030 | 0.046 | 138.40 | 1310.1 | 31.29 | 0.03 | | Pb | 1665.10 | 3.10 | 28.33 | 24.18 | 31.07 | 109.70 | 1004.05 | 25.27 | 22.90 | | As | 223.00 | 0.01 | 7.79 | 7.70 | 4.02 | 51.60 | 861.03 | 17.84 | 7.80 | | Cr | 2227.00 | 6.09 | 80.38 | 68.30 | 49.45 | 61.50 | 358.31 | 10.38 | 65.30 | | Ni | 1084.00 | 2.94 | 37.21 | 29.70 | 31.27 | 84.00 | 137.57 | 7.02 | 26.90 | | Cu | 288.00 | 3.63 | 25.19 | 23.10 | 11.10 | 44.10 | 43.32 | 3.76 | 21.20 | | Zn | 1129.16 | 6.40 | 67.19 | 63.81 | 27.26 | 40.60 | 406.01 | 13.2 | 58.50 |
|
Statistical characteristic values of heavy metal element contents in surface soil
|
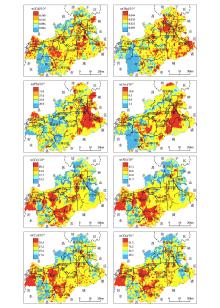
|
Spatial distribution of heavy metals in surface soil
|

| 元素 | Cd | Hg | Pb | As | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | | Cd | 1 | | | | | | | | | Hg | 0.087** | 1 | | | | | | | | Pb | 0.583** | 0.059** | 1 | | | | | | | As | 0.145** | 0.095** | 0.175** | 1 | | | | | | Cr | 0.053** | -0.035** | -0.090** | -0.067** | 1 | | | | | Ni | 0.058** | -0.042** | -0.094** | -0.066** | 0.910** | 1 | | | | Cu | 0.187** | ﹣ | ﹣ | 0.037** | 0.616** | 0.697** | 1 | | | Zn | 0.571** | 0.036** | 0.295** | 0.067** | 0.403** | 0.429** | 0.625** | 1 |
|
Correlations matrix for the heavy metals in soil
|

| 元素 | 主成分 | | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | | Cd | 0.409 | 0.775 | -0.176 | -0.133 | | Hg | 0.011 | 0.218 | 0.825 | -0.498 | | Pb | 0.170 | 0.802 | -0.191 | -0.047 | | As | 0.031 | 0.390 | 0.498 | 0.786 | | Cr | 0.829 | -0.385 | 0.054 | 0.036 | | Ni | 0.861 | -0.385 | 0.052 | 0.043 | | Cu | 0.855 | -0.116 | 0.076 | 0.050 | | Zn | 0.777 | 0.362 | -0.097 | -0.082 | | 特征值 | 2.961 | 1.884 | 1.017 | 0.090 | | 方差/% | 37.02 | 23.56 | 12.71 | 11.23 | | 贡献率/% | 37.02 | 60.57 | 73.28 | 84.46 |
|
Factors matrix of heavy metal elements in surface soil
|
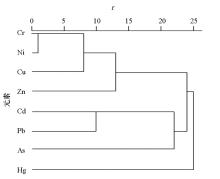
|
Hierarchical cluster analysis of heavy metal elements in surface soil
|

| 元素 | 成土母岩 | | 冲洪积物 | 玄武岩 | 火山岩 | 石灰岩 | 闪长岩 | 花岗岩 | | Cd | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.11 | | Hg | 0.034 | 0.024 | 0.03 | 0.0305 | 0.026 | 0.019 | | Pb | 24.45 | 17.57 | 25.46 | 23.235 | 26.99 | 19.96 | | As | 7.55 | 5.75 | 9.01 | 9.48 | 8.57 | 7.44 | | Cr | 68.12 | 172.50 | 74.28 | 72.2 | 60.26 | 139.78 | | Ni | 29.11 | 112.56 | 31.64 | 34.2 | 25.05 | 70.74 | | Cu | 22.57 | 46.13 | 24.78 | 25.91 | 20.55 | 30.92 | | Zn | 63.16 | 95.12 | 68.13 | 70.235 | 60.93 | 71.68 |
|
Soil heavy metal elementcontents in the different parent rocks10-6
|
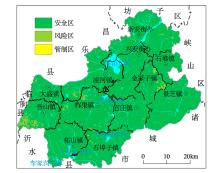
|
Comprehensive geochemical evaluation map of soil environment
|
| [1] |
崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 宋泽峰, 等. 石家庄城市土壤重金属空间分布特征及源解析[J]. 中国地质, 2016,43(2):683-690.
|
| [1] |
Cui X T, Luan W L, Song Z F, et al. A study of the spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in urban soil in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Geology in China, 2016,43(2):683-690.
|
| [2] |
冯乙晴, 刘灵飞, 肖辉林, 等. 深圳市典型工业区土壤重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017,26(6):1051-1058.
|
| [2] |
Feng Y Q, Liu L F, Xiao H L, et al. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil of typical industrial district of Shenzhen[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017,26(6):1051-1058.
|
| [3] |
李泽琴, 侯佳渝, 王奖臻. 矿山环境土壤重金属污染潜在生态风险评价模型探讨[J]. 地球科学进展, 2008,23(5):509-516.
|
| [3] |
Li Z Q, Hou J Y, Wang J Z. Potential ecological risk assessment model for heavy metal contamination of agricultural soils in mining areas[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2008,23(5):509-516.
|
| [4] |
段飞舟, 高吉喜, 何江, 等. 灌溉水质对污灌区土壤重金属含量的影响分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2005,24(3):450-455.
|
| [4] |
Duan F Z, Gao J X, He J, et al. Impact of irrigation water quality on heavy metals concentrations in surface soil of paddy field[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2005,24(3):450-455.
|
| [5] |
王腾飞, 谭长银, 曹雪莹, 等. 长期施肥对土壤重金属积累和有效性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017,36(2):257-263.
|
| [5] |
Wang T F, Tan C Y, Cao X Y, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on the accumulation and availability of heavy metals in soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017,36(2):257-263.
|
| [6] |
张英英, 施志国, 李彦荣. 不同耕作方式对民勤绿洲耕层土壤理化性状及重金属含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019,28(1):207-214.
|
| [6] |
Zhang Y Y, Shi Z G, Li Y R, et al. Effects of different tillage methods on soil physical-chemical properties and heavy metal content in Minqin Oasis[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019,28(1):207-214.
|
| [7] |
李苹, 黄勇, 林贇, 等. 北京市怀柔区土壤重金属的分布特征、来源分析及风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018,32(1):86-94.
|
| [7] |
Li P, Huang Y, Lin Y, et al. Distribution,source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil of Huairou district in Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 2018,32(1):86-94.
|
| [8] |
李芳, 钱秋芳. 土壤重金属污染研究进展[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2011,17(10):80-82,202.
|
| [8] |
Li F, Qian Q F. Advances in pollution of heavy metals in soil[J]. Anhui Agri. Sci. Bull., 2011,17(10):80-82,202.
|
| [9] |
段续川, 李苹, 黄勇, 等. 北京市密云区农业土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018,32(1):95-104.
|
| [9] |
Duan X C, Li P, Huang Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils in Miyun district of Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 2018,32(1):95-104.
|
| [10] |
刘庆, 杜志勇, 史衍玺, 等. 山东省寿光市土壤重金属环境质量评价[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2009,31(1):144-148.
|
| [10] |
Liu Q, Du Z Y, Shi Y X, et al. Evaluationon environmental quality of heavy metals in Shouguang City,Shandong Province[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxi Ensis, 2009,31(1):144-148.
|
| [11] |
黄勇, 杨忠芳, 张连志, 等. 基于重金属的区域健康风险评价——以成都经济区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2008,22(6):990-997.

|
| [11] |
Huang Y, Yang Z F, Zhang L Z, et al. Regional health risk assessmenton heavy metalsin Chengdu economic region[J]. Geoscience, 2008,22(6):990-997.
|
| [12] |
徐友宁, 张江华, 柯海玲, 等. 某金矿区农田土壤重金属污染的人体健康风险[J]. 地质通报, 2014,33(8):1239-1252.
|
| [12] |
Xu Y N, Zhang J H, Ke H L, et al. Human health risk under the condition of farmland soil heavy metals pollution in a gold mining area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014,33(8):1239-1252.
|
| [13] |
夏芳, 王秋爽, 蔡立梅, 等. 有色冶金区土壤—蔬菜系统重金属污染特征及健康风险分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2017,26(6):865-873.
|
| [13] |
Xia F, Wang Q S, Cai L M, et al. Contamination and health risk for heavy metals via consumption of vegetables grown in non-freeous metals smel ting area[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2017,26(6):865-873.
|
| [14] |
Chai J, Guo J, Chai S L, et al. Source identification of eight heavy metals in grassland soils by multivariate analysis from the Baicheng-Songyuan area,Jilin Province,Northeast China[J]. Chemosphere, 2015,134:67-75.

|
| [15] |
Cao L L, Tian H T, Yang J, et al. Multivariate analyses and evaluation of heavy metals by chemometric BCR sequential extraction method in surface sediments from Lingdingyang Bay,South China[J]. Sustainability, 2015,7:493-495.
|
| [16] |
吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析和环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2012,67(7):971-984.

|
| [16] |
Lyu J S, Zhang Z L, Liu Y, et al. Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao City[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012,67(7):971-984.
|
| [17] |
李湘凌, 周涛发, 殷汉琴, 等. 基于层次聚类法和主成分分析法的铜陵市大气降尘污染元素来源解析研究[J]. 地质评论, 2010,56(2):283-288.
|
| [17] |
Li X L, Zhou T F, Yin H Q, et al. Sources analysis of dustfall in Tongling City based on hierarchical cluster analysis and principal component analysis methods[J]. Geological Review, 2010,56(2):283-288.
|
| [18] |
王志楼, 谢学辉, 王慧萍, 等. 典型铜尾矿库周边土壤重金属复合污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2010,19(1):113-117.
|
| [18] |
Wang Z L, Xie X H, Wang H P, et al. Combined pollution character of heavy metals in soils around a typical copper tailing[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010,19(1):113-117.
|
| [19] |
张慧, 付强, 赵映慧. 松嫩平原北部土壤重金属空间分异特征及生态安全评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2013,2:165-169.
|
| [19] |
Zhang H, Fu Q, Zhao Y H. Spatial variability of soil heavy metalsand ecological quality assessment in the northern Songnen plain[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013,2:165-169.
|
| [20] |
生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 15618—2018 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2018.
|
| [20] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land[S]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing, 2018.
|
| [21] |
庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 陈磊, 等. 山东省17市土壤地球化学背景值[J]. 山东国土资源, 2019,35(1):46-56.
|
| [21] |
Pang X G, Dai J R, Chen L, et al. Soil geochemical background value of 17 cities in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2019,35(1):46-56.
|
| [22] |
Zhao Y C, Wang Z G, Sun W X, et al. Spatial interrelations and multi-scale sources of soil heavy metal variability in a typical urban-rural transition area in Yangtze River Delta region of China[J]. Geoderma, 2010,156(3/4):216-227.
|
| [23] |
David M G, Zhang C S, Owen T. Carton geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in Silvermines area,Ireland[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2004,127(2):239-248.

|
| [24] |
高吉喜, 段飞舟, 香宝. 主成分分析在农田土壤环境评价中的应用[J]. 地理研究, 2006,25(2):836-842.
|
| [24] |
Gao J X, Duan F Z, Xiang B. The application of principal component analysis to agriculture soil contamination assessment[J]. Geographical Research, 2006,25(2):836-842.
|
| [25] |
陈晓晨, 崔岩山. 城市表层土壤中重金属的小尺度空间分布——以首钢厂区附近小区为例[J]. 中科院研究生院学报, 2010,27(2):176-183.
|
| [25] |
Chen X C, Cui Y S. Small-scalespatial distribution of heavy metal sinurbantop soil: A case study in a small erea near Shougang group[J]. Journal of the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010,27(2):176-183.
|
| [26] |
姜佰文, 陆磊, 王春宏, 等. 施用有机肥对土壤重金属累积的影响及风险评价[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2020,51(4):37-44.
|
| [26] |
Jiang B W, Lu L, Wang C H, et al. Effect of organic fertilizer application on heavy metals accumulation in soil and risk assessment[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2020,51(4):37-44.
|
| [27] |
唐明海. 土壤重金属污染对农产品质量安全的影响及其防治分析[J]. 河南农业, 2019(3):48-49.
|
| [27] |
Tang M H. Effects of soil heavy metal pollution on the quality and safety of agricultural products and its control[J]. Henan Agriculture, 2019(3):48-49.
|
| [28] |
敖明, 柴冠群, 范成五, 等. 稻田土壤和稻米中重金属潜在污染风险评估与来源解析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019,35(6):198-205.
|
| [28] |
Ao M, Chai G Q, Fan C W, et al. Evaluation of potential pollution risk and source analysis of heavy metals in paddy soil and rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019,35(6):198-205.
|
| [29] |
陈雅丽, 翁莉萍, 马杰, 等. 近十年中国土壤重金属污染源解析研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019,38(10):2219-2238.
|
| [29] |
Chen Y L, Weng L P, Ma J, et al. Review on the last ten years of research on source identification of heavy metal pollution in soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019,38(10):2219-2238.
|
| [1] |
WANG Zhi-Qiang, YANG Jian-Feng, WEI Li-Xin, SHI Tian-Chi, CAO Yuan-Yuan. Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium in alkaline soil in Shizuishan area, Ningxia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 229-237. |
| [2] |
XU Yun-Feng, HAO Xue-Feng, QIN Yu-Long, WANG Xian-Feng, XIONG Chang-Li, LI Ming-Ze, WU Weng-Hui, ZHAN Han-Yu. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in Chahe area of Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 624-638. |
|
|
|
|

