|
|
|
| Optimizing the key acquisition parameters of variable-depth streamer in Xihu sag |
Fu-Qiang HUANG( ), Bin LI, Yi-Biao ZHANG, Bin HU, Qi-Kun FENG ), Bin LI, Yi-Biao ZHANG, Bin HU, Qi-Kun FENG |
| Shanghai Geophysical Branch,Sinopec Offshore Oilfield Services Company,Shanghai 201208,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Xihu sag is the largest oil-bearing sag in the East China Sea.The main reservoir of the Xihu sag is located in the middle and deep strata.Adding low frequency information is one of the core issues for solving the main geological problems in the Xihu sag.The variable-depth streamer acquisition technology can effectively suppress ghost waves,broaden the frequency band,especially the low frequency,and has the advantages of simple field operation and low cost,which is beneficial to solving the geological problems of the Xihu sag.Based on the average ghost filter of variable-depth streamer,the key acquisition parameters are theoretically analyzed,such as streamer mode and the streamer depth range.Through 2D field test,a further comparative study was carried out on the raw shot and PSTM record.It is concluded that,for the deep reservoirs of the Xihu sag,the variable-depth streamer is more clearly structured than the conventional horizontal streamer data,and the frequency band has been broadened. Among the two commonly used streamer modes,the linear streamer has better notch compensation effect,and the parabolic streamer has higher low frequency energy.When the shallowest depth of the variable-depth streamer is fixed,increasing the depth range is beneficial to obtaining more low frequency information.
|
|
Received: 21 October 2019
Published: 28 August 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
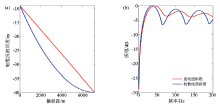
|
Different streamer modes(a) and the average amplitude spectrum(b)
|
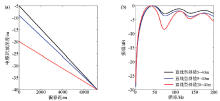
|
Linear variable-depth streamers with different minimum sinking depths(a) and the average amplitude spectrum(b)
|

|
Parabolic variable-depth streamers with different minimum sinking depths(a) and the average amplitude spectrum(b)
|
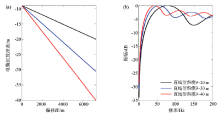
|
Linear variable-depth streamers with different maximum sinking depths(a) and the average amplitude spectrum(b)
|
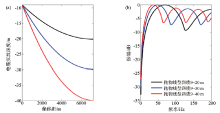
|
Parabolic variable-depth streamers with different maximum sinking depths(a) and the average amplitude spectrum(b)
|

| 方案 | 斜缆缆型 | 电缆沉放深度/m | 电缆长度/m | 覆盖次数 | 震源容量/in3 | 震源沉放深度/m | | 1 | 抛物线型 | 9~30 | 7200 | 96 | 5800 | 7 | | 2 | 抛物线型 | 9~40 | 7200 | 96 | 5800 | 7 | | 3 | 直线型 | 9~40 | 7200 | 96 | 5800 | 7 |
|
Field test parameter table of variable-depth streamer in Xihu Sag
|
|
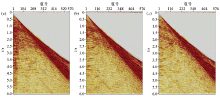
Raw shots of the different streamer mode at the same location
a—9~30 m parabolic streamer;b—9~40 m parabolic streamer;c—9~40 m linear streamer
|
|
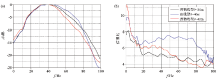
Specrtum (a) and S/N ratio (b) of the raw shots (Analysis windows:2.5~4.5 s)
|
|
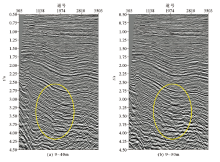
Compared with different variable-depth streamer depth range migration
|
|
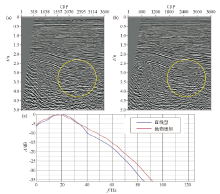
The PSTM of parabolic variable-depth streamer(a) and linear variable-depth streamer(b),comparison of their spectrum(c)
|
|
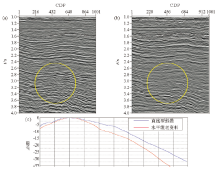
The PSTM of linear variable-depth streamer(a)and horizontal streamer(b),comparison of their spectrum(c)
|
| [1] |
周心怀, 蒋一鸣, 唐贤君. 西湖凹陷成盆背景、原型盆地演化及勘探启示[J]. 中国海上油气, 2019,31(3):1-10.
|
| [1] |
Zhou X H, Jiang Y M, Tang X J. Tectonic setting,prototype basin evolution and exploration enlightenment of Xihu sag in East China sea basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2019,31(3):1-10.
|
| [2] |
叶加仁, 顾惠荣, 贾健谊. 东海西湖凹陷油气地质条件及其勘探潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008,28(4):111-116.
|
| [2] |
Ye J R, Gu H R, Jia J Y. Petroleum geological condition and exploration potential of Xihu depression,East China sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008,28(4):111-116.
|
| [3] |
Bearnth R E, Moore N A. Broad-band recording through ghost elimination[C]// 22nd Offshore Technology Conference, 1990:579-584.
|
| [4] |
Amundsee L. Wavenumber-based filtering of marine point-source data[J]. Geophysics, 1993,58(9):1335-1348.
|
| [5] |
Soubaras R, Dowle R. Variable-depth streamer-a broadband marine solution[J]. First Break, 2010,28(12):89-96.
|
| [6] |
Soubaras R. Deghosting by joint deconvolution of a migration and a mirror migration[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2010,29(1):3406-3410.
|
| [7] |
Soubaras R, Dowle R, Sablon R. BroadSeis:Enhancing interpretation and inversion with broadband marine seismic[J]. CSEG Recorder, 2012,9:41-46.
|
| [8] |
Soubaras R. Pre-stack deghosting for variable-depth streamer data[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2012:1-5.
|
| [9] |
Soubaras R, Lafet Y. Variable-depth streamer acquisition: Broadband data for imaging and inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2013,78(2):WA27-WA39.
|
| [10] |
Lin D, Sablon R, Gao Y. Optimizing the processing flow for variable-depth streamer data[J]. First Break, 2011,29(9):89-95.
|
| [11] |
Lin D, Sablon R, Gao Y, et al. Challenges in processing variable-depth streamer data[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2011,30:82-86.
|
| [12] |
Poole G. Pre-migration receiver de-ghosting and re-datuming for variable depth streamer data[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2013:4216-4220.
|
| [13] |
张振波, 李东方. 斜缆宽频地震勘探技术在珠江口盆地的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2014,49(3):451-456,414.
|
| [13] |
Zhang Z B, Li D F. Variable-depth streamer seismic acquisition and processing in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2014,49(3):451-456,414.
|
| [14] |
张振波, 李东方, 轩义华, 等. 白云凹陷深水复杂构造区斜缆地震资料处理关键技术及应用[J]. 石油物探, 2014,53(6):657-664.
|
| [14] |
Zhang Z B, Li D F, Xuan Y H, et al. Variable-depth streamer seismic data processing in deepwater complex structure area of Baiyun Sag[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2014,53(6):657-664.
|
| [15] |
唐进, 杨凯, 顾汉明, 等. 海上变深度缆地震采集宽频机理分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015,30(5):2386-2392.
|
| [15] |
Tang J, Yang K, Gu H M, et al. The broadband mechanism analysis for marine variable-depth streamer acquisition[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015,30(5):2386-2392.
|
| [16] |
周含蕊, 宋建国, 宫云良. 两种斜缆采集正演模拟及虚反射压制效果分析[J]. CT理论与应用研究, 2016,25(3):319-330.
|
| [16] |
Zhou H R, Song J G, Gong Y L. Effectiveness analysis of forward modeling and ghost suppression for two kinds of variable-depth streamer acquisitions[J]. CT Theory and Applications, 2016,25(3):319-330.
|
| [17] |
姜雨, 陈华, 姚刚, 等. 海上变深电缆宽频宽方位地震采集现场作业难点及解决方案[J]. 海洋石油, 2016,36(4):8-13.
|
| [17] |
Jiang Y, Chen H, Yao G, et al. Difficulties and solutions to the offshore seismic survey with variable-depth streamer and wide-azimuth[J]. Offshore Oil, 2016,36(4):8-13.
|
| [18] |
刘春成, 陶杰, 焦振华, 等. 海洋“犁式”电缆采集技术研究与实践[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016,51(6):1069-1074,1047.
|
| [18] |
Liu C C, Tao J, Jiao Z H, et al. Marine plow streamer acquisition[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2016,51(6):1069-1074,1047.
|
| [19] |
王建花, 王艳冬, 刘国昌. 基于波场延拓和反演的变深度缆地震数据鬼波压制方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2017,52(5):885-893,877.
|
| [19] |
Wang J H, Wang Y D, Liu G C. A deghosting method on variable-depth streamer data based on wavefield extrapolation and inversion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2017,52(5):885-893,877.
|
| [20] |
李志鹏, 何兵寿, 杨佳佳, 等. 基于粗糙海面的最小二乘残差法变深度缆接收点鬼波压制技术[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018,30(5):71-80.
|
| [20] |
Li Z P, He B S, Yang J J, et al. Ghost wave suppression technique for variable depth cable receiving points via rough sea surface-based least squares residuals method[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018,30(5):71-80.
|
| [1] |
MA De-Zhi, WANG Wei, JIN Ming-Xia, WANG Hai-Kun, ZHANG Ming-Qiang. Generation mechanism of ghost wave in marine seismic exploration and ghost wave attenuation from marine seismic data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 175-181. |
| [2] |
Hui-Long LI, Zheng WANG, Xin SONG, Chao WU, De-Zhi MA, Meng-Chang SHI, Liang ZHAO. The application of broadband processing technology to deep towing flat streamer data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(1): 176-182. |
|
|
|
|

