|
|
|
| An integrated ore-prospecting method and model for volcanic Ta-Nb deposits in Tudiling,Zhushan County, south Qinling orogenic belt |
HUANG Jing-Meng( ), XIONG Yi-Lin, ZHANG Xiao, LU Xian-Song, ZHOU Bao, WANG Guo-Hu ), XIONG Yi-Lin, ZHANG Xiao, LU Xian-Song, ZHOU Bao, WANG Guo-Hu |
| Hubei Geological Survey,Wuhan 430034,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Tudiling large-sized Ta-Nb deposit was recently discovered in the South Qinling orogenic belt by the Hubei Geological Survey Institute. This paper introduces the methods used during the exploration process, and proposes a comprehensive prospecting method suitable for volcanic type "rare" deposits, that is, to find the target area by 1:50,000 stream sediment survey, to delineate the mineralized zone by large-scale rock profiling, to identify the ore-bearing geological bodies by mapping of volcanic lithofacies and rock combination characteristics, to constrain the surface orebodies by trenching engineering, and to verify the deep orebodies by drilling. Practice has proved that the combination of prospecting methods is economical, fast, and effective. Based on the analysis of various prospecting methods, a prospecting model is established, which is of great significance for prospecting of volcanic Ta-Nb deposits in China.
|
|
Received: 12 August 2019
Published: 26 October 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
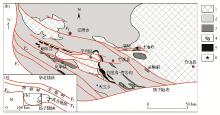
10]) and distribution of alkaline rock belt(b)
1—Neoproterozoic; 2—Paleozoic; 3—basic rock; 4—carbonatite and syenite complex; 5—trachyte volcanic rock and syenite; 6—study area location; F1—Lushan fault; F2—Shangdan fault; F3—Qingfeng-Xiangguang fault; F4—Hongchunba-Zengjiaba fault; F5—Ankang-Zhushan fault
">
|
Geotectonic location of the study area(a,revised according to literature [10]) and distribution of alkaline rock belt(b)
1—Neoproterozoic; 2—Paleozoic; 3—basic rock; 4—carbonatite and syenite complex; 5—trachyte volcanic rock and syenite; 6—study area location; F1—Lushan fault; F2—Shangdan fault; F3—Qingfeng-Xiangguang fault; F4—Hongchunba-Zengjiaba fault; F5—Ankang-Zhushan fault
|
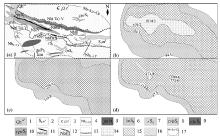
|
Analysis of 1:50 000 stream sediment measurement anomalies in Tudiling area
a—geological map of the study area;b—Nb abnormal distribution;c—Ce abnormal distribution;d—La abnormal distribution;1—Quaternary;2—first lithologic segment of Meiziya formation;3—Zhushan formation;4—Yaolinghe formation;5—diabase;6—syenite porphyry;7—trachyte;8—granitic trachyte-bearing tuff;9—trachytic fusion tuff;10—tuffaceous sericitization phyllite;11—Nb-Laorebbady and numbering;12—Nborebbady and numbering;13—fault;14—abnormal inner zone;15—abnormal middle belt;16—abnormal outer belt;17—Nb-La-Ce composite abnormal belt
|
Figure 2
">
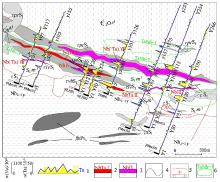
|
Plane profile of rock profile survey in Tudiling area
1—rock profile and scale(the yellow area represents Nb anomaly,the blue curve represents tantalum abnormality);2—Ta-Nb orebody and numbering;3—Nb orebody and numbering(minor Ta-bearing mineralization);4—geological boundaries;5—unidentified faults and thrust faults;6—Nb-Ta anomaly zone;other legends are the same as Figure 2
|
Figure 2
">
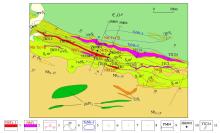
|
Geological and engineering distribution of orebody in Tudiling mining area
1—Nb-Ta orebody and numbering;2—Nb orebbody and numbering(minor Ta-bearing mineralization);3—unidentified faults and thrust faults;4—geologic boundary and occurrence;5—Nb-Ta anomaly zone;6—fluorization;7—carbonation;8—sericitization;9—survey line section and number;10—borehole position and number;11—channel exploration project location and number;other legends are the same as Figure 2
|
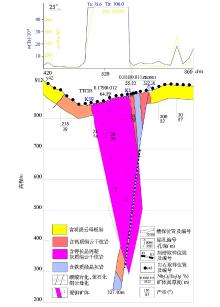
|
Survey result of exploration line section and comprehensive geological section
|

| 矿体编号 | 地表长
度/m | 厚度/m | 产状 | 岩性 | 矿体钽铌 | | 含量 | 平均品位 | | NbTaⅠ | 2050 | 28(最厚64.70 m) | 25°∠74° | 含钾长晶屑凝灰质千枚岩 | Nb2O5:0.08%~0.209%,
Ta2O5:0.008%~0.014% | Nb2O5:0.148%,
Ta2O5:0.0116% | | NbTaⅡ | 380 | 26.7(最厚36.89 m) | 20°∠58° | 粗面质晶屑岩屑凝灰岩、
含钾长晶屑凝灰质绢云千枚岩 | Nb2O5:0.08%~0.192%,
Ta2O5:0.008%~0.013% | Nb2O5:0.154%,
Ta2O5:0.011% | | NbⅢ | 1100 | 27.6(最厚29.3 m) | 23°∠40° | 粗面岩 | Nb2O5:0.08%~0.083% | Nb2O5:0.082% | | Nb(Ta)Ⅶ | 3026 | 82.5(最厚99.9 m) | 24°∠41~64° | 凝灰质绢云千枚岩 | Nb2O5:0.08%~0.107%,
Ta2O5:0.004%~0.008% | Nb2O5:0.091% | | Nb(Ta)Ⅷ | 500 | 18.99 | 26°∠65° | 粗面质凝灰熔岩 | Nb2O5:0.08%~0.147%,
Ta2O5:0.004%~0.008% | Nb2O5:0.1135% | | NbⅣ | 460 | 40.20 | 12°∠70° | 含钾长晶屑凝灰质绢云千枚岩 | Nb2O5:0.08%~0.118% | Nb2O5:0.094% |
|
Geological characteristics of tantalum-niobium orebody in Tudiling mine area
|

| 找矿要素 | 综合信息 | | 地质背景 | 岩浆岩 | 早志留世碱性岩浆岩为主,主要赋矿岩性粗面岩(铌)、粗面质凝灰熔岩(钽铌)、(含砾)岩屑晶屑凝灰岩(钽铌) | | 其他岩性 | 早志留世(含晶屑)凝灰质绢云千枚岩(钽铌) | | 构 造 | 以NWW向断层控制为主,其次为顺层近EW向断层 | | 露头标志 | 矿体露头 | 含铌粗面岩(次火山—溢流相)、含铌钽粗面质凝灰熔岩(次火山—溢流相)、含铌钽含钾长晶屑凝灰质绢云千枚岩(喷发—沉积相)及绢云母化、钾化地段 | | 围岩蚀变 | 碳酸盐化、绢云母化、萤石化(少见) | | 地球化学标志 | 水系沉积物 | Nb异常下限44×10-6,异常具两级或三级浓度分带,浓集中心明显,受粗面质火山岩类控制。组合异常元素为La、Ce,La异常下限57.8×10-6,Ce异常下限114.9×10-6,异常具两级或三级浓度分带,Nb-La-Ce组合异常的下限值均高于地壳元素丰度值约2倍,并且异常中带发现铌钽矿体可能性较大;La-Ce异常元素组合可以有效指示Nb富集。当Nb峰值达到200×10-6以上,在异常范围内发现具工业品位的铌(钽)矿体可能性较大,Nb能够有效地指示Ta富集 | | 重砂异常 | 铌铁矿、铌坦铁矿、烧绿石等重砂异常是寻找该类型矿床的直接标志 | | 岩石剖面 | 钽异常下限5×10-6,中心异常强度可达100×10-6以上;铌异常下限 120×10-6,中心异常强度可达1000×10-6以上,异常峰值带位置与矿体基本一致,与钽铌矿(化)带高度吻合 | | 山地工程 | 刻槽样结果 | 钽平均品位在 0.008%以上,直接圈定为原生钽矿体;铌平均品位在 0.08%以上,直接圈定为原生铌矿体;以铌矿化较为普遍,有钽矿化必有铌矿化;稀土总量含量较低,矿化不明显 |
|
Multi-information comprehensive prospecting model for Tudiling Ta-Nb mine area
|
| [1] |
王登红, 王瑞江, 李建康, 等. 中国三稀矿产资源战略调查研究进展综述[J]. 中国地质, 2013,40(2):361-370.
|
| [1] |
Wang D H, Wang R J, Li J K, et al. The progress in the strategic research and survey of rare earth, rare metal and rare-scattered elements mineral resources[J]. Geology in China, 2013,40(2):361-370.
|
| [2] |
程兴国, 陈新, 闫红圃, 等. 河南省方城县双山碱性正长岩型铌矿综合找矿方法及找矿模型[J]. 物探与化探, 2018,42(2):247-252.
|
| [2] |
Cheng X G, Chen X, Yan H P, et al. An integrated ore-prospecting method and model in search for Shuangshan alkali syenite Nb deposit in Fangcheng County,Henan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018,42(2):247-252.
|
| [3] |
王瑞江, 王登红, 李健康, 等. 稀有稀土稀散矿产资源及其利用开发[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015.
|
| [3] |
Wang R J, Wang D H, Li J K, et al. Rare and rare earth scattered mineral resources and their utilization and development[M]. Beijing: Geological Publiching House, 2015.
|
| [4] |
宣宁, 谢群, 黄鑫. 快速发展的中国钽铌工业[J]. 中国金属通报, 2009(38):16-19.
|
| [4] |
Xuan N, Xie Q, Huang X. Rapid development of tantalum niobium industry in China[J]. China Metal Bulletin, 2009(38):16-19.
|
| [5] |
李建康, 李鹏, 王登红, 等. 中国铌钽矿成矿规律[J]. 科学通报, 2019,64(15):1545-1566.
|
| [5] |
Li J K, Li P, Wang D H, et al. A review of niobium and tantalum metallogenic regularity in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019,64(15):1545-1566.
|
| [6] |
熊意林, 钟石玉, 李志刚, 等. 竹山土地岭一带铌钽矿床地质特征及找矿前景分析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018,32(S1):1-7,43.
|
| [6] |
Xiong Y L, Zhong S Y, Li Z G, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting potential of Niobium-Tantalum deposit in the Tudiling area,Zhushan[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018,32(S1):1-7,43.

|
| [7] |
钟石玉, 熊意林, 李志刚, 等. 庙垭铌钽稀土矿田成矿模式探讨[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018,32(S1):8-14.
|
| [7] |
Zhong S Y, Xiong Y L, Li Z G, et al. Discussion metallogenic model of Niobium-Tantalum-rare earth ore field in Miaoya area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018,32(S1):8-14.
|
| [8] |
翟明国, 吴福元, 胡瑞忠, 等. 战略性关键金属矿产资源:现状与问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019,33(2):106-111.
|
| [8] |
Zhai M G, Wu F Y, Hu R Z, et al. Critical metal mineral resources:current research status and scientific issues[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2019,33(2):106-111.
|
| [9] |
王登红, 孙艳, 代鸿章, 等. 我国“三稀矿产”的资源特征及开发利用研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2019,21(1):119-127.
|
| [9] |
Wang D H, Sun Y, Dai H Z, et al. Characteristics and exploitation of rare earth,rare metal and rare-scattered element minerals in China[J]. Engineering Science, 2019,21(1):119-127.
|
| [10] |
张国伟, 孟庆任, 赖绍聪. 秦岭造山带的结构构造[J]. 中国科学:B辑, 1995,25(9):994-1003.
|
| [10] |
Zhang G W, Meng Q R, Lai S C. Structural tectonics of the Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Science in China:Series B, 1995,25(9):994-1003.
|
| [11] |
王刚. 北大巴山紫阳—岚皋地区古生代火山岩浆事件与中生代成矿作用[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
|
| [11] |
Wang G. Metallogeny of the mesozoic and paleozoic volcanic igneous event in Ziyang-Langao arers,north Daba Mountain[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014.
|
| [12] |
刘万亮, 刘成新, 杨成, 等. 南秦岭竹溪天宝一带铌矿地质特征及找矿前景分析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2015,29(6):779-784.
|
| [12] |
Liu W L, Liu C X, Yang C, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting potential of Niobium ore of Tianbao area, Zhuxi, Southern Qinling[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2015,29(6):779-784.
|
| [13] |
Dong Y P, Zhang G, Hauzenberger C, et al. Palaeozoic tectonics and evolutionary history of the Qinling orogen:Evidence from geochemistry and geochronology of ophiolite and related volcanic rocks[J]. Lithos, 2011,122(1-2):39-56.

|
| [14] |
张成立, 高山, 张国伟, 等. 南秦岭早古生代碱性岩墙群的地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 中国科学:B辑, 2002,32(10):819-829.
|
| [14] |
Zhang C L, Gao S, Zhang G W, et al. Tgeochemistry and geological significance of the Early Paleozoic slkali dyke swarms in South Qinling[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2002,32(10):819-829.
|
| [15] |
万俊, 刘成新, 杨成, 等. 南秦岭竹山地区粗面质火山岩地球化学特征、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其大地构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2016,35(7):1134-1143.
|
| [15] |
Wan J, Liu C X, Yang C, et al. Geochemical characteristics and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of the trachytic volcanic rocks in Zhushan area of Southern Qinling Mountains and their significance[J]. Geologcal Bulletin of China, 2016,35(7):1134-1143.
|
| [16] |
杨成, 刘成新, 刘万亮, 等. 南秦岭竹溪县天宝乡粗面岩地球化学特征与铌成矿[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2017,36(5):605-618.
|
| [16] |
Yang C, Liu C X, Liu W L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of trachyte and Nb mineralization process in Tianbao Township, Zhuxi County, Southern Qinling[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2017,36(5):605-618.
|
| [17] |
王宗起, 闫全人, 闫臻, 等. 秦岭造山带主要大地构造单元的新划分[J]. 地质学报, 2009,83(11):1527-1546.

|
| [17] |
Wang Z Q, Yan Q R, Yan Z, et al. New division of the main tectonic units of the Qinling orogenic belt, central China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009,83(11):1527-1546.

|
| [18] |
马昌前, 佘振兵, 徐聘, 等. 桐柏—大别山南缘的志留纪A型花岗岩类:SHRIMP锆石年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2004,34(12):1100-1110.
|
| [18] |
Ma C Q, She Z B, Xu P, et al. Silurian a-type granitoids in the southern margin of the Tongbai-Dabieshan:Evidence from SHRIMP zircon geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2004,34(12):1100-1110.
|
| [19] |
鲁显松, 黄景孟, 熊意林, 等. 南秦岭土地岭铌钽矿床火山岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019,38(3):40-51.
|
| [19] |
Lu X S, Huang J M, Xiong Y L, et al. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb geochronology of the volcanic rocks in the Tudiling Nb-Ta deposit, south Qinling orogenic belt, and its geological implications[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019,38(3):40-51.
|
| [20] |
徐志刚. 中国成矿区带划分方案[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008.
|
| [20] |
Xu Z G. The division plan of metallogenic belt in China[M]. Beijing:Geological Publiching House, 2008.
|
| [21] |
黎彤, 倪守斌. 地球和地壳的化学元素丰度[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990.
|
| [21] |
Li T, Ni S B. Abundance of chemical elements in earth and crust[M]. Beijing:Geological Publiching House, 1990.
|
| [22] |
李石. 湖北庙垭碳酸岩地球化学特征及岩石成因探讨[J]. 地球化学, 1980(4):345-355.
|
| [22] |
Li S. Geochemical features and petrogenesis of Miaoya carbonatites,HuBei province[J]. Geochimica, 1980(4):345-355.
|
| [23] |
李石. 湖北杀熊洞碳酸岩杂岩体地球化学特征及其成因探讨[J]. 地球化学, 1991(3):245-254.
|
| [23] |
Li S. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Shaxiongdong carbonatitescomplex, Hubei province[J]. Geochimica, 1991(3):245-254.
|
| [24] |
吴敏, 许成, 王林均, 等. 庙垭碳酸岩型稀土矿床成矿过程初探[J]. 矿物学报, 2011,31(3):478-484.
|
| [24] |
Wu M, Xu C, Wang L J, et al. A preliminary study on genesis of REE deposit in Miaoya[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011,31(3):478-484.
|
| [25] |
Xu C, Campbell I H, Allen C M, et al. U-Pb zircon age, geochemical and isotopic characteristics of carbonatite and syenite complexes from the Shaxiongdong, China[J]. Lithos, 2008,105:118-128.

|
| [26] |
Xu C, Kynicky J, Chakhmouradian A R, et al. Trace-element modeling of the magmatic evolution of rare-earth-rich carbonatite from tha Miaoya deposit, central China[J]. Lithos, 2010,118:145-155.

|
| [1] |
CHEN Wei, ZHOU Xing-Peng, HE Gen-Wen, LI Wei. The application of integrated geophysical and geochemical methods to the prospecting in the Tianjingwo tungsten polymetallic ore deposit[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(4): 594-604. |
| [2] |
MIAO Yu, GUO Guang-Hua, WANG Jian-Ping, ZHANG Qi-Dao, ZHANG Xi-Chang, YANG Fei, HAN Yao. Evaluation of gold and polymetallic geochemical anomalies and ore-prospecting model in Huangzhulin area of Yangjiazhai in Luchun County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(6): 1063-1069. |
|
|
|
|

