|
|
|
| Availability and key regulator of cadmium in soil of main vegetable production areas in Tianjin |
Wei XIE1( ), Yao-Dong YANG1( ), Yao-Dong YANG1( ), Jia-Yu HOU2, Gui-Qin JIAN1, Guo-Cheng LI1, Xin-Hua ZHAO1 ), Jia-Yu HOU2, Gui-Qin JIAN1, Guo-Cheng LI1, Xin-Hua ZHAO1 |
1. Tianjin Geological Mineral Test Center,Tianjin 300191,China
2. Geological Center of Tianjin Planning and Natural Resources Bureau,Tianjin 300042,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Soil and crop samples were collected simultaneously from the main vegetable production areas of Tianjin. The concentration of available Cd, influence factors and key regulation factor were studied by correlation analysis and principal component analysis. The results show that the content of Cd in soil samples ranges from 0.21×10-6 to 1.03×10-6, with an average of 0.47×10-6, and the proportion exceeding the risk screening value (GB15618-2018) is 28%.The content of available Cd ranges from 0.05×10-6 to 0.48×10-6, with an average of 0.14×10-6. The Cd content in crop samples is lower than 0.05×10-6, which meet the food safety requirements (GB2762-2017). The content of Cd in crops is positively correlated with Cd and available Cd in soil (p<0.01). Available Cd content is negatively correlated with pH, CEC and clay content (p<0.01), positively correlated with available P content (p<0.01), but not with organic matter and Eh. Combined with principal component analysis and linear regression analysis, it can be inferred that Cd content is the dominant factor of available Cd in soil.
|
|
Received: 15 July 2019
Published: 28 August 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Yao-Dong YANG
E-mail: Chinav2012@163.com;fivess@139.com
|
|
|
|
|
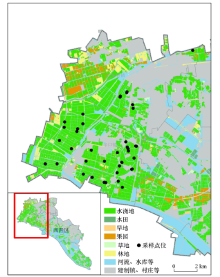
Sampling position in the study area
|

| 农作物种类 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 样本量 | | 青萝卜 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.010 | 0.006 | 11 | | 菜花 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 5 | | 苤蓝 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 5 | | 芹菜 | 0.009 | 0.024 | 0.015 | 0.007 | 4 | | 大白菜 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.001 | 3 | | 青椒 | 0.006 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.005 | 2 | | 玉米 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 5 | | 扁豆角 | | | 0.005 | | 1 | | 豆角 | | | 0.001 | | 1 | | 莴笋 | | | 0.008 | | 1 | | 小白菜 | | | 0.006 | | 1 | | 紫菜头 | | | 0.002 | | 1 |
|
Statistical values of cadmium in different vegetables
|

|
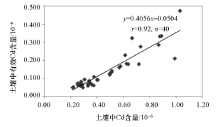
The correlation between Cd content in crops and Cd content,available Cd content in soil
|
|
The correlation between Cd and available Cd in soil
|
|
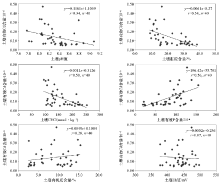
The correlation between available Cd and physical and chemical indexes in soil
|

| 主成分 | 特征值 | 贡献率/% | 累积贡献率/% | | 1 | 3.634 | 45.43 | 45.43 | | 2 | 1.560 | 19.49 | 64.92 | | 3 | 1.023 | 12.79 | 77.71 | | 4 | 0.601 | 7.51 | 85.22 | | 5 | 0.502 | 6.28 | 91.50 | | 6 | 0.443 | 5.54 | 97.04 | | 7 | 0.177 | 2.21 | 99.25 | | 8 | 0.060 | 0.76 | 100.00 |
|
Eigenvalues and proportion of principal component analysis
|

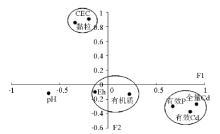
| 指标 | F1(主成分1) | F2(主成分2) | F3(主成分3) | | 有效 Cd | 0.847 | -0.367 | -0.063 | | 全量Cd | 0.911 | -0.259 | 0.001 | | 有机质 | 0.218 | -0.123 | 0.813 | | CEC | -0.204 | 0.910 | -0.190 | | Eh | -0.140 | -0.093 | 0.859 | | pH | -0.619 | -0.109 | -0.514 | | 黏粒 | -0.347 | 0.862 | -0.013 | | 有效 P | 0.668 | -0.293 | 0.125 |
|
Component Matrix with maximum variance rotation method
|
|
Loading plots of various indicators in F1 and F2
|
| [1] |
谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝. 天津某菜地土壤—蔬菜中硒与重金属含量特征及绿色富硒蔬菜筛选[J]. 环境化学, 2018,37(12):2790-2799.
|
| [1] |
Xie W, Yang Y D, Hou J Y. Characteristics of selenium and heavy metals concentrations in soils and vegetables and screening of green seleniumn-enriched vegetables in a base of Tianjin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018,37(12):2790-2799.
|
| [2] |
Arnfalk P, Wasay S A, Tokunaga S. Comparative study of Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb uptake by minerals and soil materials[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 1996,87(3):131-148.
|
| [3] |
Impellitteri C A, Saxe J K, Cochran M, et al. Predicting the bioavailability of copper and zinc in soils: Modeling the partitioning of potential bioavailable copper and zinc from solid to soil solution[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2003,22(6):1380-1386.

|
| [4] |
陈怀满. 土壤中化学物质的行为与环境质量 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002:79-134.
|
| [4] |
Chen H M. Behavior of chemical substances in soils and environmental quality [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002:79-134.
|
| [5] |
邓朝阳, 朱霞萍, 郭冰, 等. 不同性质土壤中镉的形态特征及其影响因素[J]. 南昌大学学报:工科版, 2012,34(4):341-346.
|
| [5] |
Deng Z Y, Zhu X P, Guo B, et al. Distribution and influence factors of Cd speciation on th soil with different properties[J]. Journal of Nanchang University:Engineering & Technology, 2012,34(4):341-346.
|
| [6] |
袁波, 傅瓦利, 蓝家程, 等. 菜地土壤铅、镉有效态与生物有效性研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2011,25(5):130-134.
|
| [6] |
Yuan B, Fu W L, Lan J C, et al. Study on the available and bioavailability of lead and cadmium in soil of vegetable plantation[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011,25(5):130-134.
|
| [7] |
张水勤, 王峰源, 姜慧敏, 等. 设施菜地土壤中速效磷是镉生物有效性的关键调控因子[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014,33(9):1721-1727.
|
| [7] |
Zhang S Q, Wang F Y, Jiang H M, et al. Available phosphorus is a key regulator of cadmium phytoavailability in greenhouse soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014,33(9):1721-1727.
|
| [8] |
黄顺生, 华明, 金洋, 等. 南京郊区某菜地土壤镉污染水平及其来源调查[J]. 土壤通报, 2008,39(1):129-132.
|
| [8] |
Huang S S, Hua M, Jin Y, et al. Investigation of cadmium pollution and its major sources in vegetable land in the suburb of Nanjing city[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2008,39(1):129-132.
|
| [9] |
索琳娜, 刘宝存, 赵同科, 等. 北京市菜地土壤重金属现状分析与评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016,32(9):179-186.
|
| [9] |
Suo L N, Liu B C, Zhao T K, et al. Evaluation and analysis of heavy metals in vegetable field of Beijing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016,32(9):179-186.
|
| [10] |
张怀志, 冀宏杰, 徐爱国, 等. 潍坊市菜地重金属调查与环境风险评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017,26(12):2154-2160.
|
| [10] |
Zhang H Z, Ji H J, Xu A G, et al. Investigation and environmental risk assessment of heavy metal elements in vegetable farmland of Weifang city[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017,26(12):2154-2160.
|
| [11] |
贾锐鱼, 林友红, 陈一国, 等. 西安市近郊菜园蔬菜重金属现状调查及评价[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2012,32(4):486-489.
|
| [11] |
Jia R Y, Lin Y H, Chen Y G, et al. Analysis of heavy-metal contamination of vegetables in vegetable plot of Xi’an suburb[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2012,32(4):486-489.
|
| [12] |
田效琴, 李卓, 刘永红. 成都平原农田镉污染情况及油菜镉吸收特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017,36(3):496-506.
|
| [12] |
Tian X Q, Li Z, Liu Y H. Characteristics of cadmium uptake by rape grown in cadmium contaminated farmland on Chengdu plain[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017,36(3):496-506.
|
| [13] |
宫彦章, 刘月秀, 刘姝媛, 等. 广东省林地土壤有效态锌、镉含量及其与有机质和pH的关系[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2011,32(1):15-18.
|
| [13] |
Gong Y Z, Liu Y X, Liu S Y, et al. Available Zn and Cd contents in relation to pH and Organic matter in forest soils of Guangdong province[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2011,32(1):15-18.
|
| [14] |
Kachenko A G, Singh B. Heavy metals contamination in vegetables grown in urban and metal smelter contaminated sites in Australia[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2006,169(1-4):101-123.
|
| [15] |
Wallace A, Berry W L. Dose-response curves for zinc, cadmium, and nickel in combinations of one, two, or three[J]. Soil Science, 1989,147(6):401-410.
|
| [16] |
杜彩艳, 祖艳群, 李元. pH和有机质对土壤中镉和锌生物有效性影响研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报, 2005,20(4):539-543.
|
| [16] |
Du C Y, Zu Y Q, Li Y. Effect of pH and organic matter on the bioavailability Cd and Zn in soil[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 2005,20(4):539-543.
|
| [17] |
普锦成, 符娟林, 章明奎, 等. 土壤性质对水稻土中外源镉与铅生物有效性的影响[J]. 生态环境, 2008,17(6):2253-2258.
|
| [17] |
Pu J C, Fu J L, Zhang M K, et al. Effects of soil properties on the bioavailability of added cadmium and lead in paddy soils[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2008,17(6):2253-2258.
|
| [18] |
李玉萍, 刘晓端, 宫辉力. 土壤中铅铜锌镉的吸附特性[J]. 岩矿测试, 2007,26(6):455-459.
|
| [18] |
Li Y P, Liu X D, Gong H L. Adsorption characteristics of soils for lead, copper, zinc and cadmium[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007,26(6):455-459.
|
| [19] |
陈江军, 刘波, 李智民, 等. 江汉平原典型场区土壤重金属赋存形态及其影响因素探讨[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018,32(4):551-556.
|
| [19] |
Chen J J, Liu B, Li Z M, et al. Soil heavy metal occurrence and its influencing factors in typical areas in Jianghan plain[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018,32(4):551-556.
|
| [20] |
Kirkham M B. Cadmium in plants on polluted soils: Effects of soil factors, hyperaccumulation, and amendments[J]. Geoderma, 2006,137(1):19-32.
|
| [21] |
刘世亮, 崔海燕, 介晓磊, 等. 磷锌配施对镉污染石灰性土壤中磷锌镉有效性的影响[J]. 生态环境, 2008,17(2):623-626.
|
| [21] |
Liu S L, Cui H Y, Jie X L, et al. Effect of combined application phosphorus and Zn on availability of P, Zn, Cd in Cd contaminated calcareous soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2008,17(2):623-626.
|
| [22] |
聂艳丽, 郑毅, 林克惠. 根分泌物对土壤中磷活化的影响[J]. 云南农业大学学报, 2002,17(3):281-286.
|
| [22] |
Nie Y L, Zheng Y, Lin K H. Effect of root exudates on activation of phosphates in soils[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 2002,17(3):281-286.
|
| [23] |
余贵芬, 蒋新, 孙磊, 等. 有机物质对土壤镉有效性的影响研究综述[J]. 生态学报, 2002,22(5):682-688.
|
| [23] |
Yu G F, Jiang X, Sun L, et al. A review for effect of organic substances on the availability of cadmium in soils[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002,22(5):682-688.
|
| [24] |
Almås Å R, McBride M B, Singh B R. Solubility and lability of cadmium and zinc in two soils treated with organic matter[J]. Soil Science, 2000,165(3):250-259.
|
| [25] |
Jörg R, Svetlana A, Tina F, et al. Nickel in a serpentine-enriched fluvisol: redox affected dynamics and binding forms[J]. Geoderma, 2016,263:203-214.
|
| [26] |
毛凌晨, 叶华. 氧化还原电位对土壤中重金属环境行为的影响研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 2018,31(10):1669-1676.
|
| [26] |
Mao L C, Ye H. Influence of redox potential on heavy metal behavior in soils: a review[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018,31(10):1669-1676.
|
| [27] |
Frohne T, Rinklebe J, Diaz bone R A, et al. Controlled variation of redox conditions in a floodplain soil: impact on metal mobilization and biomethylation of arsenic and antimony[J]. Geoderma, 2011,160(3-4):414-424.
|
| [1] |
HOU Jia-Yu, YANG Yao-Dong, CHENG Xu-Jiang. Distribution and sources of heavy metals in greenbelt soil in different functional zones of Tianjin City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1130-1134. |
| [2] |
XIE Wei, YANG Yao-Dong, HOU Jia-Yu, JIAN Gui-Qin, LI Guo-Cheng, ZHAO Xin-Hua. The evaluation of soil environmental quality of main walnut producing areas based on various methods of heavy metal contamination assessment in Tianjin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 207-214. |
|
|
|
|

