|
|
|
| The application of ILR transromed data factor analysis to delineating geochemical anomalies |
Guo-Shuai GENG1,2, Fan YANG3,4( ), Jian-Na GUO5 ), Jian-Na GUO5 |
1. School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China
2. Gold Geological Institute of CAPF, Langfang 065000, China
3. Beijing Institute of Geology for Mineral Resources, Beijing 100012, China
4. Research Center of Geochemical Survey and Assessment on Land Quality, China Geological Survey, Langfang 065000, China
5. Natural Resources and Planning Bureau, Langfang 065000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The reliable detection of data outliers and unusual data behavior is one of the key task in the statistical analysis of applied geochemical data, and has remained a core problem. Factor analysis is a multivariate statistical analysis method, which is used to solve the problem of complex geological origin and superimposed mineralization; nevertheless, geochemical data are compositional data, there exist their closure effects, closure has a major influence on the covariance and correlation matrices, the very base of principal component analysis (PCA) and factor analysis (FA). So the authors applied isometric logratio-transformed (ILR) to 'open' the data before FA. The study area is located in the east of East Kunlun polymetallic mineralization zone. The authors used ILR transformed 11 major elements to conduct FA, extracted four public factors and calculated the four factor scores. According to the results of FA with EDA method , the authors standardized geochemical data and delineated Au anomaly. Compared with traditional method, this method can eliminate the influence of high background values.
|
|
Received: 07 January 2019
Published: 03 March 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Fan YANG
E-mail: yangfan@igge.cn
|
|
|
|

| 一级构造单元 | 二级构造单元 | 三级构造单元 | 秦祁昆(东昆仑—祁连—北秦岭)晚加
里东造山系(Ⅰ) | Ⅰ2东昆仑造山带 | 祁漫塔格—都兰造山亚带(昆北带);伯喀里克—香日德元古宙古陆块体(昆中带);雪山峰—布尔汉布达造山亚带(昆南带) | 特提斯(东特提斯北部)华力西—印支
造山系(Ⅱ) | Ⅱ1巴颜喀拉晚印支造山带 | 布喀达坂峰—阿尼玛卿华力西、印支复合造山亚带(北巴带) |
|
Division of geotectonic classification in the east of Dongkunlun
|

|
The sketch map of deposit and geotectonic in study area
|
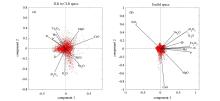
|
Biplot of principle component analysis from the major elements in the study area
a—the biplot of the first and second principal component from ILR transformed geochemical data;b—the biplot of the first and second principal component from raw geochemical data;the red dots in the picture are the scores of the first and second principal components
|
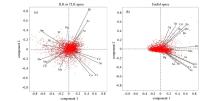
|
Biplot of principle component analysis from the ore forming elements in the study area
a—the biplot of the first and second principal component from ILR transformed geochemical data;b—the biplot of the first and second principal component from raw geochemical data;the red dots in the picture are the scores of the first and second principal components
|

| 主成分 | 特征值 | 方差贡献率/% | 累计贡献率/% | | PC1 | 2.95429 | 29.5429 | 29.5429 | | PC2 | 2.209107 | 22.09107 | 51.63397 | | PC3 | 1.451425 | 14.51425 | 66.14822 | | PC4 | 1.26463 | 12.6463 | 78.79452 | | PC5 | 0.686685 | 6.866845 | 85.66137 | | PC6 | 0.523345 | 5.233451 | 90.89482 | | PC7 | 0.461487 | 4.614866 | 95.50969 | | PC8 | 0.252381 | 2.523811 | 98.0335 | | PC9 | 0.11301 | 1.130104 | 99.1636 | | PC10 | 0.08364 | 0.8364 | 100 |
|
The eigenvalue and variance explained of principal component analysis in the study area
|

| 指标 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | | Mn | -0.07738 | -0.07873 | -0.09688 | -0.83041 | | P | 0.702332 | -0.01513 | 0.075709 | 0.038553 | | Ti | 0.710837 | -0.14553 | 0.096094 | -0.26549 | | Zr | 0.482694 | -0.18209 | -0.38805 | 0.396661 | | Al2O3 | -0.2006 | -0.8244 | -0.00632 | 0.018327 | | CaO | -0.50636 | 0.941437 | 0.227767 | 0.310812 | | Fe2O3 | 0.215612 | 0.058648 | 0.045556 | -0.63857 | | K2O | -0.29089 | -0.59256 | 0.308376 | 0.3833 | | MgO | -0.08812 | 0.649321 | 0.456313 | -0.03996 | | Na2O | -0.5376 | -0.03472 | 0.228541 | 0.462876 | | SiO2 | -0.41052 | 0.223752 | -0.9471 | 0.163893 |
|
Orthometric rotating factor loading matrix of factor analysis in the study area
|
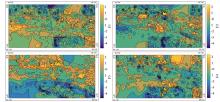
|
Four factor score maps of major component from ILR-transformated data in study area
|

|
Geochemical subdivision map in the study area
|

| 指标 | F11 | F12 | F21 | F22 | F31 | F32 | F41 | F42 | | Mn | 532.5 | 467.8 | 515 | 531 | 610 | 372.9 | 389 | 767 | | P | 604 | 341 | 437 | 457.65 | 540.45 | 323 | 424 | 454 | | Ti | 3746.5 | 1954.8 | 2704 | 3364.5 | 3481.55 | 2037 | 2609 | 3254.8 | | Zr | 215 | 113 | 136 | 166 | 160 | 121 | 165 | 149.3 | | Al2O3 | 11.6 | 10.8 | 9.1 | 13.6 | 12.1 | 7.5 | 9.6 | 11.94 | | CaO | 4.4 | 4.83 | 9.1 | 2.32 | 6.2 | 2.64 | 4.7 | 3.3 | | Fe2O3 | 4.68 | 3.06 | 3.6 | 4.84 | 4.8 | 2.77 | 3.06 | 5.25 | | K2O | 2.3 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 2.72 | 2.49 | 1.3 | 2 | 2.1 | | MgO | 1.75 | 1.13 | 1.8 | 1.51 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 1.21 | 1.53 | | Na2O | 1.8 | 2 | 1.5 | 1.82 | 2.1 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 1.68 | | SiO2 | 64.6 | 69.28 | 59.39 | 66.945 | 60.215 | 78.2 | 69.69 | 67.71 |
|
Major component median of different subdivision from the study area
|
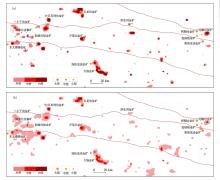
|
The comparison diagram of Au anomalies and deposits from geochemical subdivision standardized of ILR and classical method
a—Au anomalies delineated from geochemical subdivision standardition of ILR;b—Au anomalies delineated from classical method
|

|
Comparsion diagram of detecting Au outliers from subdivised standardization and classical method
a—gold outliers detected from geochemical subdivised standardization;b—gold outliers detected from classical method;c—gold outliers detected from both method;d—gold outliers detected from one of two methods
|

| 处理方法 | 异常下限值 | 圈定的异常
点数 | 占样品总数
/% | 两种都有的
异常点数 | 只在其中一种出现的
异常点数 | | 传统方法 | 2.7×10-9 | 415 | 10.4 | 307 | 108 | | 因子分区标准化 | 1 | 325 | 8.1 | | 18 |
|
Point statistics of detecting Au outliers from two methods
|
| [1] |
李宝强, 孙泽坤 . 区域地球化学异常信息提取方法研讨[J]. 西北地质, 2004,37(1):102-108.
|
| [1] |
Li B Q, Sun Z K . Study on the method of geochemical anomalies analysis[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2004,37(1) 102-108.
|
| [2] |
郝立波, 李巍, 陆继龙 , 等. 确定岩性复杂区的地球化学背景与异常的方法[J]. 地质通报, 2007,26(12):1531-1535.
|
| [2] |
Hao L B, Li W, Lu J L , et al. Method for determining the geochemical background and anomalies in areas with complex lithology[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007,26(12) 1531-1535.
|
| [3] |
李长江, 麻士华 . 矿产勘查中的分形、混沌与ANN [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999.
|
| [3] |
Li C J, Ma S H . Fractal, chaos and ANN in mineral exploration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999.
|
| [4] |
周蒂 . 分区背景校正法及其对化探异常圈定的意义[J]. 物探与化探, 1986,10(4):263-273.
|
| [4] |
Zhou D . Unit-wise adustment of geochemical background data and its significant geochemical anomaly delineation[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1986,10(4):263-273.
|
| [5] |
史长义, 张金华, 黄笑梅 . 子区中位数衬值滤波法及弱小异常识别[J]. 物探与化探, 1999,23(4):250-257.
|
| [5] |
Shi C Y, Zhang J H, Huang X M . Subregion median contrast filtering method and recognition of weak anomalies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1999,23(4):250-257.
|
| [6] |
赵荣军 . 不同方法在栾川北部化探数据处理中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2006,42(3):67-71.
|
| [6] |
Zhao R J . Application of different data processing method in geochemical exploration in the North Luanchuan[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2006,42(3):67-71.
|
| [7] |
刘大文 . 区域地球化学数据的归一化处理及应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2004,28(3):273-275.
|
| [7] |
Liu D W . The normalization of regional geochemical data and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2004,28(3):273-275.
|
| [8] |
陈建国, 夏庆霖 . 利用小波分析提取深层次物化探异常信息[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 1999,24(5):509-512.
|
| [8] |
Chen J G, Xia Q L . Wavelet-based extraction of geophysical and geochemical anomaly information[J]. Earth Science:Journal of University of Geosciences, 1999,24(5):509-512.
|
| [9] |
李随民, 姚书振, 韩玉丑 . Sufer软件中利用趋势面方法圈定化探异常[J]. 地质与勘探, 2007,43(2):72-75.
|
| [9] |
Li S M, Yao S Z, Han Y C . Using tendency analysis method to deal with geochemical data based on the Suffer software[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2007,43(2):72-75.
|
| [10] |
陈希清, 杨晓君, 陈富文 , 等. 应用MAPGIS数字高程模型提取区域地球化学异常信息的方法探讨[J]. 地球学报, 2009,30(1):119-125.
|
| [10] |
Chen X Q, Yang X J, Chen F W , et al. A discussion on the method for extracting regional geochemical anomaly based on mapgis digital elevation model[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2009,30(1):119-125.
|
| [11] |
陈明, 范继璋, 矫希国 . 化探背景与异常划分中的C型转换法[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1996,26(2):227-230.
|
| [11] |
Chen M, Fan J Z, Jiao X G . The C-type transformation method for recognition of geochemical background and anomaly[J]. Journal of Chang Chun University of Earth Sciences, 1996,26(2):227-230.
|
| [12] |
成秋明, 赵鹏大, 陈建国 , 等. 奇异性理论在个旧锡铜矿产资源预测中的应用:成矿弱信息提取和复合信息分解[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009,34(2):232-242.
|
| [12] |
Chen Q M, Zhao P D, Chen J G , et al. Application of singularity theory in prediction of tin and copper mineral deposits in Gejiu District, Yunnan, China: weak information extraction and mixing information decomposition[J]. Earth Science:Journal of University of Geosciences, 2009,34(2):232-242.
|
| [13] |
时艳香, 纪宏金, 陆继龙 , 等. 水系沉积物地球化学分区的因子分析方法与应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2004,40(5):73-76.
|
| [13] |
Shi Y X, Ji H J, Lu J L , et al. Factor analysis method and application of stream sediment geochemical partition[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2004,40(5):73-76.
|
| [14] |
时艳香 . 区域地球化学单元的概念、方法及应用研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2004.
|
| [14] |
Shi Y X . Research of regional geochemical Units: concept, methods and applications[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2004.
|
| [15] |
赵玉岩, 郝立波, 陆继龙 . 利用水系沉积物识别基岩类型的方法研究——以大兴安岭浅覆盖区为例[J]. 吉林大学学报:自然科学版, 2005,35(S):147-150.
|
| [15] |
Zhao Y Y, Hao L B, Lu J L . The technique of inveting bedrock types by residual stream sediment in Daxing’anling shallow overlay[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2005,35(S):147-150.
|
| [16] |
郝立波, 陆继龙, 李龙 , 等. 区域化探数据在浅覆盖区地质填图中的应用方法研究[J]. 中国地质, 2007,34(4):710-715.
|
| [16] |
Hao L B, Lu J L, Li L , et al. Method of using regional geochemical data in geological mapping in shallow overburden areas[J]. Geology in China, 2007,34(4):710-715.
|
| [17] |
时艳香, 郝立波, 陆继龙 , 等. 因子分类法在黑龙江塔河地区地质填图中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报:自然科学版, 2008,38(5):899-903.
|
| [17] |
Shi Y X, Hao L B, Lu J L , et al. Application of factor classification in geological mapping in Tahe area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2008,38(5):899-903.
|
| [18] |
董毅 . 因子分析在水系沉积物测量地球化学分区中的应用探讨——以青海都兰地区为例[J]. 矿产与地质, 2008,22(1):78-82.
|
| [18] |
Dong Y . Discussion of applying factor analysis to the geochemical subareas measurement in stream sediment:A case study of Dulan area in Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2008,22(1):78-82.
|
| [19] |
赵少卿, 魏俊浩, 高翔 , 等. 因子分析在地球化学分区中的应用:以内蒙在石板井地区1∶5万岩屑地球化学测量数据为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012,31(2):27-34.
|
| [19] |
Zhao S Q, Wei J H, Gao X , et al. Factor analysis in the geochemical subdivisions: Taking 1∶50 000 debris geochemical survey in the Shibanjing area of Inner Mongolia as an example[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012,31(2):27-34.
|
| [20] |
Filzmoser P, Hron K. Reimann C . Univariate statistical analysis of environmental (compositional) data:problems and possibilities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2009,407:6100-6108.
|
| [21] |
Pawlowsky-Glahn V, Buccianti A , Buccianti A. compositional data analysis: theory and application[M]. London:John Wiley & Sons, 2011: 378.
|
| [22] |
Aitchison J . The statistical analysis of compositional data[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), 1982,44(2):139-177.
|
| [23] |
Pawlowsky-Glahn V, Egozcue J J . Spatial analysis of compositional data: a historical review[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016,164:28-32.
|
| [24] |
Pawlowsky-Glahn V, Egozcue J J, Tolosana-Delgado R . Modeling and analysis of compositional data[M]. UK: John Wiley and Sons, 2015: 272.
|
| [25] |
Filzmoser P, Hron K. Reimann C . Principal component analysis for compositional data with outliers[J]. Environmentrics, 2009,20(6):621-632.
|
| [26] |
Tucky J W . Exploratory data analysis[M]. Massachussetts:Addison-Wedley Reading, 1977: 506.
|
| [27] |
Hoaglin D C, Mosteller F, Tukey J W . Understanding robust and exploratory data analysis(2nd edition)[M]. New York:John Wiley & Sons, 2000: 472.
|
| [28] |
史长义 . 勘查数据分析(EDA) 技术的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 1993,11:52-58.
|
| [28] |
Shi C Y . Application of exploratory data analysis technology[J]. Geolgy and Prospecting, 1993,11:52-58.
|
| [29] |
Reimmann C, Filzmoser P, Garrett R G . Background and threshold: critical comparison of metholds determination[J]. Science of the Total Enveiroment, 2005,346(1-3):1-16.
|
| [30] |
Reimmann C, Garrett R G . Geochemical background-concept and reality[J]. Science of the Total Enveiroment 3, 2005,50(1-3):12-27.
|
| [31] |
Grunsky E C . The evaluation of geochemical survey data: data analysis and statestical methods using geographic information systems[G]//Harris J R.Gis for the Earth Sciences, Geological Association of Canada Special Publication 44. Geological Association of Canada, St. John’s, 2006: 229-283.
|
| [32] |
Carranza E J M . Geochemical anomaly and mineral prospectivity mapping in GIS [M]. Oxford: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, 2009.
|
| [33] |
丁清峰 . 东昆仑造山带成矿作用与矿产资源评价[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2004.
|
| [33] |
Ding Q F . Metallogenesis and mineral resources assessment in Eastern Kunlun orogenic belt[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2004.
|
| [34] |
马进全, 郝平, 杨晓琴 , 等. 中华人民共和国地球化学图说明书—I-47-[7](麻多幅)、I-47-[8](扎陵湖幅)[R]. 青海省地质调查院, 2000.
|
| [34] |
Ma J Q, Hao P, Yang X Q , et al. Specification of geochemical map of the People’s Republic of China—I-47-[7]、I-47-[8][R]. Qinghai Geological survey Institute, 2000.
|
| [1] |
GENG Guo-Shuai, YANG Fan. The application of Mahalanobis distance to the delineation of multivariate outliers in the East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 440-449. |
| [2] |
LI Huan, HUANG Yong, ZHANG Qin-Rui, JIA San-Man, XU Guo-Zhi, YE Bei-Bei, HAN Bing. Soil geochemical characteristics and influencing factors in Beijing Plain[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 502-516. |
|
|
|
|

