0 引言
岩性识别是地质研究过程中非常重要的基础工作,尤其是在近地表以及深部无法直接采样区的地质研究中,准确地刻画深部岩石类型及其结构关系,可以为能源矿产勘探、深部结构与构造等研究提供重要的地质信息。因此采用什么数据、什么方法来进行岩性识别是一项极具价值的研究工作。传统(地表)地质填图已远不能满足深部探测的需要。随着多源地学数据(地质、地球物理、地球化学、遥感以及钻井数据等)的获取、地球物理三维反演技术和三维地质建模的发展,深部岩性识别已成为现实。但目前对多源数据的利用并不充分,尚未有效地利用多种物性参数进行岩性识别。因此,如何利用多源不同类型、属性地学数据所反映的岩性信息,从高维数据空间准确地进行岩性识别是亟待解决的难题,对深部探测和地学数据融合也具有重要的科学意义。
目前岩性识别主要有直接手段(岩芯、手标本以及薄片鉴定等)和间接手段(重磁、地震、电磁、测井、遥感、地球化学等)。从深部探测来讲,钻井岩芯可能是唯一的岩石标本,但只是点数据,而遥感(面数据)只能探测地表情况,且受地表覆盖影响大;因此地球物理方法在地下深部岩性识别研究中将发挥重要作用。而物性(密度、磁化率、电导率、纵横波速度等)是岩性和地球物理场之间的纽带,因此,通过地球物理反演物性,再联合其他地质数据进行岩性的识别具有可行性。地震反演是进行岩性识别的有效方法,可以利用地震不同的弹性参数,如利用纵横波速度、密度[1-2]、波阻抗、振幅、频率、相位[3-5]对目标岩体(流体)进行识别,但是当岩相间的地震响应差别不明显时,依靠波形的分类结果无法准确刻画岩性且地震方法成本高。在测井识别岩性方面,可以利用交会图版[6-9]或者基于统计、聚类、支持向量机以及神经网络等技术[10-14]进行岩性识别,测井方法在精度、算法以及技术上都有明显的优势,但是只能识别钻孔附近小范围内的岩性,难以进行大面积或是没有钻孔地区的岩性识别。利用重磁技术识别岩性主要依靠密度与磁化率比值,例如采用交会图版结合逻辑运算识别岩性[15-16],重磁数据覆盖面积广,采样密度高,容易获得大规模的岩性识别,但是在无约束情况下,垂向分辨较差,多解性强。
单一的地球物理方法往往很难获得理想识别结果,因此联合多个地球物理方法的岩性识别成为主流方式。在多源数据识别岩性方面,对于存在岩性与物性对应关系的模糊区域,以地震反射特征为约束,利用重磁电资料识别了具有密度、磁性和电阻率等特征差异的火成岩岩性[17]。近年来随着机器学习(machine learning)的兴起,该算法已被广泛应用于岩性识别。如利用多种地球物理数据基于模糊聚类分析[18]将岩石进行分类识别。利用地球化学数据和地球物理数据对岩性进行多元回归分析[19-20]或者多准则决策方法识别。利用无监督模糊分区聚类对航空伽马射线数据与陆地卫星波段数据联合进行岩性识别[21]。应用受限玻尔兹曼机(restricted boltzmann machine)和随机森林模型到区域尺度多参数地球科学数据集,从而预测斑岩铜金矿床的远景区域。还有采用随机森林法(random forests)和自组织映射技术(SOM,self-organising maps)来识别连续的火山单元子类,由于算法只针对部分地球科学或地质参数进行岩性识别,因此无法针对不同类型的参数进行统一处理。虽然各类算法都有改进,但是岩性识别结果唯一,对模糊区间的多种可能性无法准确表述。
理论上讲,通过不同地质、地球物理技术可以获得地下物性结构,如密度结构、速度结构、电阻率结构、磁性结构等,那么如何将这些物性结构转换为岩性是值得研究的问题,实质上这是一个模式识别问题。通常来讲,岩性与物性的对应关系并不总是明确的,在交会图上存在较大的重叠区域,从而使得基于规则的分类方法难以解决该问题。在前人的研究基础之上,考虑到贝叶斯方法是非规则分类,该方法依据类的概率、概率密度,并按照某种规则使得分类结果从统计上达到最佳。基于此,笔者提出了基于自适应核密度估计的贝叶斯概率岩性识别方法,完成了从物性到岩性的转换。该方法具有较强的泛化能力,预测的岩性分类结果带有概率参数,可以存在模糊区间,提供多种岩性分类结果。该方法具有较强可扩展性,可以有任意数量类型的输入参数(允许存在缺省参数)以及任意数量的岩性分类输出。通过实验对比了传统的高斯密度、固定带宽核密度以及自适应带宽核密度对岩石物性数据判别的效果,说明了该方法具有良好岩性识别效果。
1 基本原理
1.1 贝叶斯分类
贝叶斯算法是基于统计学的基本算法之一,假设各个条件之间相互独立,可以得到朴素贝叶斯算法。如果我们将岩石的类型表示为c事件,将岩石属性表示为x事件,岩石类型c和对应属性x是发生在同一空间的两个事件,假设某研究区的完整岩石类型c是由两种岩石类型c1、c2、…、cn构成,c1、c2、…、cn中一个岩石种类出现必然伴随着某一属性x的发生,即若x发生,则c必然有一个会发生,根据概率可以得到样本集的已知各类别ci的先验概率以及各类条件概率P(x/ci)。对于未知样本,贝叶斯公式可以计算出待测样本分属各类的概率,称为后验概率。
使用贝叶斯定理来预测后验概率最大的类,主要是估计每一类的概率密度函数,通过多元正态分布来建模。朴素贝叶斯分类器基于条件独立性假设,是概率分类器中最简单的分类器,在很多情况下具有相当高的分类准确率,因此以高效率和良好的泛化能力而著称。对于某个测区,已知该地区的物性分布特征(如密度、磁化率、电阻率等)以及部分的岩石样本,假设属性之间相互独立,可以使用贝叶斯分类器来对整个测区的岩石类型进行预测。概率分类器的优点在于在得到分类结果的同时,会对每一种类别进行概率计算,对于岩性的识别而言,可以通过概率或相对概率来人为判定分类结果的可信度而不仅仅依靠算法本身的置信度来决定,小概率区间会提供一个模糊带,模糊带的类别区分结果可能不唯一。
贝叶斯分类器通过对每个未知样点x和每个类ci来估计其后验概率P(ci/x),即计算未知样本x属于ci类岩石的概率,从而选择最大概率的类作为未知样本x最终的预测类型。利用贝叶斯定理,后验概率P(ci/x)可以表示为:
其中:P(x/ci)定义为假设真实类是ci时观察到x的概率,称为似然;P(ci)是类ci发生的先验概率;P(x)指从全部样本中观察到x的概率,可以表示为
对于给定的一点x,P(x)是确定的。用fi(x)表示未知样本x属于ci类的概率密度,似然用概率密度可以表示为P(x/ci)=2afi(x),其中a表示邻近x的一个极小区间,因此可以得到后验概率的计算公式:
由式(2)可知,概率密度函数是影响分类结果的一个重要因素,由于大部分岩石物性参数是基本遵循正态分布的规律,这里考虑了传统的高斯公式作为概率密度函数,然而样本本身并不完全遵循正态分布,为了极大地避免由于选定高斯函数的影响,同时考虑使用核密度估计的方法,核密度估计的优点在于核函数的选取对于最终分类结果影响不大,更适用于类正态数据样本,这会在之后的模型测试中加以验证。
1.2 自适应核密度估计
其中:n表示所有已知样本的总个数,h表示带宽,也可以称为窗宽或滑动参数,x表示随机样本,Xi表示第i个已知样本,K(·)表示核函数。核函数的作用相当于权函数,可以根据距离分配各个样本点对总体密度估计贡献的不同程度,常见的有高斯核函数,三角核函数,二次核函数等多种表达形式,由于大部分的物性分布都遵循正态分布的原则,因此这里采用高斯核函数,即K(t)=
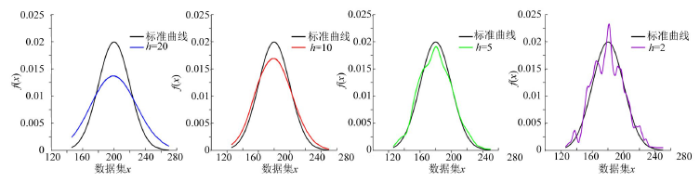
图1展示了对于1 200组完全正态分布的样本,选取不同带宽得到的概率密度函数曲线图,可以得到,对于该组数据而言,下列所选带宽的结果拟合程度最高的是h=5时,当所选带宽h过大,会造成核密度估计曲线过于平滑,从而失去应有的特征细节。带宽h过小,会导致核密度估计曲线光滑性差,过于粗糙,会产生过拟合的问题。对于高斯核函数,最优带宽为:
图1
图1
不同带宽下概率密度函数曲线
Fig.1
Probability density function curve under different bandwidth
岩石的物性参数往往存在较大的差异,而每种参数的误差范围也不同,因此实际操作中固定带宽的方法可能并不适用于岩性的识别,加上在实际采样中,受限于各种地理和人为因素的影响,无法保证样本的稀疏程度一致,对于不同质量的样本,无法用同一带宽来进行密度估计,需要对不同稀疏度的样本分别讨论带宽,因此相比于固定带宽法,滑动变带宽更能满足岩性预测的要求。令带宽值随着数据的密度变化自动进行适当的调整,实现滑动变带宽的方法,主要是基于积分均方误差,通过计算每个点的最优带宽值,得到变带宽函数h(x)。针对滑动窗口的实现过程,于传强等[27]给出了详细的推导过程,关于滑动变带宽的算法流程如下:
第一,根据固定带宽的经验公式,选择样本组的最优固定带宽hopt以及对应的核密度估计函数 fopt(x),
第二, 根据给定的估计点,求取优化后的带宽
其中c=0.375π-0.5
第三,优化后的核密度估计函数记为
上述计算的带宽在数据质量相对较好的情况下往往会出现过拟合现象,反而结果不尽如人意,因此在实际的分类过程中,当计算得到固定带宽以及优化后的带宽后,需要对带宽的差值进行判定,对于二者相差不大的情况(差值需要根据样本的数量和质量人为给定),采用优化前的带宽。将优化后的核密度估计函数作为贝叶斯模型的概率密度函数,针对某一未知样本,可以得到该样本归属于每一类的概率密度,通过比较得到最大概率类别作为预测的类。
2 模型测试
表1 模型参数统计
Table 1
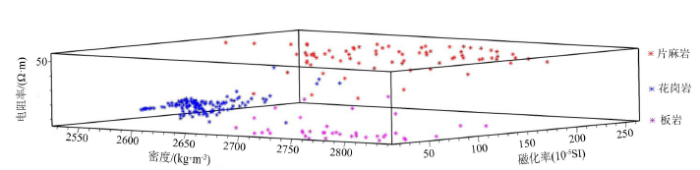
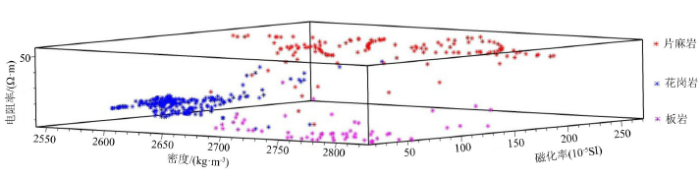
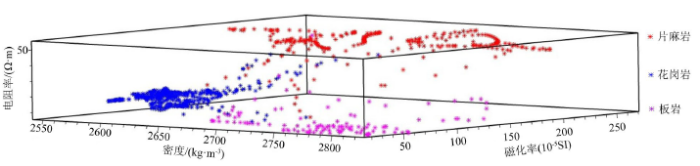
| 岩石名称 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | 磁化率/(10-5SI) | 电阻率/(Ω·m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 板 岩 | 2630~2850 | 0~160 | 3~8 |
| 片麻岩 | 2570~2830 | 180~280 | 40~60 |
| 花岗岩 | 2580~2640 | 0~160 | 10~30 |
图2
图2
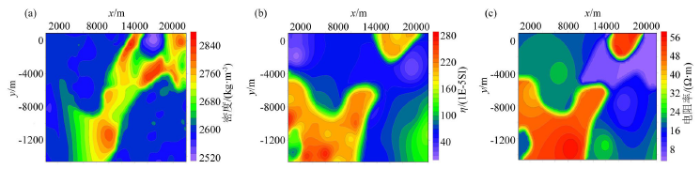
模型物性
a—模型密度;b—模型磁化率;c—模型电阻率
Fig.2
Physical properties of the model
a— density of the model;b—magnetic susceptibility of the model;c—resistivity of the model
图3
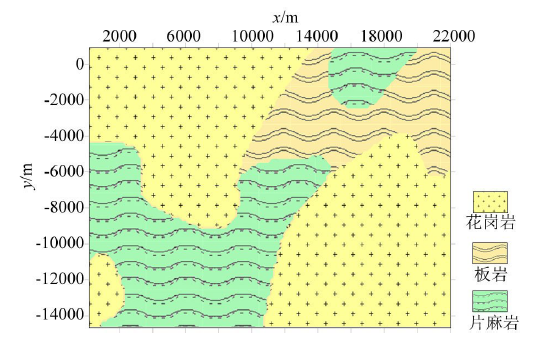
图3
岩石分布
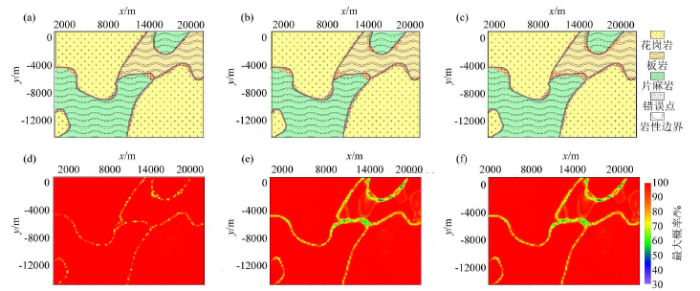
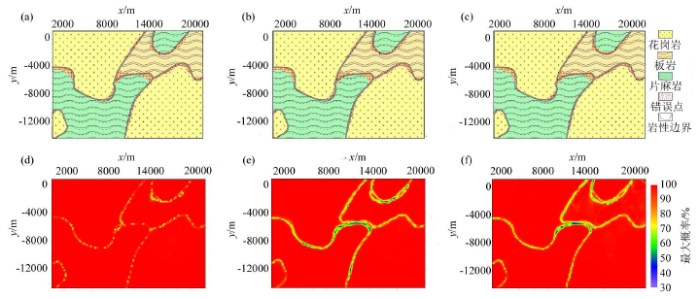
该模型共有8 690个样本点,分别选取250、435、870个点作为训练样本,其他点作为测试样本,
Fig.3
rock distribution of the model
图4
图4
250点训练样本物性参数交互图
Fig.4
Interaction diagram of physical parameters of 250 training samples
图5
图5
250点训练样本分类结果
a~f分别表示对于250个训练样本点的传统高斯分类、固定带宽的核密度估计、自适应带宽的核密度估计的贝叶斯分类结果以及其对应的概率分布
Fig.5
Classification results of 250 training samples
Figures a~f respectively represent the Bayesian classification results, corresponding probability distribution map of the traditional Gaussian classification, fixed bandwidth kernel density estimation, adaptive bandwidth kernel density estimation for 250 training sample points
图6
图6
435点训练样本物性参数交互图
Fig.6
Interaction diagram of physical parameters of 435 training samples
图7
图7
435点训练样本分类结果
a~f分别表示对于435个训练样本点的传统高斯分类、固定带宽的核密度估计、自适应带宽的核密度估计的贝叶斯分类结果以及其对应的概率分布
Fig.7
Classification results of 435 training samples
Figures a~f respectively represent the Bayesian classification results, corresponding probability distribution map of the traditional Gaussian classification, fixed bandwidth kernel density estimation, adaptive bandwidth kernel density estimation for 435 training sample points
图8
图8
869点训练样本物性参数交互图
Fig.8
Interaction diagram of physical parameters of 869 training samples
图9
图9
869点训练样本分类结果
a~f分别表示对于869个训练样本点的传统高斯分类、固定带宽的核密度估计、自适应带宽的核密度估计的贝叶斯分类结果以及其对应的概率分布
Fig.9
Classification results of 435 training samples
Figures a~frespectively represent the Bayesian classification results, corresponding probability distribution map of the traditional Gaussian classification, fixed bandwidth kernel density estimation, adaptive bandwidth kernel density estimation for 869 training sample points
表2 模型错误率统计
Table 2
| 训练样本/个 | 错误率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 传统高斯算法 | 固定带宽核密度估计 | 自适应带宽核密度估计 | |
| 250 | 4.52 | 4.48 | 4.17 |
| 435 | 4.58 | 4.51 | 4.09 |
| 870 | 4.46 | 4.37 | 4.20 |
从表2的错误率上而言,在同样的训练样本下,基于自适应核密度估计的贝叶斯概率模型明显优于其他两类模型。由此可知,贝叶斯概率密度模型对于深部岩性识别的方法是有效可行的,而基于自适应核密度估计的贝叶斯概率模型相比于其他概率密度模型而言效果相对较好。
通过测试不同训练样本对于分类结果的影响,最终可以得到针对该模型,训练样本每类都少于40个时便无法进行合理的岩性识别,当然并非训练样本的数量越多越好,样本质量对于识别结果也有着决定性作用。
通过对比3种概率密度方法得到的分类结果可知,基于自适应带宽的贝叶斯概率模型下的分类错误率是相对较低的且在模糊区有一个明显的低概率带,因此,模型二将针对模型一中435点训练样本在自适应带宽下的测试样本进行概率差下的统计分析。
若两种类型岩石的预测概率差在拟定的差值之内,就认为该未知样本属于这两类岩性的概率相同,对于3种岩性也同样适用,对于该模型而言,若3种岩性的概率差都在拟定的差值内,则认为无法对该样本进行岩性识别,选择更大的概率差,意味着模型的容错率降低,同时,识别类型唯一的样本可信度也随之变大,针对不同的概率差,预测结果不同。
图10为概率差在10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%概率差下的岩性预测结果,白色区域表示3种岩性被认为是等概率的情况,即无法识别的区域,同时,浅色区域代表可能为两种岩性。在无法进行准确的岩性识别的区域进行人工识别或者二次识别,避免了机器学习在岩性识别过程中由于算法本身的局限性,导致预测结果唯一且无法进行人工推断可信度的问题,在机器学习和人工识别中找寻一个平衡,发挥二者优势,在提高岩性识别效率和准确度的同时使得预测结果明朗可操作。
图10
图10
预测分类结果
a~f依次为概率差在10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%时的分类结果
Fig.10
Forecast classification results
a~f are the classification results when the probability difference is 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50% and 60% respectively
3 结论与建议
笔者将基于自适应核密度估计的贝叶斯概率模型应用到岩性识别中,该方法的优势在于,对于有一定重合区域的物性参数,可以有效地进行未知区域的岩性识别,提高计算的精度和效率,将多种物性参数进行合理的处理解释,提高数据利用率,通过各个数据之间的相互作用,最终获得岩性识别结果。
从本文的模型可以看出,基于自适应核密度估计的贝叶斯概率模型能够较好地刻画未知地区岩性的类别和轮廓,对于模糊区也可以较好地进行判定。事实上,该方法并不局限于以上几种参数,对于其他的物性参数也可以进行同样的处理,识别结果的精度也依靠于更多类型的物性参数和更好质量的训练样本。
参考文献
岩性反演的完整方法第一部分:理论
[J].
Complete lithology inversion method of the first part theory
[J].
基于马尔科夫随机场的岩性识别方法
[J].
Lithologic discrimination method based on Markov random-field
[J].
综合地球物理方法识别准噶尔盆地的岩性圈闭
[J].
Discussion on identifying method for identification of lithologic traps in Junggar Basin by comprehensive geophysical method
[J].
应用地震波形分类技术识别岩相的适用性和局限性
[J].
The applicability and limitations of the seismic wave-form classification technology to the identification of lithological facies
[J].
A Bayesian model for lithology/fluid class prediction using a Markov mesh prior fitted from a training image
[J].
三塘湖盆地火山岩岩性识别方法
[J].
Methods for lithology discrimination of volcanics in Santanghu Basin
[J].
利用交会图法识别国外M油田岩性与流体类型的研究
[J].
DOI:10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.03.037
URL

2.5CU,BK162API.2)油气层有效孔隙度PHIE>20%,SW2Ω·m;水层的有效孔隙度PHIE>20%,但是SW>55%,BK
Research on the identification of the lithology and fluid type of foreign Moilfield by using the crossplot method
[J].
DOI:10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.03.037
URL

2.5CU and BK162API; 2)for hydrocarbon bearing formation:PHIE>20%,SW2 Ω·m;for water bearing formation PHIE>20%,but SW>55% and BK
文昌13-1油田低阻油层测井岩性识别方法研究
[J].
Study on identification method of logging lithology for low resistivity reservoir in Wenchang 13-1 Oilfield
[J].
交会图技术在火山岩岩性与裂缝识别中的应用
[J].
Application of crossplot technique to the determination of lithology composition and fracture identification of igneous rock
[J].
利用逐步法和Fisher判别法识别储层岩性
[J].
Identifying reservoir lithology by step-by-step method and Fisher discriminant
[J].
基于小波神经网络的ODP1148A井岩性预测
[J].为对大洋钻探计划(ODP) 1148A井岩性收获率低的层位和涂片分析之外的井段进行岩性预测, 得到更全面的岩性信息, 设计出了一个以“morlet”小波为隐含层传递函数的三层小波神经网络.将总样本中的一部分作为学习样本, 用于小波神经网络的训练, 另一部分作为测试样本, 用于检验小波神经网络预测岩性正确与否以及预测结果的误差评价.经过对该小波神经网络反复测试和调整, 最终得到了一个误差最小的神经网络, 其测试结果显示岩性预测符合率60%以上的占总体的60%以上.在没有岩心资料或取芯收获率低的层段, 可将其用于粗略的岩性参考.将经测试后较满意的小波神经网络应用于整口井的岩性预测, 得到该井的详细岩性信息.该岩性预测结果弥补了岩心涂片分析数据较少, 以及该井岩心收获率低的层位的岩性空白.本文将小波神经网络应用于测井岩性预测方法的探讨可为人工智能与地球物理测井相结合提供新的思路.
Tang YThe lithology prediction of ODP hole 1148A based on the wavelet neural network
[J].In order to predict the lithological characters of the low core recovery intervals of the hole 1148A of the Ocean Drilling Program (ODP) and of the intervals beyond the smear analysis, and to obtain more detailed lithology information, a wavelet neural network of three layers with ‘morlet’ wavelet as the transfer function of the hidden layer was devised and programmed based on the MATLAB software. The lithological smear samples of the ODP site 1148A were divided into two parts. One part of the total samples was designed as the learning sample used to train the net, and the other part was employed as the test sample planed to test whether the predicted lithology was true and to evaluate its error. After testing and adjusting the designed wavelet neural network over and over again, finally a most appropriate one was proposed with the right parameters and the minimum error. The test results showed that those with the lithology prediction coincidence rate of 60% and above accounted for more than sixty percent of all the test samples. These results can be used as a rough lithology reference at intervals with no core or low core recovery rate. When this optimal wavelet neural network was applied to the lithology prediction for the ODP hole 1148A, the lithological information of the whole hole was obtained, including sand, silt and clay contents at all intervals in this hole. This result was a supplementary to the relatively rare smear analysis data and it filled in the blanks of the low core recovery intervals of this hole. The method of applying the wavelet neural network to the log data for lithology prediction can provide a new idea for the combination of the artificial intelligence and the geophysical well logging.
基于连续限制玻尔兹曼机的支持向量机岩性识别方法
[J].
Lithology identification method based on continuous restricted Boltzmann machine and support vector machine
[J].
基于深度学习的测井岩性识别方法研究与应用
[J].
Research and application of logging lithology identification based on deep learning
[J].
Automatic lithology prediction from well logging using kernel density estimation
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.012 URL [本文引用: 1]
岩性识别技术现状与进展
[J].
Current status and progress of lithology identification technology
[J].
基于重磁反演的三维岩性填图试验——以安徽庐枞矿集区为例
[J].开展大型矿集区深部精细结构探测研究,通过岩性识别与填图实现矿集区5km以内“透明化”,发现深部矿产、揭示成矿规律是实现资源可持续发展的主要途径。鉴于重力和磁力数据覆盖面积广、采样密度高,重磁三维反演算法比较成熟,采用重磁反演进行岩性填图是现阶段实现三维岩性填图最有可能的途径。本文以安徽庐枞矿集区为例,提出了基于重力、磁力三维反演的岩性填图流程并开展了填图试验。在分析岩性和密度、磁化率关系的基础上,采用高精度的重力和航磁数据,进行先验信息约束的重磁三维反演,对反演所得的密度体和磁化率体进行逻辑拓扑运算,获得了庐枞矿集区地下5km以内五类主要岩性的三维分布。岩性填图结果显示的浅部特征与地表地质填图结果基本吻合,更重要的是反映了深部岩性的变化,弥补了地表地质填图的不足。庐枞矿集区岩性填图试验结果表明,开展基于重磁三维反演的岩性填图,是了解矿集区深部岩性特征,发现深部矿产的有效方法。
3D lithologic mapping test based on 3D inversion of gravity and magnetic data: A case study in Lu-Zong ore concentration district, Anhui Province
[J].Through lithologic mapping to achieve ore concentration district transparent within 5km depth is the main way to realize deep fine structures study, to explore deep mineral resources and to reveal metallogenic regularity of large-scale ore district. Owing to the wide covered area, high sampling density and mature three-dimensional inversion algorithm of gravity and magnetic data, so gravity and magnetic inversion become the most likely way to achieve three-dimensional lithologic mapping at the present stage. In this paper, we take Lu-Zong (Lujiang County to Zongyang County in Anhui Province, East China) ore concentration district as an example, we proposed lithologic mapping flow based on 3D inversion of gravity magnetic and then carry out the lithologic mapping test. Based on the analysis of relations between lithology and density and magnetic susceptibility, 3D inversion with prior information of high-precision gravity and aeromagnetic data were carried out. Then, we use logical topology operations between density 3D model and susceptibility 3D model obtained three-dimensional distribution of five main type lithologies in the Lu-Zong ore concentration district within 5km depth. The result of lithologic mapping not only showed that the shallow characteristics and surface geological mapping are basically coincide, more importantly reveals the deeper lithologic changes, it make up the insufficient of surface geological mapping. The lithologic mapping test results in Lu-Zong ore concentration district showed that Ethological mapping using 3D inversion of gravity and magnetic is a effective method to reveal the lithological characteristics and to explore deep mineral resources in ore concentration district.
识别火成岩岩性的综合物探技术
[J].
Integrated geophysical techniques for identification of igneous rocks
[J].
Automated compilation of pseudo-lithology maps from geophysical data sets: A comparison of Gustafson-Kessel and fuzzy c-means cluster algorithms
[J].
DOI:10.1071/EG11014
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The fuzzy partitioning Gustafson-Kessel cluster algorithm is employed for rapid and objective integration of multi-parameter Earth-science related databases. We begin by evaluating the Gustafson-Kessel algorithm using the example of a synthetic study and compare the results to those obtained from the more widely employed fuzzy c-means algorithm. Since the Gustafson-Kessel algorithm goes beyond the potential of the fuzzy c-means algorithm by adapting the shape of the clusters to be detected and enabling a manual control of the cluster volume, we believe the results obtained from Gustafson-Kessel algorithm to be superior. Accordingly, a field database comprising airborne and ground-based geophysical data sets is analysed, which has previously been classified by means of the fuzzy c-means algorithm. This database is integrated using the Gustafson-Kessel algorithm thus minimising the amount of empirical data processing required before and after fuzzy c-means clustering. The resultant zonal geophysical map is more evenly clustered matching regional geology information available from the survey area. Even additional information about linear structures, e. g. as typically caused by the presence of dolerite dykes or faults, is visible in the zonal map obtained from Gustafson-Kessel cluster analysis.
Joint inversion of geochemical data and geophysical logs for lithology identification in CCSD main hole
[J].
Lithology and mineralogy recognition from geochemical logging tool data using multivariate statistical analysis
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.06.041
URL
PMID:28688247
[本文引用: 1]

The availability of a deep well that penetrates deep into the Ultra High Pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks is unusual and consequently offers a unique chance to study the metamorphic rocks. One such borehole is located in the southern part of Donghai County in the Sulu UHP metamorphic belt of Eastern China, from the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling Main hole. This study reports the results obtained from the analysis of oxide log data. A geochemical logging tool provides in situ, gamma ray spectroscopy measurements of major and trace elements in the borehole. Dry weight percent oxide concentration logs obtained for this study were SiO2, K2O, TiO2, H2O, CO2, Na2O, Fe2O3, FeO, CaO, MnO, MgO, P2O5 and Al2O3. Cross plot and Principal Component Analysis methods were applied for lithology characterization and mineralogy description respectively. Cross plot analysis allows lithological variations to be characterized. Principal Component Analysis shows that the oxide logs can be summarized by two components related to the feldspar and hydrous minerals. This study has shown that geochemical logging tool data is accurate and adequate to be tremendously useful in UHP metamorphic rocks analysis.
A machine learning-based approach to exploration targeting of porphyry Cu-Au deposits in the Dehsalm district, Eastern Iran
[J].
Remarks on some nonparametric estimates of a density function
[J].
On estimation of a probability density function and mode
[J].
Choice of kernel function for density estimation
[J].
DOI:10.1109/tpami.1980.4767013
URL
PMID:21868899
[本文引用: 1]

Let l=f^n(x) be the kernel estimate of a density f(x) from a sample of size n. Wahba [6] has developed an upper bound to E[f(x)-l=f^n(x)]2. In the present paper, we find the kernel function of finite support [m=-T, T] that minimizes Wahba's upper bound. It is Q(y) = (1 + am=-1) (2T)m=-1 [1-m=-a|y|a] where a = 2-pm=-1, p m=ge 1.
Kernel density estimation ofactuarial loss functions
[J].
The estimation of the gradient of adensity function with applications in pattern recognition
[J].
基于估计点的滑动窗宽核密度估计算法
[J].针对核密度估计中窗宽确定困难的问题,提出了基于估计点的滑动变窗宽核密度估计算法。通过采用固定窗宽的密度估计函数代替假设的正态分布密度函数的方法,对估计域中的每一估计点求取其最优窗宽值,实现了窗宽根据样本的分布情况,在不同的估计点自动调整窗宽的取值。文中给出了算法的具体推导以及实现步骤,给出了对比试验。结果表明,新算法在估计结果的精度、平滑度等方面比现有固定窗宽的算法有明显提高。
Slide Bandwidh Kernel Density Estimation Algorithm Based on Estimate Point
[J].