|
|
|
| Grain size effect and chemical speciation of elements in tailings from the Han-Xing iron deposit: Implications for resource utilization and environmental protection |
CHANG Hao1( ), YUAN Zhao-Xian2( ), YUAN Zhao-Xian2( ) ) |
1. No.1 Geological Team of Hebei Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration, Handan 056000, China
2. Institute of Resource and Environmental Engineering, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang 050031, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Despite bearing valuable recyclable elements, mine tailings pose environmental risks. However, there is a lack of studies on the geochemical characteristics of tailings in China and abroad, hindering their appropriate treatment and reuse. This study collected tailing samples from the Han-Xing Iron deposit in Hebei Province, China and conducted the analysis and tests of these samples. This study determined the concentrations and chemical speciation (i.e., exchangeable, carbonate-bound, Fe-Mn oxide-bound, organic-bound, and residual forms) of elements including Fe, Co, S, Cu, and Zn in tailing particles with varying grain sizes. Accordingly, it explored the implications for the exploitation and utilization of tailing resources, along with the assessment of environmental risks. This study provides deeper insights into the geochemical characteristics of tailings, producing positive impacts on the exploitation and utilization of tailing resources, as well as the prevention of environmental risks.
|
|
Received: 08 October 2023
Published: 22 April 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
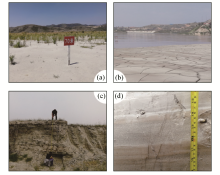
|
Pictures of tailings from Han-Xing Fe deposits
a—the tailings pond of Houjin, Xishimen; b—the tailings pond of Jianshanbei, Beiminghe; c—the tailings pond of Xisizhuang; d—strat-ification of coarse and fine tailings
|

| 元素 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 均值 | 富集系数 | 元素 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 均值 | 富集系数 | | Co | 17.9 | 187.2 | 53.1 | 0.96 | Be | 0.69 | 3.00 | 1.71 | 0.01 | | Fe | 1.6 | 13.5 | 4.2 | 0.54 | Mo | 0.14 | 5.20 | 1.01 | <0.01 | | Ti | 1266 | 4199 | 2161 | 0.47 | Cr | 13.7 | 218.0 | 47.7 | <0.01 | | S | 0.01 | 3.90 | 1.43 | 0.28 | Ag | 0.01 | 0.50 | 0.04 | <0.01 | | Zr | 73.1 | 284.3 | 133.0 | 0.24 | Sn | 0.4 | 6.9 | 1.2 | <0.01 | | Nb | 1.96 | 15.60 | 5.60 | 0.22 | Bi | 0.03 | 2.70 | 0.20 | <0.01 | | Cu | 24.8 | 529.0 | 88.8 | 0.13 | Sb | 0.05 | 1.40 | 0.30 | <0.01 | | V | 34.1 | 229.0 | 70.1 | 0.08 | Ba | 129.3 | 666.0 | 284.0 | / | | Zn | 0.1 | 614.0 | 49.6 | 0.06 | Cd | 0.05 | 0.80 | 0.10 | / | | Ni | 6.6 | 136.7 | 21.3 | 0.05 | Ce | 27.9 | 87.3 | 47.4 | / | | Mn | 489 | 3616 | 998 | 0.03 | La | 14.2 | 64.1 | 29.4 | / | | W | 0.13 | 37.10 | 2.60 | 0.03 | Sr | 91.5 | 608.0 | 182.0 | / | | Li | 8.3 | 77.0 | 26.0 | 0.02 | Y | 10.0 | 28.7 | 16.6 | / | | Pb | 0.7 | 119.3 | 8.6 | 0.02 | Yb | 0.8 | 2.4 | 1.5 | / | | As | 2.1 | 23.5 | 6.4 | 0.01 | | | | | |
|
Statistics of element contents in tailing samples from Han-Xing Fe deposits
|

粒度
特征 | 各粒径占比/% | 合计 | | >0.5 mm | 0.5~0.1 mm | 0.1~0.075 mm | <0.075 mm | | 细 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 98.2 | 100 | | 中细 | 0.2 | 16.1 | 7.5 | 76.2 | 100 | | 中 | 0.2 | 68.0 | 14.2 | 17.6 | 100 | | 中粗 | 1.6 | 87.3 | 6.3 | 4.8 | 100 | | 粗 | 14.2 | 73.3 | 3.1 | 9.4 | 100 |
|
Granular composition of tailing samples from Han-Xing Fe deposits
|
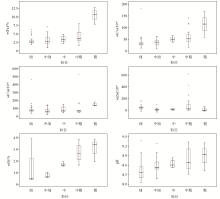
|
Comparison of element contents in tailings with different particle sizes
|
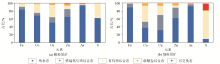
|
Chemical speciation of important elements in tailings with different particle sizes
|
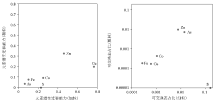
|
Comparison of elemental migration potential in tailings with different particle sizes
|
| [1] |
Pan H J, Zhou G H, Cheng Z Z, et al. Advances in geochemical survey of mine tailings project in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139:193-200.
|
| [2] |
冯聪. 提升我国矿产资源开发利用水平的思考[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2018, 31(4):20-24.
|
| [2] |
Feng C. Considerations on improving the exploitation and utilization of mineral resources in China[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 2018, 31(4):20-24.
|
| [3] |
Hudson-Edwards K A, Jamieson H E, Lottermoser B G. Mine wastes:Past,present,future[J]. Elements, 2011, 7(6):375-380.
|
| [4] |
Tang L, Liu X M, Wang X Q, et al. Statistical analysis of tailings ponds in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 216:106579.
|
| [5] |
Lottermoser B G. Recycling,reuse and rehabilitation of mine wastes[J]. Elements, 2011, 7(6):405-410.
|
| [6] |
Jamieson H E. Geochemistry and mineralogy of solid mine waste:Essential knowledge for predicting environmental impact[J]. Elements, 2011, 7(6):381-386.
|
| [7] |
Mulenshi J, Gilbricht S, Chelgani S C, et al. Systematic characterization of historical tailings for possible remediation and recovery of critical metals and minerals-The Yxsjöberg case[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 226:106777.
|
| [8] |
Plumlee G S, Morman S A. Mine wastes and human health[J]. Elements, 2011, 7(6):399-404.
|
| [9] |
赵一阳, 喻德科. 黄海沉积物地球化学分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1983, 14(5):432-446.
|
| [9] |
Zhao Y Y, Yu D K. Geochemical analysis of the sediments of the Huanghai sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1983, 14(5):432-446.
|
| [10] |
杜德文, 石学法, 孟宪伟, 等. 黄海沉积物地球化学的粒度效应[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(1):78-82.
|
| [10] |
Du D W, Shi X F, Meng X W, et al. Geochemical granularity effect of sediment in the Yellow Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2003, 21(1):78-82.
|
| [11] |
熊尚发, 朱园健, 周茹, 等. 白水黄土—红粘土化学风化强度的剖面特征与粒度效应[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(5):812-821.
|
| [11] |
Xiong S F, Zhu Y J, Zhou R, et al. Chemical weathering intensity and its grain-size dependence for the loess-red clay deposit of the Baishui section,Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(5):812-821.
|
| [12] |
刘汉粮, 迟清华, 王玮, 等. 内蒙古中东部残山丘陵草原覆盖区化探方法研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(3):382-388.
|
| [12] |
Liu H L, Chi Q H, Wang W, et al. Geochemical methods for grassland-covered hilly terrains in central-eastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(3):382-388.
|
| [13] |
关天霞, 何红波, 张旭东, 等. 土壤中重金属元素形态分析方法及形态分布的影响因素[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(2):503-512.
|
| [13] |
Guan T X, He H B, Zhang X D, et al. The methodology of fractionation analysis and the factors affecting the species of heavy metals in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 42(2):503-512.
|
| [14] |
胡忻, 陈茂林, 吴云海, 等. 城市污水处理厂污泥化学组分与重金属元素形态分布研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2005, 24(2):387-391.
|
| [14] |
Hu X, Chen M L, Wu Y H, et al. Chemical components and heavy metals in sludge from wastewater treatment plant[J]. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science, 2005, 24(2):387-391.
|
| [15] |
谢华林, 张萍, 贺惠, 等. 大气颗粒物中重金属元素在不同粒径上的形态分布[J]. 环境工程, 2002, 20(6):55-57,5.
|
| [15] |
Xie H L, Zhang P, He H, et al. Distribution of heavy metal elements in the different diametral atmospheric particulate matters[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2002, 20(6):55-57,5.
|
| [16] |
沈保丰, 翟安民, 李增慧, 等. 冀南邯邢式铁矿成矿地质条件分析[J]. 地质学报, 1981, 55(2):127-138,164.
|
| [16] |
Shen B F, Zhai A M, Li Z H, et al. The analysis of geological conditions for mineralization of the iron deposits of Han-Xing subtype in southern Hebei[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 1981, 55(2):127-138,164.
|
| [17] |
郑建民. 冀南邯邢地区夕卡岩铁矿成矿流体及成矿机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2007.
|
| [17] |
Zheng J M. Ore-forming fluid and mechanism of skarn iron deposit in Hanxing area,southern Hebei Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2007.
|
| [18] |
徐国志, 邓金火, 徐锦鹏. 河北邯邢式铁矿尾矿地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(9):1439-1444.
|
| [18] |
Xu G Z, Deng J H, Xu J P. Geochemical characteristics of Hanxing style iron ore tailings,Hebei Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(9):1439-1444.
|
| [19] |
秦飞, 李倩, 季宏兵, 等. 密云县潮河流域沿岸铁矿集中区土壤中稀土元素的地球化学特征及粒度效应[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2014, 32(1):108-116.
|
| [19] |
Qin F, Li Q, Ji H B, et al. Geochemical characteristics and granularity effect of rare earth elements in soils from iron ore areas along the Chao River[J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2014, 32(1):108-116.
|
| [20] |
王亚平, 黄毅, 王苏明, 等. 土壤和沉积物中元素的化学形态及其顺序提取法[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(8):728-734.
|
| [20] |
Wang Y P, Huang Y, Wang S M, et al. Chemical speciation of elements in sediments and soils and their sequential extraction process[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2005, 24(8):728-734.
|
| [21] |
胡文, 王海燕, 查同刚, 等. 北京市凉水河污灌区土壤重金属累积和形态分析[J]. 生态环境, 2008, 17(4):1491-1497.
|
| [21] |
Hu W, Wang H Y, Zha T G, et al. Soil heavy metal accumulation and speciation in a sewage-irrigated area along the Liangshui River,Beijing[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2008, 17(4):1491-1497.
|
| [22] |
陈天虎, 冯军会, 徐晓春, 等. 尾矿中硫化物风化氧化模拟实验研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2002, 21(3):298-302.
|
| [22] |
Chen T H, Feng J H, Xu X C, et al. Simulation experiments on weathering and oxidation of sulfide minerals in mine tailings[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2002, 21(3):298-302.
|
| [23] |
Carmona D M, Faz Cano Á, Arocena J M. Cadmium,copper,lead,and zinc in secondary sulfate minerals in soils of mined areas in Southeast Spain[J]. Geoderma, 2009, 150(1/2):150-157.
|
| [24] |
牛晓鹏. 方铅矿、黄铜矿和黄铁矿表面氧化与可浮性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019.
|
| [24] |
Niu X P. Study on surface oxidation and floatability of galena,chalcopyrite and pyrite[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019.
|
| [25] |
生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 15618—2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
|
| [25] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment,State Administration for Market Supervision and Administration. GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.
|
| [1] |
CUI Yuan-jun, LI Xiao-peng, DONG Jian, HU Xue-ping. THE CHEMICAL SPECIATION DISTRIBUTION AND TRANSITION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AROUND GOLD ORE DISTRICTS AS WELL AS CITIES AND TOWNS IN YANTAI, SHANDONG PROVINCE[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(6): 1100-1106. |
| [2] |
PAN Zi-ping, QIAO Wen-lang, MENG Wei, HE Shao-lin, LI Chao-jin, YAN Cheng-zhi, WANG Fang. CHEMICAL SPECIATION OF CADMIUM IN SOIL OF GUIYANG CITY AND ITS ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(4): 737-742. |
|
|
|
|

