|
|
|
| Application of ground-penetrating radar in detecting the internal structures of the ancient Great Wall in Linhai City |
YANG Hao1( ), ZOU Jie2, CHENG Dan-Dan1, YU Jing-Lan1 ), ZOU Jie2, CHENG Dan-Dan1, YU Jing-Lan1 |
1. China Research Institute of Radiowave Propagation,Qingdao 266000,China
2. Xinjiang Highway and Bridge Test and Testing Center Co.,Ltd.,Urumqi 830000,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Non-destructive testing of the internal structural characteristics of ancient buildings is the key to preserving cultural relics.To determine the structures and internal defects of the ancient Great Wall in Linhai City,this study performed non-destructive testing of the wall structures in different orientations using a ground-penetrating radar (GPR) combining 100 MHz and 270 MHz antennas.The testing results show significant structural stratification in the ancient Great Wall.The GPR signal-reflected images reveal clear internal wall defects like pores,cracks,voids,and other hidden dangers.This study demonstrates the reliability of the GPR in detecting structures and defects of ancient walls,there by providing technical support for the structural protection of the ancient Great Wall.
|
|
Received: 19 March 2024
Published: 08 January 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
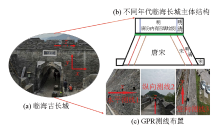
|
Schematic diagram of the main structure of Linhai Ancient Great Wall
|
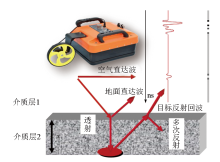
|
Schematic diagram of GPR detection
|

| 因素名称 | 因素符号 | 相关公式 | 符号含义 | | 埋深 | h | h= vt | v—电磁波波速,m/ns
t—双程走时,ns | | 衰减系数 | β | | f—电磁频率,Hz
μ—介质磁导率,H/m
σ—介质电导率,mS/m | | 介电常数 | εr | | c—光速,3×108m/ns | | 反射系数 | r | | / | | 水平分辨率 | Δx | | H0—垂直测距,m
λ—电磁波波长,m | | 垂直分辨率 | Δh | | / |
|
Key factors of GPR detection principle
|

| 介质 | 电导率/
(ms·m-1) | 相对介
电常数 | 波速/
(m·ns-1) | 衰减系数/
(dB·m-1) | | 空气 | 0 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | | 水 | 10-4 | 81 | 0.033 | 0.1 | | 砂(干) | 10-7~10-3 | 4~6 | 0.15 | 0.01 | | 砂(湿) | 10-4~10-2 | 30 | 0.06 | 0.03~0.3 | | 黏土(湿) | 10-1~1 | 5~40 | 0.06 | 1~300 | | 青砖 | 10-4 | 7~9 | 0.1~0.12 | 0.03 | | 墙体土 | 10-5 | 9~14 | 0.08~0.1 | 0.03~0.06 |
|
Relative permittivity of different media
|

| 测线 | 天线频率/MHz | 时窗/ns | 采样频率/(samples·s-1) | 采样间隔/cm | 叠加次数 | 触发方式 | 探测深度/m | | 1 | 270 | 80 | 128 | 1 | 16 | 距离触发 | 2~3 | | 2 | 100 | 200 | 128 | 1 | 16 | 距离触发 | 5 | | 3 | 270 | 80 | 128 | 1 | 16 | 距离触发 | 2~3 |
|
Antenna frequency and GPR parameter settings for different survey lines
|

|
GPR data processing before(a) and after(b) comparison diagram
|
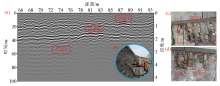
|
Detection results of outer wall structural layer
|
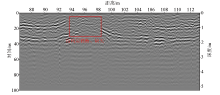
|
Map of GPR detection results for survey line 1
|
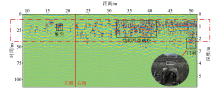
|
Map of GPR detection results for survey line 2
|
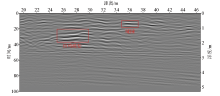
|
Map of GPR detection results for survey line 3
|
| [1] |
王亚清, 武毅, 查恩来. 探地雷达技术在山海关古城墙隐伏缺陷探测中的应用研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2010, 7(1):93-96.
|
| [1] |
Wang Y Q, Wu Y, Zha E L. The application of GPR to the detection of defects of the Shanhaiguan wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2010, 7(1):93-96.
|
| [2] |
宗鑫, 王心源, 刘传胜, 等. 探地雷达在地下考古遗存探测中的实验与应用[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2016, 18(2):272-281.
|
| [2] |
Zong X, Wang X Y, Liu C S, et al. Experiments and applications of ground penetrating radar in the investigation of subsurface archaeological interest[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2016, 18(2):272-281.
|
| [3] |
刘国辉, 董茂干, 张建南. 探地雷达技术在长城墙体检测中的应用[J]. 工程勘察, 2006, 34(6):63-66.
|
| [3] |
Liu G H, Dong M G, Zhang J N. Application of ground penetrating rader to wall-body inspecting of the great wall[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2006, 34(6):63-66.
|
| [4] |
刘岩. 探地雷达在水工建筑地基病害检测中的运用[J]. 黑龙江水利科技, 2018, 46(11):130-131.
|
| [4] |
Liu Y. Ground penetrating radar application in defect detection of hydraulic structure foundation[J]. Heilongjiang Hydraulic Science and Technology, 2018, 46(11):130-131.
|
| [5] |
李长生, 杜翠, 刘杰, 等. 基于探地雷达的路桥过渡段病害检测识别方法[J]. 铁道建筑, 2022, 62(8):19-22.
|
| [5] |
Li C S, Du C, Liu J, et al. Detection and identification method of subgrade-bridge transition section diseases based on ground penetrating radar[J]. Railway Engineering, 2022, 62(8):19-22.
|
| [6] |
陈裕权. 探地雷达法在公路隐性病害检测中的应用[J]. 大众标准化, 2022(17):170-172.
|
| [6] |
Chen Y Q. Application of ground penetrating radar method in highway hidden disease detection[J]. Popular Standardization, 2022(17):170-172.
|
| [7] |
杨美群, 邹友泉, 刘静. 探地雷达在高速公路路面隐性病害检测的应用[J]. 公路, 2022, 67(8):86-91.
|
| [7] |
Yang M Q, Zou Y Q, Liu J. Application of ground penetrating radar in detection of hidden diseases on expressway pavement[J]. Highway, 2022, 67(8):86-91.
|
| [8] |
朱楠男, 李家存, 叶培盛. 探地雷达在古墓遗址探测中的应用——以北京市通州区古墓群探测为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(3):577-582.
|
| [8] |
Zhu N N, Li J C, Ye P S. The application of the ground penetrating radar(GPR) to the detection of Ruins of ancient tombs[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(3):577-582.
|
| [9] |
王亮, 王绪本, 李正文. 探地雷达在金沙遗址考古探测中的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2008, 32(4):401-403.
|
| [9] |
Wang L, Wang X B, Li Z W. The application of ground penetrating radar to the archeological exploration of Jinsha Ruins[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(4):401-403.
|
| [10] |
覃谭, 赵永辉, 林国聪, 等. 探地雷达在上林湖越窑遗址水下考古中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(3):624-630.
|
| [10] |
Qin T, Zhao Y H, Lin G C, et al. The application of GPR to underwater archaeological investigation of Shanglinhu Yue kiln relics[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(3):624-630.
|
| [11] |
鹿金秒. 临海古长城江南八达岭[J]. 浙江国土资源, 2007(8):58-59.
|
| [11] |
Lu J M. Linhai ancient great wall Jiangnan Badaling[J]. Zhejiang Land & Resources, 2007(8):58-59.
|
| [12] |
曾昭发, 刘四新, 冯晅, 等. 探地雷达原理与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2010.
|
| [12] |
Zeng Z F, Liu S X, Feng X, et al. Principle and application of ground penetrating radar[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2010.
|
| [13] |
赵文轲. 探地雷达属性技术及其在考古调查中的应用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013.
|
| [13] |
Zhao W K. The study of ground penetrating radar attribute technology for archaeological prospection[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013.
|
| [14] |
张春城. 浅地层探地雷达中的信号处理技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2005.
|
| [14] |
Zhang C C. Research on signal processing technology of shallow subsurface ground penetrating radar[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2005.
|
| [1] |
YIN Da, XIN Guo-Liang, SUN Xue-Chao, ZHANG You-Yuan, ZHANG Qi-Dao. Design and implementation of key technologies for real-time three-dimensional ground-penetrating radar[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1): 194-200. |
| [2] |
XI Yu-He, WANG Hong-Hua, WANG Yu-Cheng, WU Qi-Ming. Application of the minimum entropy method based on a velocity-controlled moving window to the reverse time migration of ground-penetrating radars[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1250-1260. |
|
|
|
|

