|
|
|
| Application of three-dimensional magnetic anomaly inversion in magnetite exploration |
ZHAO Bai-Ru1,2( ), LI Hou-Pu3( ), LI Hou-Pu3( ), ZHANG Heng-Lei1,2 ), ZHANG Heng-Lei1,2 |
1. School of Geophysics and Geomatics, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan 430074, China
2. Key Laboratory of Geological Survey and Evaluation of Ministry of Education, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan 430074, China
3. School of Electrical Engineering, Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Galinge iron deposit in Qinghai is overlain by deposits measuring greater than 150 m in thickness. The great burial depths of ore bodies lead to gentle magnetic anomaly morphology, making it difficult to characterize the spatial distribution of ore bodies. Therefore, this study employed three-dimensional magnetic anomaly inversion to determine the three-dimensional distribution characteristics of subsurface magnetic intensity in the study area. Given the prior information of non-magnetic surrounding rocks, the three-dimensional magnetic intensity model clearly presented the spatial distribution of the ore bodies and reflected the presence of intense magnetic bodies at depths of less than 500 m in existing boreholes. Accordingly, it can be inferred that there exist concealed ore bodies at depths exceeding 500 m in the study area. The results of this study suggest that three-dimensional magnetic anomaly inversion can effectively improve target identification, providing clear information on the horizontal positions, depths, and scales of magnetic ore bodies. The proposed inversion method can offer strong support for drilling design and reserve estimation, warranting promotion in detailed exploration of solid minerals.
|
|
Received: 15 April 2024
Published: 08 January 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
24])
">
|
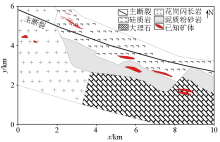
The geological map in Galinge depoist(adapted from Zhang et al.[24])
|

| 岩矿名称 | 标本数 | 几何平均值 | | κ/(4π·10-6SI) | Jr/(10-3A·m-1) | | 致密块状磁铁矿 | 149 | 5.01×105 | 6.40×104 | | 稀疏浸染状磁铁矿 | 171 | 4.23×104 | 2.86×104 | | 磁铁矿化黄铁矿 | 19 | 5.90×104 | 2.56×104 | | 含磁铁矿磁黄铁矿 | 27 | 1.02×104 | 2.34×103 | | 磁铁矿化矽卡岩 | 56 | 1.23×104 | 6.41×103 | | 磁铁矿化硅质角岩 | 9 | 9.2×104 | 7.36×103 | | 磁铁矿化辉石岩 | 25 | 8.27×104 | 9.97×103 | | 矿化大理岩 | 12 | 1.33×103 | 4.88×102 | | 矽卡岩化大理岩 | 47 | 1.49×103 | 4.91×102 | | 细晶闪长岩 | 3 | 1.07×103 | 8.15×102 | | 泥质硅质岩 | 16 | 3.77×102 | 1.98×102 |
|
Magnetic measurement data sheet for rock and mineral specimens in the study area
|
Figure 3, edited according to Wang et al.[3])
">
|
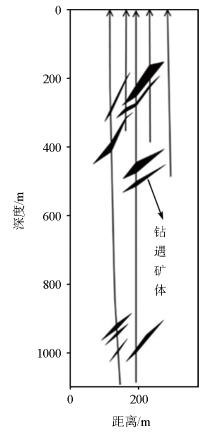
Cross-section of borehole line 9
(with the location of the section as shown in Figure 3, edited according to Wang et al.[3])
|
|
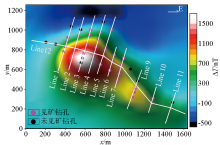
Magnetic anomaly ΔT in the study area
|
|
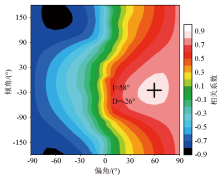
The correlation coefficient diagram between the RTP anomaly and the vertical derivative of the normalized magnetic source intensity
|
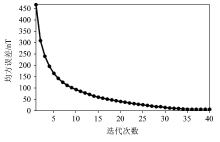
|
Inverse iteration mean square error curve
|
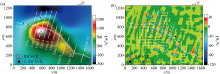
|
Three-dimensional inversion fitting of magnetic anomalies (a) and residual magnetic anomalies (b)
|
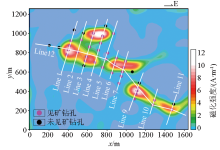
|
Three-dimensional magnetization intensity horizontal slice at 200 meters depth
|
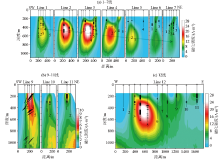
|
Three-dimensional magnetization intensity depth slice
(The arrow lines represent the drillhole locations, and the black blocks represent the ore ranges illustrated by the drilling)
|
| [1] |
吴小霞, 保广英, 伊有昌, 等. 青海省尕林格富铁矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2007, 15(4):36-40.
|
| [1] |
Wu X X, Bao G Y, Yi Y C, et al. The study on the genesis and geological characteristics of Galinge high-grade iron deposit of Qinghai Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2007, 15(4):36-40.
|
| [2] |
何书跃, 祁兰英, 舒树兰, 等. 青海祁漫塔格地区斑岩铜矿的成矿条件和远景[J]. 地质与勘探, 2008, 44(2):14-22.
|
| [2] |
He S Y, Qi L Y, Shu S L, et al. Metallogenic environment and potential in the Qimantage porphyry copper deposit,Qinghai[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2008, 44(2):14-22.
|
| [3] |
汪钟莲, 王永国, 王智茂, 等. 地面磁测资料反演与井中磁测联合找矿——以尕林格铁多金属矿床Ⅱ矿段为例[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(1):61-67.
|
| [3] |
Wang Z L, Wang Y G, Wang Z M, et al. Joint prospecting of ground magnetic survey data inversion and borehole magnetic survey:A case study of Galinge Fe-polymetallic deposit[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(1):61-67.
|
| [4] |
袁洋, 崔益安, 陈波, 等. 基于BTTB矩阵的快速高精度三维磁场正演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(3):1107-1124.
|
| [4] |
Yuan Y, Cui Y A, Chen B, et al. Fast and high accuracy 3D magnetic anomaly forward modeling based on BTTB matrix[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(3):1107-1124.
|
| [5] |
李丽丽, 周建业, 马国庆, 等. 起伏观测面约束的重磁数据快速联合物性反演方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2024, 39(4),1447-1456.
|
| [5] |
Li L L, Zhou J Y, Ma G Q, et al. A study of fast joint physical inversion methods of gravity and magnetic data with undulating observation surface constraints[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2024, 39(4),1447-1456.
|
| [6] |
李玉录, 邢利娟, 拜占红, 等. 综合物探方法在青海省跃进山铁矿勘查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(5):889-895.
|
| [6] |
Li Y L, Xing L J, Bai Z H, et al. The application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting method to the exploration of the Yuejinshan iron deposit in Qinghai[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(5):889-895.
|
| [7] |
张明君, 严加永. 重磁3D反演在新疆伊吾县宝山铁矿找矿增储中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2014, 50(1):156-161.
|
| [7] |
Zhang M J, Yan J Y. Application of gravity and magnetic 3D inversion to ore search and reserve increase in the Baoshan iron deposit,Yiwu County,Xinjiang[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2014, 50(1):156-161.
|
| [8] |
刘璎, 孟贵祥, 严加永, 等. 重磁3D物性反演技术在金属矿勘探中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011, 47(3):448-455.
|
| [8] |
Liu Y, Meng G X, Yan J Y, et al. Application of 3D property inversion for gravity and magnetic data to metal mineral exploration[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2011, 47(3):448-455.
|
| [9] |
胡斌, 贾正元, 张贵宾, 等. 青藏高原冈底斯带及邻区重磁三维反演及岩浆岩特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(4):1362-1376.
|
| [9] |
Hu B, Jia Z Y, Zhang G B, et al. Three-dimensional inversion of gravity and magnetic data and its application in the study on the characteristics of magmatic rocks in the Gangdise belt and adjacent areas,Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(4):1362-1376.
|
| [10] |
赵理芳, 李希元, 李成立, 等. 基于重、磁、电法的多宝山矿集区隐伏斑岩体识别与深部找矿实践[J]. 矿床地质, 2022, 41(6):1217-1231.
|
| [10] |
Zhao L F, Li X Y, Li C L, et al. Recognition of concealed porphyry body and deep prospecting practice in Duobaoshan ore concentration area based on gravity,magnetic and electromagnetic surveys[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2022, 41(6):1217-1231.
|
| [11] |
索奎, 张贵宾, 梅岩辉, 等. 重磁三维反演伊犁盆地中部密度和磁性结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(8):3410-3419.
|
| [11] |
Suo K, Zhang G B, Mei Y H, et al. Density and magnetic susceptibility distribution of central Yili Basin by three-dimensional inversion of gravity and magnetic data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(8):3410-3419.
|
| [12] |
严加永, 吕庆田, 陈向斌, 等. 基于重磁反演的三维岩性填图试验——以安徽庐枞矿集区为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(4):1041-1053.
|
| [12] |
Yan J Y, Lyu Q T, Chen X B, et al. 3D lithologic mapping test based on 3D inversion of gravity and magnetic data:A case study in Lu-Zong ore concentration district,Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(4):1041-1053.
|
| [13] |
饶椿锋, 于鹏, 胡书凡, 等. 基于加权模型参数的归一化磁源强度三维反演[J]. 石油物探, 2017, 56(4):599-606.
|
| [13] |
Rao C F, Yu P, Hu S F, et al. The 3D inversion of the normalized source strength data based on weighted model parameters[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2017, 56(4):599-606.
|
| [14] |
王婕, 姚长利, 李泽林. 磁异常揭示的峨眉山大火成岩省的深部结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(4):1394-1404.
|
| [14] |
Wang J, Yao C L, Li Z L. Deep structure in the Emeishan large igneous province revealed by inversion of magnetic anomalies[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(4):1394-1404.
|
| [15] |
张志厚, 路润琪, 廖晓龙, 等. 基于全卷积神经网络的磁异常及磁梯度异常反演[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(1):325-337.
|
| [15] |
Zhang Z H, Lu R Q, Liao X L, et al. Inversion of magnetic anomaly and magnetic gradient anomaly based on fully convolution network[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(1):325-337.
|
| [16] |
李泽林, 姚长利, 郑元满, 等. 数据空间磁异常模量三维反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(10):3804-3814.
|
| [16] |
Li Z L, Yao C L, Zheng Y M, et al. 3D data-space inversion of magnetic amplitude data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(10):3804-3814.
|
| [17] |
张恒磊, 耿美霞, 胡祥云. 基于曲波压缩的重磁异常三维反演及其应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2023, 58 (4):993-1001.
|
| [17] |
Zhang H L, Geng M X, Hu X Y. Three-dimensional inversion of gravity/magnetic anomalies based on curvelet compression and its applications[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2023, 58(4):993-1001.
|
| [18] |
Li Y G, Oldenburg D W. Fast inversion of large-scale magnetic data using wavelet transforms and a logarithmic barrier method[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2003, 152(2):251-265.
|
| [19] |
朱朝吉, 周肇武, 刘天佑, 等. 高精度磁测找矿效果:以青海尕林格矿区为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011, 47(2):277-283.
|
| [19] |
Zhu C J, Zhou Z W, Liu T Y, et al. Application of high-precision magnetic survey to prospecting:A case study in the Galinge ore district of Qinghai Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2011, 47(2):277-283.
|
| [20] |
Zhang H L, Ravat D, Marangoni Y R, et al. NAV-Edge:Edge detection of potential-field sources using normalized anisotropy variance[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(3):43-53.
|
| [21] |
Zhang H L, Ravat D, Hu X Y. An improved and stable downward continuation of potential field data:The truncated Taylor series iterative downward continuation method[J]. Geophysics, 2013, 78(5):75-86.
|
| [22] |
刘双, 刘天佑, 曾琴琴. 根据磁异常确定磁性体上顶埋深的几种反演方法——以尕林格矿区磁测资料解释为例[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2012, 9(4):413-418.
|
| [22] |
Liu S, Liu T Y, Zeng Q Q. On inversion methods of estimating top buried depth of magnetic body based on magnetic anomalies:A case study of magnetic datainterpretation in Galinge mining area[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2012, 9(4):413-418.
|
| [23] |
Huang L, Zhang H L, Sekelani S, et al. An improved Tilt-Euler deconvolution and its application on a Fe-polymetallic deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 114:103114.
|
| [24] |
Zhang H L, Li H P, Hu X Y. Fine interpretation of magnetic data for a concealed mineral deposit:A case study of the Fe-polymetallic deposit from Western China[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2024, 228:105468.
|
| [25] |
Zhang H L, Ravat D, Marangoni Y R, et al. Improved total magnetization direction determination by correlation of the normalized source strength derivative and the reduced-to-pole fields[J]. Geophysics, 2018, 83(6):75-85.
|
| [26] |
张恒磊, 刘天佑, 朱朝吉, 等. 高精度磁测找矿效果—以青海尕林格矿区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(1):12-16.
|
| [26] |
Zhang H L, Liu T Y, Zhu C J, et al. The effects of applying high-precision magnetic survey:A case study of the Galinge ore district in Qinghai province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(1):12-16.
|
| [27] |
宋双, 张恒磊. 向下延拓在深部矿产勘探中的应用——以青海某矿区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1195-1199.
|
| [27] |
Song S, Zhang H L. The application of downward continuation to deep mineral exploration:A case study of an ore district in Qinghai Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6):1195-1199.
|
| [28] |
张恒磊, Y.R.Marangoni, 左仁广, 等. 改进的各向异性标准化方差探测斜磁化磁异常源边界[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57 (8):2724-2731.
|
| [28] |
Zhang H L, Y R Marangoni, Zuo R G, et al. The improved anisotropy normalized variance for detecting non-vertical magnetization anomalies[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(8):2724-2731.
|
| [1] |
MA Zhen-Bo, ZHOU Chang-Yu, RUAN Jin-Ping, ZHANG Wen-Yan. Effective information extraction from high-order pseudo-random electromagnetic signals in urban environments:A case study of a rail transit engineering area in Jinan City, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(6): 1709-1719. |
| [2] |
JIANG Guo-Qing, HAO She-Feng, YU Yong-Xiang, Du Jian-Guo, LI Ming, SHANG Tong-Xiao, SONG Jing-Lei. Landslide survey based on three-dimensional resistivity inversion: A case study of the Xuelang Mountain scenic spot, Wuxi, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(6): 1720-1729. |
|
|
|
|

