|
|
|
| Application of wide-field electromagnetic sounding method to deep prospecting in the Mangling ore concentration area in North Qinling: A case study of the Yaozhuang ore district |
ZHANG Xiao-Tuan1( ), LI Xin-Lin1,2( ), LI Xin-Lin1,2( ), ZHOU Bin1,2,3, GAO Wei-Qiang1 ), ZHOU Bin1,2,3, GAO Wei-Qiang1 |
1. Shaanxi Institute of Geological Survey, Xi'an 710004, China
2. Shaanxi Geological Survey Planning Research Center, Xi'an 710068, China
3. School of Earth Science and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Mangling ore concentration area with intense magmatic activity has become a focal area for deep prospecting in the North Qinling tectonic belt in recent years. The formation of molybdenum deposits in this area is closely related to small Late Jurassic acidic intrusions. To achieve breakthroughs in deep ore prospection within this area, this study conducted the wide-field electromagnetic sounding over the concealed Yaozhuang intrusion delineated based on gravity anomalies. The results indicate the presence of pronounced high-resistivity anomalies at depth, and it is inferred that the protruding part of the anomalies corresponds to the concealed Yaozhuang intrusion. The resistivity inversion results roughly delineated the variations in the top surface of the intrusion, with the elevations and N-S width of the top surface estimated at -300~620 m and 1300~1600 m, respectively. Drilling in the most favorable deep mineralized part confirmed the presence of the concealed intrusion and concealed molybdenum ore bodies. The results of this study demonstrate that the wide-field electromagnetic sounding method exhibits great sounding depths and high resolutions, serving as an effective method for deep ore prospecting in the Mangling ore concentration area.
|
|
Received: 20 February 2024
Published: 08 January 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
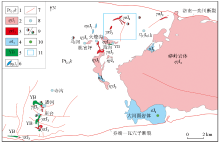
|
The geological sketch map of the Mangling ore concentration area
1—Neo-Mesoproterozoic Kuanping rock group;2—late Jurassic monzogranite;3—late Jurassic granite porphyry;4—late Jurassic diorite;5—late Jurassic phreatic breccia;6—late Jurassic diorite porphyry;7—fault;8—molybdenum deposit;9—lead-zinc deposit/copper-lead-zinc deposit;10—copper deposit;11—Yaozhuang ore district
|
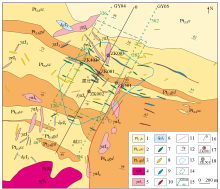
|
Simplified geological map of Yaozhuang ore district
1—Neo-Mesoproterozoic Xiewan Formation;2—Neo-Mesoproterozoic Sichakou Formation;3—Neo-Mesoproterozoic Guangdongping Formation;4—late Jurassic monzogranite;5—late Jurassic granite porphyry;6—late Jurassic diorite porphyry;7—pyrite silicified altered rock;8—quartz vein;9—lead-zinc ore body;10—molybdenum-tungsten ore body;11—fault;12—occurrence;13—Yaozhuang concealed intrusion;14—metallogenetic prospective areas of molybdenum by WFEM;15—WFEM profile station, number of line and point;16—exploration line 0 profile;17—experimental verification drill hole;18—design drill hole
|

| 填图单位 | 岩性名称 | 样品
数/块 | ρ/(Ω·m) | | 变化范围 | 均值 | 晚侏罗世
侵入岩体 | 花岗斑岩 | 30 | 169.5~3937.8 | 1524.0 | | 二长花岗岩 | 32 | 254~2450.3 | 1383.2 | 中—新元古界
广东坪岩组 | 钠长阳起片岩 | 31 | 68.2~487.7 | 214.2 | 中—新元古界
四岔口岩组 | 黑云石英片岩 | 31 | 198.4~1910.9 | 785.3 |
|
Electrical parameter statistic of rock in the research area
|
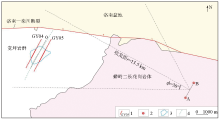
|
Schematic diagram of wide field electromagnetic work layout
1—WFEM profile;2—power supply pole distance;3—Yaozhuang concealed intrusion;4—high-tension line
|
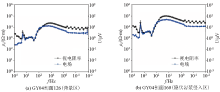
|
Frequency variation curves following electrical field and apparent resistivity curves at experimental points
|
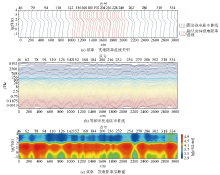
|
Apparent resistivity comprehensive section of GY04 profile
|
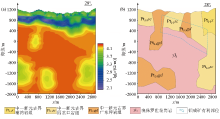
|
Inversion resistivity section(a)and geological interpretation (b)of GY04 by WFEM
|
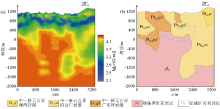
|
Inversion resistivity section(a)and geological interpretation (b)of GY05 by WFEM
|
28])
">
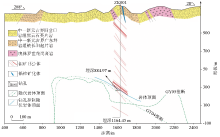
|
Comprehensive cross-sectional map of exploration line 0 in the Yaozhuang ore district(modified by Zhou et al. [28])
|
| [1] |
李诺, 陈衍景, 张辉, 等. 东秦岭斑岩钼矿带的地质特征和成矿构造背景[J]. 地学前缘, 2007, 14(5):186-198.
|
| [1] |
Li N, Chen Y J, Zhang H, et al. Molybdenum deposits in East Qinling[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(5):186-198.
|
| [2] |
卢欣祥, 罗照华, 黄凡, 等. 小岩浆大流体成大矿与透岩浆流体成矿作用——以东秦岭—大别山成矿带钼矿床为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(5):1554-1570.
|
| [2] |
Lu X X, Luo Z H, Huang F, et al. “Small” magma and “big” fluid lead to form large scale deposit and transmagmatic fluid mineralization:Take for example of Mo deposits in eastern Qinling-Dabie mountain metallogenic belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(5):1554-1570.
|
| [3] |
柯昌辉, 王晓霞, 李金宝, 等. 北秦岭马河钼矿区花岗岩类的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(1):267-278.
|
| [3] |
Ke C H, Wang X X, Li J B, et al. Geochronology and geological significance of the granites from the Mahe Mo deposit in the North Qinling[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(1):267-278.
|
| [4] |
柯昌辉, 王晓霞, 杨阳, 等. 北秦岭南台钼多金属矿床成岩成矿年龄及锆石Hf同位素组成[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(6):1562-1576.
|
| [4] |
Ke C H, Wang X X, Yang Y, et al. Rock-forming and ore-forming ages of the Nantai Mo polymetallic deposit in North Qinling Mountains and its zircon Hf isotope composition[J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(6):1562-1576.
|
| [5] |
张元厚, 毛景文, 简伟, 等. 东秦岭地区钼矿床研究现状及存在问题[J]. 世界地质, 2010, 29(2):188-202.
|
| [5] |
Zhang Y H, Mao J W, Jian W, et al. Present status of research on molybdenum deposit in eastern Qinling and the problems remained[J]. Global Geology, 2010, 29(2):188-202.
|
| [6] |
Fan P, Xi A H, Zhou B, et al. Discovery of Yaozhuang stock and deep ore prospecting implication for the western mangling orefield in North Qinling terrane,Central China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10:830453.
|
| [7] |
周斌, 李新林. 北秦岭蟒岭地区斑岩型—热液脉型钼矿深部找矿勘查技术方法研究[C]// 第二届全国矿产勘查大会, 2023.
|
| [7] |
Zhou B and Li X L. Research in deep prospecting and exploration technology and method of of porphyry-magmatic hydrothermal molybdenum deposit in Mangling area,North Qinling[C]// The 2nd National Mineral Exploration Conference, 2023.
|
| [8] |
滕吉文, 薛国强, 宋明春. 第二深度空间矿产资源探查理念与电磁法找矿实践[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(10):3975-3985.
|
| [8] |
Teng J W, Xue G Q, Song M C. Theory on exploring mineral resources in the second deep space and practices with electromagnetic method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(10):3975-3985.
|
| [9] |
滕吉文. 高精度地球物理学是创新未来的必然发展轨迹[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(4):1131-1144.
|
| [9] |
Teng J W. High-precision geophysics:The inevitable development track of the innovative future[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(4):1131-1144.
|
| [10] |
杨海涛, 刘新伟, 汪超, 等. 蠎西寺沟斑岩—矽卡岩型钨钼矿物化探异常特征及找矿模型[J]. 地质与勘探, 2022, 58(5):929-939.
|
| [10] |
Yang H T, Liu X W, Wang C, et al. Geophysical and geochemical anomaly characteristics and ore prospecting model for the sigou porphyry-skarn type tungsten-molybdenum deposit in mangxi area[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2022, 58(5):929-939.
|
| [11] |
程红军, 陈川, 展新忠, 等. 隐伏矿床成矿预测理论与方法新进展[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(3):456-463.
|
| [11] |
Cheng H J, Chen C, Zhan X Z, et al. New progress in the prediction theory and prospecting method for concealed deposits[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2017, 53(3):456-463.
|
| [12] |
陈后扬, 李帝铨, 凌帆, 等. 朱溪钨铜矿的广域电磁法深部探测[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2022, 32(10):3227-3243.
|
| [12] |
Chen H Y, Li D Q, Ling F, et al. Deep exploration of wide field electromagnetic method in Zhuxi W-Cu deposit[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 32(10):3227-3243.
|
| [13] |
何继善. 广域电磁测深法研究[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 41(3):1065-1072.
|
| [13] |
He J S. Wide field electromagnetic sounding methods[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology Edition, 2010, 41(3):1065-1072.
|
| [14] |
何继善. 大深度高精度广域电磁勘探理论与技术[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(9):1809-1816.
|
| [14] |
He J S. Theory and technology of wide field electromagnetic method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(9):1809-1816.
|
| [15] |
何继善. 广域电磁法理论及应用研究的新进展[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(5):985-990.
|
| [15] |
He J S. New research progress in theory and application of wide field electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5):985-990.
|
| [16] |
何继善. 伪随机信号广域电磁法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2023.
|
| [16] |
He J S. Wide-area electromagnetic method of pseudo-random signal[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2023.
|
| [17] |
凌帆, 朱裕振, 周明磊, 等. 广域电磁法在南华北盆地长山隆起页岩气资源潜力评价中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(2):369-376.
|
| [17] |
Ling F, Zhu Y Z, Zhou M L, et al. Shale gas potential assessment of Changsan uplift area in southern North China basin by using wide field electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(2):369-376.
|
| [18] |
王润生, 张保涛, 柳森, 等. 胶东牟平—乳山成矿带金青顶金矿广域电磁法探测效果分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2022, 58(2):381-390.
|
| [18] |
Wang R S, Zhang B T, Liu S, et al. Application effects of the wide field electromagnetic method in the jinqingding gold deposit in Muping- Rushan metallogenic belt,Jiaodong peninsula[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2022, 58(2):381-390.
|
| [19] |
邵炳松, 阮传侠, 赵苏民, 等. 广域电磁法在郑州地区深部地热资源勘查中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2023, 59(2):316-327.
|
| [19] |
Shao B S, Ruan C X, Zhao S M, et al. The application of wide field electromagnetic method to deep geothermal resources exploration in Zhengzhou area[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2023, 59(2):316-327.
|
| [20] |
王丹丹, 张交东, 刘旭锋, 等. 广域电磁法在豫西地区济源凹陷古生界油气勘探中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2023, 59(2):328-336.
|
| [20] |
Wang D D, Zhang J D, Liu X F, et al. Application of the wide field electromagnetic method to Paleozoic oil and gas exploration in the Jiyuan depression of western Henan Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2023, 59(2):328-336.
|
| [21] |
董云鹏, 张国伟, 朱炳泉. 北秦岭构造属性与元古代构造演化[J]. 地球学报, 2003, 24(1):3-10.
|
| [21] |
Dong Y P, Zhang G W, Zhu B Q. Proterozoic tectonics and evolutionary history of the North Qinling terrane[J]. Acta Geosicientia Sinica, 2003, 24(1):3-10.
|
| [22] |
王洪军, 熊玉新. 广域电磁法在胶西北金矿集中区深部探测中的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(5):1039-1047.
|
| [22] |
Wang H J, Xiong Y X. The application of wide field electromagnetic method to deep exploration in Jiaoxibei (northwest Shandong) gold concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5):1039-1047.
|
| [23] |
李帝铨, 肖教育, 张继峰, 等. WFEM与CSAMT在新元煤矿富水区探测效果对比[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1359-1366.
|
| [23] |
Li D Q, Xiao J Y, Zhang J F, et al. Comparison of application effects of WFEM and CSAMT in water-rich area of Xinyuan Coal Mine[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1359-1366.
|
| [24] |
汤中立, 焦建刚, 闫海卿, 等. 小岩体成(大)矿理论体系[J]. 中国工程科学, 2015, 17(2):4-18,2.
|
| [24] |
Tang Z L, Jiao J G, Yan H Q, et al. Theoretical system for(large) deposit formed by smaller intrusion[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2015, 17(2):4-18,2.
|
| [25] |
汤中立, 钱壮志, 姜常义, 等. 岩浆硫化物矿床勘查研究的趋势与小岩体成矿系统[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(1):1-9.
|
| [25] |
Tang Z L, Qian Z Z, Jiang C Y, et al. Trends of research in exploration of magmatic sulfide deposits and small intrusions metallogenic system[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(1):1-9.
|
| [26] |
Sillitoe R H. Porphyry copper systems[J]. Economic Geology, 2010, 105(1):3-41.
|
| [27] |
金露英, 秦克章, 李光明, 等. 斑岩钼—热液脉状铅锌银矿成矿系统特征、控制因素及勘查指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(12):3813-3839.
|
| [27] |
Jin L Y, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. Characteristics,controlling factors and exploration implications of porphyry molybdenum-hydrothermal vein-style lead-zinc-silver metallogenic systems[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(12):3813-3839.
|
| [28] |
周斌, 范鹏, 杨文博, 等. 陕西典型小岩体成矿预测与勘查示范成果报告[R]. 西安市:陕西省地质调查规划研究中心, 2024.
|
| [28] |
Zhou B, Fan P, Yang W B, et al. Report on metallogenic prediction and exploration demonstration of typical small rock masses in Shaanxi province[R]. Xi’an:Shaanxi geological survey planning research center, 2024.
|
|
|
|

