|
|
|
| Analysis of soil heavy metal influencing factors and sources in typical small watersheds in shallow mountainous area |
SHI Jing-Tao1( ), LIU Jun-Jian1( ), LIU Jun-Jian1( ), ZHANG Jun-Chao2, WANG Jiang-Yu-Long1, JIANG Yu-Ge1, WANG Mo1, LI Heng-Fei1, YANG Wen-Hao1, YAN Xiang-Jin3 ), ZHANG Jun-Chao2, WANG Jiang-Yu-Long1, JIANG Yu-Ge1, WANG Mo1, LI Heng-Fei1, YANG Wen-Hao1, YAN Xiang-Jin3 |
1. Langfang Natural Resources Comprehensive Survey Center,China Geological Survey,Langfang 065000,China
2. Pingquan Soil and Water Conservation Construction Service Center,Pingquan 067500,China
3. Mudanjiang Natural Resources Comprehensive Survey Center,China Geological Survey,Mudanjiang 157000,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study investigated the contents of eight heavy metals and related oxides in rocks with different lithologies and the soils formed in the Puhe river basin of Pingquan City. Based on the above investigation, this study analyzed the influencing factors and sources of soil heavy metals in the typical small watershed of the shallow mountainous area, aiming to provide theoretical support for water conservation and ecological restoration in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Based on the contents and spatial distributions of soil heavy metals and combined with regional geological setting, this study delved into the influencing factors and sources of heavy metal elements in topsoil, deep soil, and soil parent materials using multiple statistical methods. The results show that heavy metals in topsoil and deep soil exhibited relatively similar contents and coupled spatial distributions. In terms of vertical distributions, the correlation coefficients of heavy metals were negative between topsoil and soil parent materials but positive between deep soil and soil parent materials. As indicated by the results, in the topsoil, elements Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Pb are primarily derived from soil parent materials, while elements Cd, Hg, and As are subjected to the influence of mining. In contrast, the eight heavy metals in the deep soil predominantly stem from soil parent materials, with anthropogenic factors contributing to Cd and As.
|
|
Received: 19 June 2023
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
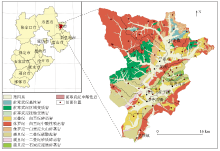
|
Geological diagram and sampling location of the study area
|

| 项目 | 统计参数 | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Hg | As | | 表层土壤 | 最大值 | 1374.0 | 369.0 | 192.0 | 172.0 | 2.070 | 57.2 | 0.221 | 33.7 | | 最小值 | 14.6 | 11.6 | 4.9 | 11.2 | 0.050 | 9.3 | 0.011 | 2.1 | | 平均值 | 86.1 | 37.3 | 30.9 | 82.3 | 0.199 | 26.5 | 0.040 | 9.9 | | 标准差 | 159.1 | 44.1 | 26.3 | 26.1 | 0.280 | 7.4 | 0.034 | 5.5 | | 变异系数/% | 184.7 | 118.1 | 85.0 | 31.7 | 140.4 | 27.9 | 87.0 | 55.2 | | 深层土壤 | 最大值 | 1975.0 | 443.0 | 234.0 | 219.0 | 3.190 | 53.2 | 0.290 | 30.5 | | 最小值 | 8.8 | 3.4 | 1.1 | 4.5 | 0.018 | 6.0 | 0.005 | 1.0 | | 平均值 | 96.5 | 39.4 | 33.1 | 84.8 | 0.207 | 25.1 | 0.033 | 9.0 | | 标准差 | 238.6 | 53.2 | 35.6 | 29.3 | 0.453 | 5.9 | 0.045 | 5.5 | | 变异系数/% | 247.4 | 134.8 | 107.6 | 34.6 | 218.8 | 23.6 | 138.2 | 61.2 | | 成土母岩 | 最大值 | 2542.0 | 652.0 | 307.0 | 350.0 | 3.250 | 59.7 | 4.124 | 116.7 | | 最小值 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 2.9 | 0.028 | 5.2 | 0.004 | 0.4 | | 平均值 | 85.1 | 34.6 | 27.5 | 72.4 | 0.229 | 21.6 | 0.101 | 6.3 | | 标准差 | 320.7 | 84.0 | 52.3 | 64.1 | 0.530 | 10.2 | 0.528 | 17.0 | | 变异系数/% | 376.7 | 242.6 | 190.2 | 88.4 | 231.7 | 47.3 | 520.9 | 269.0 | | 背景值[16] | 河北省表层 | 68,3 | 30.8 | 21.8 | 78.4 | 0.094 | 21.5 | 0.036 | 13.6 | | 河北省深层 | 72.6 | 34.1 | 23.0 | 78.4 | 0.097 | 25.1 | 0.022 | 14.2 |
|
The content of heavy metals in surface and deep soils and matrixes and corresponding statistical parameters
|
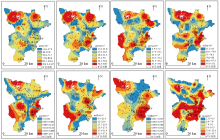
|
Spatial distribution of heavy metal content in surface soil
|

| 岩性单元 | 采样位置 | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Hg | As | | 第四系 | 表层土壤 | 77.57 | 33.73 | 33.21 | 78.87 | 0.180 | 29.80 | 0.033 | 8.15 | | 深层土壤 | 61.90 | 27.15 | 23.45 | 74.45 | 0.145 | 27.80 | 0.022 | 6.46 | | 成土母岩 | 61.10 | 27.00 | 18.60 | 75.40 | 0.065 | 17.20 | 0.008 | 0.59 | 中生代
碎屑岩 | 表层土壤 | 63.07 | 29.94 | 23.66 | 75.09 | 0.124 | 27.03 | 0.039 | 9.94 | | 深层土壤 | 60.67 | 29.96 | 22.64 | 75.05 | 0.096 | 25.43 | 0.018 | 7.37 | | 成土母岩 | 28.85 | 16.44 | 14.97 | 54.16 | 0.144 | 20.40 | 0.001 | 3.34 | 中生代中
酸性岩 | 表层土壤 | 52.53 | 23.54 | 29.33 | 82.56 | 0.156 | 28.07 | 0.032 | 6.87 | | 深层土壤 | 57.06 | 26.34 | 27.13 | 84.80 | 0.152 | 27.90 | 0.024 | 7.72 | | 成土母岩 | 21.99 | 11.48 | 23.06 | 69.76 | 0.246 | 26.91 | 0.015 | 3.38 | 中生代
火山碎屑岩 | 表层土壤 | 63.50 | 29.97 | 21.50 | 66.93 | 0.105 | 25.27 | 0.025 | 9.28 | | 深层土壤 | 69.50 | 34.13 | 26.37 | 76.17 | 0.120 | 26.27 | 0.016 | 9.30 | | 成土母岩 | 26.97 | 19.05 | 11.42 | 51.40 | 0.054 | 25.63 | 0.034 | 1.40 | 震旦纪—二叠
纪碳酸盐岩 | 表层土壤 | 56.19 | 29.28 | 23.88 | 72.44 | 0.230 | 23.74 | 0.043 | 12.11 | | 深层土壤 | 56.30 | 29.74 | 22.78 | 71.96 | 0.112 | 22.54 | 0.020 | 9.77 | | 成土母岩 | 24.60 | 18.53 | 7.00 | 38.08 | 0.071 | 10.99 | 0.022 | 3.45 | 震旦纪—石
炭纪泥质
碎屑岩 | 表层土壤 | 66.94 | 47.72 | 44.30 | 106.6 | 0.608 | 27.00 | 0.097 | 19.23 | | 深层土壤 | 69.07 | 43.88 | 45.30 | 93.37 | 0.473 | 26.62 | 0.119 | 19.17 | | 成土母岩 | 130.80 | 94.84 | 93.22 | 194.60 | 0.916 | 31.82 | 0.112 | 255.50 | 前寒武纪
基性岩 | 表层土壤 | 141.7 | 73.10 | 52.18 | 110.2 | 0.380 | 22.70 | 0.026 | 14.21 | | 深层土壤 | 95.28 | 56.98 | 85.63 | 113.9 | 0.872 | 18.12 | 0.024 | 10.41 | | 成土母岩 | 35.45 | 42.38 | 101.7 | 116.5 | 0.505 | 14.52 | 0.023 | 4.17 | 前寒武纪
变质岩 | 表层土壤 | 80.81 | 32.89 | 37.49 | 79.80 | 0.107 | 23.67 | 0.025 | 7.71 | | 深层土壤 | 94.36 | 38.21 | 44.51 | 91.92 | 0.142 | 22.30 | 0.032 | 6.33 | | 成土母岩 | 119.20 | 30.66 | 18.42 | 59.74 | 0.091 | 20.42 | 0.026 | 1.41 |
|
Average values of heavy metals in soil and host rocks in different soil-forming host rock units in the study area
|
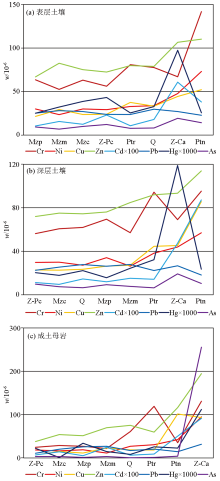
|
Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in surface soil, deep soil and forming soil matrix
Q—Quaternary system;Mzc—Mesozoic clastic rock;Mzm—Mesozoic acid rock; Mzp—Mesozoic pyroclastic rock;Z-Pc—Sinian-Permian carbonate rocks;Z-Ca—Sinian-Carboniferous argillaceous clastic rock; Ptn—Precambrian base rock; Ptr—Precambrian metamorphic rock
|
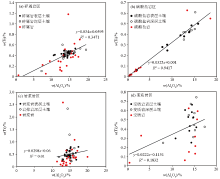
|
Scatter plots of Al2O3 and Ti of the original rock, surface and deep soil in the study area
|
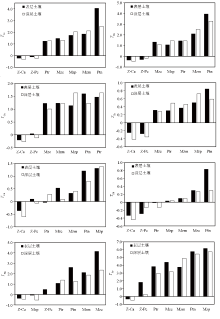
|
Migration coefficient of heavy metal elements in surface and deep soils
Mzc—Mesozoic clastic rock; Mzm—Mesozoic acid rock; Mzp—Mesozoic pyroclastic rock; Z-Pc—Sinian-Permian carbonate rocks; Z-Ca—Sinian-Carboniferous argillaceous clastic rock; Ptn—Precambrian base rock; Ptr—Precambrian metamorphic rock
|

| 指标 | SiO2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | K2O | Na2O | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Hg | As | | SiO2 | 1 | -0.941** | -0.958** | 0.629** | 0.391 | 0.565** | 0.316 | 0.321 | 0.116 | 0.297 | 0.395 | 0.033 | 0.693** | 0.163 | 0.218 | | CaO | -0.969** | 1 | 0.940** | -0.837** | -0.652** | -0.757** | -0.479* | -0.516* | -0.334 | -0.501* | -0.604** | -0.146 | -0.822** | -0.213 | -0.305 | | MgO | -0.688** | 0.573** | 1 | -0.729** | -0.494* | -0.686** | -0.480* | -0.363 | -0.153 | -0.376 | -0.456* | -0.066 | -0.750** | -0.194 | -0.239 | | Al2O3 | 0.879** | -0.929** | -0.581** | 1 | 0.895** | 0.931** | 0.723** | 0.707** | 0.573** | 0.702** | 0.799** | 0.270 | 0.862** | 0.234 | 0.391 | | Fe2O3 | 0.792** | -0.856** | -0.540** | 0.962** | 1 | 0.866** | 0.652** | 0.777** | 0.710** | 0.822** | 0.869** | 0.409 | 0.767** | 0.331 | 0.474* | | K2O | 0.692** | -0.706** | -0.480* | 0.819** | 0.827** | 1 | 0.763** | 0.564** | 0.406 | 0.573** | 0.721** | 0.105 | 0.740** | 0.100 | 0.185 | | Na2O | 0.743** | -0.717** | -0.518* | 0.650** | 0.539** | 0.455* | 1 | 0.316 | 0.183 | 0.378 | 0.468* | 0.161 | 0.425* | 0.256 | 0.322 | | Cr | 0.716** | -0.774** | -0.483* | 0.900** | 0.932** | 0.773** | 0.411 | 1 | 0.949** | 0.907** | 0.771** | 0.516* | 0.785** | 0.488* | 0.709** | | Ni | 0.491* | -0.529** | -0.307 | 0.703** | 0.722** | 0.617** | 0.166 | 0.878** | 1 | 0.892** | 0.730** | 0.588** | 0.686** | 0.451* | 0.728** | | Cu | 0.476* | -0.533** | -0.187 | 0.700** | 0.713** | 0.659** | 0.147 | 0.787** | 0.871** | 1 | 0.765** | 0.698** | 0.772** | 0.558** | 0.704** | | Zn | 0.561** | -0.582** | -0.329 | 0.670** | 0.676** | 0.611** | 0.170 | 0.817** | 0.928** | 0.856** | 1 | 0.516* | 0.843** | 0.370 | 0.468* | | Cd | -0.178 | 0.171 | 0.320 | -0.159 | -0.227 | -0.049 | -0.352 | -0.066 | 0.311 | 0.394 | 0.434* | 1 | 0.470* | 0.790** | 0.565** | | Pb | 0.662** | -0.672** | -0.462* | 0.681** | 0.691** | 0.578** | 0.303 | 0.698** | 0.626** | 0.614** | 0.750** | 0.070 | 1 | 0.371 | 0.486* | | Hg | -0.402 | 0.402 | 0.152 | -0.356 | -0.366 | -0.326 | -0.180 | -0.326 | -0.263 | -0.230 | -0.303 | 0.061 | -0.254 | 1 | 0.598** | | As | -0.291 | 0.305 | 0.100 | -0.213 | -0.219 | -0.208 | -0.271 | -0.047 | 0.290 | 0.234 | 0.323 | 0.663** | 0.115 | 0.332 | 1 |
|
Pearson correlation coefficients of eight heavy metals and oxides in surface soil samples (no base color) and deep soil samples (gray base color)
|

| 项目 | TCr | TNi | TCu | TZn | TCd | TPb | THg | TAs | | 粉粒 | 0.224 | 0.262* | 0.199 | 0.215 | 0.030 | 0.094 | 0.330* | 0.136 | | 细砂 | 0.328* | 0.324* | 0.140 | 0.291* | 0.084 | 0.076 | 0.219 | 0.115 | | 中砂 | -0.036 | -0.094 | -0.110 | -0.097 | -0.128 | -0.093 | -0.256 | -0.192 | | 粗砂 | -0.319* | -0.290* | -0.118 | -0.254 | -0.100 | -0.098 | -0.241 | -0.071 | | pH | -0.314* | -0.248 | -0.246 | -0.269* | -0.025 | 0.156 | 0.099 | 0.096 |
|
Correlation between soil pH and texture and migration coefficient of heavy metal elements
|

| 参数 | 粉粒
(0.002~
0.05mm) | 细砂
(0.05~
0.25mm) | 中砂
(0.25~
0.5mm) | 粗砂
(0.5~
1mm) | pH | | 最小值 | 4.87 | 14.35 | 6.96 | 5.92 | 5.96 | | 最大值 | 36.08 | 52.79 | 34.46 | 43.08 | 8.87 | | 平均值 | 14.66 | 38.59 | 22.70 | 21.06 | 7.71 | | 标准差 | 4.93 | 6.93 | 5.22 | 7.29 | 0.73 | | 变异系数 | 33.61 | 17.95 | 23.00 | 34.64 | 9.46 |
|
Statistics of the proportion of soil texture and pH value %
|

| 指标 | 表层土壤 | 深层土壤 | | F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | | Cr | 0.873 | -0.367 | 0.931 | -0.222 | | Ni | 0.954 | 0.008 | 0.916 | -0.156 | | Cu | 0.917 | 0.046 | 0.952 | -0.068 | | Zn | 0.977 | 0.064 | 0.828 | -0.352 | | Cd | 0.368 | 0.785 | 0.754 | 0.510 | | Pb | 0.778 | -0.191 | 0.820 | -0.369 | | Hg | -0.330 | 0.555 | 0.668 | 0.661 | | As | 0.291 | 0.864 | 0.784 | 0.233 | | 特征值 | 4.401 | 1.849 | 5.602 | 1.089 | | 方差/% | 55.018 | 23.108 | 70.019 | 13.611 |
|
Soil heavy metal element factor loading in the study area
|
| [1] |
Aelion C M, Davis H T, McDermott S, et al. Soil metal concentrations and toxicity:Associations with distances to industrial facilities and implications for human health[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2009, 407(7):2216-2223.
|
| [2] |
Wang Y Z, Duan X J, Wang L. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution:Case study in Jiangsu Province[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020,710:134953.
|
| [3] |
韩志轩, 王学求, 迟清华, 等. 珠江三角洲冲积平原土壤重金属元素含量和来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(9):3455-3463.
|
| [3] |
Han Z X, Wang X Q, Chi Q H, et al. Occurrence and source identification of heavy metals in the alluvial soils of Pearl River Delta region,South China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(9):3455-3463.
|
| [4] |
Manta D S, Angelone M, Bellanca A, et al. Heavy metals in urban soils:A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily),Italy[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2002, 300(1-3):229-243.
|
| [5] |
汪春鹏, 尤建功, 孙浩, 等. 辽阳市土壤重金属含量特征及潜在风险评价[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(10):1680-1687.
|
| [5] |
Wang C P, You J G, Sun H, et al. Characteristics and potential risk assessment of heavy metal contents in urban soil,Liaoyang City[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(10):1680-1687.
|
| [6] |
Rastegari M M, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, et al. Distribution,source identification and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in urban areas of Isfahan Province,Iran[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2017,132:16-26.
|
| [7] |
孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 甘凤伟, 等. 承德市滦河流域土壤重金属地球化学基线厘定及其累积特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8):3753-3763.
|
| [7] |
Sun H Y, Wei X F, Gan F W, et al. Determination of heavy metal geochemical baseline values and its accumulation in soils of the Luanhe River Basin,Chengde[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(8):3753-3763.
|
| [8] |
李甫, 刘俊建, 葛建平, 等. 典型水源涵养区废弃矿山生态修复效益评价指标体系研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2023, 32(5):44-52.
|
| [8] |
Li F, Liu J J, Ge J P, et al. Study on benefit evaluation index system of abandoned mine ecological restoration in typical water conservation area[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2023, 32(5):44-52.
|
| [9] |
刘瑞平, 徐友宁, 张江华, 等. 青藏高原典型金属矿山河流重金属污染对比[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(12):2154-2168.
|
| [9] |
Liu R P, Xu Y N, Zhang J H, et al. A comparative study of the content of heavy metals in typical metallic mine rivers of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(12):2154-2168.
|
| [10] |
Liao G L, Liao D X, Li Q M. Heavy metals contamination characteristics in soil of different mining activity zones[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(1):207-211.
|
| [11] |
郝红, 高博, 王健康, 等. 滦河流域沉积物中重金属分布特征及风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):1000-1005.
|
| [11] |
Hao H, Gao B, Wang J K, et al. Distribution characteristic and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Luanhe River[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):1000-1005.
|
| [12] |
王关玉, 潘懋, 刘锡大, 等. 山东省土壤中元素含量与母质的关系[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 1992, 28(4):475-485.
|
| [12] |
Wang G Y, Pan M, Liu X D, et al. On the relationship between the concentrations of elements in soil and the types of soil-forming parent material in Shandong Province,China[J]. Acta Scicentiarum Naturalum Universitis Pekinesis, 1992, 28(4):475-485.
|
| [13] |
朱自娟, 左丽君, 张增祥, 等. 1987-2015年京津冀西北水源涵养区生态格局时空变化[J]. 草业科学, 2020, 37(7):1325-1336.
|
| [13] |
Zhu Z J, Zuo L J, Zhang Z X, et al. Analysis of spatial and temporal changes of regional ecological pattern in the northwest of Jingjinji as water conservation area during the past 30 years[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(7):1325-1336.
|
| [14] |
宋运红, 杨凤超, 刘凯, 等. 三江平原耕地土壤重金属元素分布特征及影响因素的多元统计分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5):1064-1075.
|
| [14] |
Song Y H, Yang F C, Liu K, et al. A multivariate statistical analysis of the distribution and influencing factors of heavy metal elements in the cultivated land of the Sanjiang Plain[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5):1064-1075.
|
| [15] |
周墨, 唐志敏, 张明, 等. 江西赣州地区土壤—水稻系统重金属含量特征及健康风险评价[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(12):2149-2158.
|
| [15] |
Zhou M, Tang Z M, Zhang M, et al. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-rice system in the Ganzhou area,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(12):2149-2158.
|
| [16] |
中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社,1990.
|
| [16] |
China Environmental Monitoring Station. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press,1990.
|
| [17] |
马宏宏, 彭敏, 刘飞, 等. 广西典型碳酸盐岩区农田土壤—作物系统重金属生物有效性及迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1):449-459.
|
| [17] |
Ma H H, Peng M, Liu F, et al. Bioavailability,translocation,and accumulation characteristic of heavy metals in a soil-crop system from a typical carbonate rock area in Guangxi,China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1):449-459.
|
| [18] |
冯志刚, 刘威, 张兰英, 等. 贫Cd碳酸盐岩发育土壤Cd的富集与超常富集现象——以贵州岩溶区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(4):533-544.
|
| [18] |
Feng Z G, Liu W, Zhang L Y, et al. Enrichment and supernormal enrichment phenomenon of Cd in soils developed on Cd-poor carbonate rocks:A case study of Karst areas in Guizhou,China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(4):533-544.
|
| [19] |
Zhong X, Chen Z W, Li Y Y, et al. Factors influencing heavy metal availability and risk assessment of soils at typical metal mines in Eastern China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020,400:123289.
|
| [20] |
高云峰, 徐友宁, 张江华. 秦岭某钼矿区开发对东川河流域Cd的影响[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(12):2241-2250.
|
| [20] |
Gao Y F, Xu Y N, Zhang J H. Evaluation of Cd pollution of a molybdenum ore area in Dongchuan River Basin of the Qinling Mountain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(12):2241-2250.
|
| [21] |
郑国东. 广西北部湾地区表层土壤重金属分布特征及其影响因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
|
| [21] |
Zheng G D. Factors influencing the distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in topsoil acrossBeibu gulf of guangxi[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2016.
|
| [22] |
Zeng F R, Ali S, Zhang H T, et al. The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(1):84-91.
|
| [23] |
Young G M, Nesbitt H W. Processes controlling the distribution of Ti and Al in weathering profiles,siliciclastic sediments and sedimentary rocks[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1998, 68(3):448-455.
|
| [24] |
张坤, 季宏兵, 褚华硕, 等. 黔西南喀斯特地区红色风化壳的物源及元素迁移特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2018, 46(3):257-266.
|
| [24] |
Zhang K, Ji H B, Chu H S, et al. Material sources and element migration characteristics of red weathering crusts in southwestern Guizhou[J]. Earth and Environment, 2018, 46(3):257-266.
|
| [25] |
王秋艳, 文雪峰, 魏晓, 等. 碳酸盐岩风化和成土过程的重金属迁移富集机理初探及环境风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(1):119-130.
|
| [25] |
Wang Q Y, Wen X F, Wei X, et al. Heavy metal migration and enrichment mechanism and the environmental risks during the weathering and soil formation of carbonate rocks[J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(1):119-130.
|
| [26] |
蒋玉莲. 贵州六盘水碳酸盐岩成壤过程中重金属的迁移富集机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021.
|
| [26] |
Jiang Y L. The migration and enrichment mechanism of heavy metals in the process of carbonate pedogenesis in Liupanshui,Guizhou[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2021.
|
| [27] |
Huang P M. Feldspars,olivines,pyroxenes,and amphiboles[G]//SSSA book series.Madison,WI, USA:Soil Science Society of America,2018:975-1050.
|
| [28] |
陈静生, 王飞越, 宋吉杰, 等. 中国东部河流沉积物中重金属含量与沉积物主要性质的关系[J]. 环境化学, 1996, 15(1):8-14.
|
| [28] |
Chen J S, Wang F Y, Song J J, et al. Relation of geochemical and surface properties to heavy metal concentrations of sediments from eastern Chinese Rivers[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1996, 15(1):8-14.
|
| [29] |
谭文峰, 刘凡, 李永华, 等. 土壤铁锰结核中锰矿物类型鉴定的探讨[J]. 矿物学报, 2000, 20(1):63-67.
|
| [29] |
Tan W F, Liu F, Li Y H, et al. Methodological study of identifying mangnese minerals in fe-mn nodules of soils[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2000, 20(1):63-67.
|
| [30] |
Nachtegaal M, Sparks D L. Effect of iron oxide coatings on zinc sorption mechanisms at the clay-mineral/water interface[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2004, 276(1):13-23.
|
| [31] |
Otunola B O, Ololade O O. A review on the application of clay minerals as heavy metal adsorbents for remediation purposes[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2020,18:100692.
|
| [32] |
Hardy M, Cornu S. Location of natural trace elements in silty soils using particle-size fractionation[J]. Geoderma, 2006, 133(3/4):295-308.
|
| [33] |
Dixon J B, Schulze D G. Soil mineralogy with environmental applications[R]. Soil Science Society of America Inc, 2002.
|
| [34] |
Hou S N, Zheng N, Tang L, et al. Effect of soil pH and organic matter content on heavy metals availability in maize (Zea mays L.) rhizospheric soil of non-ferrous metals smelting area[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2019, 191(10):634.
|
| [35] |
匡荟芬, 胡春华, 吴根林, 等. 结合主成分分析法(PCA)和正定矩阵因子分解法(PMF)的鄱阳湖丰水期表层沉积物重金属源解析[J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(4):964-976.
|
| [35] |
Kuang H F, Hu C H, Wu G L, et al. Combination of PCA and PMF to apportion the sources of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Poyang during the wet season[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(4):964-976.
|
| [36] |
Boruvka L, Vacek O, Jehlička J. Principal component analysis as a tool to indicate the origin of potentially toxic elements in soils[J]. Geoderma, 2005, 128(3/4):289-300.
|
| [37] |
Nanos N, Rodríguez Martín J A. Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in soils:Spatial variability in the Duero River Basin (Spain)[J]. Geoderma, 2012,189-190:554-562.
|
| [38] |
Zhang P, Hu R J, Zhu L H, et al. Distributions and contamination assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of western Laizhou Bay:Implications for the sources and influencing factors[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 119(1):429-438.
|
| [39] |
曾咏梅, 毛昆明, 李永梅. 土壤中镉污染的危害及其防治对策[J]. 云南农业大学学报, 2005, 20(3):360-365.
|
| [39] |
Zeng Y M, Mao K M, Li Y M. Damage of the cadmium(Cd) pollution in soil and its control[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 2005, 20(3):360-365.
|
| [40] |
Han F X, Banin A, Su Y, et al. Industrial age anthropogenic inputs of heavy metals into the pedosphere[J]. Naturwissenschaften, 2002, 89(11):497-504.
|
| [41] |
Abedin M J, Cotter-Howells J, Meharg A A. Arsenic uptake and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) irrigated with contaminated water[J]. Plant and Soil, 2002, 240(2):311-319.
|
| [42] |
吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(7):971-984.
|
| [42] |
Lyu J S, Zhang Z L, Liu Y, et al. Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao city[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(7):971-984.
|
| [1] |
SUN Hong-Lin, LIU Tie-Hua, LIU Tie, ZHANG Zhan-Rong, CHEN Zhi-Xing. Multi-source frequency-domain seismic exploration technique and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 618-628. |
| [2] |
CHEN Xing-Peng, WANG Liang, LONG Xia, XI Zhen-Zhu, QI Qing-Xin, XUE Jun-Ping, DAI Yun-Feng, HU Zi-Jun. Distribution patterns of the electromagnetic fields of orthogonal horizontal magnetic dipoles as sources in CSRMT[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 721-735. |
|
|
|
|

