|
|
|
| Comparative analysis of stereo and planar sources for slope breaks |
CHEN Feng-Ying1,2( ), WANG Xiang-Chun2, SUN Jian3, LI Can-Ping1, REN Xiao-Qing4 ), WANG Xiang-Chun2, SUN Jian3, LI Can-Ping1, REN Xiao-Qing4 |
1. School of Electronics and Information Engineering,Guangdong Ocean University,Zhanjiang 524088,China
2. School of Geophysics and Information Technology,China University of Geosciences (Beijing),Beijing 100083,China
3. Data Processing Center(Zhanjiang),Geophysical Research Institute,Geophysical Services,China Oilfield Services Limited,Zhanjiang 524057,China
4. Sinopec Green Energy Geothermal Development Co.,Ltd.,Baoding 071800,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Deep-water areas have gradually become the exploration targets of offshore oil and gas resources.Due to the intricate geological conditions of these areas,seismic imaging of moderately deep reservoirs suffers low signal-to-noise ratios and resolution,inevitably affecting the exploration and exploitation of oil and gas resources.To improve the quality of seismic data of moderately deep reservoirs in deep-water areas,this study first acquired seismic data at the same location in a slope break using stereo and planar sources under the same acquisition parameters.Then,after being processed using the same workflow,the seismic data were subjected to comparative analysis from the perspective of wavelets,shot gather spectra,near-trace spectra,superimposed profile spectra,and final imaging.The results indicate that the wavelets of a stereo source outperformed those of a planar source in terms of energy intensity and ghost reflection interference.Moreover,for moderately deep reservoirs of the deep-water area,a stereo source exhibited broader frequency bands and especially rich frequencies within 30~80 Hz.These features enhanced the resolution of seismic profiles and the imaging quality of seismic data.Thus,compared to planar sources,stereo sources enjoy more advantages in improving seismic imaging of moderately deep reservoirs in deep-water areas.Therefore,stereo sources can be employed to acquire seismic data of moderately deep reservoirs with complex geological conditions in deep-water areas,and the purpose is to improve the imaging quality of seismic data.
|
|
Received: 05 May 2023
Published: 16 April 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 子阵 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 容量
/in3 | 深度
/m | 容量
/in3 | 深度
/m | 容量
/in3 | 深度
/m | 容量
/in3 | 深度
/m | 容量
/in3 | 深度
/m | 容量
/in3 | 深度
/m | 容量
/in3 | 深度
/m | | 1 | 40×2 | 5 | 40 | 5 | 150×2 | 5 | 70 | 5 | 100×2 | 5 | 70 | 5 | 150 | 5 | | 2 | 40×2 | 6.5 | 40 | 6.5 | 210 | 6.5 | 210 | 6.5 | 70×2 | 8 | 100 | 8 | 150 | 8 | | 3 | 40×2 | 6.5 | 40 | 6.5 | 210 | 6.5 | 210 | 6.5 | 70×2 | 8 | 100 | 8 | 150 | 8 | | 4 | 40×2 | 5 | 40 | 5 | 150×2 | 5 | 70 | 5 | 100×2 | 5 | 70 | 5 | 150 | 5 |
|
Stereo source gun layout
|

| 震源 | 平面震源 | 立体震源 | | 炮间距/m | 37.5 | 37.5 | | 震源沉放深度/m | 6.5 | 6.5
6(立体震源) | | 气枪容量/in3 | 3680 | 3680 | | 空气压力/psi | 2000 | 2000 | | 采样率/ms | 1 | 1 | | 记录长度/s | 12 | 12 | | 截频/Hz | 3~400 | 3~400 | | 道数 | 576 | 576 | | 电缆长度/m | 7200 | 7200 | | 道间距/m | 12.5 | 12.5 | | 电缆深度/m | 12 | 12 | | 采集方向/(°) | 351 | 351 | | 最小偏移距/m | 205 | 205 |
|
Source seismic data acquisition parameters
|
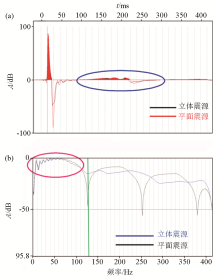
|
The wavelet comparison between the three-dimensional source and the planar source
a—time domain waveform diagram;b—spectral diagram
|
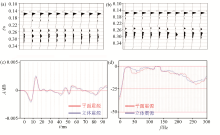
|
Direct wave data and the comparison of extracted wavelet in time-frequency domain
a—stereoscopic source data;b—planar source data;c、d—wavelet and its spectral extracted in direct wave respectively
|
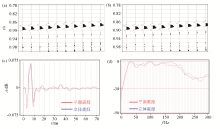
|
Comparison of submarine data and extracted wavelet in time and frequency domains
a—stereoscopic source data;b—planar source data;c、d—direct wave extraction wavelet and spectral diagram,respectively
|
|
Data and spectrum of the shot set after decontamination
a—three-dimensional source gun set in shallow water;b—planar source gun set in shallow water;c—three-dimensional source gun set in deep water;d—planar source gun set in deep water;e—shallow water and shallow layer spectrum;f—shallow water and deep layer spectrum;g—deep water and deep layer spectrum;h—deep water and shallow layer spectrum
|
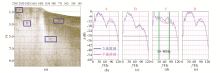
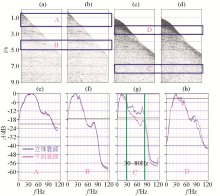
|
Spectrum analysis of short-pass data
a—short cut profile and the location of A shallow water and shallow layer,B shallow water and deep layer,C deep water and deep layer,D deep water and shallow layer;b—shallow water and shallow layer spectrum;c—shallow water and deep layer spectrum;d—deep water and deep layer spectrum;e—deep water and shallow layer spectrum
|
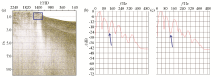
|
Spectrum analysis of short-pass submarine data
a—short-pass profile;b—stereoscopic source spectrum;c—planar source spectrum
|
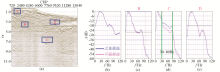
|
Spectrum analysis before migration
a—overlay section and the location of A shallow water and shallow layer,B shallow water and deep layer,C deep water and deep layer,D deep water and shallow layer;b—shallow water and shallow layer spectrum;c—shallow water and deep layer spectrum;d—deep water and deep layer spectrum;e—deep water and shallow layer spectrum
|
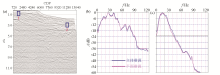
|
Spectrum characteristics of stereoscopic source and planar source in shallow water and deep water
a—offset profile;b—spectrum at position 1;c—spectrum at position 2
|
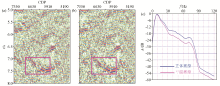
|
Imaging profile of stereoscopic source(a) and planar source(b) and imaging spectrum characteristics of stereoscopic source and planar source(c)
|
| [1] |
Yang H C, Zhang J Z, Wu Z Q, et al. Joint reverse-time imaging condition of seismic towed-streamer and OBN data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 1809, 19:3007305.
|
| [2] |
Dai W, Huang Y S, Schuster G T. Least-squares reverse time migration of marine data with frequency-selection encoding[J]. Geophysics, 2013, 78(4):S233-S242.
|
| [3] |
Li Q Q, Fu L Y, Wei W, et al. Stable and high-efficiency attenuation compensation in reverse-time migration using wavefield decomposition algorithm[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10):1615-1619.

|
| [4] |
苏欣. 立体延迟气枪阵列的优化设计方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
|
| [4] |
Su X. Research on optimization design method of three-dimensional delay air gun array[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2020.
|
| [5] |
夏季, 金星, 蔡辉腾, 等. 大容量气枪震源子波时频特性及其影响因素[J]. 中国地震, 2016, 32(2):249-260.
|
| [5] |
Xia J, Jin X, Cai H T, et al. The time-frequency characteristic of large volume air-Gun source wavelet and its influencing factors[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 2016, 32(2):249-260.
|
| [6] |
Cambois G, Long A, Parkes G, et al. Multi-level airgun array:A simple and effective way to enhance the low frequency content of marine seismic data[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded, 2009.
|
| [7] |
全海燕, 陈小宏, 韦秀波, 等. 气枪阵列延迟激发技术探讨[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2011, 46(4):513-516.
|
| [7] |
Quan H Y, Chen X H, Wei X B, et al. Discussion on delayed excitation technology of air Gun array[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2011, 46(4):513-516.
|
| [8] |
王建花, 李绪宣, 温书亮, 等. 立体阵列气枪震源研究及在南海深水区地震资料采集中的应用[C]// 中国地球物理学会第二十七届年会论文集, 2011:608.
|
| [8] |
WangJ H, LiX X, WenS L, et al. Research and application of offshore tridimensional air-gun array seismic source in deepwater area of South China Sea[C]// Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of the Chinese Geophysical Society, 2011:608.
|
| [9] |
唐松华, 李斌, 张异彪, 等. 立体阵列组合技术在南黄海盆地的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(5):64-70.
|
| [9] |
Tang S H, Li B, Zhang Y B, et al. Application of tridimensional delayed excitation air-Gun array in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(5):64-70.
|
| [10] |
陈浩林, 宁书年, 熊金良, 等. 气枪阵列子波数值模拟[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2003, 38(4):363-368.
|
| [10] |
Chen H L, Ning S N, Xiong J L, et al. Numerical simulation of air-Gun array wavelet[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2003, 38(4):363-368.
|
| [11] |
杨光亮, 朱元清. 气枪震源深部探测子波模拟[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2008, 28(6):91-95.
|
| [11] |
Yang G L, Zhu Y Q. Air-Gun wavelet simulation for deep curst exploration[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2008, 28(6):91-95.
|
| [12] |
杨怀春, 高生军. 海洋地震勘探中空气枪震源激发特性研究[J]. 石油物探, 2004, 43(4):323-326.
|
| [12] |
Yang H C, Gao S J. The signatures of seismic wavelet excited by air guns in marine seismic survey[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2004, 43(4):323-326.
|
| [13] |
李绪宣, 温书亮, 顾汉明, 等. 海上气枪阵列震源子波数值模拟研究[J]. 中国海上油气, 2009, 21(4):215-220.
|
| [13] |
Li X X, Wen S L, Gu H M, et al. A numerical simulation of wavelets from offshore air-Gun array seismic source[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2009, 21(4):215-220.
|
| [14] |
王雷, 刘怀山, 丁西凯. 立体延时气枪震源子波模拟[C]// 第十四届国家安全(军事)地球物理学术研讨会论文集, 2018:238-242.
|
| [14] |
Wang L, Liu H S, Ding X K. Stereo-delay air gun source wavelet simulation[C]// Proceedings of the 14th National Security(Military) Geophysical Symposium, 2018:238-242.
|
| [15] |
盖永浩, 李列, 欧阳敏. 海洋宽频地震采集系统及其应用[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(2):198-201.
|
| [15] |
Gai Y H, Li L, Ouyang M. Marine broadband seismic acquisition system and its application[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2020, 27(2):198-201.
|
| [16] |
李玉剑, 张异彪, 刘璐晨, 等. 南黄海中-古生界地震勘探震源设计及其应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(2):200-212.
|
| [16] |
Li Y J, Zhang Y B, Liu L C, et al. Seismic source specially designed for the Meso-Paleozoic strata and its applicaton to South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(2):200-212.
|
| [17] |
杨宸, 徐德卫, 刘怀山. 海洋地震立体观测震源特性分析[C]// 国家安全地球物理丛书(十七)——生态环境与地球物理, 2021:75-81.
|
| [17] |
Yang C, Xu D W, Liu H S. Analysis of Source Characteristics of Marine Seismic Stereoscopic Observation[C]//. National Security Geophysics Series (XVII):Ecological Environment and Geophysics, 2021:75-81.
|
| [18] |
任婷, 彭海龙, 覃殿明, 等. 深水区直达波子波提取气泡效应压制技术[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018, 53(2):243-250,219.
|
| [18] |
Ren T, Peng H L, Qin D M, et al. De-bubble based on wavelet extraction from direct wave in deep water[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 53(2):243-250,219.
|
| [19] |
王守君, 王征. 海上地震资料零相位化处理技术研究[J]. 石油物探, 2012, 51(4):402-407.
|
| [19] |
Wang S J, Wang Z. Zero-phase processing and its application on marine seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2012, 51(4):402-407.
|
| [20] |
黄平, 路中侃. 地震频谱分析在气水分布研究中的应用[J]. 石油物探, 1995, 34(2):71-75,93.
|
| [20] |
Huang P, Lu Z K. Application of seismic spectral analysis to study water-gas distribution[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 1995, 34(2):71-75,93.
|
| [1] |
MA Guo-Kai, WEI Ding-Yong, LIU Ai-You, LIN Wan-Shun. Application of shallow seismic exploration technique in defect detection of PCCP used in the middle route of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2): 525-530. |
| [2] |
WU Jiao-Bing, LI Jun-Liang, JIANG Lan, LU Jun-Hong, PAN Li-Li, WEI Wang-Qiu. The application of comprehensive geophysical method to the identification of active faults in Luocheng County,Guangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 346-354. |
|
|
|
|

