|
|
|
| Seismic characteristics of the paleo-underground river system in Ordovician carbonate paleo-buried hills in the western Lungu area |
DAN Guang-Jian1( ), ZHOU Cheng-Gang1, LIU Yun-Hong2, LI Xiang-Wen1, ZHANG Liang-Liang1, ZHANG Ming1, WANG Chun-Yang1 ), ZHOU Cheng-Gang1, LIU Yun-Hong2, LI Xiang-Wen1, ZHANG Liang-Liang1, ZHANG Ming1, WANG Chun-Yang1 |
1. Korla Branch of GRI of BGP Inc.,Korla 841000,China
2. BGP Inc.,China National Petroleum Corporation,PanJing 124010,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Many karst fracture-vug reservoirs have been found in the Ordovician carbonate paleo-buried hills in the Lungu area,Tarim Basin.Hydrocarbons are mainly enriched in these fracture-vug reservoirs,which are mainly related to the paleo-underground river system in carbonate paleo-buried hills.The paleo-underground river system is well developed,especially in the western Lungu area.The fracture-vug reservoirs related to the paleo-underground river system have strong longitudinal and lateral heterogeneity,and ascertaining the seismic and geological characteristics of the paleo-underground river system in this area is the key to the efficient development of fracture-vug reservoirs in this area.Based on the characteristics of modern karst underground rivers and the log and drilling data of this area,this study established a geological model of underground rivers for forward modeling.The study results are as follows.The underground river system developing under the tight limestone setting showed continuously linear strong reflections on the seismic profile.The seismic amplitude decreased as the height and width of underground rivers decreased,and higher seismic amplitude corresponded to larger underground river caves and lower filling velocity.The amplitude can accurately characterize the horizontal range of the underground river on the seismic profile.Meanwhile,the frequency and phase can describe the outline of the underground river on the seismic profile,but the outline described was larger than that of the real underground river.The main channels of the underground river system were prone to be filled with mud.By contrast,the branch channels had a low filling probability and thus serve as the main areas for both the occurrence of underground river reservoirs and the hydrocarbon accumulation.
|
|
Received: 14 February 2022
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
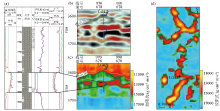
|
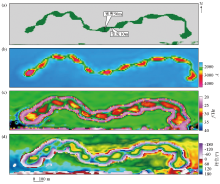
Calibrating downhole seismic chart of underground river of well LG42
a—columnar chart of ordovician of well LG42;b—seismic sections through well LG42;c—inversion section through well LG42;d—the inversion attribute plane map of Ordovician buried hill in LG42 well area
|
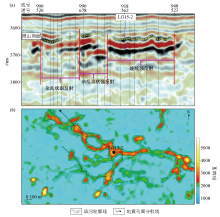
|
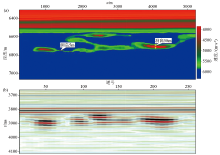
Seismic profile along the underground rivers (a) and planar graph of amplitude attribute of Ordovician buried hill in LG15-2 well area(b)
|
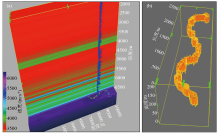
|
Three dimensional forward velocity model(a)and three dimensional geological model of underground river(b)
|
|
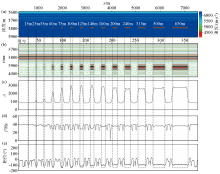
Seismic profile of forward results(a)、(b)and planar map of amplitude attribute of forward results(c)
|
|
Plan of underground river geological model and plan of amplitude, frequency and phase attributes of forward seismic results
a—geological model;b—planar map of amplitude attribute;c—planar map of peak spectral frequency;d—planar map of average instantaneous phase
|
|
Geological model of underground river with different filling degree and seismic profile of forward modeling results
a—forward geological model;b—forward seismic profile
|
|
Forward modeling of underground river model with the same height and length variation and corresponding seismic attribute curve
a—geological model;b—forward modeling result;c—seismic reflection amplitude curve of underground rivers;d—peak spectrum frequency curve of underground rivers seismic reflection;e—average instantaneous phase curve of underground rivers seismic reflection
|
|
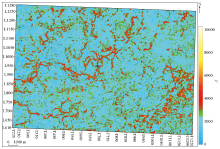
Plan of root mean square attribute of 0~100 ms seismic amplitude under Ordovician buried hill in Lunguxi-Lungu 7 area
|
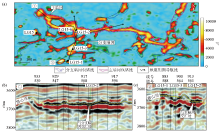
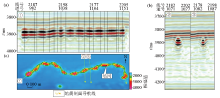
|
Plan and section of underground river system in Lungu 15 well block
a—rms amplitude attribute map;b—seismic profile of the main underground river;c—seismic profile of the branches underground river
|
| [1] |
胡中平. 溶洞地震波“串珠状”形成机理及识别方法[J]. 中国西部油气地质, 2006, 2(4):423-426.
|
| [1] |
Hu Z P. Mechanism and distinction method forthe seismic "string beads" characteristic[J]. West China Petroleum Geosciences, 2006, 2(4):423-426.
|
| [2] |
吴俊峰, 姚姚, 撒利明. 碳酸盐岩特殊孔洞型构造地震响应特征分析[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2007, 42(2):180-185.
|
| [2] |
Wu J F, Yao Y, Sa L M. Analysis on seismic response of special cavernous structure of carbonate[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 42(2):180-185.
|
| [3] |
李凡异, 魏建新, 狄帮让, 等. 碳酸盐岩溶洞的“串珠”状地震反射特征形成机理研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2012, 47(3):385-391.
|
| [3] |
Li F Y, Wei J X, Di B R, et al. Research on the mechanism of the formation of the "beaded" seismic reflection characteristics of carbonate karst caves[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2012, 47(3):385-391.
|
| [4] |
闵小刚, 顾汉明, 朱定. 塔河油田孔洞模型的波动方程正演模拟[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2006, 29(3):187-191.
|
| [4] |
Ming X G, Gu H M, Zhu D. Wave equation forward modeling of cavern models in Tahe oil-field[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2006, 29(3):187-191.
|
| [5] |
姚姚, 唐文榜. 深层碳酸盐岩岩溶风化壳洞缝型油气藏可检测性的理论研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2003, 38(6):623-629.
|
| [5] |
Yao Y, Tang W B. Theoretical study on the detectability of deep carbonate karst weathered crust-cavity fractured oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2003, 38(6):623-629.
|
| [6] |
孙东, 潘建国, 雍学善, 等. 碳酸盐岩储层垂向长串珠形成机制[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2010, 45(1):101-104.
|
| [6] |
Sun D, Pan J G, Yong X S, et al. Formation mechanism of vertically long beads in carbonate reservoirs[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 45(1):101-104.
|
| [7] |
马灵伟, 顾汉明, 赵迎月, 等. 应用随机介质正演模拟刻画深水区台缘礁碳酸盐岩储层[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2013, 48(4):583-590.
|
| [7] |
Ma L W, Gu H M, Zhao Y Y, et al. Using forward modeling of stochastic media to characterize carbonate reservoirs in platform margin reefs in deep water[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2013, 48(4):583-590.
|
| [8] |
韩杰, 洪涛, 朱永峰, 等. 轮古油田奥陶系潜山洞穴型储层发育特征及油气分布控制因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(5):1-8.
|
| [8] |
Han J, Hong T, Zhu Y F, et al. Characteristics of Ordovician buried-hill cave reservoir and controlling factors of petroleum distribution of Lungu oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2016, 23(5):1-8.
|
| [9] |
张军林, 田世澄, 郑多明. 塔北隆起西部缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层表征与评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(3):497-503.
|
| [9] |
Zhang J L, Tian S C, Zheng D M. Characterization and evaluation of fracture-cavity type carbonate reservoir in the western part of Northern Tarim uplift[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(3):497-503.
|
| [10] |
徐国强, 刘树根, 李国蓉, 等. 向源潜流侵蚀岩溶作用及其成因机理——以塔河油田早海西风化壳岩溶洞穴层为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2005, 24(1):35-40.
|
| [10] |
Xu G Q, Liu S G, Li G R, et al. The mechanism of retrogressive erosion and karstification:A case study of cave formation in early hersinian weathered crust in tahe oilfield[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2005, 24(1):35-40.
|
| [11] |
李源, 鲁新便, 蔡忠贤, 等. 塔里木盆地塔河油田岩溶峡谷区海西早期洞穴系统发育模式[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(2):364-372.
|
| [11] |
Li Y, Lu X B, Cai Z X, et al. Development model of Hercynian cave system in karst canyon area of Tahe Oilfield,Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2017, 19(2):364-372.
|
| [12] |
李宗杰, 王勤聪. 塔河油田奥陶系古岩溶洞穴识别及预测[J]. 新疆地质, 2003, 21(2):181-184.
|
| [12] |
Li Z J, Wang Q C. Identification and prediction of Ordovician ancient karst caves in Tahe Oilfield[J]. XinJiang Geology, 2003, 21(2):181-184.
|
| [13] |
赵军, 祁兴中, 夏宏权, 等. 测井资料在碳酸盐岩洞—裂缝型储层产能评价中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2003, 17(1):99-104.
|
| [13] |
Zhao J, Qi X Z, Xia H Q, et al. Application of well logging data in productivity evaluation of carbonate cave-fracture reservoir[J]. Geoscience, 2003, 17(1):99-104.
|
| [14] |
罗枭, 刘俊锋, 韩杰, 等. 塔里木盆地轮古潜山暗河发育特征及其与油气富集的关系[J]. 海相油气地质, 2018, 23(4):27-34.
|
| [14] |
Luo X, Liu J F, Han J, et al. Development characteristics of underground river and its relationship with oil and gas accumulation in Lungu buried-hill,Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2018, 23(4):27-34.
|
| [15] |
孙海宁, 王晓梅, 刘来祥. AVO技术在识别充填流体溶洞中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2008, 32(4):397-400.
|
| [15] |
Sun H N, Wang X M, Liu L X. The application of avo to the predication of water-eroded caves filled with liquids for carbonate reservoirs[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(4):397-400.
|
| [16] |
张娟, 鲍典, 杨敏, 等. 塔河油田西部古暗河缝洞结构特征及控制因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2018, 25(4):33-39.
|
| [16] |
Zhang J, Bao D, Yang M, et al. Analysis on fracture-cave structure characteristics and its controlling factor of palaeo-subterranean rivers in the western Tahe Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2018, 25(4):33-39.
|
| [17] |
朱学稳. 桂林地区灰岩洞穴的溶蚀形态[J]. 中国岩溶, 1982, 1(2):93-103.
|
| [17] |
Zhu X W. Dissolution features of limestone caves in Guilin area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1982, 1(2):93-103.
|
| [18] |
雷川, 陈红汉, 苏奥, 等. 塔河地区奥陶系深埋岩溶洞穴特征及保存机制初探[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(2):27-31.
|
| [18] |
Lei C, Chen H H, Su A, et al. Characteristics and preservation mechanism of the Ordovician deep burial karst caves in Tahe area[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(2):27-31.
|
| [19] |
李阳. 塔河油田奥陶系碳酸盐岩溶洞型储集体识别及定量表征[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 36(1):1-7.
|
| [19] |
Li Y. Ordovician carbonate fracture-cavity reservoirs identification and quantitative characterization in Tahe Oilfield[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum:Edition of Natural Science, 2012, 36(1):1-7.
|
| [20] |
徐微, 陈冬梅, 赵文光, 等. 塔河油田奥陶系碳酸盐岩油藏溶洞发育规律[J]. 海相油气地质, 2011, 16(2):34-41.
|
| [20] |
Xu W, Chen D M, Zhao W G, et al. Development regularity of karstic caverns of Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in Tahe oilfield[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2011, 16(2):34-41.
|
| [21] |
张林艳. 塔河油田奥陶系缝洞型碳酸盐岩油藏的储层连通性及其油(气)水分布关系[J]. 中外能源, 2006, 11(5):32-36.
|
| [21] |
Zhang L Y. Reservoir connectivity and oil-water relationship of rock dissolved Carbonate oil reservoir in Tahe Oilfield[J]. China Foreign Energy, 2006, 11(5):32-36.
|
| [22] |
王立静. 塔河油田12区碳酸盐岩油藏溶洞特征研究[J]. 内蒙古石油化工, 2010(1):120-122.
|
| [22] |
Wang L J. Study on Karst cave characteristics of Carbonate reservoir in area 12 of Tahe oilfield[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 2010(1):120-122.
|
|
|
|

