|
|
|
| An analysis of factors influencing the selenium content in the rice-root soil system in Libo County, southern Guizhou Province |
ZHOU Wen-Long( ), YANG Zhi-Zhong( ), YANG Zhi-Zhong( ), ZHANG Tao, MANG Shi-Cai, YANG Zheng-Kun ), ZHANG Tao, MANG Shi-Cai, YANG Zheng-Kun |
| Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration, Non-Ferrous Metals and Nuclear Industry Geological Exploration Bureau of Guizhou, Guiyang 550005, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Selenium (Se), one of the trace elements essential to human body, plays an antagonistic role toward the toxicity of heavy metals. The most important, safe, and feasible way for human body to take Se is to transform Se via food chain. This study collected and analyzed 30 groups of samples of rice seeds and corresponding root soil from the natural high-quality Se-rich farmland that is widely distributed in Libo County. Based on this, this study evaluated the edible safety of rice, studied the selenium content in the rice-root soil system, and investigated the influence of the physical and chemical conditions of soil on rice's absorption and transport of selenium, aiming to provide a scientific basis for the development of Se-rich agriculture in the study area. The results are as follows. Most root soil of rice in the study area is Se-rich, with an average Se content of 0.41×10-6. The rice in the study area has an average w(Se) of 0.030 7×10-6, and green and safe rice accounted for 70%. For the root soil of rice in the study area, there is a significant positive correlation between w(Se) and w(Fe2O3), w(Al2O3), w(MgO), and w(organic matter), and there is associated relationship between w(Se) and some heavy metals including Cr and Cd. There was a significant positive correlation between Se content of rice seeds and that of root soil. By contrast, there is a significant negative correlation between the Se enrichment coefficient of rice and the contents of Se, As, Cd, Cr, Hg, Ni, Al2O3, Fe2O3, and organic matter in root soil. The results indicate that the absorption and fixation of Se by the organic matter and Fe-Al oxides in soil reduce rice's absorption and utilization rate of selenium. The negative correlation between Se enrichment coefficient of rice and the heavy metal contents of root soil suggests that Se may play a certain antagonistic role toward the absorption and transport of heavy metals in the soil-rice system. The study area is rich in Se-rich farmland resources, yet there is a risk that the contents of Cr and Cd in rice slightly exceeds relevant standards. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the ecological effects of heavy metal elements in the development of Se-rich agriculture in the study area.
|
|
Received: 02 December 2020
Published: 28 June 2022
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
YANG Zhi-Zhong
E-mail: E578064048@126.com;809439420@qq.com
|
|
|
|
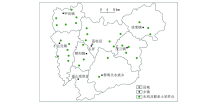
|
Sampling sites of the study area
|

| 指标 | pH | SeR | SeS | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | | 最大值 | 6.90 | 0.032 | 0.90 | 14.80 | 1.46 | 120.00 | 92.10 | 0.55 | 36.6. | 55.50 | | 最小值 | 4.58 | 0.0295 | 0.24 | 2.66 | 0.15 | 39.20 | 6.34 | 0.06 | 4.26 | 14.10 | | 平均值 | 5.37 | 0.0307 | 0.41 | 6.58 | 0.50 | 74.90 | 20.90 | 0.14 | 19.39 | 24.05 | | 变异系数/% | 11.46 | 1.99 | 33.36 | 47.35 | 66.08 | 29.65 | 80.00 | 63.60 | 46.39 | 34.22 | | K值 | 与全国对比 | 0.80 | 0.97 | 1.41 | 0.58 | 0.15 | 1.25 | 0.93 | 1.98 | 0.72 | 1.05 | | 与贵州对比 | | | 0.85 | 0.49 | 1.24 | 0.76 | 0.61 | 1.07 | 0.49 | 0.72 | | 指标 | Zn | Mn | 有机质 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | | 最大值 | 131.00 | 321.00 | 7.72 | 5.85 | 14.83 | 83.23 | 1.21 | 1.51 | 0.47 | 2.25 | | 最小值 | 18.10 | 38.30 | 2.41 | 1.28 | 5.29 | 61.79 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.32 | | 平均值 | 67.61 | 128.78 | 4.52 | 3.25 | 9.43 | 74.54 | 0.45 | 0.63 | 0.26 | 1.06 | | 变异系数/% | 43.61 | 63.65 | 27.35 | 42.73 | 30.59 | 8.91 | 57.08 | 59.10 | 32.05 | 54.85 | | K值 | 与全国对比 | 0.91 | 0.22 | 1.60 | 1.10 | 0.75 | 1.15 | 0.30 | 0.81 | 0.17 | 1.13 | | 与贵州对比 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 1.47 | | | | | | | |
|
Contents of elements in rice seed and root soil in study area(n=30)
|
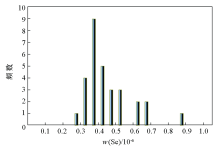
|
Histogram of Selenium content distribution in rice root soil
|

| 参数 | AsR | CdR | CrR | HgR | PbR | | 最大值(CijMax) | 0.332 | 0.780 | 1.700 | — | 0.125 | | 最小值(CijMin) | 0.152 | 0.016 | 0.450 | — | 0.036 | | 平均值(CijAve) | 0.225 | 0.093 | 0.923 | — | 0.067 | | 食品安全标准限值(Lij) | 0.5 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.02 | 0.2 | | 超标数量 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | | 超标指数(Eij) | | 4.40 | 1.09~1.70 | | | | 超标等级 | | 重度超标 | 轻度超标 | | |
|
Concentration characteristics of heavy metals in rice seed (n=30)
|

| 指标 | r | 指标 | r | 指标 | r | | As | 0.746** | Pb | 0.321 | CaO | 0.313 | | Cd | 0.465** | 有机质 | 0.373* | MgO | 0.474** | | Cr | 0.514** | pH | 0.167 | K2O | 0.462** | | Cu | 0.227 | SiO2 | -0.489** | Na2O | 0.107 | | Hg | 0.577** | Fe2O3 | 0.477** | | | | Ni | 0.526** | Al2O3 | 0.424** | | |
|
Correlation coefficient between selenium and various physical and chemical indicators in rice root soil (n=30)
|

| 指标 | r | 指标 | r | 指标 | r | | SeS | 0.167* | Ni | -0.057 | Al2O3 | -0.374** | | As | 0.279 | Pb | -0.011 | CaO | -0.168 | | Cd | 0.068 | 有机质 | -0.503** | MgO | -0.261 | | Cr | 0.099 | pH | -0.146 | K2O | -0.178 | | Cu | -0.082 | SiO2 | 0.334 | Na2O | 0.086 | | Hg | -0.024 | Fe2O3 | -0.127 | | |
|
Correlation coefficient between Se content in rice seed and index in root soil (n=30)
|
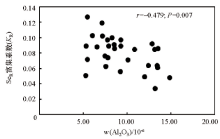
|
Scatter plot of Se enrichment factor in rice seed and Al2O3 in root soil (n=30)
|
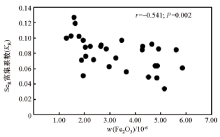
|
Scattered plots of Se enrichment factor in rice seed and Fe2O3 in root soil (n=30)
|
|
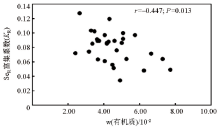
Scatter plot of Se enrichment factor in rice seed and SOM in root soil (n=30)
|
|
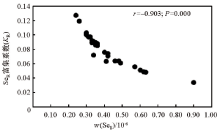
Scatter plot of Se enrichment factor in rice seed and Se in root soil (n=30)
|

| 元素 | r | 元素 | r | 元素 | r | | As | -0.699** | Pb | -0.216 | CaO | 0.320 | | Cd | -0.412* | SOM. | -0.447* | MgO | -0.508** | | Cr | -0.546** | pH | -0.122 | K2O | -0.461* | | Cu | -0.241 | SiO2 | 0.547** | Na2O | -0.154 | | Hg | -0.526** | Fe2O3 | -0.541** | SeR | -0.903** | | Ni | -0.529** | Al2O3 | -0.479** | | |
|
Correlation coefficient between Se enrichment coefficient (KR) of rice seed and physicochemical indexes of root soil (n=30)
|
| [1] |
Patrick L. Selenium biochemistry and cancer: A review of the literature[J]. Alternative Medicine Review, 2004, 9(3): 239-258.
|
| [2] |
葛晓立, 李家熙, 万国江, 等. 张家口克山病地区土壤硒的地球化学形态研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2000, 19(4):254-258.
|
| [2] |
Ge X L, Li J X, Wan G J, et al. Study on characteristics of selenium geochemical speciation in soil in Zhangjiakou Keshan disease area[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2000, 19(4): 254-258.
|
| [3] |
Tan J A, Zhu W Y, Wang W Y, et al. Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2002, 284(1): 227-235.

|
| [4] |
Fordyce F M. Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment [G]// Aolle Selinus. Essentials of Medical Geology. Uppsala, Dordrecht: Springer, 2013: 375-416.
|
| [5] |
周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 等. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究:以青塘—梅窑地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018(6):1292-1301.
|
| [5] |
Zhou M, Chen G G, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils of south Jiangxi Province: A typical area of Qingtang-Meiyao[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6):1292-1301.
|
| [6] |
周文龙, 张涛, 吴昭阳, 等. 黔南荔波地区耕地土壤中硒的分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 贵州地质, 2020, 37(3):313-319.
|
| [6] |
Zhou W L, Zhang T, Wu Z Y, et al. Characteristics of soil selenium distribution of cultivated land and its influential factors in Libo of South Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2020, 37(3):313-319.
|
| [7] |
蔡大为, 李龙波, 蒋国才, 等. 贵州耕地主要元素地球化学背景值统计与分析[J]. 贵州地质, 2020, 37(3):233-239.
|
| [7] |
Cai W, Li L B, Jiang G C, et al. Statistics and analysis of geochemical background of main elements of cultivated land in Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2020, 37(3):233-239.
|
| [8] |
Matos R P, Lima V M P, Windmoller C C, et al. Correlation between the natural levels of selenium and soil physiochemical characteristics from Jequitinhonha Vally(MG), Brazil[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 172: 195-202.

|
| [9] |
Samazíková P, Praus L, Száková J, et al. The effect of organic matter rich amendments on selenium mobility in soil[J]. Pedosphere, 2017, 24(9): 1-11.

|
| [10] |
付中彪, 何宁洁, 鲍征宇, 等. 赣南地区水稻—根系土系统中硒含量影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5):220-229.
|
| [10] |
Fu Z B, He N H, Bao Z Y, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of selenium content in rice-root soil system in Southern Jiangxi[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5):220-229.
|
| [11] |
姜超强, 沈嘉, 祖朝龙. 水稻对天然富硒土壤硒的吸收及转运[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(3):809-816.
|
| [11] |
Jiang C Q, Shen J, Zu C L, et al. Selenium uptake and transport of rice under different Se-enriched natural soil[J]. Chinese Jouranl of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(3):809-816.
|
| [12] |
陈锦平, 刘永贤, 潘丽萍, 等. 浔郁平原不同作物的硒富集特征及其影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6):1155-1159.
|
| [12] |
Chen J P, Liu Y X, Pan L P, et al. Selenium accumulation characteristics and its influencing factors of different crops in Xunyu Plain[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6):1155-1159.
|
| [13] |
章倩. 海南西部土壤-水稻系统硒分布特征[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2013.
|
| [13] |
Zhang Q. Distribution of Se in Soil-rice systems in West Part of Hainan Island[D]. Haikou: Hainan Unversity, 2013.
|
| [14] |
中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素平均值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
|
| [14] |
China Environmental Monitoring Station. Average value of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
|
| [15] |
张宝军, 杨林生, 王五一, 等. 大骨节病区土壤元素分布特征及其与病情的关系:以四川省塘县为例[J]. 土壤学报, 2011, 48(2):230-237.
|
| [15] |
Zhang B J, Yang L S, Wang W Y, et al. Distribution of soil elements and its relationship with kaschin-back disease in KBD afflicted regions:A case study of Rangtang County, Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2011, 48(2):230-237.
|
| [16] |
张靖源, 陈剑平, 黄韶华, 等. 广西鹿寨水稻及其种植土壤中硒质量分数分布特征[J]. 南方农业学报, 2016, 47(11):1856-1860.
|
| [16] |
Zhang J Y, Chen J P, Huang S H, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium content in rice and rhizosphere soil in Luzhai, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2016, 47(11):1856-1860.
|
| [17] |
张栋, 翟勇, 张妮, 等. 新疆水稻主产区土壤硒含量与水稻籽粒硒含量的相关性[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017(1):139-143.
|
| [17] |
Zhang D, Zhai Y, Zhang N, et al. Correlation between soil selenium content and rice grain selenium content in Xinjiang rice production areas[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2017(1):139-143.
|
| [18] |
吴永尧, 彭振坤, 罗泽民. 水稻对硒的生物富集作用动态研究[J]. 华中师范大学学报:自然科学版, 1998, 32(4):490-494.
|
| [18] |
Wu Y Y, Peng Z K, Luo Z M. Research on the dynamics of bioaccumulation of Se in rice[J]. Journal of Central China Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 1998, 32(4):490-494.
|
| [19] |
Wang Z J, Gao Y X. Biogeochemical cycling of selenium in Chinese environments[J]. Applied Geochemical, 2001, 16(11/12): 1345-1351.
|
| [20] |
Huang S, Hua M, Feng J, et al. Assessment of selenium pollution in agriculture soil in the Xuzhou District, Northwest Jiangsu, China[J]. Journal Environment Science, 2009, 21(4): 481-487.

|
| [21] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会,国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 2726—2017 食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
|
| [21] |
National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China,State Food and Drug Administration. GB 2726—2017 National Food Safety Standard Limits of Contaminants in Foods[S]. 北京: China Standard Press, 2017.
|
| [22] |
李杰, 朱立新, 康志强. 南宁市郊周边农田土壤—农作物系统重金属元素迁移特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):43-52.
|
| [22] |
Li J, Zhu L X, Kang Z Q. Characteristics of transfer and their influencing factors of heavy metals soil-crop system of peri-urban agricultural soil of Nanning, South China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):43-52.
|
| [23] |
胡艳华, 王加恩, 蔡子华, 等. 浙北嘉善地区土壤硒的含量、分布及其影响因素初探[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(6):84-88.
|
| [23] |
Hu Y H, Wang J E, Cai Z H, et al. Content, distribution and influencing factors of selenium in soil of Jiashan Area, Northern Zhejiang Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(6):84-88.
|
| [24] |
刘永贤, 陈锦平, 潘丽萍, 等. 浔郁平原富硒土壤成因及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6):1139-1144.
|
| [24] |
Liu Y X, Chen J P, Pan L P, et al. Studies on causes and influential factors of selnium-rich Soil in Xunyu Plain[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6):1139-1144.
|
| [25] |
Yang Z F, Tao Y U, Hou Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan island[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5): 837-849.
|
| [26] |
曾庆良, 余涛, 王锐. 土壤硒含量影响因素及富硒土地资源区划研究:以湖北恩施沙地为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 33(1):105-112.
|
| [26] |
Zeng Q L, Yu T, Wang R. The influencing factors of selenium in soils and classifying the selenium-rich soil resources in the typical area of Enshi, Hubei[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 33(1):105-112.
|
| [27] |
Supriatin S, Weng L, Comans R N J. Selenium-rich dissolved organic matter determines selenium uptake in wheat grown on low-selenium arable land soil[J]. Plant and Soil, 2016, 408(1/2): 76-94.
|
| [28] |
Matos R P, Lima V M P, Windmoller C C, et al. Correlation between the nature levels of selenium and soil physicochemical characteristics from the Jequitinhonha Valley(MG), Brazil[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 172: 195-202.

|
| [29] |
徐文波, 朱建明, 秦海波, 等. 铁/锰和铝氧化物吸附硒的行为研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2017, 37(3):357-365.
|
| [29] |
Xu W P, Zhu J M, Qin H B, et al. A study on selenium oxyanions adsorbed onto Iron/Manganese/Aluminum oxides[J]. Acta Mineralogicasinica, 2017, 37(3):357-365.
|
| [30] |
Winkel L H, Johnson C A, Lenz M, et al. Environment selenium research: From microscopic to global understanding[J]. Environment Science & Technology, 2012, 46(2): 571-579.

|
| [31] |
吴永尧, 罗泽民, 彭振坤. 水稻对硒的生物富集分布[J]. 湖南师范大学:自然科学学报, 1998, 21(4):76-79.
|
| [31] |
Wu Y Y, Luo Z M, Peng Z K. Studies of the selenium bio-accumulation and distribution in rice[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Human Normal University, 1998, 21(4):76-79.
|
| [32] |
Johnsson L. Selenium uptake by plants as a function of soil type, organic matter content and pH[J]. Plant and Soil, 1991, 133(1): 57-64.

|
| [33] |
罗杰, 王佳媛, 游远航, 等. 硒在土壤—水稻系统中的迁移转化规律[J]. 西南师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 37(3):60-66.
|
| [33] |
Luo J, Wang J Y, You Y H, et al. Migration and transformation of Se in the soil-rice system[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2012, 37(3):60-66.
|
| [34] |
Liu J, Peng Q, Liang D L, et al. Effect of aging on the fraction distribution and bioavailability of selenium in three different soils[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144: 2351-2359.

|
| [35] |
Li Z, Liang D, Peng Q, et al. Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability: A review[J]. Geoderma, 2017, 295: 69-79.

|
| [36] |
周小娟, 张嫣, 祝莉玲, 等. 武汉市侏儒—消泗地区农田系统中硒的分布特征及有效性研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4):158-163.
|
| [36] |
Zjou X J, Zhang Y, Zhu L L, et al. Research on selenium distribution and effectiveness in the farm system in Zhuru and Xiaosi areas, Wuhan City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(4):158-163.
|
| [37] |
刘帅, 吴志超, 赵亚荣, 等. 外源硒对镉胁迫下菜心 Fe、Mn、 Cu、Zn 吸收与转运的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(3):431-439.
|
| [37] |
Liu S, Wu Z C, Zhao Y R, et al. Effects of selenium on the uptake and transport of trace elements by cadmium-stressed flowering Chinese cabbage[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(3):431-439.
|
| [38] |
Kikkert J, Berkelaar E. Plant uptake and translocation of inorganic forms Slenium[J]. Archives of Environment Contamination & Toxicology, 2013, 65(3): 485-465.
|
| [39] |
Djanaguiraman M, Devi D D, Shanker A K, et al. Selenium-an antioxidative protectant in soybean during senescence[J]. Pant & Soil, 2005, 272(1/2): 77-86.
|
| [40] |
Shanker K, Srivastava M M. Uptake and translocation of selenium by maize (Zea mays) from its environmentaly important forms[J]. Journal Environmental Biology, 2001, 22(3): 225-228.
|
| [41] |
Zhang Y, Pan G, Chen J, et al. Uptake and transport of selenite and selenite by soybean seedings of two genotypes[J]. Plant and Soil, 2003, 253(2): 437-443.

|
| [42] |
Wang D, Zhou F, Yang W, et al. Selenium redistribution during aging in different Chinese soil and the dominant influential factors[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 182: 284-292.
|
|
|
|

