|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and genesis of selenium in soil in Xuancheng City, Anhui Province |
XING Run-Hua( ) ) |
| Geological Survey of Anhui Province, Hefei 230001,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study investigates the geochemical characteristics and genesis of selenium (Se) in the soil in Xuancheng City, Anhui Province using the samples of surface and deep soil collected through a 1:250 000 multi-purpose geochemical survey. The results are as follows. The Se content in the surface soil in Xuancheng City is (0.12~8.80)×10-6, with an average of 0.44×10-6. Se-sufficient and Se-rich soils are widely distributed in the study area, accounting for 61.90% and 35.63%, respectively. Se-rich soils are mainly distributed in the Ningdun Town in Ningguo City-Fulingtown in Jixi County, Yangong Town in Jingxian County-Baikeshu area in Xuanzhou District, Chencun Village-Chikeng Mountain in Jingxian County, and Xinhang Town in Guangde County. The Se content in the soil is mainly controlled by parent rocks and soil-forming parent materials. Se content is high in soils in the distribution areas of carbonaceous shale and carbonaceous siliceous mudstones, such as the SinianLantian Formation and Cambrian Hetang and Yangliugang formations, as well as Permian, Triassic, Carboniferous, Cambrian, and Ordovician limestone distribution area. In contrast, Se content is low in Yanshanian intermediate-acid intrusive rocks and Quaternary distribution area. In terms of soil-forming parent materials, Se content is higher in soils with parent materials of carbonate, light clastic rocks, and epimetamorphic rocks than that in soils with parent materials of Late Pleistocene loess, alluvium, and acid rocks. In terms of soil type, Se content is higher in limestone soil, skeleton soil, stonysoil, and red soil than paddy soil, yellow-cinnamon soil, and fluvo-aquic soil. Se content in soil is correlated closely with physicochemical indices, such as V, Cd, Ba, Ag, Zn, Mo, U, Ni, Sb, P, S, and organic matter. Meanwhile, total Se content is correlated closely with bioavailable Se content. Furthermore, all the 47 rice samples collected in the study area are rich in selenium, with a selenium accumulation rate of 100%. However, tea and maize are not rich in Se, and some types of vegetables are rich in Se. Therefore, different types of crops have different absorption capacities of Se in the soil.
|
|
Received: 09 June 2021
Published: 21 June 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
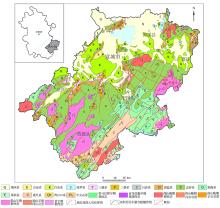
|
Location and geological map of Xuancheng City
|

| 检测项目 | 处理方法 | 分析方法 | 检测依据 | | 土壤全量Se | 0.5000 g试料,艾斯卡熔剂半熔、热水提取 | 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) | DZ/T 0258—2014 | | 土壤浸提性Se | 0.4 mol/L稀硝酸溶液浸提 | 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) | LY/T1210~1280—1999 | | 农作物Se | 微波消解法 | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | DZ/T 0253—2014、DD2005—03 |
|
Supporting scheme of sample analysis method
|

| 指标 | 分析方法 | 要求检出限/10-6 | 配套方法检出限/10-6 | 测定范围/10-6 | | 土壤全量Se | AFS | 0.01 | 0.008 | 0.008~100 | | 土壤浸提性Se | AFS | | 0.005 | | | 农作物Se | ICP-MS | | 0.005 | |
|
Detection limit of sample analysis method
|
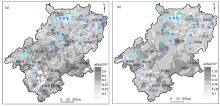
|
Geochemical map of Se elements in surface(a) and deep(b) soils of Xuancheng City
|

土壤Se
含量等级 | 含量值
/10-6 | 表层土壤 | 深层土壤 | | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | | 缺乏 | ≤0.125 | 8 | 0.06 | 1797 | 14.56 | | 边缘 | 0.125~0.175 | 248 | 2.01 | 3196 | 25.90 | | 适量 | 0.175~0.40 | 7639 | 61.90 | 6059 | 49.10 | | 高 | 0.40~3.0 | 4397 | 35.63 | 1288 | 10.44 | | 过剩 | >3.0 | 48 | 0.39 | 0 | 0.00 |
|
Se content classification and area proportion of surface and deep soil in the investigation area
|

| 分级 | 明显贫化 | 贫化 | 含量相当 | 相对富集 | 明显富集 | 强富集 | | Se表深比 | ≤0.5 | 0.5~0.8 | 0.8~1.2 | 1.2~1.5 | 1.5~2.0 | >2.0 | | 占全区比例/% | 0.89 | 2.02 | 13.10 | 16.78 | 29.02 | 38.19 |
|
Se enrichment degree of surface soil relative to deep soil
|

| 主要岩性 | 主要地层 | 表层土壤 | 深层土壤 | | w(Se)/10-6 | 样品数 | w(Se)/10-6 | 样品数 | | 含炭质岩系 | 震旦系蓝田组、皮园村组,寒武系荷塘组、杨柳岗组等 | 1.23 | 175 | 0.57 | 44 | | 含锰地层 | 南华系雷公坞组 | 1.05 | 34 | 0.39 | 10 | | 以灰岩为主 | 二叠系栖霞组—大隆组、栖霞组—长兴组,石炭—二叠系金陵组—船山组等 | 0.69 | 70 | 0.45 | 17 | | 含煤地层 | 石炭—二叠系王胡村组—高骊山组等 | 0.56 | 33 | 0.35 | 3 | | 泥质灰岩、钙质泥岩、钙质砂岩等 | 奥陶系印渚埠组—宁国组、胡乐组—长坞组等,寒武系团山组—青坑组,三叠系殷坑组—南陵湖组,古近系舜山集组、双塔寺组等 | 0.49 | 172 | 0.34 | 86 | | 以砂岩、砂砾岩为主 | 泥盆系五通组,南华系休宁组,志留系地层,白垩系地层等 | 0.41 | 1200 | 0.26 | 355 | | 粉质黏土 | 第四系戚家叽组 | 0.35 | 149 | 0.16 | 37 | | 砂、砂质黏土 | 第四系芜湖组 | 0.32 | 387 | 0.18 | 103 | | 黏土、粉质黏土 | 第四系下蜀组 | 0.31 | 117 | 0.15 | 32 | | 中酸性侵入岩 | 燕山期中酸性侵入岩 | 0.28 | 479 | 0.16 | 115 |
|
Statistical table of soil Se content formed by main strata (lithology) in the survey area
|

| 母质类型 | 表层土壤 | 深层土壤 | | 样品数 | 平均值/10-6 | 样品数 | 平均值/10-6 | | 碳酸盐岩类风化物母质 | 290 | 0.61 | 66 | 0.38 | | 浅色碎屑岩类风化物母质 | 1243 | 0.55 | 324 | 0.31 | | 浅变质岩类风化物母质 | 32 | 0.39 | 9 | 0.26 | | 网纹红土母质 | 213 | 0.35 | 48 | 0.18 | | 红色碎屑岩类风化物母质 | 243 | 0.34 | 67 | 0.19 | | 晚更新世黄土母质 | 134 | 0.32 | 35 | 0.19 | | 河流冲积物母质 | 383 | 0.32 | 103 | 0.18 | | 酸性岩类风化物母质 | 491 | 0.29 | 112 | 0.17 |
|
Comparison of soil Se content formed by different parent materials in the investigated area
|
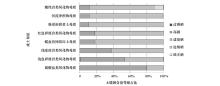
|
Grade proportion of soil selenium content in different soil forming parent materials
|
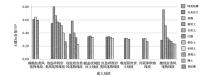
|
Comparison of Se content of main soil types in different soil forming parent materials
|

| 母质类型 | 回归方程 | 相关系数 | 样品数 | | 全区 | y=0.916x+0.210 | 0.434 | 3079 | | 浅变质岩类风化物母质 | y=1.323x+0.070 | 0.557 | 32 | | 浅色碎屑类风化物岩母质 | y=1.430x+0.123 | 0.488 | 1228 | | 红色碎屑岩类风化物母质 | y=0.591x+0.231 | 0.398 | 243 | | 酸性岩类风化物母质 | y=0.600x+0.189 | 0.385 | 473 | | 网纹红土母质 | y=0.425x+0.271 | 0.352 | 212 | | 碳酸盐岩类风化物母质 | y=0.211x+0.529 | 0.226 | 274 | | 晚更新世黄土母质 | y=0.066x+0.309 | 0.224 | 132 | | 河流冲积物母质 | y=0.280x+0.263 | 0.145 | 378 |
|
Regression equation of Se content in surface and deep soil of different parent materials
|

| 元素 | Se | V** | Mo** | Cr** | U** | Ba** | Ag** | Sb** | Ni** | | r | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.49 | | 元素 | Zn** | Cd** | P** | Corg** | C** | N** | I** | As** | S** | | r | 0.44** | 0.44** | 0.41** | 0.37** | 0.37** | 0.36** | 0.35** | 0.34** | 0.33** | | 元素 | Br** | Y** | B** | Sc** | Tl** | Hg** | TFe2 | Ti** | MgO** | | r | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.20 | | 元素 | Cu** | Mn** | Co** | F** | Pb** | Ge** | Li** | Bi** | La** | | r | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.05 | | 元素 | Ga* | CaO | Au | W | Be | Nb | Ce | pH* | Si | | r | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.00 | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.02 | -0.03 | -0.04 | -0.04 | | 元素 | Sn** | Al2 | Cl** | Rb** | K2O** | Th** | Sr** | Zr** | Na2O** | | r | -0.05 | -0.07 | -0.07 | -0.08 | -0.08 | -0.10 | -0.14 | -0.23 | -0.25 |
|
Correlation coefficient between Se and other elements in topsoil
|
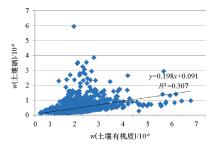
|
Correlation between soil selenium and organic matter
|

| 作物种类 | 总样品数 | 富硒样品数 | 富硒率/% | 富硒标准/10-6 | | 水稻 | 47 | 47 | 100 | ≥0.04 | | 韭菜 | 4 | 3 | 75 | 0.01~0.1 | | 辣椒 | 11 | 3 | 27.3 | 0.01~0.1 | | 茄子 | 6 | 1 | 16.7 | 0.01~0.1 | | 丝瓜 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.01~0.1 | | 玉米 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0.01~0.1 | | 茶叶 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.25~4.0 | | 瓜蒌籽 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.07~0.3 | | 山核桃 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.07~0.3 |
|
Statistical table of selenium enrichment in crops
|
| [1] |
崔剑波. 生态环境中的生命元素Se与健康的研究[J]. 生态学进展, 1989, 6(4):243-251.
|
| [1] |
Cui J B. Study on relationship between life element selemium and health in eco-environment[J]. Advances in Ecology, 1989, 6(4):243-251.
|
| [2] |
李家熙, 张光第, 葛晓云, 等. 人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000.
|
| [2] |
Li J X, Zhang G D, Ge X Y, et al. Prediction and geochemical environmental character of human selenium imbalances[M]. Beijing: Geological Press House, 2000.
|
| [3] |
张丽珊, 朱岩, 可夫, 等. 东北大骨节病区主要土壤腐殖酸Se与大骨节病关系的研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 1990, 1(4):333-337.
|
| [3] |
Zhang L S, Zhu Y, Ke F, et al. Study on relations between Kaschin-Beck disease and content of selenium bounded by humic acids in soil in Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1990, 1(4):333-337.
|
| [4] |
谭见安, 朱文郁, 李日邦, 等. 克山病与环境硒等生命元素的关系[J]. 中国地方病学杂志, 1991(5):269-274.
|
| [4] |
Tan J A, Zhu W Y, Li R B, et al. New progress in the causal association of Keshan disease with environmental selenium in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 1991(5):269-274.
|
| [5] |
周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [5] |
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [6] |
鄢明才, 迟清华. 中国东部地壳与岩石的化学组成[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997.
|
| [6] |
Yan M C, Chi Q H. The chemical compositions of the continental crust and rocks in the eastern part of China.[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997.
|
| [7] |
奚小环, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 基于大数据的中国土壤背景值与基准值及其变化特征研究——写在《中国土壤地球化学参数》出版之际[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1095-1108.
|
| [7] |
Xi X H, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. Big data based studies of the variation features of Chinese soil's background value versus reference value:A paper writtenon the occasion of Soil Geochemical Parameters of China's publication[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1095-1108.
|
| [8] |
中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集编纂委员会. 中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989.
|
| [8] |
Compilation Committee of Endemic Diseases and Environmental Atlas of the People's Republic of China. The atlas of endemic diseases and their environments in the People's Republic of China[M]. Baijing: Science Press, 1989.
|
| [9] |
杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):837-849.
|
| [9] |
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):837-849.
|
| [10] |
蔡立梅, 王硕, 温汉辉, 等. 土壤硒富集空间分布特征及影响因素研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(10):83-90.
|
| [10] |
Cai L M, Wang S, Wen H H, et al. Enrichment spatial distribution characteristics of soil selenium and its influencing factors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(10):83-90.
|
| [11] |
余飞, 张风雷, 张永文, 等. 重庆典型农业区土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):830-838.
|
| [11] |
Yu F, Zhang F L, Zhang Y W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influential factors of soil selenium in typical agricultural area,Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):830-838.
|
| [12] |
郭莉, 杨忠芳, 阮起和, 等. 北京市平原区土壤中硒的含量和分布[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):859-864.
|
| [12] |
Guo L, Yang Z F, Ruan Q H, et al. Content and distribution of selenium in soil of Beijing plain[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):859-864.
|
| [13] |
余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等. 恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6):1119-1125.
|
| [13] |
Yu T, Yang Z F, Wang R, et al. Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6):1119-1125.
|
| [14] |
陈富荣, 李明辉, 邢润华, 等. 安徽省富硒资源地球化学详查与开发利用总体实施方案[R]. 安徽省地质调查院, 2019:8-9.
|
| [14] |
Chen F R, Li M H, Xing R H, et al. Detailed geochemical survey and utilization of selenium-rich resources in Anhui Province[R]. Geological Survey of Anhui Province, 2019:8-9.
|
| [15] |
陶春军, 贾十军, 梁红霞, 等. 安徽琴溪地区土壤硒元素有效性及开发研究[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2014, 35(1):67-72.
|
| [15] |
Tao C J, Jia S J, Liang H X, et al. Research on availability and development of selenium-richsoil in Qinxi area,Anhui Province[J]. Resources Survey and Enviroment, 2014, 35(1):67-72.
|
| [16] |
陶春军, 贾十军, 邢润华, 等. 安徽独山富硒区土壤硒元素迁移转化规律及开发研究[J]. 地质学刊, 2014, 38(1):83-87.
|
| [16] |
Tao C J, Jia S J, Xing R H, et al. Selenium migration and transformation rules and development inselenium-rich soil in Dushan of Anhui[J]. Journal of Geology, 2014, 38(1):83-87.
|
| [17] |
夏飞强, 张祥, 杨艳, 等. 安徽省宁国市土壤和农产品硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2021, 53(3):585-593.
|
| [17] |
Xia F Q, Zhang X, Yang Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils and agricultural products in Ningguo city, Anhui province[J]. Soils, 2021, 53(3):585-593.
|
| [18] |
DZ/T 0295—2016 土地质量地球化学评价规范[S].
|
| [18] |
DZ/T 0295—2016 Specification of land quality geochemical assessment[S].
|
| [19] |
张明, 杨忠芳, 陈岳龙, 等. 湖南洞庭湖地区土壤Hg的来源[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(11):1464-1469.
|
| [19] |
Zhang M, Yang Z F, Chen Y L, et al. Sources of Hg in soils of the Dongting Lake area,Hunan,China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(11):1464-1469.
|
| [20] |
张明, 陈国光, 刘红樱, 等. 长江三角洲地区土壤重金属含量及其分异特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2012, 43(5):1098-1103.
|
| [20] |
Zhang M, Chen G G, Liu H Y, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metal in soils of Yangtze River Delta[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 2012, 43(5): 1098-1103.
|
| [21] |
王美珠, 章明奎. 我国部分高硒低硒土壤的成因初探[J]. 浙江大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 1996, 22(1):89-93.
|
| [21] |
Wang M Z, Zhang M K. A discussion on the cause of high-Se and low-Se soil formation[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University, 1996, 22(1):89-93
|
| [22] |
杨志强, 李杰, 郑国东, 等. 广西北部湾沿海经济区富硒土壤地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1260-1264,1269.
|
| [22] |
Yang Z Q, Li J, Zheng G D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Beibu Gulf coastal economic zone of Guangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6):1260-1264,1269.
|
| [23] |
刘晓波, 张华, 金立新, 等. 四川省屏山县土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(10):2246-2252.
|
| [23] |
Liu X B, Zhang H, Jin L X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in Pingshan of Sichuan Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(10):2246-2252.
|
| [24] |
章海波, 骆永明, 吴龙华, 等. 香港土壤研究Ⅱ:土壤硒的含量、分布及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2005, 42(3):404-410.
|
| [24] |
Zhang H B, Luo Y M, Wu L H, et al. Hong Kong soil researches Ⅱ: Distribution and content of selenium in soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2005, 42(3):404-410.
|
| [25] |
杨琼, 侯青叶, 顾秋蓓, 等. 广西武鸣县典型土壤剖面Se的地球化学特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(4):456-462.
|
| [25] |
Yang Q, Hou Q Y, Gu Q B, et al. Study of geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil seleniumin the typical soil profiles in Wuming county of Guangxi[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(4):456-462.
|
| [26] |
郦逸根, 董岩翔, 郑洁, 等. 浙江富硒土壤资源调查与评价[J]. 第四纪研究, 2005, 25(3):323-330.
|
| [26] |
Li Y G, Dong Y X, Zheng J, et al. Selenium:Abundant soilsurvey andassessment in Zhejiang[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2005, 25(3):323-330.
|
| [27] |
张光弟, 葛晓立, 张绮玲, 等. 湖北恩施硒中毒区土壤硒的分布及其控制因素[J]. 中国地质, 2001, 28(9):36-40.
|
| [27] |
Zhang G D, Ge X L, Zhang Q L, et al. Se distribution and its contral factor in soil polluted by seleniumin Enshi,Hubei[J]. Geology of China, 2001, 28(9):36-40.
|
| [1] |
JIANG Bing, LIU Yang, WU Zhen, ZHANG De-Ming, SUN Zeng-Bing, MA Jian. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in irrigation water and soils in the Gaomi area, Shandong Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1348-1353. |
| [2] |
NAN Zhe, WANG Lin-Shi, HOU Xu, ZHAI Zheng-Bo, WANG Yang, LIU Yang. Geological and geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of rare element and rare earth element deposits in Saima alkaline complex[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 670-680. |
|
|
|
|

