|
|
|
| Near-surface response of hydrocarbon-consuming microorganisms to the fault-karst reservoirs in Shunbei oil and gas field |
CAO Fei1( ), YANG Min1, BAO Dian1, CHEN Yin-Jie2, WANG Guo-Jian2 ), YANG Min1, BAO Dian1, CHEN Yin-Jie2, WANG Guo-Jian2 |
1. SINOPEC Northwest Oilfield Company,Urumqi 830011,Chian
2. Wuxi Research Institute of Petroleum Geology,Research Institute of Exploration and Production,SINOPEC,Wuxi 214126,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract As an ultra-deep fault-karst reservoir located in the Tarim Basin of Xinjiang,the Shunbei oil and gas field prosses the characteristics of the large burial depth and fault development in the target formations.This oil and gas field is difficult to explore due to the low signal-to-noise ratio and low resolution of seismic signal data since seismic signals are absorbed by the desert surface and thereby suffer severe attenuation.The microbial prospecting developing based on the theory of vertical hydrocarbon microseepage can detect the oil and gas-bearing properties of fault zones.This technology,combined with geophysical exploration,can improve the success rate of the prediction of the oil and gas-bearing properties of fault zones.This experimental study of microbial prospecting in fault zone No.5 in the Shunbei oil and gas field shows that the abundance anomalies of hydrocarbon-consuming microorganisms show good near-surface response to fault-karst reservoirs.Compared to areas with vegetation,hydrocarbon-consuming microorganisms (including methane- and butane-oxidizing bacteria) as indicators of microbial prospecting in desert areas are characterized by low measured values and slight fluctuation.However,hydrocarbon-consuming microorganisms can better reflect the near-surface information induced by the vertical microseepage of deep-buried oil and gas since they are less disturbed by other microbial communities due to the special ecological conditions in desert areas.According to the application results,the high-amplitude anomalies of both methane- and butane-oxidizing bacteria are primarily distributed in the vicinity of fault zone No.5,and favorable anomalies also occur in the vicinity of fault zone No.1 in the Shunbei oil and gas field.Furthermore,the strike of these anomalies roughly coincides with that of fault zones,indicating that the microbial anomaly zones correlate strongly with fault-karst reservoirs.Therefore,the microbial prospecting for hydrocarbons has great application prospects in the exploration of the fault-karst reservoirs.
|
|
Received: 25 February 2021
Published: 21 June 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Bitmap of seismic interpretation and microbial exploration sampling points in Shunbei study area
|

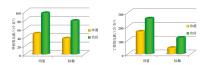
| 指标 | 甲烷氧化菌 | 丁烷氧化菌 | | 地貌 | 沙漠 | 农田 | 沙漠 | 农田 | | 样本数/个 | 1055 | 134 | 1055 | 135 | | 极小值/(只·g-1) | 3.00 | 10.00 | 29.00 | 85.00 | | 中位值/(只·g-1) | 43.00 | 81.00 | 160.00 | 235.00 | | 极大值/(只·g-1) | 618.00 | 630.00 | 616.00 | 782.00 | | 均值/(只·g-1) | 48.89 | 96.83 | 162.73 | 256.93 | | 标偏/(只·g-1) | 37.43 | 78.66 | 43.37 | 116.92 | | 变异系数 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.27 | 0.46 |
|
Comparison table of characteristic values of microbial indexes in different landforms
|
|
Comparison of microbial characteristic values between farmland and desert landform areas
|

| 地貌 | 中位值/(只·g-1) | 极大值/(只·g-1) | 均值/(只·g-1) | 标准偏差/(只·g-1) | 变异系数 | | 沙漠 | 0.27 | 4.48 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.80 | | 农田 | 0.33 | 1.25 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.63 |
|
Comparison table of microbial structure characteristics between farmland and desert
|

|
Histogram of microbial structure characteristics in different geomorphologic areas
|
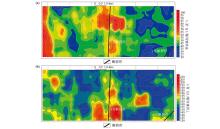
|
Isoline map of microbial index plane in Shunbei study area
a—methane oxidizing bacteria;b—butane oxidizing bacteria
|
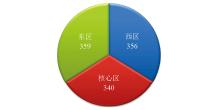
|
Comparison between the core area and the periphery of the Shunbei 5 fault zone
|

| 特征值 | 分区 | MOB | BOB | MOB/BOB | | 均值 | 西区 | 46.00 | 161.88 | 0.29 | | 核心区 | 53.94 | 167.91 | 0.33 | | 东区 | 40.42 | 158.65 | 0.27 | | 标准差 | 西区 | 28.29 | 36.55 | 0.18 | | 核心区 | 47.96 | 48.18 | 0.31 | | 东区 | 24.27 | 44.40 | 0.17 | | 变异系数 | 西区 | 0.61 | 0.23 | 0.61 | | 核心区 | 0.89 | 0.29 | 0.93 | | 东区 | 0.60 | 0.28 | 0.64 |
|
Comparison table of characteristic values between the core area and peripheral indexes of the Shunbei 5 fault zone
|
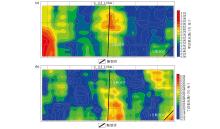
|
Planar contour map of microbial fluctuation rate in Shunbei study area
a—methane oxidizing bacteria;b—butane oxidizing bacteria
|
| [1] |
焦方正. 塔里木盆地顺北特深碳酸盐岩断溶体油气藏发现意义与前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(2):207-216.
|
| [1] |
Jiao F Z. Significance and prospect of ultra-deep carbonate fault-karst reservoirs in Shunbei area,Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(2):207-216.
|
| [2] |
邓尚, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区主干走滑断裂带差异活动特征及其与油气富集的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5):878-888.
|
| [2] |
Deng S, Li H L, Zhang Z P, et al. Characteristics of differential activities in major strike-slip fault zones and their control on hydrocarbon enrichment in Shunbei area and its surroundings,Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5):878-888.
|
| [3] |
黄太柱. 塔里木盆地塔中北坡构造解析与油气勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(3):257-267.
|
| [3] |
Huang T Z. Structural interpretation and petroleum exploration targets in northern slope of middle Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(3):257-267.
|
| [4] |
周翼, 陈学强, 江民, 等. 塔克拉玛干沙漠区浅表层对地震波的吸收衰减作用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016, 51(2):218-223.
|
| [4] |
Zhou Y, Chen X Q, Jiang M, et al. Seismic wave absorption caused by near-surface in Taklimakan Desert[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2016, 51(2):218-223.
|
| [5] |
孔剑冰, 庄道川, 高雁, 等. 塔里木盆地沙漠区低信噪比地震资料静校正和去噪方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2005, 29(3):257-260.
|
| [5] |
Kong J B, Zhang D C, Gao Y, et al. A study of static correction and deno ising method for low signal to noise ratio seismic data from the desert area of tarim basin and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2012, 2005, 29(3):257-260.
|
| [6] |
贾丽华, 曾庆才, 段洪有, 等. 塔中沙漠地区深层地震资料处理方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2002, 26(3):232-235.
|
| [6] |
Jia L H, Zeng Q C, Duan H Y, et al. Deep seismic data processing technique for central taklimakan desert area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2002, 26(3):232-235.
|
| [7] |
汤玉平, 顾磊, 许科伟, 等. 油气微生物勘探机理及应用[J]. 微生物学通报, 2016, 43(11):2386-2395.
|
| [7] |
Tang Y P, Gu L, Xu K W, et al. Research and application of microbial exploration for oil and gas[J]. Microbiology China, 2016, 43(11):2386-2395.
|
| [8] |
Atlasrm. 石油微生物学[M].黄第藩,译. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1991.
|
| [8] |
Atlasrm. Petroleum Microbiology[M].Translated by Huang Difan. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1991.
|
| [9] |
杨帆, 沈忠民, 汤玉平, 等. 准噶尔盆地春光探区油气微生物指示[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(7):804-812.
|
| [9] |
Yang F, Shen Z M, Tang Y P, et al. Hydrocarbon microbial prospecting in Chunguang exploration area,Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(7):804-812.
|
| [10] |
汤玉平, 蒋涛, 任春, 等. 地表微生物在油气勘探中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(4):546-549.
|
| [10] |
Tang Y P, Jiang T, Ren C, et al. The application of edaphic microbe to oil and gas exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(4):546-549.
|
| [11] |
梅海, 林壬子, 梅博文, 等. 油气微生物检测技术:理论、实践和应用前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(6):888-893.
|
| [11] |
Mei H, Lin R Z, Mei B W, et al. Microbial oil-gas detection technologies:theory,practice and application prospect[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(6):888-893.
|
| [12] |
陈绪云, 朱秀香, 曹自成, 等. 顺托果勒地区及周缘奥陶系油气藏分布特征与成因浅析[J]. 新疆地质, 2017, 35(1):74-78.
|
| [12] |
Chen X Y, Zhu X X, Cao Z C, et al. Distribution characteristics and origin of Ordovician oil and gas reservoirs in Shuntuoguole region and its periphery[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2017, 35(1):74-78.
|
| [13] |
王国建, 汤玉平, 赵克斌, 等. 油气化探技术在川西坳陷油气勘探中的应用[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(11):1643-1649.
|
| [13] |
Wang G J, Tang Y P, Zhao K B, et al. Application of hydrocarbon geochemical exploration technique inoil and gas exploration in western Sichuan depression,China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(11):1643-1649.
|
| [14] |
张水昌, 高志勇, 李建军, 等. 塔里木盆地寒武系—奥陶系海相烃源岩识别与分布预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(3):285-294.
|
| [14] |
Zhang S C, Gao Z Y, Li J J, et al. Identification and distribution of marine hydrocarbon source rocks in the Ordovician and Cambrian of the Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(3):285-294.

|
| [15] |
赵孟军, 王招明, 潘文庆, 等. 塔里木盆地满加尔凹陷下古生界烃源岩的再认识[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(4):417-423.
|
| [15] |
Zhao M J, Wang Z M, Pan W Q, et al. Lower Palaeozoic source rocks in Manjiaer Sag,Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(4):417-423.

|
| [16] |
漆立新. 塔里木盆地下古生界碳酸盐岩大油气田勘探实践与展望[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(6):771-779.
|
| [16] |
Qi L X. Exploration practice and prospects of giant carbonate field in the Lower Paleozoic of Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(6):771-779.
|
| [17] |
张保涛, 于炳松, 朱光有, 等. 塔中北斜坡富油气区油气分布规律与富集主控因素研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):271-280.
|
| [17] |
Zhang B T, Yu B S, Zhu G Y, et al. Research on hydrocarbon distribution regularity and main accumulationcontrolling factors of Tazhong northern slope hydrocarbon-rich region[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1):271-280.
|
| [18] |
马庆佑, 沙旭光, 李玉兰, 等. 塔中顺托果勒区块走滑断裂特征及控油作用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012, 34(2):120-124.
|
| [18] |
Ma Q Y, Sha X G, Li Y L, et al. Characteristics of strike-slip fault and its controllingon oil in Shuntuoguole region,middle Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2012, 34(2):120-124.
|
| [19] |
朱秀香, 陈绪云, 曹自成. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒低隆起顺托1井区油气成藏模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(1):41-49.
|
| [19] |
Zhu X X, Chen X Y, Cao Z C. Hydrocarbon accumulation mode of Shuntuo 1 well blockin the Shuntuoguole lower uplift,Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(1):41-49.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Jing, LIANG Qian-Yong, ZHANG Li, ZHONG Guang-Jian. Near-surface oil and gas geochemical characteristics and exploration prospect of the western depression of Taiwan Strait Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(4): 657-664. |
| [2] |
REN Chun, TANG Yu-Ping, HE Jin-Fa, GAO Jun-Yang, XU Ke-Wei. The application of gene quantitative technique to oil and gas prospecting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(5): 976-980. |
|
|
|
|

