|
|
|
| Researches on the selection of key parameters in AMT 2D nonlinear conjugate inversion for railway tunnel exploration |
ZHAO Guang-Xue1( ), RUAN Shuai2, WU Su-Yuan1 ), RUAN Shuai2, WU Su-Yuan1 |
1. Hengda Century (Beijing) Geophysics Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100020, China
2. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In this paper, the authors analyzed the suitability of 2D nonlinear conjugate inversion method in railway tunnel AMT exploration under complex topographic and geological conditions. Based on typical modeling and inversion research, researchers can find out the best key parameters to control inversion algorithm so as to avoid fake abnormalities shown on inversion results. Researches show that 2D nonlinear conjugate inversion works well in railway tunnel AMT exploration. If the true model is like the model type described in this paper, inversion result can be efficiently improved by inverting TE&TM mode data, inverting frequencies less than 1 000 Hz, using small smooth factor and choosing the half space initial model close to the shallow layers' resistivity.
|
|
Received: 17 December 2019
Published: 29 April 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
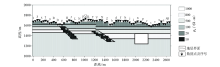
|
Typical forward grid of geological model
|
Figure 1)
">
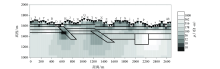
|
Rough mesh TE mode inversion results (The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|
Figure 1)
">
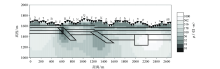
|
Fine mesh TE mode inversion results (The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|
Figure 1)
">
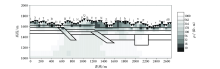
|
Rough mesh TM mode inversion results (The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|
Figure 1)
">
|
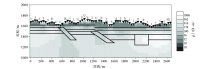
Fine mesh TM mode inversion results (The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|
Figure 1)
">
|
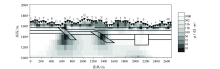
Rough mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|
Figure 1)
">
|
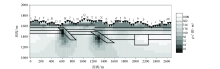
Fine mesh TM+TE mode inversion results (The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|

| 网格类型 | 图号 | 反演模式 | 迭代次数 | 最终RMS误差 | | 粗糙 | 图2 | TE | 100 | 2.18 | | 精细 | 图3 | TE | 100 | 0.53 | | 粗糙 | 图4 | TM | 100 | 2.02 | | 精细 | 图5 | TM | 100 | 0.55 | | 粗糙 | 图6 | TE+TM | 100 | 2.6 | | 精细 | 图7 | TE+TM | 100 | 0.45 |
|
Inversion RMS error of different grids and different modes
|
Figure 1)
">
|
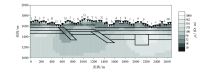
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE mode inversion results(The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|
Figure 1)
">
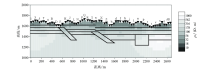
|
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TM mode inversion results(The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|
Figure 1)
">
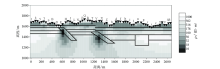
|
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (The legend is the same as Figure 1)
|

| 图名 | 反演数据频带/Hz | 反演模式 | 迭代次数 | 最终RMS误差 | | 图3 | 10 000~10 | TE | 100 | 0.53 | | 图8 | 1 000~10 | TE | 16 | 0.46 | | 图4 | 10 000~10 | TM | 100 | 0.55 | | 图9 | 1 000~10 | TM | 100 | 0.36 | | 图7 | 10 000~10 | TE+TM | 73 | 0.49 | | 图10 | 1 000~10 | TE+TM | 100 | 0.38 |
|
Inversion RMS error of different frequency bands
|
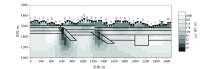
|
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (smooth factor 0.3)
|
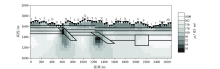
|
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (smooth factor 3)
|
|
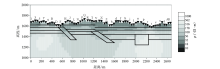
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (smooth factor 30)
|
|
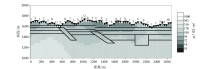
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (smooth factor 300)
|

| 反演结果图示 | 正则化因子 | 反演模式 | 迭代次数 | 最终RMS误差 | | 图11 | 0.3 | TE+TM | 100 | 0.22 | | 图12 | 3 | TE+TM | 100 | 0.38 | | 图13 | 30 | TE+TM | 37 | 1.24 | | 图14 | 300 | TE+TM | 100 | 3.46 |
|
Inversion RMS error of different smooth factors
|
|
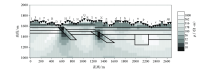
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (initial model 10 Ω·m)
|
|
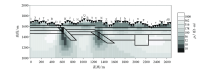
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (initial model 100 Ω·m)
|
|
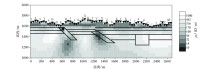
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (initial model 500 Ω·m)
|
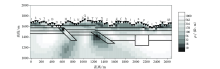
|
1 000~10 Hz Fine mesh TE+TM mode inversion results (initial model 1 000 Ω·m)
|

| 图名 | 初始模型电阻率/(Ω·m) | 反演模式 | 迭代次数 | 最终RMS误差 | | 图15 | 10 | TE+TM | 100 | 0.42 | | 图16 | 100 | TE+TM | 100 | 0.22 | | 图17 | 500 | TE+TM | 100 | 0.24 | | 图18 | 1 000 | TE+TM | 100 | 0.5 |
|
Inversion RMS error of different initial models
|
| [1] |
Rodi W L, Mackie R L. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2001,66:174-187.

|
| [2] |
Constable C S, Parker R L, Constable C G. Occam's inversion: a practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data[J]. Geophysics, 1987,52:289-300.

|
| [3] |
苗景春, 阮帅, 张悦. 音频大地电磁测深法对正、逆断层的精细解释[J]. 物探与化探, 2013,37(4):681-686.

|
| [3] |
Miao J C, Ruan S, Zhang Y. The application of the audio magnetotelluric sounding method to the precise interppetation of narmal and reverse faults[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013,37(4):681-686.

|
| [4] |
汤井田, 任政勇, 化希瑞. 地球物理学中的电磁场正演与反演[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007,22(4):1181-1194.

|
| [4] |
Tang J T, Ren Z Y, Hua X R. The forward modeling and inversion in geophysical electromagnetic field[J]. Progress in Geophysics Issue, 2007,22(4):1181-1194.
|
| [5] |
陈小斌, 赵国泽, 汤吉, 等. 大地电磁自适应正则化反演算法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2005,48(4):937-946.

|
| [5] |
Chen X B, Zhao G Z, Tang J, et al. An adaptive regularized inversion algorithm for magnetotelluric data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005,48(4):937-946.
|
| [6] |
胡祖志, 胡祥云, 何展翔. 大地电磁非线性共轭梯度拟三维反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006,49(4):1226-1234.

|
| [6] |
Hu Z Z, Hu X Y, He Z X. Pseudo-three-dimensional magnetotelluric inwesion using nonlinear conjugate gradients[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006,49(4):1226-1234.
|
| [7] |
蔡义宇, 肖调杰, 宋滔. 二维大地电磁各向异性参数对视电阻率的影响研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020,35(1):86-93.
|
| [7] |
Cai Y Y, Xiao T J, Song T. Influence of two-dimensional magnetotelluric anistropic parameters on apparent resistivities[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020,35(1):86-93.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Li-Zhen, SUN Cheng-Yu, WANG Zhi-Nong, LI Shi-Zhong, JIAO Jun-Feng, YAN Ting-Rong. First-arrival wave travel time-based tomography inversion with surface wave information as constraints[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1198-1205. |
| [2] |
JIANG Shou-Jin, CHEN Yong-Ling, LI Huai-Yuan, HU Jun-Feng. Resistivity of moraine deposits in the Tangbu section, Dongcuoqu, southeastern Tibet[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 73-80. |
|
|
|
|

