|
|
|
| The application of hydrocarbon and superimposed halo method to the Woxi gold deposit, Hunan Province |
CHEN Hai-Long1( ), XIAO Qi-Peng1, LIANG Ju-Hong2 ), XIAO Qi-Peng1, LIANG Ju-Hong2 |
1. Research Institute of Hunan Provincial Nonferrous Metal Geological Exploration Bureau, Changsha 410015, China
2. Hunan Chenzhou Mining Co.,Ltd.,Yuanling 419607,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In order to solve the problem of deep prospecting in the Yuershanore ore block and its peripheral Hongyanxi-Ma'erqiaooreblock in the Woxi mining area, the authors carried out the tests of structural superimposition halo and hydrocarbon mercury comprehensive gas measurement in this area. Based on the study of the evolution law of hydrocarbon and mercury components in different geological bodies and different elevations and the characteristics of geochemical hydrocarbon and mercury anomalies formed in the upper soil of the orebody, the authors summarized the structure and superposition characteristics of soil geochemical anomaly field as well as the corresponding relationship with space so as to carry out the deep prospecting prediction. In addition, the test of the hydrocarbon and mercury superposition halo was carried out in the Hongyanxi-Ma'erqiao prediction areain the periphery. Based on the comprehensive study of prospecting methods, it is found that there are two different types of superposition fields in the soil geochemical field of Hongyanxi-Maherqiao ore block: one is deep source superposition field, where the correlation between Au and hydrocarbon components is good, the hydrocarbon anomaly components are complete, the Au and Hg anomalies are good, with deep source ore-forming hydrothermal superposition, and the deep prospecting potential is great; the other is syngenetic superposition field, where the correlation between Au and hydrocarbon components is poor, the element combination is relatively simple, and there is no hydrocarbon component anomaly, exhibiting little significance for ore prospecting.The hydrocarbon anomaly mode is dominated by dual bimodal anomaly mode, and there is a good hydrocarbon mercury comprehensive superposition anomaly in the low value area between the two peaks of hydrocarbon anomaly, indicating that there is a parallel blind vein in the depth. Drilling verification shows that the deep source superposition field has a gold orebody with a real thickness of 8.58 m and an average grade of 3.55×10-6 gold, while the syngenetic superposition field only has gold mineralization. Good prediction results have been achieved.
|
|
Received: 07 April 2020
Published: 29 April 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
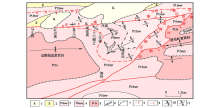
|
Simplified geological map of structure
1—Cretaceous system;2—Sinian system;3—Wuqiangxi formation of Banxi group;4—Madiyi formation of Banxi group;5—Xiaomuping formation of Lengjiaxi group;6—alterated rock;7—unconformity surface; 8—normal fault;9—thrust fault;10—syncline;11—anticline
|

|
Cross section of line-87 in Yuershan Au,Sb,W deposit
1—Quaternary system;2—Wuqiangxi formation of Banxi group;3—Madiyi formation of Banxi group;4—drifting dust;5—slate;6—sandy slate;7—fault and number;8—vein and number;9—alterated rock
|

| 类型 | 参数 | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 异丁 | 正丁 | 异戊 | 正戊 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 汞 | | 土壤 | B层 | 2.84 | 0.16 | 0.089 | 0.053 | 0.087 | 0.025 | 0.061 | 1.36 | 0.53 | 26.2 | | C层 | 3.12 | 0.25 | 0.121 | 0.056 | 0.131 | 0.027 | 0.135 | 1.75 | 0.83 | 21.8 | | -40目 | 1.26 | 0.070 | 0.034 | 0.006 | 0.017 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.245 | 0.072 | 38.76 | | -80目 | 1.25 | 0.053 | 0.028 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.007 | 0.020 | 0.301 | 0.075 | 38.49 | | -120目 | 1.95 | 0.140 | 0.074 | 0.014 | 0.037 | 0.015 | 0.030 | 0.353 | 0.117 | 41.32 | | -160目 | 2.42 | 0.162 | 0.127 | 0.027 | 0.097 | 0.018 | 0.072 | 0.787 | 0.302 | 31.41 | | -200目 | 2.56 | 0.185 | 0.130 | 0.023 | 0.093 | 0.016 | 0.085 | 0.628 | 0.354 | 34.64 | | 岩石 | -120目 | 26.9 | 1.68 | 1.07 | 0.118 | 0.452 | 0.115 | 0.246 | 2.61 | 1.41 | 0.03 | | -160目 | 29.0 | 2.15 | 1.27 | 0.159 | 0.493 | 0.129 | 0.232 | 4.55 | 1.98 | 0.34 | | -200目 | 28.1 | 2.61 | 1.58 | 0.166 | 0.471 | 0.184 | 0.276 | 5.05 | 1.59 | 0.39 |
|
Content characteristics of hydrocarbon mercury with different granularity and horizon of sample
|

| 参数 | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 异丁 | 正丁 | 异戊 | 正戊 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 汞 | | 区域 | 平均值 | 161 | 34.4 | 20.6 | 1.46 | 6.5 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 28.8 | 21.3 | 2.2 | | Cv | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.99 | | 矿区 | 平均值 | 817 | 150 | 69.0 | 4.7 | 21 | 3.7 | 5.6 | 125 | 82 | 3.9 | | Cv | 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.56 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 2.5 |
|
Hydrocarbon background values of Madiyi formation primary halo in mine district
|

| 地层 | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 异丁 | 正丁 | 异戊 | 正戊 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 吸附汞 | | 冷家溪组 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 7.2 | | 马底驿组 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 23 | | 五强溪组 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 18 | | 白垩系 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 3.19 |
|
Content ratios of geochemical indexs in soils and rocks of different strata in mine district (aenrichment cofficients)
|

| Au | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 异丁 | 正丁 | 异戊 | 正戊 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 汞 | | 背景值 | 8.9 | 161 | 34.4 | 20.6 | 1.46 | 6.5 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 28.8 | 21.3 | 2.2 | | 矿体 | 3000 | 5877 | 865 | 272 | 17 | 79 | 12 | 22 | 747 | 504 | 36 | | 强蚀变 | 1246 | 4331 | 626 | 199 | 13 | 62 | 10 | 17 | 576 | 411 | 36 | | 弱蚀变 | 284 | 1010 | 163 | 59 | 4 | 18 | 3 | 5 | 138 | 91 | 89 | | 未蚀变 | 28 | 501.2 | 81.8 | 31.5 | 2.0 | 9.2 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 64.6 | 40.9 | 6.5 |
|
Content characteristics of hydrocarbon and merury in different geobody in mine district
|

| 指标 | Sb | W | Au | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 异丁 | 正丁 | 异戊 | 正戊 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 汞 | | Sb | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | W | 0.06 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | Au | 0.64 | 0.18 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | 甲烷 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.63 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | 乙烷 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.64 | 0.99 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | 丙烷 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.56 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | 异丁 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.55 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | 正丁 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.57 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | | | | | | | 异戊 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.54 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | | | | | | 正戊 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.57 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | | | | | 乙烯 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.68 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 1.00 | | | | 丙烯 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.72 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 1.00 | | | 汞 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 0.70 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 1.00 |
|
Calculation results of relevant parametersin Yuershan district
|
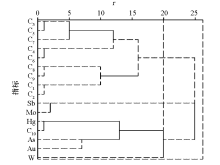
|
General graph of R-type cluster analysis of V6-vein in Yuershan district
|
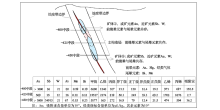
|
Sketch of element vertical zoning mode of V6-vein in Yuershan district
|

| 指标 | Sb | W | Au | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 异丁 | 正丁 | 异戊 | 正戊 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 汞 | | Sb | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | W | 0.37 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | Au | 0.45 | 0.85 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | 甲烷 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | 乙烷 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.30 | 0.76 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | 丙烷 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.47 | 0.80 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | 异丁 | 0.32 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.57 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | 正丁 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.39 | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.78 | 1.00 | | | | | | | 异戊 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 1.00 | | | | | | 正戊 | 0.45 | -0.03 | 0.02 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.66 | 0.79 | 1.00 | | | | | 乙烯 | 0.48 | -0.09 | -0.09 | -0.03 | -0.13 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 1.00 | | | | 丙烯 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 1.00 | | | 汞 | 0.62 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.26 | 1.00 |
|
Relevant parameters of soil elements in Yuershan district
|
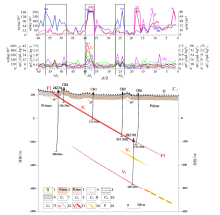
|
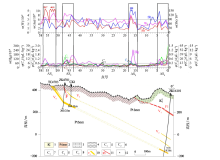
Soil geochemistry profiles of line 87 in Yuershan district
1—Quaternary system;2—Wuqiangxi formation of Banxi group;3—Madiyi formation of Banxi group;4—drifting dust;5—slate;6—sandy slate;7—methane;8—ethane,propane;9—isobutane,N-butane,isopentane,N-contour;10—ethylene;11—propylene;12—fault and number;13—vein and number;14—alterated rock;15—sampling point
|
|
Soil geochemistry profiles of line 161 in Maerqiao district
1—Cretaceous system;2—Madiyi formation of Banxi group;3—graywacke;4—slate;5—methane;6—ethane,propane;7—isobutane,N-butane,isopentane,N-contour;8—ethylene;9—propylene;10—vein and number;11—alteration zone;12—sampling point
|

| 指标 | Sb | W | Au | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 异丁 | 正丁 | 异戊 | 正戊 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 汞 | | Sb | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | W | 0.29 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | Au | 0.66 | 0.29 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | 甲烷 | 0.39 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | 乙烷 | 0.44 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.84 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | 丙烷 | 0.65 | 0.06 | 0.51 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | 异丁 | 0.62 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.75 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | 正丁 | 0.62 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 1.00 | | | | | | | 异戊 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 0.71 | 0.61 | 1.00 | | | | | | 正戊 | 0.63 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 1.00 | | | | | 乙烯 | 0.67 | 0.11 | 0.49 | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 0.83 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 1.00 | | | | 丙烯 | 0.41 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 0.45 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.49 | 1.00 | | | 汞 | 0.64 | 0.18 | 0.71 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.29 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.35 | 1.00 |
|
Relevant parameters of line 131 soil elements in Hongyanxi district
|
|
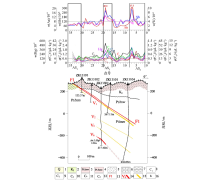
Soil geochemistry profiles of line 131 in Hongyanxi deposit
1—Quaternary system;2—Cretaceous system;3—Wuqiangxi formation of Banxi group;4—Madiyi formation of Banxi group;5—drifting dust;6—graywacke;7—slate;8—methane;9—ethane,propane;10—isobutane,N-butane,isopentane,N-contour;11—ethylene;12—propylene;13—fault and number;14—vein and number;15—alterated rock;16—sampling point
|

| 指标 | Sb | W | Au | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 异丁 | 正丁 | 异戊 | 正戊 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 汞 | | Sb | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | W | 0.11 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | Au | 0.18 | 0.38 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | 甲烷 | (0.04) | (0.18) | (0.06) | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | 乙烷 | (0.07) | (0.16) | (0.07) | 0.99 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | 丙烷 | 0.15 | (0.11) | (0.03) | 0.87 | 0.87 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | 异丁 | 0.21 | (0.17) | (0.02) | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.85 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | 正丁 | 0.24 | (0.05) | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.84 | 1.00 | | | | | | | 异戊 | 0.21 | (0.19) | (0.05) | 0.43 | 0.40 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 0.74 | 1.00 | | | | | | 正戊 | 0.28 | (0.00) | 0.02 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 1.00 | | | | | 乙烯 | 0.60 | (0.05) | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 1.00 | | | | 丙烯 | 0.44 | (0.15) | 0.06 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 1.00 | | | 汞 | 0.55 | (0.05) | 0.15 | 0.02 | (0.01) | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.40 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.81 | 0.54 | 1.00 |
|
Relevant parameters of line 161 soil elements in Maerqiao district
|

| 矿段 | 特征值 | Hg | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | | 全区 | 异常下限 | 120 | 6 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 13 | 3 | | 红岩溪 | 异常均值 | 188 | 7.5 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 24.4 | 3.9 | | 衬值 | 1.56 | 1.25 | 2.17 | 2.33 | 1.87 | 1.3 | | 马儿桥 | 异常均值 | 177 | 5.84 | 0.56 | 0.27 | 10.57 | 1.94 | | 衬值 | 1.47 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.9 | 0.81 | 0.64 |
|
Contrast value of each abnormal element of Hongyanxi-Ma'erqiao ore block
|
| [1] |
陈远荣, 戴塔根, 贾国相, 等. 金属矿床有机烃气常见异常模式和成因机理研究[J]. 中国地质, 2001,15(87):738-742.
|
| [1] |
Chen Y R, Dai T G, Jia G X, et al. The common anomaly pattern of organic hydrocarbon of metallic ore deposit and its mechanism study[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2001,15(87):738-742.
|
| [2] |
李生郁, 徐丰孚. 轻烃与硫化物气体测量寻找金矿隐伏矿方法试验[J]. 物探与化探, 1997,45(2):499-504.
|
| [2] |
Li S Y, Xu F F. The test of light hydrocarbon and sulphide gas measurement for gold concealed ore[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1997,45(2):499-504.
|
| [3] |
李生郁, 徐丰孚. 土壤空隙烃气测量及其初步应用效果[C] //第五届全国勘查地球化学学术讨论会论文集, 1994.
|
| [3] |
Li S Y, Xu F F. Measurement of hydrocarbon gas in soil voids and its preliminary application effect[C] //Proceedingsof 5th National Symposium on Exploration Geochemistry, 1994.
|
| [4] |
祁士华, 阮天健. 金矿床上的轻烃异常研究[R]. 中国地质大学(北京), 1996.
|
| [4] |
Qi S H, Ruan T J. Research of hydrocarbon anomalies in gold deposits [R]. China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 1996.
|
| [5] |
殷鸿福, 张文怀, 张志坚 .等. 生物成矿系统论[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1999.
|
| [5] |
Yin H F, Zhang W H, Zhang Z J, et al. Biomineralization system theory [M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1999.
|
| [6] |
胡凯. 金矿床中的有机质及其成矿作用[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 1998,17(2):71-75.

|
| [6] |
Hu K. Organic matter and its mineralization in gold deposits[J]. Geochemical Bulletin of Minerals and Rocks, 1998,17(2):71-75.
|
| [7] |
陈远荣, 贾国相, 徐庆鸿. 气体集成快速定位预测隐伏矿新技术研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003.
|
| [7] |
Chen Y R, Jia G X, Xu Q H. Study on new technology of gas integrated rapid location and prediction of concealed ore[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003.
|
| [8] |
陈远荣, 戴塔根, 当玉涛, 等. 有机烃气法在个旧锡矿松树脚矿田中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2001,25(3):180-184.

|
| [8] |
Chen Y Y, Dai T G, Dang Y T, et al. The application of organic hydrocarbon gas technique to the Songshujiao ore field in the Gejiu tin mine,Yunnan province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2001,25(3):180-184.

|
| [9] |
蒋惠俏, 陈远荣, 黄祥林, 等. 烃气测量法在龙口铅锌矿区找矿预测中的应用[J]. 金属矿山, 2013,42(1):104-106,154.

|
| [9] |
Jiang H Q, Chen Y R, Huang X L, et al. Application of hydrocarbon measurement to evaluation and prediction of ore prospecting in Longkou lead-zinc deposit[J]. Metal Mine, 2013,42(1):104-106,154.

|
| [10] |
徐庆鸿, 陈远荣, 毛景文, 等. 有机烃在预测隐伏金矿床中的应用及其成因探索[J]. 地质论评, 2005,51(5):105-112.
|
| [10] |
Xu Q H, Cheng Y R, Mao J W, et al. Application for hydrocarbon in prognosis buried gold deposits and implicaton for genesis[J]. Geological Review, 2005,51(5):105-112.
|
| [11] |
贾国相, 陈远荣, 姚锦其, 著.中国特色景观油气综合化探技术[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002.
|
| [11] |
Jia G X, Chen Y R, Yao J Q. Comprehensive geochemical exploration technology of landscape oil and gas with Chinese characteristics[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002.
|
| [12] |
徐庆鸿, 谢文清, 陈远荣. 福建邱庄金矿综合地球化学异常分带模型与找矿预测标志[J]. 地质与勘探, 2005,41(1):56-61.
|
| [12] |
Xu Q H, Xie W Q, Chen Y R. Comprehensive geochemical anomaly zoning model and prospecting prediction criteria of Qiuzhuang gold deposit, Fujian Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2005,41(1):56-61.
|
| [13] |
中国地球化学研究所. 有机地球化学论文集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986.
|
| [13] |
China Institute of Geochemistry. Papers on organic geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1986.
|
| [14] |
谢桃园, 陈远荣, 张璟, 等. 烃气测量法在黑龙江乌拉嘎金矿区找矿预测评价中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2010,46(3):506-514.
|
| [14] |
Xie T Y, Cheng Y R, Zhang J, et al. Application of hydrocarbon measurement to evaluation and prediction of mineralization in the Wulaga gold deposit of Heilongjiang province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2010,46(3):506-514.
|
| [15] |
段炼, 陈远荣, 段海东, 等. 烃气测量法在黄土覆盖区找矿中探索研究[J]. 矿产与地质, 2016,30(2):234-239.
|
| [15] |
Duan L, Chen Y R, Duan H D, et al. Research on hydrocarbon method in the prospecting of the loess covered area[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2016,30(2):234-239.
|
| [16] |
张苗苗, 陈远荣. 烃气测量法在陕西略阳煎茶岭金矿床及其外围地区的应用[D]. 桂林:桂林工学院, 2009.
|
| [16] |
Zhang M M, Chen Y R. Application of hydrocarbon gas measurement in Jianchaling gold deposit and its peripheral area,Lueyang, Shaanxi Province[D]. Guilin:Guilin University of Technology, 2009.
|
| [17] |
李惠, 禹斌, 李德亮, 等. 构造叠加晕找盲矿法及研究方法[J]. 地质与勘探, 2013,49(1):154-161.
|
| [17] |
Li H, Yu B, Li D L, et al. Prediction of blind ore bodies using structural superimposed halo and research methods[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2013,49(1):154-161.
|
| [18] |
李惠, 张国义, 王支农, 等. 构造叠加晕法在预测金矿区深部盲矿中的应用效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2003,27(6):438-440.

|
| [18] |
Li H, Zhang G Y, Wang Z N, et al. The effect of applying structural superimposed halos to the prognosis of deep blind orebodies in the gold ore district[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2003,27(6):438-440.

|
| [19] |
李惠. 石英脉和蚀变岩型金矿床地球化学异常模式[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991.
|
| [19] |
Li H. Geochemical anomaly patterns of quartz veins and altered rock gold deposits[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1991.
|
| [20] |
李惠, 张国义, 禹斌. 金矿区深部盲矿预测的构造叠加晕模型及找矿效果[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006.
|
| [20] |
Li H, Zhang G Y, Yu B. Structural superposition halo model and prospecting effect of blind ore prediction in deep gold area [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing Press, 2006.
|
| [21] |
彭南海. 湖南沅陵沃溪金—锑—钨矿床地质地球化学特征及成因研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学, 2017.
|
| [21] |
Peng N H. Study on geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of Woxi Au-Sb-Wdeposit Yuanling, Hunan province[D]. Changsha:Central South University, 2017.
|
| [22] |
中国人民武装警察部队黄金指挥部. 湖南省沃溪式金矿地质[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1996.
|
| [22] |
Gold Headquarters of the Armed Police of the Chinese People's Armed Police Force. Geology of Woxi-Type stratabound gold deposit, Hunan Province[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1996.
|
| [23] |
罗献林. 论湖南前寒武系金矿床的形成时代[J]. 桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1989,9(1):25-34.
|
| [23] |
Luo X L. On the epoch of the formation of precambrian gold deposits in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Guilin College of Geology, 1989,9(1):25-34.
|
| [24] |
黎盛斯. 湖南金矿地质概论[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1991.
|
| [24] |
Li S S. Introductionof Hunan gold deposits[M]. Changsha: Journal of Central South University, 1991.
|
| [25] |
孟宪伟, 窦明晓, 余先川. 地球化学场分解的理论与方法[J]. 地球科学进展, 1994,6(6):59-64.
|
| [25] |
Meng X W, Dou M X, Yu X C. The theories and methods on the dispersion of geochemical field[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1994,6(6):59-64.
|
| [26] |
戚长谋. 元素地球化学分类探讨[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 1997,21(4):361-365.
|
| [26] |
Qi C M. A discussion for geochemical classification of elements[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Science, 1997,21(4):361-365.
|
| [27] |
王秀璋. 中国改造型金矿床地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1992.
|
| [27] |
Wang X Z. Geochemistry of reformed gold deposits in China [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1992.
|
| [28] |
中国科学院黄金科技领导小组. 中国金矿地质地球化学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993.
|
| [28] |
Gold Technology Leading Group of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Geological and geochemical study of gold deposits in China [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993.
|
| [29] |
吴锡生. 化探数据处理方法[M]. 北京: 冶金出版社, 2008.
|
| [29] |
Wu X S. Data processing method of geochemical exploration[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Publishing House, 2008.
|
| [30] |
吴二, 陈远荣. 基于烃汞综合气体测量技术的金矿深部找矿预测[D]. 桂林:桂林工学院, 2014.
|
| [30] |
Wu E, Chen Y R. The gas measurement technology of hydrocarbon mercury to forecast deep hidden gold deposits[D]. Guilin:Guilin University of Technology, 2014.
|
| [31] |
吴二, 陈远荣, 刘巍, 等. 烃气测量法在辽宁白云金矿找矿潜力评价中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2014,38(2):248-254.

|
| [31] |
Wu E, Chen Y Y, Liu W, et al. The application of hydrocarbon determination method to the prospecting potential evaluationof the Baiyun gold deposit in Liaoning[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014,38(2):248-254.

|
| [32] |
陈远荣, 戴塔根, 庄晓蕊, 等. 烃汞气体组分垂向运移的主要控制因素[J]. 中国地质, 2001,28(8):28-32.
|
| [32] |
Chen Y R, Dai T G, Zhuang X R, et al. Main controlling factors for vertical migration of hydrocarbon comp onents such as hydrocar-bons and mercury[J]. Chinese Geology, 2001,28(8):28-32.
|
| [1] |
ZHENG Xu-Ying, XU Ke-Wei, GU Lei, WANG Guo-Jian, LI Guang-Zhi, GUO Jia-Qi, ZOU Yu, BORJIGIN Tenger. Distribution of microorganisms in the typical geothermal field environment and its significance for geothermal exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1127-1136. |
| [2] |
YUAN Yu-Ting, LIU Xue-Min, WANG Xue-Qiu, TAN Qin-Ping. Sulfur-lead isotopes based tracing of the metal element anomalies identified in the total metal measurement of surface fine-grained soils: A case study of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type concealed gold deposit[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1083-1097. |
|
|
|
|

