|
|
|
| A test study of 2D joint inversion of marine CSEM and MT based on unstructured triangular grid |
AI Zheng-Min1,2( ), YE Yi-Xin1,2, TANG Wen-Wu1,2, CHEN Xiao1,2, DU Jia-Ming1,2 ), YE Yi-Xin1,2, TANG Wen-Wu1,2, CHEN Xiao1,2, DU Jia-Ming1,2 |
1. Fundamental Science on Radioactive Geology and Exploration Technology Laboratory, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
2. School of Geophysics and Measurement and Control Technology, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In this paper, an unstructured triangular grid combined with a fast Occam algorithm is used to carry out a two-dimensional joint inversion study of marine controlled source electromagnetic (CSEM) and magnetotelluric (MT) data. The unstructured triangular grid can accurately simulate undulating terrain and complex geological structures. Fine meshing is used for the inversion target area, and the other area is divided by coarse meshing, which reduces unnecessary calculations under the premise of meeting accuracy. For the purpose of realizing the joint inversion, the CSEM and MT data are assembled to the same inversion data set, and the relevant weight factors of the CSEM and MT data are constructed from the joint inversion data weight formula, which controls the fitting weights of different data. Finally, inversion calculations are performed on different models, and the results show that the joint inversion has a higher degree of recovery of seafloor structures and anomalous bodies than a single inversion, which verifies the reliability of the joint inversion algorithm.
|
|
Received: 29 July 2020
Published: 01 March 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
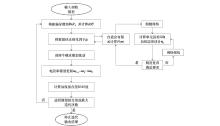
|
Schematic diagram of the joint inversion process
|
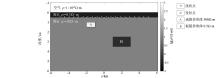
|
Two-dimensional model with flat seafloor
|
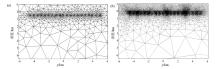
|
Schematic diagram of adaptive forward meshing (taking CSEM mesh as an example)
a—the first optimized mesh containing 1 445 nodes and 2 849 triangular elements; b—the final mesh after the 12th adaptive refinement, containing 43 127 nodes and 86 139 triangular elements; the diagram only shows the abnormal area in the middle part of the model
|
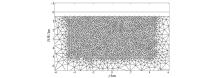
|
Inversion mesh division of the initial model
|
|
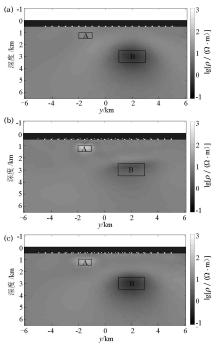
Inversion results of the simple two-dimensional model
a—MT data inversion result; b—CSEM data inversion result; c—CSEM+MT data joint inversion result
|
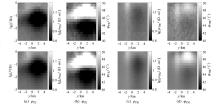
|
Comparison of pseudo-section diagrams of MT observation data (top) and MT forward responses of joint inversion model (bottom)
|
|
Amplitude and phase fitting diagram of the CSEM observation data and model response of the joint inversion result with the emission source at y=0
|

| 方法 | 数据个数 | 耗时/min | 拟合差RMS | 粗糙度 | 迭代次数 | | MT | 1280 | 157.7 | 2.7435 | 9.4157 | 20 | | CSEM | 1226 | 368.5 | 1.0099 | 13.76 | 15 | | CSEM+MT | 2506 | 1247.3 | 2.8047 | 13.02 | 21 |
|
List of time-consuming, RMS misfit, roughness and iteration number of inversion
|
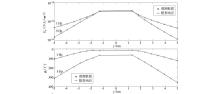
|
Joint inversion results with different q value
a—q=2;b—q=0.5;c—q=10;d—q=0.1
|
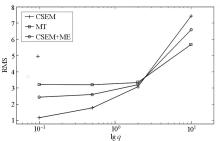
|
The final RMS value of joint inversion with different q value
|
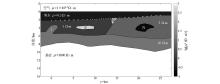
|
Two-dimensional complex ocean model
|
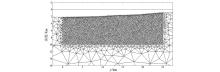
|
Inversion mesh division of the initial model
|
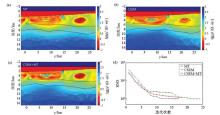
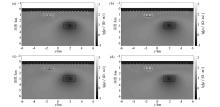
|
Inversion result
a—MT data inversion result; b—CSEM data inversion result; c—CSEM+MT data joint inversion result; d—RMS diagram
|
| [1] |
Constable S, Srnka L J. An introduction to marine controlled-source electromagnetic methods for hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Geophysics, 2007,72(2):3-12.
|
| [2] |
Constable S. Ten years of marine CSEM for hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Geophysics, 2010,75(5):67-81.
|
| [3] |
汪海峰, 邓明, 陈凯. 海底电磁接收机新进展[J]. 物探与化探, 2016,40(4):809-815.

|
| [3] |
Wang H F, Deng M, Chen K. New progress of submarine electromagnetic receivers[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016,40(4):809-815.

|
| [4] |
陈凯, 景建恩, 赵庆献, 等. 海底可控源电磁接收机及其水合物勘查应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017,60(11):4262-4272.
|
| [4] |
Chen K, Jing J E, Zhao Q X, et al. Submarine controllable source electromagnetic receiver and its application in hydrate exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017,60(11):4262-4272.
|
| [5] |
Key K, Weiss C. Adaptive finite-element modeling using unstructured grids: The 2D magnetotelluric example[J]. Geophysics, 2006,71(6):G291-G299.

|
| [6] |
Li Y G, Key K. 2D marine controlled-source electromagnetic modeling:Part 1—An adaptive finite-element algorithm[J]. Geophysics, 2007,72(2):WA51-WA62.
|
| [7] |
Key K, Ovall J S. A parallel goal-oriented adaptive finite element method for 2.5-D electromagnetic modelling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2011,186(1):137-154.

|
| [8] |
韩波, 胡祥云, 黄一凡, 等. 基于并行化直接解法的频率域可控源电磁三维正演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015,58(8):2812-2826.
|
| [8] |
Han B, Hu X Y, Huang Y F, et al. 3D frequency domain CSEM modeling using a parallel direct solver[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015,58(8):2812-2826.
|
| [9] |
韩骑, 胡祥云, 程正璞, 等. 自适应非结构有限元MT二维起伏地形正反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015,58(12):4675-4684.
|
| [9] |
Han Q, Hu X Y, Chen Z P, et al. A study of two dimensional MT inversion with steep topography using the adaptive unstructured finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015,58(12):4675-4684.
|
| [10] |
叶益信, 李予国, 刘颖, 等. 基于局部加密非结构网格的海洋可控源电磁法三维有限元正演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016,59(12):4747-4758.
|
| [10] |
Ye Y X, Li Y G, Liu Y, et al. 3D finite element modeling of marine controlled source electromagnetic fields using locally refined unstructured meshes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016,59(12):4747-4758.
|
| [11] |
陈晓, 于鹏, 张罗磊, 等. 大地电磁与地震正则化同步联合反演[J]. 地震地质, 2010,32(3):402-408.

|
| [11] |
Chen X, Yu P, Zhang L L, et al. Synchronous joint inversion of magnetotelluric and seismic regularization[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2010,32(3):402-408.

|
| [12] |
陈晓, 于鹏, 邓居智, 等. 基于宽范围岩石物性约束的大地电磁和地震联合反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016,59(12):4690-4700.
|
| [12] |
Chen X, Yu P, Deng J Z, et al. Joint inversion of magnetotelluric and seismic based on wide range of rock property constraints[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016,59(12):4690-4700.
|
| [13] |
Commer M, Newman G A. Three-dimensional controlled-source electromagnetic and magnetotelluric joint inversion[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2009,178(3):1305-1316.

|
| [14] |
Sasaki Y. 3D inversion of marine CSEM and MT data: An approach to shallow-water problem[J]. Geophysics, 2013,78(1):59-65.
|
| [15] |
Blatter D, Key K, Ray A, et al. Bayesian joint inversion of controlled source electromagnetic and magnetotelluric data to image freshwater aquifer offshore New Jersey[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2019,218(3):1822-1837.

|
| [16] |
Constable S C, Parker R L, Constable C G. Occam’s inversion-a practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data[J]. Geophysics, 1987,52(3):289-300.

|
| [17] |
Key K. MARE2DEM: A 2-D inversion code for controlled-source electromagnetic and magnetotelluric data[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2016,207(1):571-588.

|
| [18] |
徐世浙. 地球物理中的有限单元法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994: 159-170.
|
| [18] |
Xu S Z. The finite element method in geophysics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994: 159-170.
|
| [19] |
Franke A, Borner R, Spitzer K, et al. Adaptive unstructured grid finite element simulation of two-dimensional magnetotelluric fields for arbitrary surface and seafloor topography[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2007,171(1):71-86.

|
| [20] |
Bank R E, Xu J C. Asymptotically exact a posteriori error estimators, Part Ⅱ: General unstructured grids[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2003,41:2313-2332.

|
| [21] |
Ovall J S. Asymptotically exact functional error estimators based on superconvergent gradient recovery[J]. Numerical Mathematics, 2006,102:543-558.

|
| [22] |
Wiik T, Hokstad K, Ursin B, et al. Joint contrast source inversion of marine magnetotelluric and controlled-source electromagnetic data[J]. Geophysics, 2013,78(6):315-327.
|
| [23] |
Bennington N L, Zhang H, Thurber C H, et al. Joint inversion of seismic and magnetotelluric data in the Parkfield Region of California using the normalized cross-gradient constraint[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2015,172(5):1033-1052.

|
| [24] |
熊彬, 罗天涯, 蔡红柱, 等. 起伏地形大地电磁二维反演[J]. 物探与化探, 2016,40(3):587-593.

|
| [24] |
Xiong B, Luo T Y, Cai H Z, et al. Two-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion of undulating terrain[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016,40(3):587-593.

|
| [25] |
Shewchuk J R. Triangle: Engineering a 2D quality mesh generator and Delaunay triangulator[C]// Workshop on Applied Computational Geometry. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1996: 203-222.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Bao-Feng, WANG Qi-Nian, GUO Xin, GUAN Da-Wei, CHEN Tong-Gang, FANG Wen. Gravity survey and audio magnetotellurics-based insights into the deep structures and geothermal resource potential of the Rucheng Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1147-1156. |
| [2] |
XUE Dong-Xu, LIU Cheng, GUO Fa, WANG Jun, XU Duo-Xun, YANG Sheng-Fei, ZHANG Pei. Predicting the geothermal resources of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, based on soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1169-1178. |
|
|
|
|

