|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of uranium-rich granites in Lincang area |
TIAN Jian-Min1( ), XU Zheng-Qi1,2( ), XU Zheng-Qi1,2( ), YIN Ming-Hui1, LI Tao1, SUN Kang3 ), YIN Ming-Hui1, LI Tao1, SUN Kang3 |
1.College of Geoscience, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China
2.Sichuan Key Laboratory of Geoscience and Nuclear Technology, Chengdu 610059, China
3.Mechanical Design Sixth Design and Research Institute Co., Ltd., Zhengzhou 450000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Petrographic and geochemical study and U-Pb dating of uranium-rich granite bodies in Lincang area were carried out for Shuangjiang 701 and Fengqing 901 uranium mines, with the purpose of exploring the relationship between petrogenesis type, diagenetic tectonic background and uranium mineralization. The results show that Lincang uranium-rich granite body has high Si (up to 90.11%, averaging 71.6%), rich alkali, high potassium and high Ca, thus belonging to high Al and high potassium calcium alkaline series rocks. U-Pb zircon dating yielded 214±12 Ma, and thus Lincang uranium-rich granite body was formed in Late Indochina. Rare earth elements show a slightly rightward "V" shape, with obvious fractionation of light and heavy rare earth elements (w(LREE)/w(HREE) 7.26 on average), obvious negative Eu anomaly (δEu=0.28 ~ 0.49), relative enrichment of Rb, U and Th, and relative loss of Ba, Nb, Sr, Ti and Eu. Comprehensive analysis shows that Lincang uranium-rich granite belongs to S-type granite with obvious differentiation, which must have originated from melting of upper crust material and was formed in a mountain-building and rift environment in late collision, belonging to the simultaneous collision of granite related to the Lancang River collision zone. Its high content of uranium provided part of the uranium source for the uranium mineralization process. Uranium elements were transported to the vicinity of the fault fracture zone and was enriched to form granite-type uranium deposits by leaching.
|
|
Received: 27 November 2019
Published: 26 October 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
XU Zheng-Qi
E-mail: 1067239658@qq.com;547510779@qq.com
|
|
|
|
21])
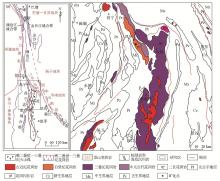
a—structure location map;b—geological sketch of the study area
">
|
Geological map of Sanjiang area(revised according to reference [21])
a—structure location map;b—geological sketch of the study area
|

|
Petrological characteristics of Lincang granite
a—porphyritic biotitemonzonite granite, containing multiple quartz veins; b—irregularly dark inclusions in medium-fine-grained granite; c—self-formed pentagonal quartz crystals in motley granite; d—self-shaped quartz particles, hematite is seriously mineralized; e—potassium feldspar is surrounded by quartz, and polycrystalline twin crystals develop; f—potassium feldspar card-type twin crystal, part of the potassium feldspar is kaolinized, plagioclase sericite;e and f are cross-polarized images;Q—quartz; Kf—potassium feldspar; Pl—plagioclase; Bi—biotite
|

| 编号 | 含量/10-6 | w(Th)/
w(U) | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 208Pb/232Th | 238U/232Th | 年龄(Ma)±1σ | | Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | | YN057-01 | 49.9 | 444.3 | 1427.1 | 0.31 | 0.052 | 0.265 | 0.036 | 0.010 | 2.606 | 305.6±64.8 | 238.5±6.3 | 228.7±2.5 | | YN057-03 | 34.2 | 322.2 | 877.4 | 0.37 | 0.050 | 0.262 | 0.038 | 0.012 | 2.279 | 198.2±78.7 | 236.3±7.6 | 237.9±3.0 | | YN057-04 | 47.5 | 506.3 | 1136 | 0.45 | 0.053 | 0.266 | 0.036 | 0.013 | 1.863 | 322.3±77.8 | 239.9±7.0 | 230.8±2.4 | | YN057-05 | 55.3 | 483.3 | 1532.9 | 0.32 | 0.050 | 0.246 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 2.623 | 194.5±66.7 | 223.7±5.6 | 224.5±2.1 | | YN057-07 | 31.1 | 306.2 | 802.9 | 0.38 | 0.051 | 0.255 | 0.036 | 0.012 | 2.160 | 235.3±90.7 | 230.6±7.7 | 229.5±2.6 | | YN057-08 | 31.4 | 375.5 | 807.4 | 0.47 | 0.051 | 0.246 | 0.035 | 0.011 | 1.779 | 239±72.2 | 223.4±8.6 | 220.9±2.7 | | YN057-09 | 19.4 | 179.4 | 465.2 | 0.39 | 0.058 | 0.290 | 0.036 | 0.014 | 2.145 | 527.8±102.8 | 258.4±9.8 | 230±3.1 | | YN057-10 | 33.4 | 492.7 | 768.1 | 0.64 | 0.050 | 0.236 | 0.034 | 0.012 | 1.291 | 190.8±92.6 | 215±7.4 | 216.2±2.3 | | YN057-11 | 35.5 | 448.1 | 893.9 | 0.5 | 0.050 | 0.237 | 0.035 | 0.011 | 1.652 | 189±77.8 | 215.8±6.1 | 218.7±2.4 | | YN057-12 | 47.3 | 507.9 | 1266.8 | 0.4 | 0.050 | 0.245 | 0.035 | 0.011 | 2.081 | 213±41.7 | 222.8±6.1 | 222.9±2.2 | | YN057-13 | 15.9 | 212.7 | 368.4 | 0.58 | 0.053 | 0.270 | 0.037 | 0.011 | 1.435 | 320.4±110.2 | 242.7±9.7 | 234.9±3.3 | | YN057-14 | 16.3 | 160.8 | 436.9 | 0.37 | 0.052 | 0.248 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 2.273 | 333.4±98.1 | 224.6±8.5 | 219.6±2.7 | | YN057-15 | 57.4 | 817.9 | 1280.4 | 0.64 | 0.053 | 0.266 | 0.036 | 0.012 | 1.317 | 309.3±68.5 | 239.6±6.7 | 230.4±2.3 | | YN057-16 | 40 | 351.5 | 1108 | 0.32 | 0.053 | 0.262 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 2.652 | 344.5±66.7 | 236.1±6.3 | 224.8±2.4 | | YN057-17 | 31.3 | 236.2 | 879.2 | 0.27 | 0.055 | 0.280 | 0.037 | 0.013 | 3.006 | 420.4±78.7 | 250.4±8.0 | 232.5±2.6 | | YN057-18 | 24.8 | 254 | 681.9 | 0.37 | 0.049 | 0.235 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 2.247 | 200.1±95.4 | 214.5±7.4 | 220.5±2.6 | | YN057-19 | 32.9 | 479.3 | 789.7 | 0.61 | 0.052 | 0.246 | 0.034 | 0.012 | 1.378 | 298.2±81.5 | 223.3±7.0 | 215.7±2.6 | | YN057-20 | 36.9 | 401 | 1031.8 | 0.39 | 0.052 | 0.247 | 0.034 | 0.011 | 2.158 | 272.3±70.4 | 223.8±6.1 | 218.3±2.3 | | YN057-21 | 34.6 | 344.9 | 957.2 | 0.36 | 0.051 | 0.250 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 2.358 | 261.2±90.7 | 226.8±7.2 | 222.9±2.7 | | YN057-22 | 24.9 | 269.8 | 652.5 | 0.41 | 0.050 | 0.246 | 0.036 | 0.012 | 2.014 | 211.2±88.9 | 223.6±7.3 | 226.8±2.9 | | YN057-23 | 21.8 | 230.9 | 570.9 | 0.4 | 0.051 | 0.246 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 2.056 | 220.4±100 | 223±8.5 | 223.9±3.0 | | YN057-24 | 33.9 | 337.2 | 890.8 | 0.38 | 0.053 | 0.260 | 0.036 | 0.013 | 2.199 | 324.1±72.2 | 235±6.3 | 226.6±2.8 | | YN057-25 | 36.4 | 415.7 | 954.1 | 0.44 | 0.053 | 0.260 | 0.036 | 0.011 | 1.909 | 320.4±68.5 | 235±6.0 | 226.1±2.5 | | YN057-26 | 56.4 | 392.1 | 1686.9 | 0.23 | 0.055 | 0.265 | 0.035 | 0.013 | 3.575 | 413±68.5 | 238.7±6.1 | 221.7±3.1 |
|
Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating results of Lincang rich uranium granite
|

|
Fengqing YN057 granite zircon CL image
|
|
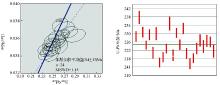
YN057 zircon U-Pb age concord map
|

| 指标 | 双江样品 | 凤庆样品 | 中国
花岗岩[24] | 世界
花岗岩[25] | | YN027 | YN028 | YN029 | YN030 | YN031 | YN050 | YN051 | YN052 | YN053 | YN054 | YN055 | YN056 | YN057 | | SiO2 | 69.9 | 70.41 | 71.61 | 72.34 | 70.53 | 74.75 | 83 | 79.32 | 90.11 | 72.45 | 42.69 | 61.77 | 72.49 | 71.99 | 71.3 | | Al2O3 | 14.24 | 12.94 | 14.86 | 14.32 | 12.34 | 6.27 | 7.6 | 7.31 | 4.39 | 13.72 | 1.19 | 8.01 | 14.41 | 13.86 | 14.32 | | Fe2O3 | 1.77 | 4.08 | 1.59 | 1.47 | 3.41 | 4.79 | 3.72 | 2.73 | 1.99 | 2.12 | 14.97 | 5.1 | 1.9 | 1.37 | 1.21 | | MgO | 1.14 | 0.82 | 0.73 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.28 | 0.56 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.71 | | CaO | 1.63 | 0.62 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 1.18 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.3 | 0.52 | 0.69 | 0.12 | 0.05 | | Na2O | 1.11 | 0.15 | 2.92 | 3.15 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.8 | 7.3 | 2.25 | 2.76 | 3.81 | 4.07 | | K2O | 5.13 | 4.21 | 4.57 | 4.75 | 4.7 | 2.42 | 2.4 | 3.14 | 1.43 | 6 | 0.16 | 3.23 | 4.92 | 3.42 | 3.66 | | MnO | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.004 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 1.55 | 1.84 | | TiO2 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.2 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.31 | | P2O5 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.3 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.2 | 0.12 | | FeO | 0.89 | 0.58 | 0.92 | 1.29 | 0.56 | 0.66 | 2.62 | 0.47 | 0.59 | 0.7 | 0.65 | 0.68 | 1.44 | 1.7 | 1.64 | | 烧失量 | 4.55 | 5.73 | 2.77 | 2.41 | 5.6 | 5.04 | 2.39 | 2.42 | 1.23 | 3.19 | 6.68 | 4.77 | 1.69 | | | | Total | 100.86 | 100 | 100.88 | 101.29 | 99.97 | 94.52 | 102.6 | 95.99 | 100.11 | 100.16 | 74.62 | 87.66 | 101.43 | | | | A/NK | 2.28 | 2.97 | 1.98 | 1.81 | 2.31 | 2.48 | 3.02 | 2.25 | 2.93 | 2.02 | 0.16 | 1.46 | 1.88 | | | | A/CNK | 1.81 | 2.6 | 1.87 | 1.7 | 1.89 | 2.41 | 2.94 | 2.2 | 2.84 | 1.93 | 0.15 | 1.33 | 1.72 | | | | Na2O+K2O | 6.24 | 4.36 | 7.49 | 7.9 | 5.34 | 2.53 | 2.51 | 3.26 | 1.5 | 6.8 | 7.46 | 5.48 | 7.68 | | |
|
Analysis results of main elements of rich uranium granite in Lincang area %
|
|
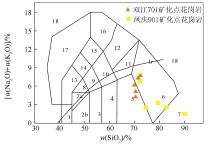
Alkali-silicon (TAS) classification map of magma(igneous rock) system
Ir—Irvine dividing line is alkaline at the top and sub-alkaline at the bottom. 1—peridot gabbro; 2a—alkaline gabbro; 2b—subalkaline gabbro; 3—gabbro diorite; 4—diorite; 5—granodiorite; 6—granite; 7—siliconite; 8—bellmanite; 9—dellmanite; 10—dellmanite; 11—quartzite diorite; 12—synorite; 13—parsonite gabbro; 14—para-feldspar diorite; 15—para-feldspar syenite; 16—para-syenite syenite; 17—para-long diorite; 18—neonite,phosphorite,coarse white garnet
|
|
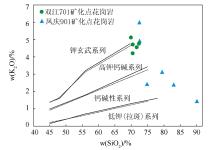
SiO2-K2O discrimination diagram
|
|
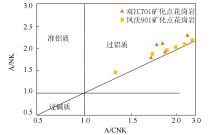
A/NK-A/CNK discrimination diagram of aluminum-quasi-aluminum granite
|
|
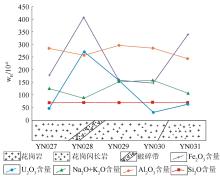
Element content and sampling position
|

| 元素 | 双江样品 | 凤庆样品 | | YN027 | YN028 | YN029 | YN030 | YN031 | YN050 | YN051 | YN052 | YN053 | YN054 | YN055 | YN056 | YN057 | | La | 25.40 | 16.20 | 28.20 | 22.60 | 28.70 | 13.60 | 11.70 | 14.80 | 11.50 | 29.80 | 2.37 | 20.70 | 49.50 | | Ce | 56.90 | 34.80 | 57.10 | 41.70 | 62.40 | 27.60 | 23.20 | 29.00 | 17.40 | 63.40 | 2.66 | 37.90 | 81.50 | | Pr | 7.67 | 4.48 | 6.87 | 5.14 | 7.73 | 3.37 | 3.13 | 3.40 | 2.72 | 6.87 | 0.47 | 4.90 | 10.70 | | Nd | 25.80 | 17.70 | 28.00 | 20.90 | 27.30 | 12.30 | 11.20 | 13.00 | 9.96 | 26.30 | 2.17 | 18.70 | 38.80 | | Sm | 6.26 | 5.64 | 7.12 | 4.27 | 9.28 | 2.53 | 2.49 | 2.54 | 1.87 | 6.09 | 0.70 | 3.85 | 7.87 | | Eu | 0.75 | 0.88 | 1.06 | 0.53 | 1.60 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 0.39 | 0.70 | | Gd | 4.51 | 5.59 | 5.97 | 3.64 | 11.40 | 1.81 | 1.89 | 1.84 | 1.62 | 4.59 | 0.89 | 3.32 | 6.60 | | Tb | 0.81 | 1.31 | 1.19 | 0.53 | 2.78 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.82 | 0.20 | 0.52 | 1.18 | | Dy | 4.11 | 7.92 | 6.34 | 2.76 | 17.60 | 1.27 | 1.48 | 1.54 | 1.29 | 3.66 | 1.04 | 2.87 | 6.05 | | Ho | 0.74 | 1.60 | 1.11 | 0.52 | 3.97 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.69 | 0.22 | 0.51 | 1.16 | | Er | 2.02 | 3.72 | 2.92 | 1.43 | 10.00 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.72 | 1.88 | 0.58 | 1.39 | 3.21 | | Tm | 0.32 | 0.59 | 0.46 | 0.23 | 1.36 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.54 | | Yb | 1.91 | 3.02 | 2.29 | 1.40 | 6.57 | 0.96 | 1.05 | 0.97 | 0.81 | 2.15 | 0.75 | 1.54 | 3.59 | | Lu | 0.26 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.45 | | Be | 6.40 | 8.21 | 6.79 | 6.14 | 6.05 | 2.06 | 3.60 | 2.08 | 1.59 | 5.26 | 2.49 | 5.76 | 6.52 | | Sc | 6.70 | 6.34 | 6.52 | 5.32 | 4.47 | 2.99 | 2.90 | 3.28 | 1.66 | 4.83 | 0.41 | 2.83 | 5.82 | | V | 45.80 | 28.20 | 32.10 | 22.50 | 38.80 | 15.20 | 21.80 | 11.60 | 6.98 | 20.70 | 58.30 | 383.00 | 25.10 | | Cr | 15.90 | 11.60 | 12.40 | 10.60 | 10.60 | 3.30 | 3.40 | 3.61 | 2.35 | 6.66 | 9.64 | 8.47 | 9.24 | | Co | 8.57 | 18.60 | 9.80 | 3.34 | 2.49 | 1.09 | 0.56 | 0.43 | 0.35 | 2.05 | 16.40 | 19.30 | 2.94 | | Ni | 5.63 | 10.90 | 6.63 | 5.58 | 2.02 | 0.94 | 1.41 | 1.26 | 0.88 | 4.07 | 2.18 | 2.89 | 3.55 | | Cu | 21.00 | 22.00 | 23.70 | 17.40 | 17.70 | 100.00 | 50.30 | 196.00 | 62.20 | 48.40 | 727.00 | 703.00 | 3.76 | | Zn | 12.90 | 29.80 | 29.60 | 22.60 | 23.40 | 288.00 | 764.00 | 290.00 | 146.00 | 2407.00 | 59322.00 | 33929.00 | 140.00 | | Ga | 21.40 | 21.00 | 23.80 | 19.00 | 18.20 | 13.00 | 11.50 | 9.77 | 5.94 | 19.00 | 31.00 | 25.70 | 19.20 | | Rb | 289.00 | 294.00 | 306.00 | 271.00 | 268.00 | 217.00 | 212.00 | 211.00 | 124.00 | 403.00 | 13.90 | 226.00 | 313.00 | | Sr | 48.80 | 58.70 | 61.30 | 72.90 | 64.90 | 6.91 | 10.60 | 5.09 | 2.32 | 28.40 | 7.09 | 17.50 | 60.20 | | Y | 20.00 | 52.90 | 33.70 | 14.60 | 145.00 | 9.17 | 8.50 | 9.17 | 9.01 | 20.50 | 7.98 | 16.70 | 32.20 | | Mo | 2.04 | 1.59 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 1.58 | 0.75 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 52.40 | 1.15 | 0.17 | | Cd | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.50 | 4.29 | 1.27 | 1.17 | 4.04 | 251.00 | 114.00 | 0.76 | | In | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 1.66 | 0.80 | 0.03 | | Sb | 2.08 | 11.60 | 3.54 | 0.76 | 13.30 | 47.50 | 5.63 | 46.90 | 31.30 | 0.65 | 250.00 | 46.40 | 0.30 | | Cs | 23.60 | 70.80 | 28.50 | 19.70 | 48.90 | 12.70 | 8.17 | 5.07 | 3.11 | 11.70 | 1.34 | 13.80 | 15.40 | | Ba | 496.00 | 191.00 | 379.00 | 328.00 | 445.00 | 117.00 | 178.00 | 152.00 | 61.30 | 487.00 | 11.40 | 211.00 | 456.00 | | Tl | 2.08 | 10.10 | 1.91 | 1.53 | 15.90 | 1.63 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 0.69 | 2.65 | 0.50 | 1.58 | 1.92 | | Pb | 37.50 | 333.00 | 126.00 | 49.70 | 620.00 | 9446.00 | 551.00 | 10751.00 | 955.00 | 2219.00 | 28776.00 | 19703.00 | 89.00 | | Bi | 1.06 | 2.34 | 0.52 | 0.57 | 1.60 | 15.90 | 0.68 | 2.82 | 5.28 | 2.07 | 29.60 | 23.50 | 0.75 | | Th | 23.40 | 18.70 | 22.80 | 19.30 | 9.97 | 3.98 | 9.54 | 9.07 | 7.36 | 33.00 | 0.63 | 18.60 | 36.20 | | U | 45.90 | 268.00 | 158.00 | 30.20 | 64.00 | 7.65 | 3.49 | 11.60 | 3.38 | 10.90 | 1751.00 | 1179.00 | 8.26 | | Nb | 13.50 | 11.40 | 13.50 | 11.20 | 9.81 | 4.93 | 3.89 | 6.21 | 3.24 | 11.40 | 0.26 | 6.34 | 12.40 | | Ta | 2.64 | 2.16 | 2.42 | 2.31 | 1.85 | 1.13 | 1.05 | 1.45 | 0.84 | 2.98 | 0.06 | 1.58 | 2.64 | | Zr | 97.50 | 103.00 | 118.00 | 102.00 | 110.00 | 21.70 | 15.20 | 21.50 | 14.80 | 26.90 | 1.15 | 25.30 | 60.20 | | Hf | 3.72 | 3.51 | 4.04 | 3.44 | 3.25 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 0.79 | 0.63 | 1.03 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 2.32 |
|
Analysis results of trace and rare earth elements in Lincang rich uranium granite 10-6
|
27])
">
|
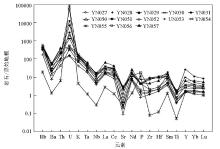
Trace element original mantle standardized spider map(the standardized value is quoted from Sun and McDonough[27])
|
27])
">
|
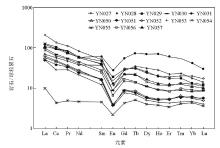
Rare earth element chondrite standardization pattern(the standardized value is quoted from Sun and McDonough[27])
|

|
Discrimination diagram of genetic types of uranium-enriched granites
a—TiO2-Zr discrimination diagram;b—granite ACF diagram
|
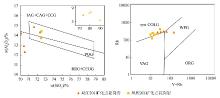
|
Distinguishing diagram of the main and trace element structure environment of granite
IAG—island arc granite; CAG—continental arc granite; CCG—continent collision granite; POG—post-orogenic granite; RRG—rift-related granite; CEUG—continental tectonic uplift and granite; syn-COLG—co-crash granite; VAG—volcanic arc granite; WPG—in-plate granite; ORG—ocean ridge granite
|
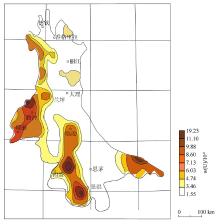
|
Uranium geochemical anomaly map of the Yunnan section of the Sanjiang (revised according to reference [24])
|
| [1] |
杜乐天, 王玉明. 华南花岗岩型、火山岩型、碳硅泥岩型、砂岩型铀矿成矿机理的统一性[J]. 放射性地质, 1984(3):1-10.
|
| [1] |
Du L T, Wang Y M. The unity of metallogenic mechanism of granite type, volcanic type, carbosilicate mudstone type and sandstone type uranium deposits in South China[J]. Radiogeology, 1984(3):1-10.
|
| [2] |
王联魁. 华南花岗岩铀矿中硅化带—绿泥石化带—碱长交代体三位一体的演化模式[J]. 岩石学报, 1986,1(2):1-14.
|
| [2] |
Wang L K. The Trinity evolution model of silicified zone, Chloritized zone and alkali feldspar metasomatic body in granite uranium deposits of South China[J]. Actapetrologica Sinica, 1986,1(2):1-14.
|
| [3] |
倪师军, 胡瑞忠, 金景福. 寻找隐伏铀矿床的一种可能的地球化学模式[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通讯, 1996(1):6-9.
|
| [3] |
Ni S J, Hu R Z, Jin J F. Looking for a possible geochemical model for hidden uranium deposits[J]. Mineral Petroleum and Geochemical Communications, 1996(1):6-9.
|
| [4] |
Dahlkamp F J. Uranium deposits of the world[M]. Berlin:Springer, 2009.
|
| [5] |
胡国成. 华南花岗岩型铀矿成因探究[J]. 中山大学研究生学刊:自然科学·医学版, 2011,32(2):9-16.
|
| [5] |
Hu G C. Genesis of granite type uranium deposits in South China[J]. Graduate Journal of Sun Yatsen University:Natural Science, Medical Edition, 2011,32(2):9-16.
|
| [6] |
赵春江, 周四春, 刘晓辉, 等. 隐伏花岗岩铀矿上方的X荧光异常特征及其找矿意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2012,36(6):1055-1058.
|
| [6] |
Zhao C J, Zhou S C, Liu X H, et al. The characteristics of X-ray fluorescence anomalies above concealed granite uranium deposits and their prospecting significance[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012,36(6):1055-1058.
|
| [7] |
牟平, 潘家永, 钟福军, 等. 诸广—下庄铀矿集区产铀与非产铀花岗岩地球化学特征及成因对比研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2015,35(S1):325-326.
|
| [7] |
Mou P, Pan J Y, Zhong F J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and Genesis comparison of uranium producing and non uranium producing granites in Zhuguang-Xiazhuang uranium ore concentration area[J]. Actamineralogica Sinica, 2015,35(S1):325-326.
|
| [8] |
周航兵, 潘家永, 钟福军, 等. 粤北长江铀矿田细粒黑云母花岗岩的成因及其与铀成矿关系[J]. 矿物岩石, 2018,38(1):10-19.
|
| [8] |
Zhou H B, Pan J Y, Zhong F J, et al. Genesis of fine-grained biotite granite and its relationship with uranium mineralization in the Yangtze River uranium ore field in northern Guangdong[J]. Mineral Rocks, 2018,38(1):10-19.
|
| [9] |
徐争启, 宋昊, 尹明辉, 等. 华南地区新元古代花岗岩铀成矿机制——以摩天岭花岗岩为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2019,35(9):2695-2710.
|
| [9] |
Xu Z Q, Song H, Yin M H, et al. Uranium mineralization mechanism of Neoproterozoic granites in South China: A case study of Motianling granites[J]. Actapetrologica Sinica, 2019,35(9):2695-2710.
|
| [10] |
钟大赉, 等. 滇川西部古特提斯造山带[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 176-177.
|
| [10] |
Zhong D Z, et al. Guttis qrogenic belt in western Yunnan and Sichuan [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998: 176-177.
|
| [11] |
李文昌, 潘桂棠, 侯增谦, 等. 西南“三江”多岛弧盆—碰撞造山成矿理论与勘查技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010.
|
| [11] |
Li W C, Pan G T, Hou Z Q, et al. Metallogenic theory and exploration technology of “Three Rivers” multi island arc basin collision orogeny in Southwest China [M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 2010.
|
| [12] |
Wang B D, Wang L Q, Pan G T, et al. U-Pb zircon dating of Early Paleozoic gabbro from the Nantingheophiolite in the Changning-Menglian suture zone and its geological implication[J]. China Science Bulletin, 2013,58(8):920-930.

|
| [13] |
邓军, 王庆飞, 李龚健. 复合造山和复合成矿系统:三江特提斯例析[J]. 岩石学报, 2016,32(8):2225-2247.
|
| [13] |
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J. Composite orogeny and composite metallogenic system: A case study of Sanjiang Tethys[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016,32(8):2225-2247.
|
| [14] |
彭头平, 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 等. 澜沧江南段早中生代酸性火成岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及构造意义[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2006,36(2):123-132.
|
| [14] |
Peng T P, Wang Y J, Fan W M, et al. Shrimp zircon U-Pb dating and tectonic significance of early Mesozoic acid igneous rocks in the South Lancang section[J]. Chinese Science:Series D, 2006,36(2):123-132.
|
| [15] |
刘德利, 刘继顺, 张彩华, 等. 滇西南澜沧江结合带北段云县花岗岩的地质特征及形成环境[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2008,27(1):23-31.
|
| [15] |
Liu D L, Liu J S, Zhang C H, et al. Geological characteristics and forming environment of Yunxian granite in the northern segment of Lancangjiang junction zone in the south of Western Yunnan[J]. Journal of Rock Mineralogy, 2008,27(1):23-31.
|
| [16] |
孔会磊, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 等. 滇西三江地区临沧花岗岩的岩石成因:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2012,28(5):1438-1452.

|
| [16] |
Kong H L, Dong G C, Mo X X, et al. Petrogenesis of Lincang granite in Sanjiang area, western Yunnan: geochemistry, zircon UPB chronology and Hf isotope constraints[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012,28(5):1438-1452.

|
| [17] |
廖世勇, 尹福光, 王冬兵, 等. 滇西“三江”地区临沧花岗岩基中三叠世碱长花岗岩的发现及其意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014,33(1):1-12.
|
| [17] |
Liao S Y, Yin F G, Wang D B, et al. Discovery and significance of Triassic alkali feldspar granite in Lincang granitic batholith in Sanjiang area, western Yunnan[J]. Journal of Rock Mineralogy, 2014,33(1):1-12.
|
| [18] |
晏中海. 云南省临沧地区花岗岩型铀矿成矿条件分析[C]// 中国核学会2017年学术年会论文集(二), 2017: 616-621.
|
| [18] |
Yan Z H. Analysis of metallogenic conditions of granite-type uranium deposits in Lincang area, Yunnan Province[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 Annual Conference of Chinese Nuclear Society (2), 2017: 616-621.
|
| [19] |
Peng T P, Wilde S A, Wang Y J, et al. Mid-Triassic felsic igneous rocks fromthe southern Lancangjiang Zone, SW China: Petrogenesis and implicationsfor the evolution of Paleo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 2013, 168-169(2):15-32.
|
| [20] |
冯明月, 何德宝. 华南富铀花岗岩和产铀花岗岩特征[J]. 铀矿地质, 2012,28(4):199-207.
|
| [20] |
Feng M Y, He D B. Characteristics of uranium-rich granites and uranium-producing granites in South China[J]. Geology of Uranium Ore, 2012,28(4):199-207.
|
| [21] |
孙康. 云南临沧印支—燕山期花岗岩地球化学特征及铀成矿条件分析[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2018.
|
| [21] |
Sun K. Geochemical characteristics of Indosinian-Yanshan period granite in Lincang, Yunnan, and uranium mineralization conditions[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology, 2018.
|
| [22] |
路远发. GeoKit: 一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包地球化学[J]. 地球化学, 2004,33(5):459-464.
|
| [22] |
Lu Y F. GeoKit: A geochemical tool package built with VBA for geochemistry[J]. Geochimica, 2004,33(5):459-464.
|
| [23] |
王舫, 刘福来, 刘平华, 等. 澜沧江南段临沧花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014,30(10):3034-3050.
|
| [23] |
Wang F, Liu F L, Liu P H, et al. Zircon U-Pb age and tectonic significance of Lincang granite in South Lancang Section[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014,30(10):3034-3050.
|
| [24] |
谢学锦. 西南地区76种元素地球化学(第1版)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008.
|
| [24] |
Xie X J. Geochemistry of 76 elements in Southwest China(1st edition)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2008.
|
| [25] |
Li T. Elements abundance of China’s continental crust and its sedimentary layer and upper continental crust[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 1995,14(1):26-32.

|
| [26] |
徐争启, 倪师军, 张成江, 等. 桂北摩天岭地区花岗岩体特征与铀成矿作用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.
|
| [26] |
Xu Z Q, Ni S J, Zhang C J, et al. Characteristics of granite bodies and uranium mineralization in the Motianling area of northern Guangxi [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014.
|
| [27] |
Sun S S, McDonough W S. Chemical and isotopic systematics ofoceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]. New York: Oxford Univ Press, 1989.
|
| [28] |
杨振德. 一条巨型花岗岩推覆体[J]. 云南地质, 1995,14(2):99-108.
|
| [28] |
Yang Z D. A giant granite nappe[J]. Yunnan Geology, 1995,14(2):99-108.
|
| [29] |
杨振德. 云南临沧花岗岩的冲断叠瓦构造与推覆构造[J]. 地质科学, 1996,31(2):130-139.
|
| [29] |
Yang Z D. Thrust imbrication structure and nappe structure of Lincang granite, Yunnan[J]. Geological Science, 1996,31(2):130-139.
|
| [30] |
李兴林. 临沧复式花岗岩基的基本特征及形成构造环境的研究[J]. 云南地质, 1996,15(1):1-18.
|
| [30] |
Li X L. Study on the basic characteristics and tectonic environment of Lincang composite granitic batholith[J]. Yunnan Geology, 1996,15(1):1-18.
|
| [31] |
Sone M S, Metcalfe I. Parallel Tethyan sutures in mainland Southeast Asia: New insights for Palaeo-Tethys closure and implications for the Indosinian orogeny[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2008,340(2-3):166-179.
|
| [32] |
Chappell B W, White A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 1992,83:1-26.
|
| [33] |
Clemens J D, Stevens G, Farina F. The enigmatic sources of I-typegranites: The peritecticconnexion[J]. Lithos, 2011,126(3):174-181.
|
| [34] |
Chappell B W, Bryant C J, Wyborn D. Peraluminous I-type granites[J]. Lithos, 2012,153(8):142-153.

|
| [35] |
Rudnick R L, Fountain D M. Nature and composition of the continental crust: a lower crustal perspective[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995,33:267-309.
|
| [36] |
沈上越, 冯庆来, 刘本培. 三江地区南澜沧江带火山岩构造岩浆类型[J]. 矿物岩石, 2002,22(3):66-71.
|
| [36] |
Shen S Y, Feng Q L, Liu B P. Types of tectonic magma of volcanic rocks in the Nanlancang River belt of Sanjiang area[J]. Mineral Rock, 2002,22(3):66-71.
|
| [37] |
俞赛赢, 李昆琼, 施玉萍, 等. 临沧花岗岩基中段花岗闪长岩类研究[J]. 云南地质, 2003,22(4):426-442.
|
| [37] |
Yu S Y, Li K Q, Shi Y P, et al. Study on granodiorite in the middle segment of Lincang granite base[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2003,22(4):426-442.
|
| [38] |
莫宣学, 沈上越, 朱勤文. 三江中南段火山岩蛇绿岩与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998.
|
| [38] |
Mo X X, Shen S Y, Zhu Q W. Volcanic ophiolites and metallogenesis in the middle and south of Sanjiang [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1998.
|
| [39] |
刘英俊, 曹励明. 元素地球化学导论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987.
|
| [39] |
Liu Y J, Cao L M. Introduction to elemental geochemistry [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987.
|
| [40] |
肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002.
|
| [40] |
Xiao Q H, Deng J F, Ma D Q, et al. Thinking and methods of granite research [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002.
|
| [1] |
WANG Zhi-Qiang, YANG Jian-Feng, WEI Li-Xin, SHI Tian-Chi, CAO Yuan-Yuan. Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium in alkaline soil in Shizuishan area, Ningxia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 229-237. |
| [2] |
XU Yun-Feng, HAO Xue-Feng, QIN Yu-Long, WANG Xian-Feng, XIONG Chang-Li, LI Ming-Ze, WU Weng-Hui, ZHAN Han-Yu. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in Chahe area of Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 624-638. |
|
|
|
|

