|
|
|
| The result analysis of the comparison between SAG-2M and KSS31M marine gravimeters |
Fei-Fei ZHANG1,2,3,4,5( ), Jian-Wei SUN1,2, Bo HAN1,2, Run-Lin DU1,2, Wan-Yin WANG3,4,5( ), Jian-Wei SUN1,2, Bo HAN1,2, Run-Lin DU1,2, Wan-Yin WANG3,4,5( ) ) |
1. The Key Laboratory of Gas Hydrate,Ministry of Natural Resources,Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology,Qingdao 266071,China
2. Laboratory for Marine Mineral Resources,Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology,Qingdao 266071,China
3. Insititute of Gravity and Magnetic Technology,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710054,China
4. College of Geology Engineering and Geomatics,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710054,China
5. Key Laboratory of Western China’s Mineral Resources and Geological Engineering,Ministry of Education,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710054,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract A comparison for the marine gravimeters on the same vessel was carried out between SAG-2M marine gravimeter developed by China and KSS31M marine gravimeter designed by Germany in order to test the technical performance and data reliability of SAG-2M marine gravimeter. The raw gravity data acquired from these two marine gravimeters were preprocessed according to the standards of marine geologic survey to obtain the free air gravity anomalies, and the comparison and relativity for those two types of gravity data were studied by analyzing the cross-point differences, survey lines and grid data. The result shows that the SAG-2M marine gravimeters have the same level of measurement accuracy with the KSS31M marine gravimeter because there is a highly linear relationship between the data from two marine gravimeters with an approximately similar variation trend. Based on the results of comparison, it is concluded that the self-developed SAG-2M marine gravimeter shares the similar standard of measurement accuracy with the KSS31M marine gravimeter with a stabilized technical performance, which provides an important reference for the future application of SAG-2M marine gravimeter.
|
|
Received: 18 February 2020
Published: 28 August 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Wan-Yin WANG
E-mail: ffeizhang@126.com;wwy7902@chd.edu.cn
|
|
|
|

|
The main frame of SAG-2 Mmarine gravimeter
|

| 技术参数 | SAG-2M | KSS31M | | 测量范围/(10-5 m·s-2) | ±20000 | ±10000 | | 横摇 | 全姿态 | ±40° | | 纵摇 | 全姿态 | ±40° | | 静态精度/(10-5 m·s-2) | 0.02 | 0.02 | | 动态精度/(10-5 m·s-2) | 1 | 0.5~2 | | 主机尺寸、重量 | 29 cm×26 cm×28 cm、18 kg | 68 cm×53 cm×53 cm、72 kg |
|
The comparison of technical parameters between SAG-2M marine gravimeter and KSS31M marine gravimeter
|

|
KSS31 Mmarine gravimeter
|
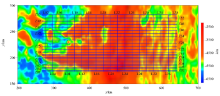
|
Distribution map of survey lines (residual topographic map)
|

| 仪器名称 | KSS31M(联络线) | SAG-2M(联络线) | | mad | rms | std | mad | rms | std | | KSS31M(主测线) | 0.6033 | 0.8163 | 0.8172 | 0.5038 | 0.6576 | 0.6582 | | SAG-2M(主测线) | 0.5094 | 0.6760 | 0.6767 | 0.4905 | 0.6506 | 0.6513 |
|
The crossover error between two gravimeters10-5 m/s2
|
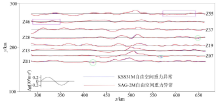
|
The free air gravity anomaly profile map of parts of survey lines
|
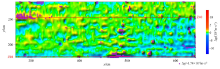
|
The distribution map of grid data deviation
|

| 测线名 | rab | mad/(10-5 m·s-2) | rms/(10-5 m·s-2) | std/(10-5 m·s-2) | | Z01 | 0.9969465 | 1.028 | 1.28 | 0.76 | | Z07 | 0.9980488 | 0.49 | 0.84 | 0.68 | | Z13 | 0.9966732 | 0.76 | 0.98 | 0.62 | | Z19 | 0.9960449 | 0.59 | 0.78 | 0.51 | | Z28 | 0.9938768 | 0.81 | 1.10 | 0.74 | | Z37 | 0.9972808 | 0.65 | 0.82 | 0.49 | | Z46 | 0.9957206 | 0.63 | 0.81 | 0.52 | | Z55 | 0.9949318 | 0.73 | 1.01 | 0.70 | | 平均值 | 0.711 | 0.9525 | 0.6275 |
|
The deviation of the same survey line between two gravimeters
|

| rab | mad/(10-5 m·s-2) | rms/(10-5 m·s-2) | std/(10-5 m·s-2) | | 0.9945 | 0.59 | 0.83 | 0.58 |
|
The grid data deviation between two gravimeters
|
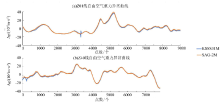
|
Contrast diagram of free air gravity anomaly with larger data deviation
|
| [1] |
黄谟涛, 翟国君, 管铮, 等. 海洋重力场测定及其应用[M]. 北京: 测绘出版社, 2005.
|
| [1] |
Huang M T, Zhai G J, Guan Z, et al. Determination and application of marine gravity field[M]. Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Press, 2005.
|
| [2] |
张训华, 赵铁虎, 等. 海洋地质调查技术[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2017.
|
| [2] |
Zhang X H, Zhao T H, et al. Survey technologies of marine geology[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2017.
|
| [3] |
李建成, 陈俊勇, 宁津生, 等. 地球重力场逼近理论与中国2000似大地水准面的确定[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2003.
|
| [3] |
Li J C, Chen J Y, Ning J S, et al. Theory of the Earth’s gravity field approximation and determination of China Quasi-geoid 2000[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 2003.
|
| [4] |
黄谟涛, 翟国君, 欧阳永忠, 等. 海洋磁场重力场信息军事应用研究现状与展望[J]. 海洋测绘, 2011,31(1):71-76.
|
| [4] |
Huang M T, Zhai G J, Ouyang Y Z, et al. Prospects and development in the military applications of marine gravity and magnetic information[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2011,31(1):71-76.
|
| [5] |
刘敏, 黄谟涛, 欧阳永忠, 等. 海空重力测量及应用技术研究进展与展望(一):目的意义与技术体系[J]. 海洋测绘, 2017,37(2):1-5.
|
| [5] |
Liu M, Huang M T, Ouyang Y Z, et al. Development and prospect of air-sea gravity survey and its applications, part Ⅰ: Objective, significance and technical system[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2017,37(2):1-5.
|
| [6] |
耿启立. 重力仪国外代表产品及国内研发最新进展[J]. 地质装备, 2016,17(1):27-30.
|
| [6] |
Geng Q L. Representative products of gravity instruments abroad and the latest development of domestic R&D[J]. Geological Equipment, 2016,17(1):27-30.
|
| [7] |
修睿, 郭刚, 薛正兵, 等. 海空重力仪的技术现状及新应用[J]. 导航与控制, 2019,18(1):35-43.
|
| [7] |
Xiu R, Guo G, Xue Z B, et al. Technical current situation and new application of marine/aviation gravimeter[J]. Navigation and Control, 2019,18(1):35-43.
|
| [8] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检疫总局. GB/T 12763.8—2007海洋调查规范第8部分:海洋地质地球物理调查.[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007.
|
| [8] |
General Administration of Quality Supervision and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 12763.8—2007 Specifications for oceanographic survry-part 8:Marine geolopy and geophysics survey.[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2007.
|
| [9] |
国家海洋局908专项办公室. 地球物理调查技术规程[S]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005.
|
| [9] |
Special Project Office of National Bureau of Oceanography. Specifications for geophysics survey[S]. Beijing: Oceanographic Press, 2005.
|
| [10] |
刘敏, 黄谟涛, 欧阳永忠, 等. 海空重力测量及应用技术研究进展与展望(三):数据处理与精度评估技术[J]. 海洋测绘, 2017,37(4):1-10.
|
| [10] |
Liu M, Huang M T, Ouyang Y Z, et al. Development and prospect of air-sea gravity survey and its applications, part Ⅲ: Data processing and precision evaluation[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2017,37(4):1-10.
|
| [11] |
黄谟涛, 刘敏, 吴太旗, 等. 海空重力测量关键技术指标体系论证与评估[J]. 测绘学报, 2018,47(11):1537-1548.
|
| [11] |
Huang M T, Liu M, Wu T Q, et al. Research and evaluation on key technological target system for marine and airborne gravity surveys[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Gartographica Sinica, 2018,47(11):1537-1548.
|
| [12] |
欧阳永忠, 邓凯亮, 陆秀平, 等. 多型航空重力仪同机测试及其数据分析[J]. 海洋测绘, 2013,33(4):6-11.
|
| [12] |
Ouyang Y Z, Deng K L, Lu X P, et al. Tests of Multi-type airborne gravimeters and data analysis[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2013,33(4):6-11.
|
| [13] |
张向宇, 徐行, 廖开训, 等. 多型号海洋重力仪的海上比测结果分析[J]. 海洋测绘, 2015,35(5):71-74,78.
|
| [13] |
Zhang X Y, Xu X, Liao K X, et al. Result analysis for different types of gravimeters in sea trials[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2015,35(5):71-74,78.
|
| [14] |
张振波, 赵俊峰, 付永涛, 等. GT-1M海洋重力仪与KSS31M海洋重力仪的对比[J]. 海洋科学, 2015,39(5):85-91.
|
| [14] |
Zhang Z B, Zhao J F, Fu Y T, et al. The Comparison between GT-2M and KSS31M marine gravitymeters[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015,39(5):85-91.
|
| [15] |
Kovrizhnykh P, Shagirov B, Geoken , et al. Marine gravity survey at the Caspian with GT-2M, Chekan AM and L&R gravimeters: comparison of accuracy[R]. Russia: Moscow State University, 2011.
|
| [16] |
Bodensee Gravitymeter Geosystem GMBH. 《Instruction manual for marine gravity meter system KSS 31M》[M], 2004.
|
| [17] |
顾兆峰, 张志珣, 杨慧良, 等. KSS31M海洋重力仪静态观测结果及分析[J]. 海洋测绘, 2005,25(2):66-68.
|
| [17] |
Gu Z F, Zhang Z X, Yang H L, et al. The static measurement result of KSS31M marine gravimeter and its analysis[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2005,25(2):66-68.
|
| [18] |
付永涛, 王先超, 谢天峰. KSS31M型海洋重力仪动态性能的分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2007,31(6):29-33.
|
| [18] |
Fu Y T, Wang X C, Xie T F. Verifying the dynamic properties of KSS31M marine gravity-meter by the observed gravity reading and GPS data[J]. Marine Sciences, 2007,31(6):29-33.
|
| [19] |
付永涛, 王先超, 谢天峰. KSS31M型海洋重力仪在海边静态观测的结果[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007,22(1):308-311.
|
| [19] |
Fu Y T, Wang X C, Xie T F. The static measurement of KSS31M marine gravity-meter at coast[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007,22(1):308-311.
|
| [20] |
欧阳永忠. 海空重力测量数据处理关键技术研究[D]. 武汉:武汉大学, 2013.
|
| [20] |
Ouyang Y Z. On key technologies of data processing for air-sea gravity surveys[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2013.
|
| [21] |
魏子卿. 2000中国大地坐标系[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2008,28(6):1-5.
|
| [21] |
Wei Z Q. China geodetic coordinate system 2000[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2008,28(6):1-5.
|
| [22] |
《数学手册》编写组. 数学手册[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1979.
|
| [22] |
Writing Group of 《Mathematical Directory》. Mathematical directory[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1979.
|
| [23] |
於宗俦, 鲁林成. 测量平差基础[M]. 北京: 测绘出版社, 1983.
|
| [23] |
Yu Z C, Lu L C. Foundation of measurement adjustment[M]. Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Press, 1983.
|
| [1] |
CHEN Xiu-Juan, LIU Zhi-Di, LIU Yu-Xi, CHAI Hui-Qiang, WANG Yong. Research into the pore structure of tight reservoirs:A review[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 22-31. |
| [2] |
XIAO Guan-Hua, ZHANG Wei, CHEN Heng-Chun, ZHUO Wu, WANG Yan-Jun, REN Li-Ying. Application of shallow seismic reflection surveys in the exploration of urban underground space in Jinan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 96-103. |
|
|
|
|

