|
|
|
| Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of Liujiang River Catchment |
Xiao-Yu ZHONG1, Tian-Sheng WU1, Jie LI1( ), Guo-Dong ZHEN1, Xiao-Xiong ZHUO1, Dong-Chao GUAN2, Lei WANG3, Bing-Ji MO4 ), Guo-Dong ZHEN1, Xiao-Xiong ZHUO1, Dong-Chao GUAN2, Lei WANG3, Bing-Ji MO4 |
1. Guangxi Geological Survey,Nanning 530023,China
2. Guangxi Geological and Mineral Testing Research Center,Nanning 530023,China
3. Geology Team No.4 of Guangxi, Nanning 530031, China
4. Institute of Regional Geological Survey of Guangxi,Guilin 541003,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In this study, 91 sediment samples were collected from the middle and lower reaches of Liujiang River. The geochemical characteristics of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, Zn and other elements were analyzed. The current pollution situation and potential risks were predicted and evaluated, and the sources of heavy metals were analyzed. The results show that: The spatial dispersion of elements in the sediments of Liujiang River Catchment is relatively large, and the distribution of heavy metal elements shows strong regional characteristics.Distribution of heavy metal elements in Liujiang River Catchment shows strong regional characteristics.As, Cr, Cu, Hg and Ni are mainly from natural sources, while Cd and Pb are mainly from human sources. The high-value areas of Cd natural source contribution mainly distribute in Longjiang River Catchment, while the high-value areas of industrial and mining sources contribution mainly distribute around Jincheng River and Liuzhou District of Liujiang River.
|
|
Received: 11 April 2019
Published: 03 March 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Jie LI
E-mail: 187292565@qq.com
|
|
|
|
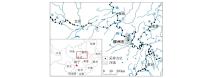
|
The location of Liujiang Rriver and the distribution of sampling points
|

| 污染程度 | 无 | 轻度 | 偏中度 | 中度 | 偏重度 | 重度 | 严重 | | Igeo | ≤0 | 0~1 | 1~2 | 2~3 | 3~4 | 4~5 | >5 | | 级别 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|
The relation between the Igeo and excessed standard of heavy metal
|

| 元素 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 背景值/10-6 | 24.17 | 459 | 106 | 30.9 | 203.8 | 45.65 | 33 | 117 |
|
Reference value of heavy metals in middle part of Guangxi surface soil
|

| 单因子潜在风险系数 | 单因子风险等级 | 潜在生态危害指数RI | 多因子风险等级 | | <40 | 低 | <150 | 低 | | 40~80 | 中 | 150~300 | 中 | | 80~160 | 较高 | 300~600 | 较高 | 160~320
≥320 | 高
极高 | >600
>600 | 极高
极高 |
|
Pollution grade for the single heavymetal and potential ecological risk index
|

| 参数 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | Mn | P | S | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | Corg | | 最小值 | 2.2 | 0.06 | 23.4 | 6.6 | 0.016 | 8.5 | 6.3 | 19.1 | 75.4 | 154 | 92 | 3.55 | 1.45 | 0.07 | 0.15 | | 平均值 | 17.6 | 1.04 | 53.7 | 21.6 | 0.12 | 22.5 | 32.7 | 112 | 688 | 422 | 262 | 9.79 | 3.77 | 0.58 | 0.68 | | 最大值 | 45.8 | 6.86 | 89.1 | 52 | 0.474 | 38.9 | 169 | 503 | 1275 | 2173 | 2129 | 17.1 | 6.59 | 3.94 | 2.5 | | 变异系数 | 0.49 | 0.91 | 0.26 | 0.39 | 0.61 | 0.34 | 0.8 | 0.69 | 0.42 | 0.5 | 0.83 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.97 | 0.63 |
|
Contents of heavy metals in sediments of Liujiang Rriver Catchment
|
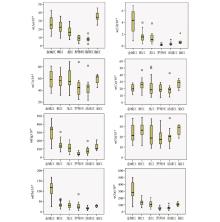
|
Comparison of heavy metal elements contents in different reaches
|

| 河段 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 融江 | -0.06 | -0.02 | -1.45 | -0.83 | -1.32 | -1.40 | -0.81 | -0.73 | | 柳江 | -0.77 | 1.05 | -1.51 | -0.93 | -1.14 | -1.42 | -0.62 | -0.45 | | 金城江 | -0.51 | 2.33 | -1.48 | -1.24 | -0.16 | -1.65 | 1.04 | 0.68 | | 龙江 | -1.20 | 0.69 | -1.48 | -1.25 | -1.60 | -1.83 | -0.78 | -0.81 | | 洛清江 | -2.28 | -1.01 | -1.87 | -1.35 | -2.02 | -1.84 | -1.58 | -1.70 | | 罗秀河 | -2.23 | -2.00 | -1.86 | -1.38 | -2.96 | -1.95 | -1.00 | -1.92 |
|
Igeo index of heavy metals in sediments of Liujiang Rriver Catchment
|

| 河段 | | RI | | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 金城江 | 11.23 | 266.33 | 1.12 | 3.31 | 58.15 | 2.58 | 16.95 | 2.70 | 362.37 | | 柳江 | 9.31 | 102.90 | 1.07 | 4.10 | 28.83 | 2.89 | 5.15 | 1.16 | 155.41 | | 龙江 | 7.02 | 87.52 | 1.12 | 3.71 | 22.51 | 2.35 | 4.87 | 0.97 | 130.07 | | 罗秀河 | 3.63 | 13.88 | 0.89 | 3.17 | 8.83 | 2.13 | 4.87 | 0.45 | 37.84 | | 洛清江 | 3.39 | 26.49 | 0.86 | 3.21 | 17.12 | 2.25 | 2.72 | 0.51 | 56.56 | | 融江 | 14.69 | 53.26 | 1.11 | 4.35 | 25.38 | 2.91 | 4.36 | 0.93 | 106.99 | | 平均 | 8.46 | 100.89 | 1.05 | 3.79 | 28.17 | 2.63 | 6.18 | 1.17 | 152.34 |
|
Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of Liujiang Rriver Catchment
|

| 公因子 | 方差贡献 | 元素 | 因子 | 元素 | 因子 | | 特征值 | 贡献率 | 累积贡献率% | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | | 1 | 8.942 | 55.885 | 55.885 | As | 0.64 | 0.57 | -0.16 | Zn | 0.30 | 0.92 | 0.14 | | 2 | 3.293 | 20.584 | 76.469 | Cd | 0.17 | 0.94 | 0.02 | P | 0.46 | 0.01 | 0.58 | | 3 | 1.168 | 7.301 | 83.769 | Cr | 0.84 | 0.31 | 0.31 | S | -0.08 | 0.61 | 0.67 | | 4 | 0.703 | 4.394 | 88.163 | Cu | 0.90 | 0.07 | 0.26 | Mn | 0.86 | 0.19 | -0.12 | | 5 | 0.574 | 3.585 | 91.748 | Hg | 0.25 | 0.90 | 0.13 | Al2O3 | 0.94 | 0.05 | 0.14 | | 6 | 0.337 | 2.107 | 93.855 | F | 0.25 | 0.90 | 0.13 | Fe2O3 | 0.90 | 0.27 | 0.26 | | 7 | 0.268 | 1.677 | 95.533 | Ni | 0.92 | 0.21 | 0.21 | CaO | 0.02 | 0.70 | 0.11 | | 8 | 0.243 | 1.519 | 97.052 | Pb | 0.14 | 0.86 | 0.32 | Corg | 0.46 | 0.38 | 0.74 |
|
Results of PCA of heavy metal concentrations in sediments of Liujiang Rriver Catchment
|

| 元素来源 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 自然源 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.68 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.36 | 0.45 | | 人为源 | 工矿业 | 0.14 | 0.44 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.52 | 0.33 | | 农业 | -0.14 | -0.09 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.07 | | 不确定源 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.17 | | 0.15 | | R2 | 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.95 |
|
Source contribution ratios of heavy metal
|
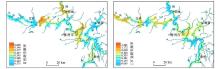
|
The contribution maps of major sources to Cd
|
| [1] |
刘伟, 陈振楼, 许世远 , 等. 上海市小城镇河流沉积物重金属污染特征研究[J]. 环境科学, 2006,27(3):538-543.
|
| [1] |
Liu W, Chen Z L, Xu S Y , et al. Pollution character of heavy metals in river sediments from small towns,Shanghai[J]. Environmental Science, 2006,27(3):538-543.
|
| [2] |
Suresh G, Sutharsan P, Ramasamy V , et al. Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments,India[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2012,84:117-124.
|
| [3] |
张伟, 张洪, 单保庆 . 北运河源头区沙河水库沉积物重金属污染特征研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012,33(12):4284-4290.
|
| [3] |
Zhang W, Zhang H, Shan B Q . Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in the sediments from Shahe reservoir,the upper reach of the north canal river[J]. Environmental Science, 2012,33(12):4284.
|
| [4] |
王瑞霖, 程先, 孙然好 . 海河流域中南部河流沉积物的重金属生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2014,1(10):3740-3747.
|
| [4] |
Wang R L, Cheng X, Sun R H . Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in the southern and central Haihe river[J]. Environmental Science, 2014,1(10):3740-3747.
|
| [5] |
杨昆, 贺磊, 许乃中 , 等. 柳江流域生态系统服务价值的影响研究[J]. 生态科学, 2016,35(4), 148-156.
|
| [5] |
Yang K, He L, Xu N Z , et al. The study of ecosystem service values of Liujiang River Basin[J]. Ecological Science, 2016,35(4), 148-156.
|
| [6] |
Müller G . Index of geoaccumulation in sdiments of the Rhine River[J]. Geojournal, 1969,2:108-118.
|
| [7] |
滕彦国, 庹先国, 倪师军 , 等. 应用地质累积指数评价沉积物中重金属污染:选择地球化学背景的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2002,25(2):7-9.
|
| [7] |
Teng Y G, Tuo X G, Shijun Ni , et al. Applying geo-accumulation index to assess heavy metal pollution in sediment:influence of different geochemical backgrounds[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002,25(2):7-9.
|
| [8] |
Santos B J C, Beltran R, Gomez A J L . Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel River(southwest Spain)[J]. Environment International, 2003(129):69-77.
|
| [9] |
Larks H L . An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control:A sedi-mentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980,14(2):975-1001.
|
| [10] |
Weeks J M, Combr S D W . Ecological risk assessment of soil[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2005,69(5):601-613.
|
| [11] |
Thurston G D, Spengler J D , et al. A auantitative assessment of source contribution to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan boston[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1985,19(1):9-25.
|
| [12] |
Song Y, Xie S D, Zhang Y H , et al. Source apportionment of PM2. 5 in Beijing using principal component analysis absolute principal component scores and UNMIX[J]. Science of the Total Environ-ment, 2006,372(1):278-286.
|
| [13] |
Luo X S, Ip C C M, Li W , et al. Spatial-temporal variations, sources, and transport of airborne inhalable metals (PM10) in urban and rural areas of northern China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics Discussions, 2014,14(9):13133-13165.
|
| [14] |
Yuan X, Deng X, Shen Z , et al. Speciation and potential remobilization of heavy metals in sediments of the Taihu Lake, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2007,26(4):384-393.
|
| [15] |
Sofowote U, Marvin C H , et al. Source apportionment of PAH in hamilton harbour suspended sedi-ments: Comparison of two factor analysis methods[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008,42(3):6007-6014.
|
| [16] |
Zhou F, Gprdon H H, Guo H C , et al. Spatio-temporal patterns and source apportionment of coastal water pollution in eastern Hong Kong[J]. Water Research, 2007,41(6):3429-3439.
|
| [17] |
吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋 , 等. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2012,67(7):109-122.
|
| [17] |
Lyu J S, Zhang Z L, Liu Y , et al. Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao city[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2012,67(7):109-122.
|
| [18] |
Stafilov T R, Sajn B, Boev J , et al. Distribution of some elements in surface soil over the Kavadarci region,Republic of Macedonia[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010,61(7):1515-1530.
|
| [19] |
于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 林燕萍 , 等. 泉州城市表层土壤中金属元素来源分析[J]. 矿物学报, 2012,32(1):156-165.
|
| [19] |
Yu R L, HU G R, Lin Y P , et al. Sources of metals in the urban topsoil of Quanzhou city[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinia, 2012,32(1):156-165.
|
| [20] |
陈国潮, 何振立, 黄昌勇 . 菜茶果园红壤微生物量磷与土壤磷以及磷植物有效性之间的关系研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2001,38(1):75-80.
|
| [20] |
Chen G C, He Z L, Huang C Y . Study on relationships among microbial biomass P, soil P and plant-availability of P in red soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2001,38(1):75-80.
|
| [21] |
Joergensen R G, Scheu S . Response of soil microorganisms to the addition of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in a forest Rendzina[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 1999,31:215-219.
|
| [22] |
周彩云, 魏宗强, 颜晓 , 等. 不同施肥处理对水稻土颗粒有机碳与磷的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2016,38(2):398-402.
|
| [22] |
Zhou C Y, Wei Z Q, Yan Xi , et al. Effects of different fertilization regimes on organic carbon and phosphorus status in particulate fractions of paddy soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2016,38(2):398-402.
|
| [23] |
陈丹青, 谢志宜, 张雅静 , 等. 基于PCA/APCS和地统计学的广州市土壤重金属来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016,25(6):1014-1022.
|
| [23] |
Chen D Q, Xie Z Y, Zhang Y J , et al. Source apportionment of soil heavy metals in Guang-zhou based on the PCA/APCS model and geostatistics[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016,25(6):1014-1022.
|
| [24] |
瞿明凯, 李卫东, 张传荣 , 等. 基于受体模型和地统计学相结合的土壤镉污染源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013,33(5):854-860.
|
| [24] |
Qu M K, Li W D, Zhang C R , et al. Source apportionment of soil heavy metal Cd based on the combination of receptor model and geostatistics.[J]. China Environmental Science, 2013,33(5):854-860.
|
| [25] |
刘慧琳, 葛畅, 沈强 , 等. 铁矿废弃地复垦土壤重金属来源解析研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019,38(2):75-82.
|
| [25] |
Liu H L, Ge C, Shen Q , et al. Source apportionment of heavy metals in reclaimed soil of iron mine wasteland[J]. Journal of Agro Environment Science, 2019,38(2):75-82.
|
| [1] |
XIAO Gao-Qiang, XIANG Long-Zhou, DAI Da-Long, GAO Xiao-Hong, ZONG Qing-Xia. Geochemical characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in granitic magmatic soil: A case study of the Jiucheng-Jiemao area in Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1135-1146. |
| [2] |
YU Yong-Peng, YAN Zhao-Tao, MAO Xing-Jun, YANG Yan-Cheng, MA Yong-Xiang, HUANG Peng-Cheng, LU Ai-Guo, ZHANG Guang-Bing. The application of the comprehensive electric and seismic method to coal exploration in the huge Cenozoic coverage area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1231-1238. |
|
|
|
|

