|
|
|
| Contamination situation and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in water and sediments of Dongdagou area, Baiyin |
Zhao-Rong ZHANG1, Xing-Xing DUAN2, Ming-Zhe XIA1( ) ) |
1. School of Earth Science and Resources, Chang’an University, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi
2. Xi’an Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, China Geological Survey, Xi’an 710054, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In order to provide scientific reference for the ecological control of the water and the risk assessment of sediment treatment, the authors analyzed the content level, the distribution characteristics and the content change trend of heavy metals such as Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, As and Hg in water and Cr, Zn, Pb, Cu, Cd and Hg in sediments. The Nemerow Index and the Potential Ecological Risk Index were used to evaluate the accumulation degree and potential risk of heavy metal pollution in water bodies and sediments. The results show that the average content of six heavy metals in water is in the range of 0.005 7~4.796 0 mg/L, and the content exhibits the order of Zn>Cu>Cd>Pb>As>Hg. The content of As in the water body shows an increasing trend with water flow, while the other heavy metals content in water decreases obviously with the water flow. The average content of six heavy metals in the sediments is in the range of (61.6~5 999.3)×10 -6, with the order of Zn>Pb>Cu>Cd>Cr>Hg. The content of heavy metals in the sediments of the river sections has undulating changes, but the overall change trend is that the content of heavy metals in the sediments decreases obviously with flowing water. The main heavy metal pollutants in Dongdagou water are Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd, and the single factor pollution degree is in order of Cd>Pb>Zn>Cu. The Dongdagou water evaluated by the Nemerow Index shows that there are different degrees of polluted water in the river. The contaminations in sediments are heavy metal pollutants Cd, Hg, Pb and Cu, and the degree of ecological risk is in order of Cd>Hg>Pb>Cu>Zn>Cr. The evaluation of the sediments in Dongdagou by using the Potential Ecological Risk Index shows that the total potential ecological risk index of the sediments in the whole section of Dongdagou is serious.
|
|
Received: 14 November 2018
Published: 31 May 2019
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Ming-Zhe XIA
E-mail: zymzxia@chd.edu.cn
|
|
|
|
|
Satellite image map of the reserch and samplings ares
|

| 等级划分 | 内梅罗污染指数 | 污染等级 | | Ⅰ | PN≤0.7 | 清洁(安全) | | Ⅱ | 0.7<PN≤1.0 | 尚清洁(警戒线) | | Ⅲ | 1.0<PN≤2.0 | 轻度污染 | | Ⅳ | 2.0<PN≤3.0 | 中度污染 | | Ⅴ | PN≥3.0 | 重度污染 |
|
Classification of pollution degree
|

| 单因子污染物污染指数 | 潜在生态风险参数 | 潜在生态风险指数RI | | 分级范围 | 等级 | 分级范围 | 等级 | 分级范围 | 等级 | | <1 | 低度 | <40 | 低度 | RI<150 | 低度 | | 1≤<3 | 中度 | 40≤<80 | 中度 | 150≤RI<300 | 中度 | | 3≤<6 | 重度 | 80≤<160 | 较重 | 300≤RI<600 | 重度 | | ≥6 | 严重 | 160≤<320 | 重度 | RI≥600 | 严重 | | | ≥320 | 严重 | | |
|
Classification of potential ecological risk index
|

| 元素 | 最小值
/(mg·L-1) | 最大值
/(mg·L-1) | 平均值
/(mg·L-1) | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 地表水环境质量Ⅳ级标准
/(mg·L-1) | | Cu | 0.005 | 30.63 | 4.796 | 10.55 | 2.20 | 1 | | Pb | 0.0006 | 1.019 | 0.1759 | 0.28 | 1.61 | 0.05 | | Zn | 0.07 | 77.35 | 13.34 | 25.25 | 1.89 | 2 | | Cd | 0.0003 | 0.8633 | 0.2164 | 0.27 | 1.23 | 0.005 | | As | 0.001 | 0.152 | 0.048 | 0.05 | 1.12 | 0.1 | | Hg | 0.00008 | 0.00279 | 0.00057 | 0.0009 | 1.49 | 0.001 |
|
Statistical characteristics of the heavy mental contents in the water samples
|

|
Variations in the concentrations of heavy metals in the water with water flow
|

| 样号 | pH | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cd | As | Hg | 综合污染指数 | | S1 | 4.67 | 25.96 | 2.39 | 30.42 | 117.24 | 0.07 | — | 86.6 | | S2 | 4.19 | 30.63 | 8.60 | 38.68 | 172.66 | 0.03 | — | 127.1 | | S3 | 6.78 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 1.24 | 21.44 | 0.01 | — | 15.5 | | S5 | 7.00 | 0.12 | 5.91 | 3.42 | 43.10 | 0.12 | 0.43 | 31.1 | | S6 | 7.35 | 0.35 | 20.38 | 3.22 | 94.42 | 0.52 | 2.79 | 68.3 | | S12 | 7.59 | 0.02 | 0.99 | 1.23 | 31.06 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 22.3 | | S14 | 7.65 | 0.02 | 0.76 | 0.96 | 24.84 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 17.8 | | S15 | 8.10 | 0.05 | 0.57 | 0.17 | 4.50 | 1.05 | 0.27 | 3.3 | | S16 | 8.09 | 0.08 | 1.14 | 0.19 | 4.11 | 1.25 | 0.58 | 3.0 | | S17 | 7.52 | 0.26 | 1.39 | 0.35 | 5.14 | 0.98 | 0.26 | 3.8 | | S18 | 7.29 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.84 | 1.52 | 0.10 | 1.1 | | S20 | 7.61 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.1 |
|
Water quality evaluation results of Nemerow pollution index
|

| 元素 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 甘肃省土壤背景值[25]/10-6 | | Cr | 43 | 80.1 | 61.6 | 10.6 | 0.2 | 70.2 | | Zn | 425.3 | 13800 | 5999.3 | 4417.7 | 0.7 | 68.5 | | Pb | 60.6 | 15900 | 4819.5 | 5387.4 | 1.1 | 18.8 | | Cu | 39.4 | 8449.8 | 1795.6 | 2282.6 | 1.3 | 24.1 | | Cd | 2.689 | 2908 | 502.816 | 832.31 | 1.7 | 0.116 | | Hg | 0.03 | 476.6 | 65.07 | 129.15 | 2 | 0.02 |
|
Statistical characteristics of the heavy mental contents in the sediments
|
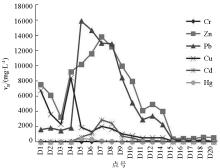
|
Variations in the concentrations of heavy metals in the sediments with water flow
|
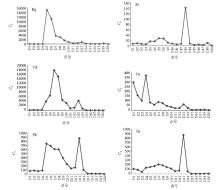
|
Variations of heavy metal enrichment with water flow
|

| 样号 | 采样位置 | Cr | Zn | Pb | Cu | Cd | Hg | RI | | D1 | | 1.7 | 110.2 | 436.9 | 1408.3 | 6452.6 | 27.5 | 8437.2 | | D2 | | 1.4 | 89.9 | 492.8 | 760.4 | 10713.4 | 53.5 | 12111.3 | | D3 | | 1.4 | 47.5 | 398.0 | 486.9 | 5808.6 | 43.0 | 6785.4 | | D4 | | 1.7 | 134.9 | 496.5 | 1753.1 | 9243.1 | 72.0 | 11701.3 | | D5 | | 2.0 | 148.9 | 4228.7 | 399.8 | 167568.1 | 23830.0 | 196177.4 | | D6 | | 2.0 | 169.3 | 3909.6 | 279.2 | 280603.4 | 17490.0 | 302453.6 | | D7 | 上游 | 1.6 | 201.5 | 3457.4 | 421.3 | 752069.0 | 5845.0 | 761995.8 | | D8 | | 1.5 | 182.5 | 3430.9 | 358.9 | 634396.6 | 4833.0 | 643203.3 | | D9 | | 1.8 | 146.0 | 2249.8 | 220.7 | 195284.5 | 2609.0 | 200511.8 | | D10 | | 2.3 | 116.6 | 1379.4 | 170.7 | 140275.9 | 1356.5 | 143301.3 | | D11 | | 1.8 | 60.7 | 783.4 | 107.0 | 40422.4 | 614.0 | 41989.3 | | D12 | | 1.7 | 72.1 | 912.1 | 115.7 | 49991.4 | 741.0 | 51834.0 | | D14 | | 2.3 | 58.8 | 606.3 | 117.1 | 35224.1 | 301.5 | 36310.1 | | D15 | | 1.2 | 6.2 | 67.5 | 20.1 | 2661.2 | 116.5 | 2872.8 | | D16 | | 1.3 | 7.1 | 75.7 | 23.8 | 2298.6 | 105.5 | 2512.0 | | D17 | 下游 | 1.9 | 6.7 | 62.4 | 25.2 | 2556.7 | 97.0 | 2749.9 | | D18 | | 2.1 | 9.3 | 68.3 | 29.3 | 4428.9 | 427.0 | 4964.9 | | D20 | | 2.0 | 8.4 | 16.1 | 8.2 | 695.4 | 1.6 | 731.6 |
|
Potential ecological harm index in sediments
|
| [1] |
贾英, 方明, 吴友军 , 等. 上海河流沉积物重金属的污染特征与潜在生态风险[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013,33(1):147-153.
|
| [1] |
Jia Y, Fang M, Wu Y J , et al. Pollution characteristics and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in river sediments of Shanghai[J]. China Environmental Science, 2013,33(1):147-153
|
| [2] |
于晓霞, 赵学强, 孙滨峰 , 等. 济南市小清河流域表层沉积物中重金属的空间分布、生态风险及源解析[J]. 西南师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2017,42(2):78-84.
|
| [2] |
Yu X X, Zhao X Q, Sun B F , et al. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments from Xiaoqinghe watershed of Jinan[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University, 2017,42(2):78-84.
|
| [3] |
Fu J, Hu X, Tao X C , et al. Risk and toxicity assessments of heavy metals in sediments and fishes from The Yangtze River and Taihu Lake, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2013,93(9):1887-1895.

|
| [4] |
Varol M . Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey)using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011,195(1):355-364.

|
| [5] |
黄淦 . 联用强化混凝与化学沉淀法去除水中重金属离子的研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学, 2008.
|
| [5] |
Huang G . Study on the removal of heavy metal lons in the water by combined intensifying coagulation and chemical precipitating[D]. Changsha:Hunan University, 2008.
|
| [6] |
黄飞, 王泽煌, 蔡昆争 , 等. 大宝山尾矿库区水体重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2016,29(11):1701-1708.
|
| [6] |
Huang F, Wang Z H, Cai K Z , et al. Pollution characteristics and potential ecological risks of heavy metals in water of Tailing zone in dabaoshan mine,Guangdong Province,China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2016,29(11) : 1701-1708.
|
| [7] |
Naicker K, Cukrowska E, Mccarthy T S . Acid mine drainage arising from gold mining activity in Johannesburg, south Africa and Environs[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2003,122(1):29-40.

|
| [8] |
张俊华, 卢翠玲, 刘玉寒 , 等. 开封城郊河道底泥重金属形态垂向分布特征及风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017,36(6):1192-1201.
|
| [8] |
Zhang J H, Lu C L, Liu Y H , et al. Vertical distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in core sediments from Kaifeng suburban rivers[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017,36(6):1192-1201.
|
| [9] |
Hakima Z, Mohamed M, Aziza M , et al. Environmental and ecological risk of heavy metals in the marine sediment from Dakhla bay, Morocco[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017,24(9):7970-7981.

|
| [10] |
李春亮, 刘文辉 . 甘肃省白银市区土壤环境质量评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2012,36(6):1014-1019.
|
| [10] |
Li C L, Liu W H . An assessment of the soil environmental quality in the downtown area of Baiyin city, Gansu Province[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2012,36(6):1014-1019.
|
| [11] |
张素娣, 吴世洋 . 白银东大沟重金属污染现状及综合治理对策[J].世界有色金属, 2013(9):72-73.
|
| [11] |
Zhang S Z, Wu S Y . Current status of heavy metal pollution in Dongdagou, Baiyin and comprehensive countermeasures[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2013(9):72-73.
|
| [12] |
李小虎, 汤中立, 初凤友 . 白银矿山水体和沉积物中重金属及其化学形态分布特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2008,36(3):218-224.
|
| [12] |
Li X H, Tang Z L, Chu F Y . Analysis on speciation and transportation of heavy metals in water and sediment in Baiyin mine[J]. Earth & Environment, 2008,36(3):218-224.
|
| [13] |
张丹, 王鑫羽, 周富强 , 等. 白银市东大沟上游河道重金属污染现状及治理方法[J].现代农业科技, 2013(16):224-224.
|
| [13] |
Zhang D, Wang X Y, Zhou F Q , et al. Status and treatment of heavy metal pollution in the upper reaches of Dongdagou, Baiyin city[J]. Modern Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013(16):224-224.
|
| [14] |
韩冰 . 白银市污水灌溉对农田环境及小麦产量质量的影响研究[J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2000(6):46-47.
|
| [14] |
Han B . Study on the influence of sewage irrigation in Baiyin city on farmland environment and wheat yield and quality[J]. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2000(6):46-47.
|
| [15] |
刘白林 . 甘肃白银东大沟流域农田土壤重金属污染现状及其在土壤—作物—人体系统中的迁移转化规律[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2017.
|
| [15] |
Liu B L . Heavy metal contamination in farmland soils and it transfer in the soil-crop-human system within the Dongdagou watershed, Baiyin, Gansu[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University, 2017.
|
| [16] |
黄河上游白银段东大沟流域重金属污染整治与生态系统修复规划[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2012.
|
| [16] |
Heavy metal pollution remediation and ecosystem restoration planning in the Dongdagou watershed of the upper section of the Yellow River [M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2012.
|
| [17] |
SL187-96 水质采样技术规程[S].
|
| [17] |
SL187-96 Technical regulation of water quality sampling[S].
|
| [18] |
GB5084-92 农田灌溉水质标准[S].
|
| [18] |
GB5084-92 Standards for irrigation water quality[S].
|
| [19] |
于国强, 李占斌, 张霞 , 等. 土壤水盐动态的BP神经网络模型及灰色关联分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009,25(11):74-79.
|
| [19] |
Yu G Q, Li Z B, Zhang X , et al. Dynamic simulation of soil water-salt using BP neural net-work model and grey correlation analysis[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2009,25(11):74-79.
|
| [20] |
阎伍玖, 陈飞星 . 长江安徽马鞍山段水质评价研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2000,14(4):104-107.
|
| [20] |
Yan W J, Chen F X . Water quality assessment on Yangtze River near Maanshan Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2000,14(4):104-107.
|
| [21] |
GB3838-2002 地表水环境质量标准[S].
|
| [21] |
GB3838-2002 Environmental quality standards for surface water[S].
|
| [22] |
Hakanson L . An ecology risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980,14:975-1001.

|
| [23] |
梅明, 文磊, 戚俊磊 , 等. 河流底泥重金属形态分析及污染评价方法综述[J]. 价值工程, 2016,35(9):8-11.
|
| [23] |
Mei M, Wen L, Qi J L , et al. Review on methods of morphological analysis of heavy metals in river sediment and pollution Evaluation[J]. Value Engineering, 2016,35(9):8-11.
|
| [24] |
杨潇瀛, 张力文, 张凤君 , 等. 土壤重金属污染潜在风险评价[J]. 世界地质, 2011,30(1):103-109.
|
| [24] |
Yang X Y, Zhang L W, Zhang F J , et al. Potential risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in soil[J]. Global Geology, 2011,30(1):103-109.
|
| [25] |
中国环境监测中心. 中国土壤背景值图集[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
|
| [25] |
China environmental monitoring center . China soil background value atlas [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
|
| [26] |
Stead-Dexter K, Ward N I . Mobility of heavy metals within freshwater sediments affected by motorway stormwater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2004,334:271-277.
|
| [27] |
倪鼎文 . 白银市东大沟流域重金属污染的防控治理对策研究[J]. 甘肃科技, 2015,31(24):6-8,11.
|
| [27] |
Ni D W . Countermeasures for prevention and control of heavy metal pollution in Dongdagou Watershed of Baiyin City[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2015,31(24):6-8,11.
|
| [1] |
WEI Hong, BAI Qing-Yun, ZHANG Peng-Zhi, ZHEN Zong-Yu. The application of seismic oil-water identification method to Guantao Formation of Bohai S oil field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6): 1394-1401. |
| [2] |
CHEN Xue-qun, LI Cheng-guang, TIAN Chan-juan, LIU Dan, XIN Guang-ming, GUAN Qing-hua. The application of high density electrical resistivity method to monitoring saltwater intrusion[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1347-1353. |
|
|
|
|

