|
|
|
| The application of gravity and magnetic three-dimensional inversion based on known information constraint in deep magnetite exploration: A case study of the Nihe iron deposit in Anhui Province |
Fan LUO1,2,3( ), Jia-Yong YAN2,3, Guang-Ming FU1,2,3 ), Jia-Yong YAN2,3, Guang-Ming FU1,2,3 |
1.School of Geophysics and Measurement-Control Technology,East China Institute of Technology,Nanchang 330013,China
2.MLR Key Laboratory of Metallogeny and Mineral Assessment,Institute of Mineral Resources,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,Beijing 100037,China
3.China Deep Exploration Center,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,Beijing 100037,China |
|
|
|
|
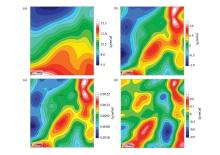
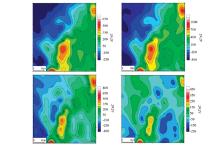
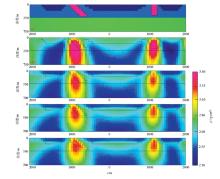
Abstract The Nihe iron deposit is a typical porphyrite type iron deposit with large burial depth,small amplitude of gravity and magnetic anomalies generated at the surface in Anhui Province. The authors selected the Nihe iron deposit to carry out gravity and magnetic inversion experiment based on known information constraint, in order to evaluate the application effect of gravity and magnetic data fine-grained and three-dimensional inversion in magnetite deep exploration: First of all, through the model test, the authors compared the three-dimensional inversion results with different known information constraints, and then extracted the residual gravity and magnetic anomalies of the Nihe iron deposit through the targeted field separation method. Then, the authors transformed the known surface geological information into physical information, and built a remnant density and magnetic susceptibility reference model to constrain gravity and magnetic three-dimensional inversion. Based on the three-dimensional distribution model of inversion density and magnetic susceptibility body, the authors confirmed the three-dimensional spatial shape of the Nihe iron orebody, and found that the result is basically consistent with geological exploration results. According to the results, the reliability of the inversion results based on the known information constrained gravity and magnetic three-dimensional inversion could be improved. For magnetite with high magnetic and high density, this method is an effective method to find and characterize deep magnetite orebody.
|
|
Received: 08 November 2016
Published: 20 February 2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

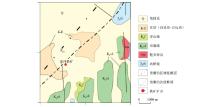
| 年代 | 岩石名称 | 地表 | 磁化率/SI | | 标本数 | 密度/(g/cm3) | | K-E | 红层(砂砾岩) | 11 | 2.43 | 微磁性 | | J3-K1 | 粗安质、安山质熔岩 | 38 | 2.51 | 0.015 | | 凝灰岩 | 40 | 2.44 | 0.010 | | 砂页岩 | 35 | 2.50 | 微磁性 | | J1-2 | 次生石英岩 | 50 | 2.51 | 微磁性 | | 正长岩 | 47 | 2.48 | 0.019 | | J3-K1 | 闪长玢岩 | 25 | 2.63 | 0.041 | | 辉石粗安(玢)岩 | 11 | 2.63 | 0.015 | | Py | 硫铁矿 | 34 | 3.17~3.51 | 0.00068~0.51 | | Mt | 磁铁矿 | 79 | 3.17~3.51 | 0.1225~0.2 | | Ah | 硬石膏矿 | 11 | 2.8~3.1 | 0~0.00004 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

| 模型体 | 深度范围/m | 密度/(g/cm3) | | 风化层 | 0~150 | 2.0 | | 围岩 | 0~340 | 2.4 | | 基岩 | 340~700 | 2.8 | | 异常体 | 0~300 | 3.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 地表出露地层 | 平均密度差/(g/cm3) | 平均磁化率/SI | | Q(第四系) | -0.60 | 无磁 | | K-E(红层) | -0.17 | 微磁 | | K1f(浮山组) | -0.16 | 0.014 | | K1sh(双庙组) | -0.16 | 0.016 | | ταμ(粗安玢岩) | 0.03 | 0.032 | | J3zh(砖桥组) | -0.09 | 0.016 |
|
|
|
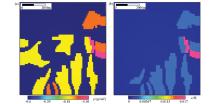
|
|
|
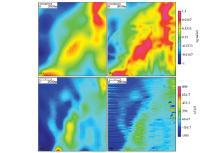
|
|
|

|
|
|
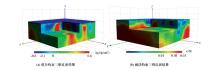
|
|
|
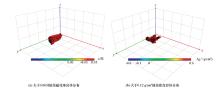
|
|
|
| [1] |
赵文广,吴明安,张宜勇,等.安徽省庐江县泥河铁硫矿床地质特征及成因初步分析[J].地质学报,2011,(5):789-801.
|
| [2] |
严加永,吕庆田,陈向斌,等.基于重磁反演的三维岩性填图试验——以安徽庐枞矿集区为例[J].岩石学报,2014,(4):1041-1053.
|
| [3] |
匡海阳. 安徽泥河铁矿深部找矿综合地质地球物理研究[D].南昌:东华理工大学,2012.
|
| [4] |
祁光. 重力反演在立体地质填图中的应用[D].长春:吉林大学,2009.
|
| [5] |
Williams N C.Geologically-constrained UBC-GIF gravity and magnetic inversions with examples from the Agnew-Wiluna greenstone belt,Western Australia[D].2008.
|
| [6] |
Boszczuk P,Cheng L Z,Hammouche H,et al.A 3D gravity data interpretation of the Matagami mining camp,Abitibi Subprovince,Superior Province,Québec,Canada:Application to VMS deposit exploration[J].Journal of Applied Geophysics,2011,75(1):77-86.
|
| [7] |
Lü Q,Qi G,Yan J.3D geologic model of Shizishan ore field constrained by gravity and magnetic interactive modeling:A case history[J].Geophysics,2012,78(1):25-35.
|
| [8] |
Anderson E D,Zhou W,Li Y,et al.Three-dimensional distribution of igneous rocks near the Pebble porphyry Cu-Au-Mo deposit in southwestern Alaska:Constraints from regional-scale aeromagnetic data[J].Geophysics,2014,79(2):B63-B79.
|
| [9] |
任启江,刘孝善,徐兆文.安徽庐枞中生代火山构造洼地及其成矿作用[M].北京:地质出版社,1991:1-191.
|
| [10] |
常印佛,刘湘培,吴言昌.长江中下游铜铁成矿带[M].北京:地质出版社,1991.
|
| [11] |
吴明安,汪青松,郑光文,等.安徽庐江泥河铁矿的发现及意义[J].地质学报,2011,85(5):802-809.
|
| [12] |
张乐骏. 安徽庐枞盆地成岩成矿作用研究[D].合肥:合肥工业大学,2011.
|
| [13] |
汪青松,吴明安,袁平,等.安徽省庐江县泥河铁矿重磁异常特征[J].地质与勘探,2012,48(1):148-154.
|
| [14] |
杜建国,常丹燕.长江中下游成矿带深部铁矿找矿的思考[J].地质学报,2011,85(5):687-698.
|
| [15] |
周涛发,范裕,袁峰,等.安徽庐枞盆地泥河铁矿床与膏盐层的成因联系及矿床成矿模式[J].地质学报,2014,88(4):562-573.
|
| [16] |
陈辉,邓居智,吕庆田,等.九瑞矿集区重磁三维约束反演及深部找矿意义[J].地球物理学报,2015,58(12):4478-4489.
|
| [17] |
刘彦,严加永,吴明安,等.基于重力异常分离方法寻找深部隐伏铁矿——以安徽泥河铁矿为例[J].地球物理学报,2012,55(12):4181-4193.
|
| [18] |
陈越. 相山铀矿田地球物理特征及深部地质结构研究[D].核工业北京地质研究院,2014.
|
| [19] |
Li Y,Oldenburg D W.3-D inversion of gravity data[J].Seg Technical Program Expanded Abstracts,1998,61(2):394-408.
|
| [20] |
Li Y,Oldenburg D W.3-D Inversion of Magnetic Data[J].Geophysics,2013,63(1):109-119.
|
| [21] |
Spicer B,Morris B,Ugalde H.Structure of the Rambler Rhyolite,Baie Verte Peninsula,Newfoundland: Inversions using UBC-GIF Grav3D and Mag3D[J].Journal of Applied Geophysics,2011,75(1):9-18.
|
| [22] |
严加永,吕庆田,吴明安,等.安徽沙溪铜矿区域重磁三维反演与找矿启示[J].地质学报,2014,88(4):507-518.
|
| [23] |
姚长利,郝天珧,管志宁.重磁反演约束条件及三维物性反演技术策略[J].物探与化探,2002,26(4):253-257.
|
| [24] |
鲍世才. 利用化极磁异常近似确定等轴状磁性体埋深[J].物探与化探,2017,41(1):98-101.
|
| [25] |
王忠敏,张培琴.二维位场的全空间解析延拓方法[J].物探与化探,1981,5(6):347-352.
|
| [26] |
王万银,王云鹏,李建国,等.利用重、磁资料研究于都-赣县矿集区盘古山地区断裂构造及花岗岩体分布[J]. 物探与化探,2014,38(4):825-834.
|
| [27] |
侯重初. 一种压制干扰的频率滤波方法[J].物探与化探,1979,3(5):50-54.
|
| [28] |
安玉林,郭良辉,张明华.169km以远地壳质量的重力校正值高精度计算及其数值特征[J].物探与化探,2015,39(1):1-11.
|
| [29] |
李雪英,孔祥琦,侯相辉.基于高通滤波的频率-空间域经验模态分解压制高频噪声[J].地球物理学进展,2012,27(3):1070-1077.
|
| [30] |
罗潇,王彦国,邓居智,等.位场异常分离方法的对比分析--以江西相山铀多金属矿田为例[J].地球物理学进展,2017,32(3):1190-1196.
|
| [31] |
徐世浙,张谔堂.介绍位场向外延拓的一个简单公式[J].物探与化探,1982,6(2):119-120.
|
| [32] |
邱耀东,聂琳娟,张兵兵.局部重力异常向上延拓的实用算法[J].测绘科学,2017,42(4):39-42,60.
|
| [1] |
CHEN Da-Lei, WANG Run-Sheng, HE Chun-Yan, WANG Xun, YIN Zhao-Kai, YU Jia-Bin. Application of integrated geophysical exploration in deep spatial structures: A case study of Jiaodong gold ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 70-77. |
| [2] |
WEN Bai-Hong, HU Qing-Hui, ZHANG Lian-Qun. Affect of configuration parameters of geobody on regularization downward continuation imaging by successive layer optimization[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6): 1553-1558. |
|
|
|
|

