|
|
|
| Marine geomagnetic field modeling based on equivalent source technology |
WANG Jun-Lu1,2( ), WANG Meng3( ), WANG Meng3( ), CHEN Hui1,2, ZHANG Xiao-Fei1,2, ZHENG Yuan-Man4, YU Bing1,2, NIE Hui-Zi5 ), CHEN Hui1,2, ZHANG Xiao-Fei1,2, ZHENG Yuan-Man4, YU Bing1,2, NIE Hui-Zi5 |
1. Development and Research Center, China Geological Survey, Beijing 100037, China
2. Technical Guidance Center for Mineral Resources of Ministry of Natural Resources, Beijing 100037, China
3. China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural Resources, Beijing 100083
4. School of Earth Exploration and Information Technology, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China
5. China Aerospace Planning and Design Group Co., Ltd,Beijing 102627,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To address the key issues in marine geomagnetic field modeling, this paper systematically explored the theoretical basis, modeling method, and optimization strategy of the equivalent source technology. By analyzing the geometric parameters and spatial configuration strategies of equivalent sources, a terrain-following vertical hexahedral equivalent source configuration scheme was proposed, significantly enhancing the accuracy of magnetic field models. In terms of algorithm implementation, a sliding window-based coverage calculation scheme was employed, effectively overcoming the bottleneck in the high-precision processing of massive magnetic survey data. Experimental results show that maintaining an overlap rate of 15%~20% in the sliding window ensures both boundary continuity and optimal computational performance. This method provides a reliable technical support for high-precision marine geomagnetic field modeling, with its effectiveness having been verified across various geological models (with the errors less than 5%).
|
|
Received: 10 April 2025
Published: 23 October 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
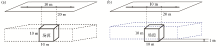
Single prism model and equivalent source setting method
a—set a model that is consistent with the actual field source for equivalent sources; b—set a model that deviates from the actual field source for equivalent sources
|
|
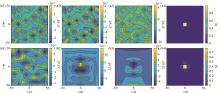
Results of equivalent source equivalence analysis based on model 1
a—the calculation result when the equivalent source position is consistent with the actual situation; b—calculation result of moving up 1 m equivalent source; a1, b1—poor fitting of raw data; a2, b2—downward 5 m error; a3, b3—upward 5 m error; a4, b4—equivalent sources for inversion reconstruction
|
|
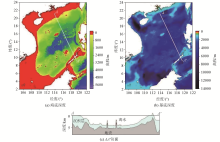
Magnetic geological model of the sea area
|
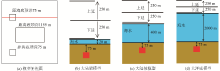
|
Simplified geological model of marine magnetic survey
|
|
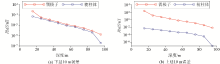
Comparison of extension accuracy between model two dipole and prism equivalent source models
|
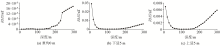
|
Error statistics of equivalent sources at different depths in model 2
|
|
Reconstructed data of 0 m plane with different equivalent source depths
|
|
Extension errors of different magnetization directions in the absence of remanence (a) and the presence of remanence (b)
|
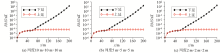
|
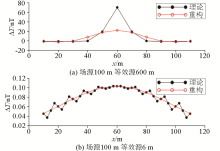
The influence of different observation network sizes on modeling accuracy in equivalent source magnetic field modeling
|
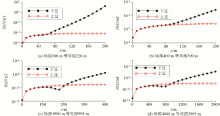
|
The influence of different equivalent source depths on modeling accuracy
|
|
The influences of different equivalent source thicknesses on modeling accuracy
|
|
The influence of different edge expansion points on modeling accuracy
|
|
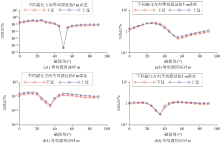
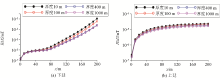
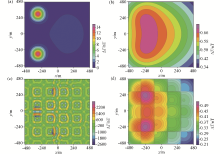
Results of traditional block method for extending the continental shelf model by 200 meters
a—downward extension theory; b—upward extension theory; c—downward simulation; d—upstream simulation
|
|
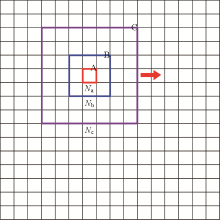
Schematic diagram of window overlay sliding window
red box—region A, extended data range; blue box—area B, observation data range; purple box—region C, equivalent source
|
|
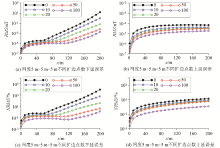
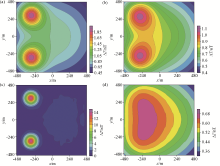
Improved block method for extending 50 meters and 200 meters results
a—extend 50 m downwards; b—extend 50 m upwards; c—extend 200 m downwards; d—extend 200 m upwards
|

| NRMS/% | 大陆架模型 | 大陆坡模型 | 大洋底模型 | | 上延 | 下延 | 上延 | 下延 | 上延 | 下延 | 实际50°
采用90° | 2.22 | 0.35 | 0.69 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 实际50°
采用50° | 2.39 | 0.4 | 0.54 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
|
Comparison of maximum errors among different models
|
| [1] |
张攀, 杜劲松, 李厚朴. 中国及邻区高分辨率三维岩石圈磁场修正球冠谐模型(CUG_CLMFM3Dv1)[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(5):1866-1880.
|
| [1] |
Zhang P, Du J S, Li H P. CUG_CLMFM3Dv1:A high-resolution revised spherical cap harmonic model of three-dimensional lithospheric magnetic field over China and surroundings[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(5):1866-1880.
|
| [2] |
李启栋, 邹维宝, 肖枫, 等. 多地磁特征量对飞行器匹配导航定位精度的提高[J/OL]. 地球物理学进展, 2024:1-15.(2024-07-29).http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DQWJ20240725001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.
|
| [2] |
Li Q D, Zou W B, Xiao F, et al. Improving the positioning accuracy of aircraft matching navigation by multiple geomagnetic features[J/OL]. China Industrial Economics, 2024:1-15.(2024-07-29).http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DQWJ20240725001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.
|
| [3] |
李启飞, 韩蕾蕾, 熊雄, 等. 潜艇目标态势对航空磁探测的影响分析[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(6):113-117.
|
| [3] |
Li Q F, Han L L, Xiong X, et al. Analysis of influence of submarine target posture on aeromagnetic detection[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2020, 45(6):113-117.
|
| [4] |
熊雄, 吴太旗, 黄贤源, 等. 地磁场模型及在海洋环境中的应用需求研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2021, 41(6):6-12.
|
| [4] |
Xiong X, Wu T Q, Huang X Y, et al. Research on geomagnetic field models and its application requirement in marine environment[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2021, 41(6):6-12.
|
| [5] |
徐文耀, 区加明, 杜爱民. 地磁场全球建模和局域建模[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2011, 26(2):398-415.
|
| [5] |
Xu W Y, Ou J M, Du A M. Geomagnetic field modelling for the globe and a limited region[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2011, 26(2):398-415.
|
| [6] |
穆文瑞. 区域地磁场建模方法技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2023.
|
| [6] |
Mu W R. Research on modeling method and technology of regional geomagnetic field[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2023.
|
| [7] |
赵静, 王涵, 嵇艳鞠, 等. 全球岩石圈地磁梯度张量场椭球谐模型构建方法与评估[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(12):4555-4573.
|
| [7] |
Zhao J, Wang H, Ji Y J, et al. Construction method and evaluation of ellipsoidal harmonic model of global lithospheric geomagnetic gradient tensor field[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(12):4555-4573.
|
| [8] |
李新星, 冯进凯, 范昊鹏, 等. 利用球谐分析方法构建局部重力场模型的可行性分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2025, 40(1):11-24.
|
| [8] |
Li X X, Feng J K, Fan H P, et al. Feasibility analysis of constructing a regional gravitational model using the method of spherical harmonics analysis[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2025, 40(1):11-24.
|
| [9] |
杜劲松, 陈超. 基于卫星磁测数据的全球岩石圈磁场建模进展与展望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(3):1017-1033.
|
| [9] |
Du J S, Chen C. Progress and outlook in global lithospheric magnetic field modelling by satellite magnetic measurements[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(3):1017-1033.
|
| [10] |
李端, 陈超, 杜劲松, 等. 多层等效源曲面磁异常转换方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(7):3055-3073.
|
| [10] |
Li D, Chen C, Du J S, et al. Transformation of magnetic anomaly data on an arbitrary surface by multi-layer equivalent sources[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(7):3055-3073.
|
| [11] |
庞旭林. 航磁异常数据曲面延拓等效源法技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.
|
| [11] |
Pang X L. Research on equivalent source method for surface continuation of aeromagnetic anomaly data[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2012.
|
| [12] |
王泽庆, 孟小红, 王俊, 等. 一种改进的等效源模型设置方案[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(3):1189-1196.
|
| [12] |
Wang Z Q, Meng X H, Wang J, et al. Improved equivalent source model setting scheme[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(3):1189-1196.
|
| [13] |
张义蜜, 熊盛青, 何涛, 等. 基于等效源法的低纬度地区曲面磁异常化极、分量及张量转换研究[J]. 地质学报, 2025, 99(5):1819-1831.
|
| [13] |
Zhang Y M, Xiong S Q, He T, et al. Reduction-to-the-pole,component and tensor conversion of surface magnetic anomalies at low latitudes based on the equivalent source method[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2025, 99(5):1819-1831.
|
| [14] |
刘芬, 王万银, 纪晓琳. 空间域和频率域平面位场延拓影响因素和稳定性分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(2):320-328.
|
| [14] |
Liu F, Wang W Y, Ji X L. Influence factors and stability analysis of plane potential field continuation in space and frequency domains[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(2):320-328.
|
| [15] |
Li Y G, Nabighian M, Oldenburg D W. Using an equivalent source with positivity for low-latitude reduction to the pole without striation[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(6):J81-J90.
|
| [16] |
姚长利, 黄卫宁, 管志宁. 综合利用位场及其垂直梯度的快速样条曲化平方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1997, 32(2):229-236,304.
|
| [16] |
Yao C L, Huang W N, Guan Z N. Fast splines conversion of curvedsurface potential field and vertical gradient data into horizontal-plane data[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1997, 32(2):229-236,304.
|
| [17] |
纪晓琳, 王万银, 熊盛青, 等. 频率域偶层位曲面位场处理和转换方法试验研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(6):2669-2678.
|
| [17] |
Ji X L, Wang W Y, Xiong S Q, et al. Experimental research using the frequency-domain dipole layer method for the processing and transformation of potential field on curved surface[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(6):2669-2678.
|
| No related articles found! |
|
|
|
|

